chapter 18- vaccines
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:38 PM on 4/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
1
New cards
vaccinations provoke a … immune response
primary
2
New cards
the primary immune response, promoted by a vaccination, leads to the formation of … and …
antibodies and memory cells
3
New cards
after vaccination, exposure to the same pathogen allows a rapid and intense … response
secondary
4
New cards
herd immunity is defined as…
immunity in most of the population
5
New cards
due to herd immunity outbreaks are … due to the lack of … individuals
sporadic, susceptible
6
New cards
R° value accounts for…
average # of people an infected person infects
7
New cards
name the type of vaccine…
* weakened pathogns
* closely mimics an actual infection
* confers lifelong cellular and humoral immunity
* weakened pathogns
* closely mimics an actual infection
* confers lifelong cellular and humoral immunity
live attenuated vaccine
8
New cards
name the type of vaccine…
* safer than live vaccines
* require repeated booster doses
* induce mostly humoral immunity
* safer than live vaccines
* require repeated booster doses
* induce mostly humoral immunity
inactivated killed vaccine
9
New cards
name the type of vaccine…
* uses antigenic fragments to stimulate an immune response
* uses antigenic fragments to stimulate an immune response
subunit vaccines
10
New cards
toxoids are…
inactivated toxins
11
New cards
the two types of subunit vaccines are…
virus-like particle vaccine and polysaccharide vaccine
12
New cards
name the type of vaccine…
* resemble intact viruses but do not contain viral genetic material
* resemble intact viruses but do not contain viral genetic material
virus-like particle vaccine
13
New cards
name the type of vaccine…
* made from molecules in pathogen’s capsule
* not very immunogenic
* made from molecules in pathogen’s capsule
* not very immunogenic
polysaccharide vaccine
14
New cards
name the type of vaccine…
* injected naked DNA produces the protein antigen encoded in the DNA
* stimulate humoral and cellular immunity
* injected naked DNA produces the protein antigen encoded in the DNA
* stimulate humoral and cellular immunity
nucleic acid (DNA) vaccine
15
New cards
name the type of vaccine…
* avirulent viruses or bacteria are genetically modified to deliver gene coding for antigens
* avirulent viruses or bacteria are genetically modified to deliver gene coding for antigens
recombinant vector (plasmid) vaccine
16
New cards
an adjuvant is a… added to vaccines to improve…
chemical additive, effectiveness
17
New cards
name two adjuvants
alums and monophosphoryl lipid A
18
New cards
name the type of vaccine…
* easier to make and alter
* less stable
* need booster shots
* requires cold storage
* easier to make and alter
* less stable
* need booster shots
* requires cold storage
mRNA vaccine
19
New cards
what is a well known mRNA vaccine
COVID-19
20
New cards
a fluorescent-antibody technique is where scientists combine … with …
fluorescent dyes with antibodies
21
New cards
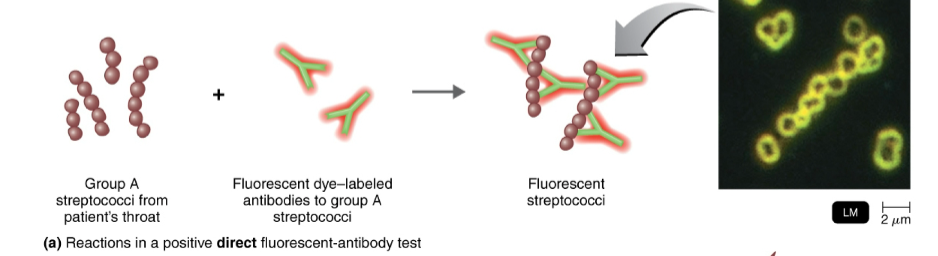
direct fluorescent-antibody (FA) tests are used to…
identify a microorganism in a clinical specimen
22
New cards
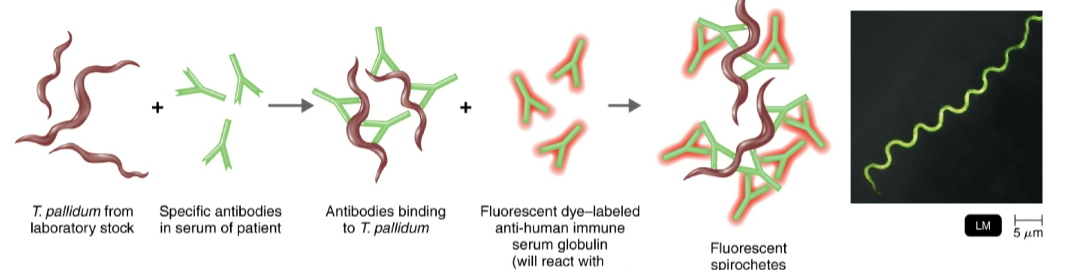
indirect fluorescent-antibody (FA) tests are used to…
detect a specific antibody in serum
23
New cards
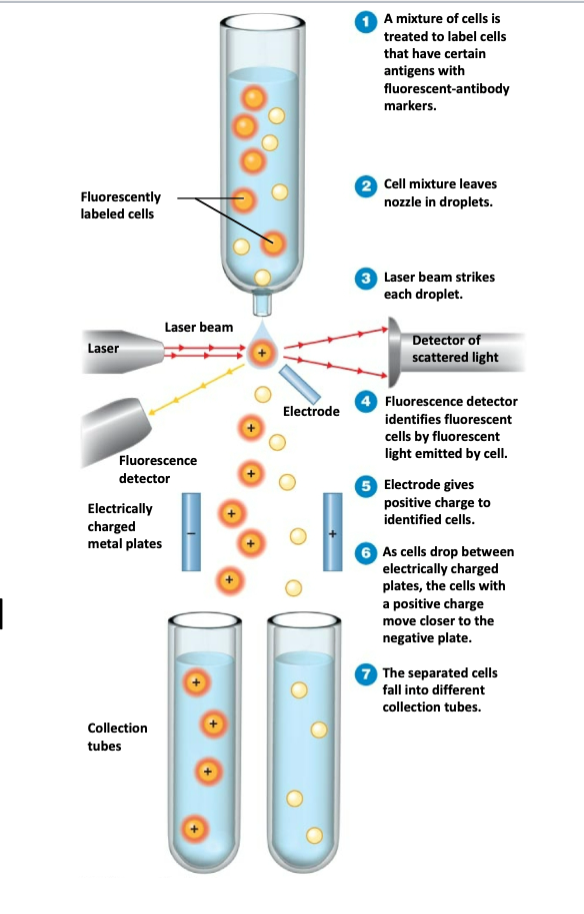
explain the three stages of the “Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorter (FACS)”
1. laser beam strikes a droplet containing a cell
2. detector determines size and fluoresce of surface molecules
3. imparts a charge to the cell, separating cells