BIO 452 Exam 2 PPT 1
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
dependent
voltage-______-Membrane properties: physiological properties of a neuron that are as important as synapses in determining neuronal activity and circuit output - usually not represented in diagrams
conditional
voltage dependent membrane properties are ___ (depend on the NT present)
metabotropic
Voltage dependent membrane properties are modified by ____ actions
ion channels
Usually voltage-dependent ionic currents are due to the effects on ____ ______
Intrinsic Oscillation
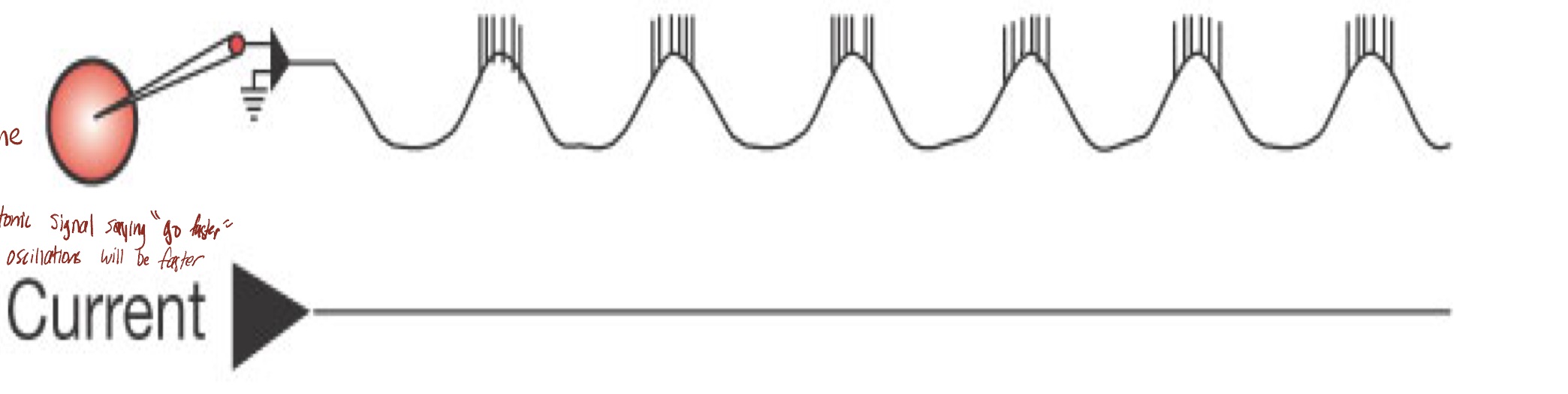
rhythmic, without
Intrinsic oscillations have ___ membrane potential oscillations ____ rhythmic synaptic input
Intrinsic oscillations
Rhythmic membrane potential oscillations without any rhythmic synaptic input
Results from interplay of multiple voltage-gated ion channels
Useful for heart pacemakers, breathing, autonomic NS
Pacing rhythmic activity pattern generated by rhythmically active circuits (brainstem breathing circuit)
No
Is modification of one ion channel enough to make an intrinsic oscillation?
lack, isolated
R15 in Aplysia is the original burster, and still exhibits oscillations when there is a ___ of rhythmic synaptic input and oscillates when ___
Larger
Invertebrate neurons are ____ than vertebrate neurons
Serotonin
In Aplysia, adding ____ made the oscillations more spaced out
Burst
Group of action potentials
TRH
In Guinea pigs, applying ___ creates oscillations
Hyperpolarized
Funny channels open when the membrane is ___
depolarize, Na, K
