5.5 Step 3. sensitivity analysis
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
1
New cards
steps of the sensitvity analysis
1. Generating the report
2. Decision variables (Variable Cells)
1. Name
2. Final Value
3. Reduced Cost
4. Objective Coefficient
1. Calculating the objective value
5. Allowable Increase/Decrease
3. Constraints
1. Constraint R.H. Side
2. Final value
1. Binding constraints
2. Non-binding constraints, Slack
3. Shadow Price
4. Allowable Increase/Decrease
2
New cards
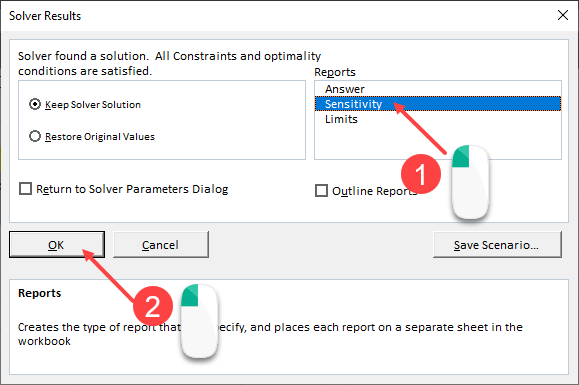
how to generate the report
click on sensitivity underneath the reports section → click ok
3
New cards
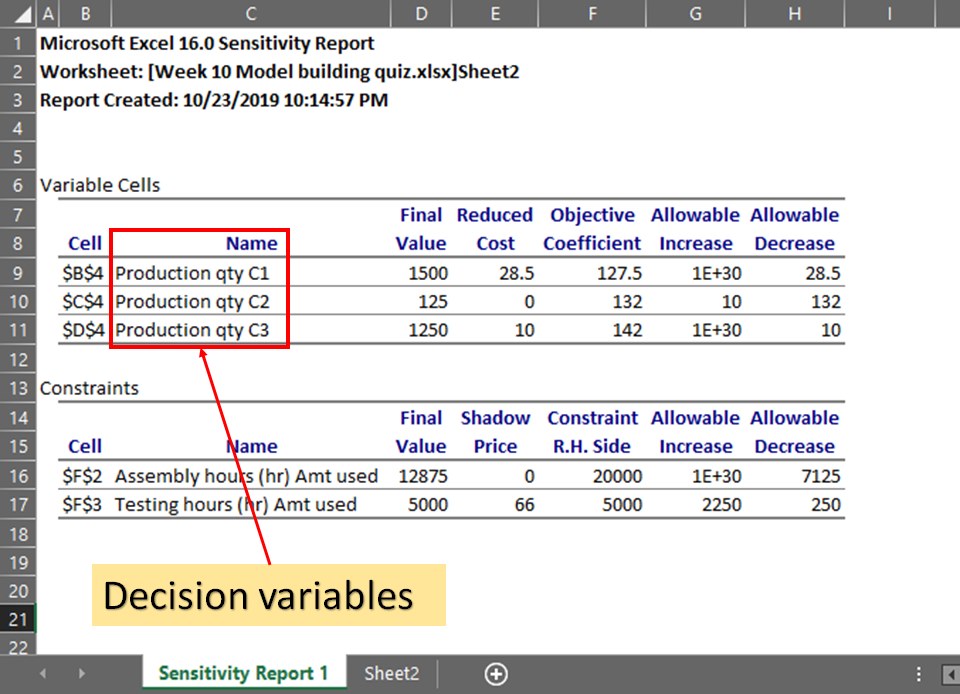
where are the decision variables located in the report?