Funny channels work to ___ the membrane (__ and ___ ions flow in to depolarize even more)
increase
To slow down heart rate, you would want to ___ voltage threshold
voltage
IK Ca is a ____ dependent potassium channel that only works when calcium is present
Spike frequency adaptation
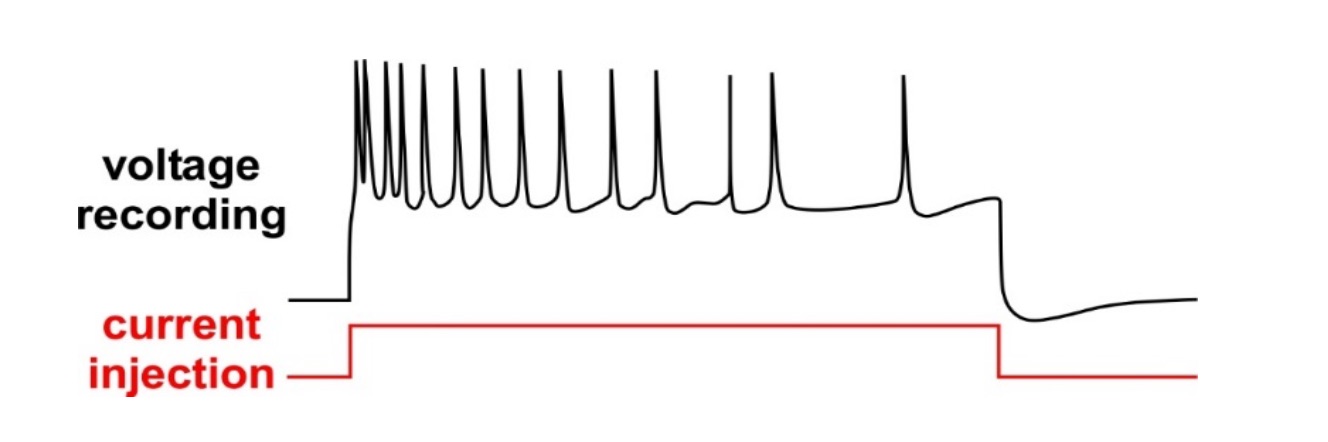
Spike frequency adaptation
Ability for action potential frequency to decrease during sustained activity
Usually due to slowly opening current that hyperpolarizes the neuron
Enables the active phase of a neuron to end its own without the need for an inhibitory synaptic input
Useful for desensitization to a stimulus
Same input but action potentials are decreasing over time
Fatigue
Spike frequency adaptation is also called ___
M
In mice: ___-Current is a slowly activating voltage-gated K+ channel
Muscarinic
M channels are ___, or Ach metabotropic channels
slower
Closing M-channels leads to a ___ EPSP
increases, tonic
An M-current blocker ___ seizures and causes ___ firing
decreases
An M-current activator ___ seizures
steady
If you get rid of the M channel, you get ___ firing
Plateau Potential
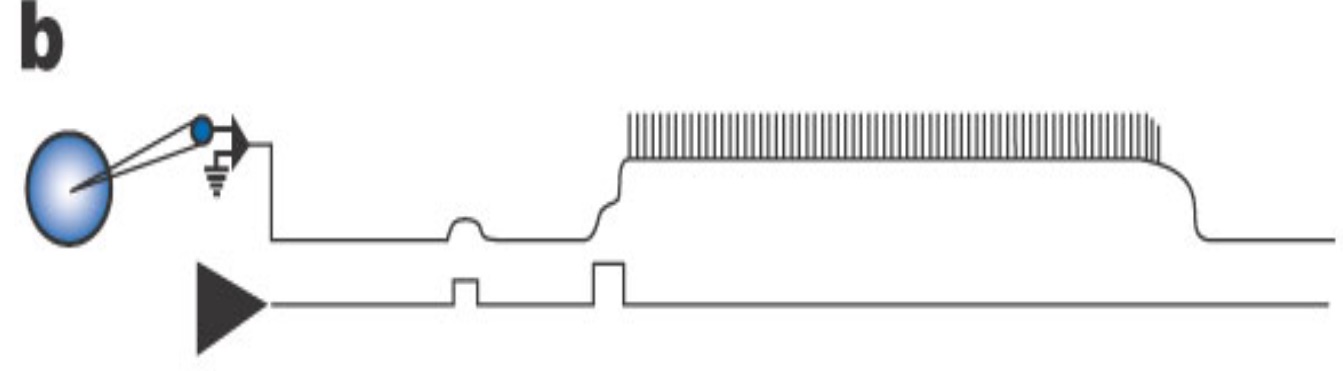
Plateau Potential
Prolonged depolarizing response
Opening of voltage gated channels that close very slowly
Maintained depolarization usually with action potentials on plateau
Self-terminates: often due to the slow build-up of a hyperpolarizing current
Useful for: bladder control and postural muscles
depolarizing
Plateau Potential: prolonged ___ response
hyperpolarizing, IPSP
Plateau Potential: self terminating and usually ends due to a slow build-up of a ____ current or a sudden ____
downstate, transient
A small ____, below threshold, firing is usually a ___ stimulus
crab, turtle
Plateau Potential: The small circuit model is ___ and the large circuit model is ____
Escape from Inhibition
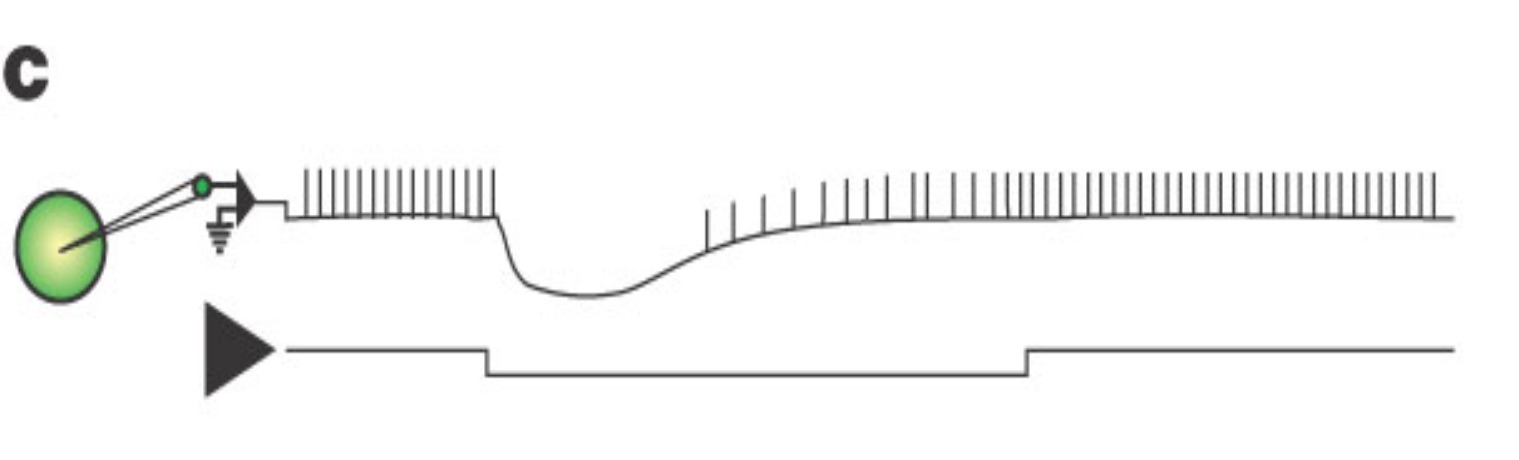
During
An escape from inhibition is the ability to depolarize ____ persisting inhibition
Escape from Inhibition
Ability to depolarize during persisting inhibition
Often results from the activation of the H current
Useful for locomotion and chewing
Enables neurons to become active even when they are still being inhibited
Helps with transitions from inhibited to excited
oscillation
Escape from Inhibition can create an ____
leech
neurogenic heartbeat in a ___ is an example of
Escape from Inhibition
Post Inhibitory Rebound
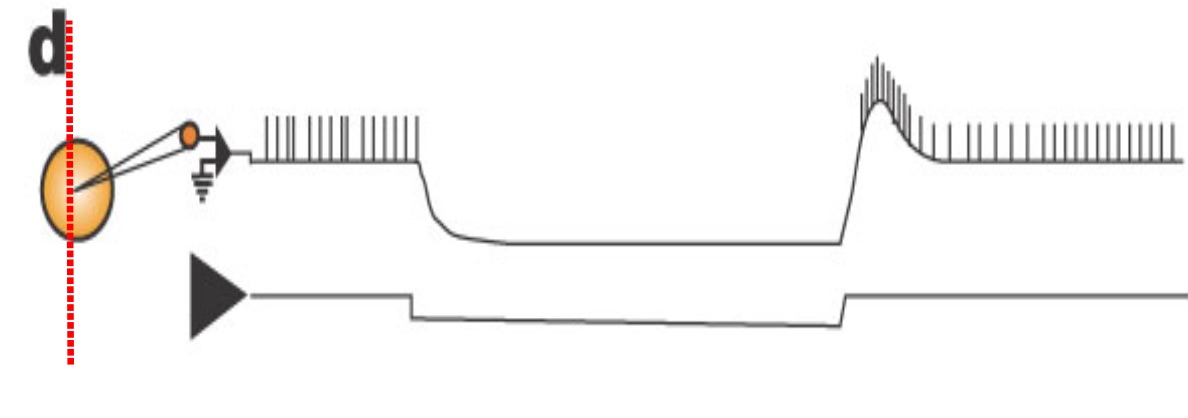
Post Inhibitory Rebound
Rapid “rebound” after a period of hyper polarization or synaptic inhibition
Overshoot of the resting potential and an action potential burst
One mechanism: Ih activation was not strong enough for escape from inhibition
Enables neurons to generate activity in response to inhibition
Very common in rhythmic circuits: walking, breathing, chewing
lobster, delayed, mice (mouse)
Small circuit Post Inhibitory Rebound is ___ and they can show ___ Post Inhibitory Rebound due to dopamine
Large circuit example is ___
synaptic
Oscillation due to another neuron is ___
intrinsic
Oscillation due to voltage gated channels or sensitivities is ___