under name
4
New cards
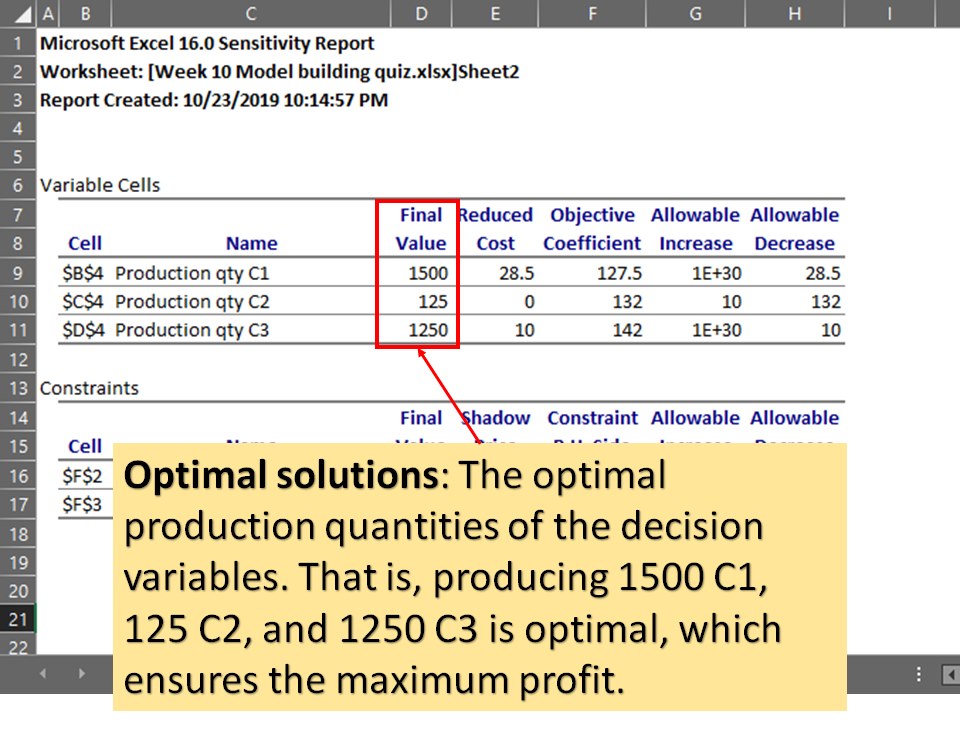
where are the optimal solutions located at in the report?
under final value
5
New cards
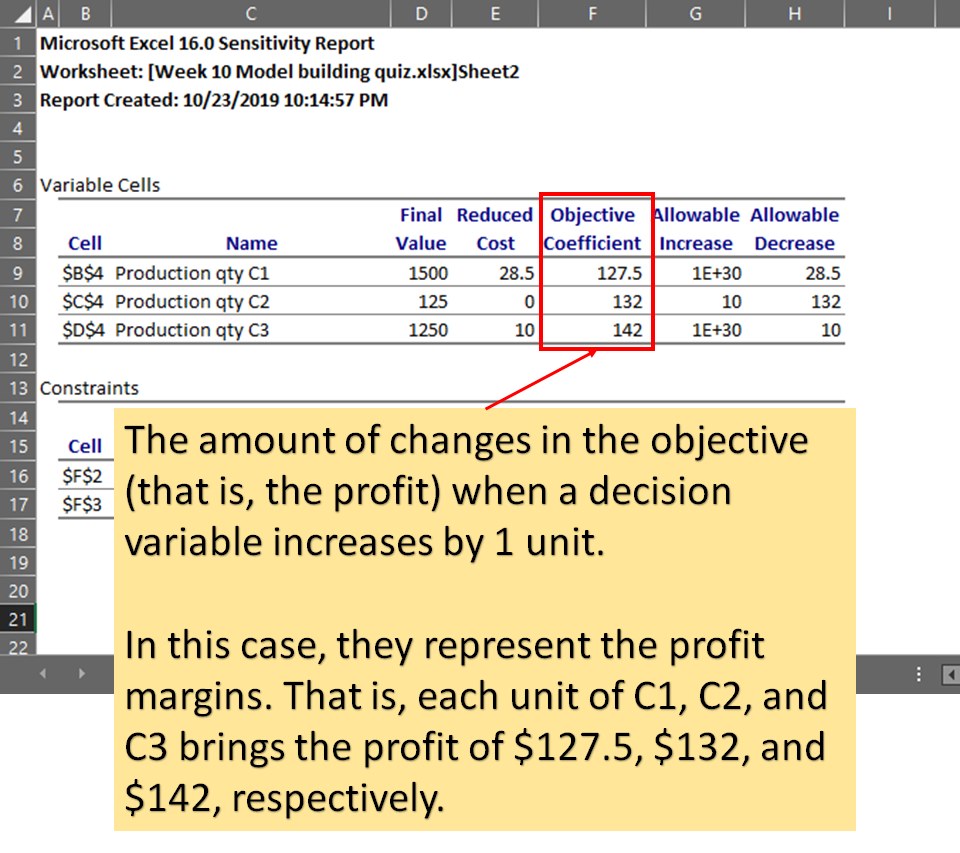
what is the objective coefficient?
the amount of changes in the objective when a decision variable increases by 1 unit
6
New cards
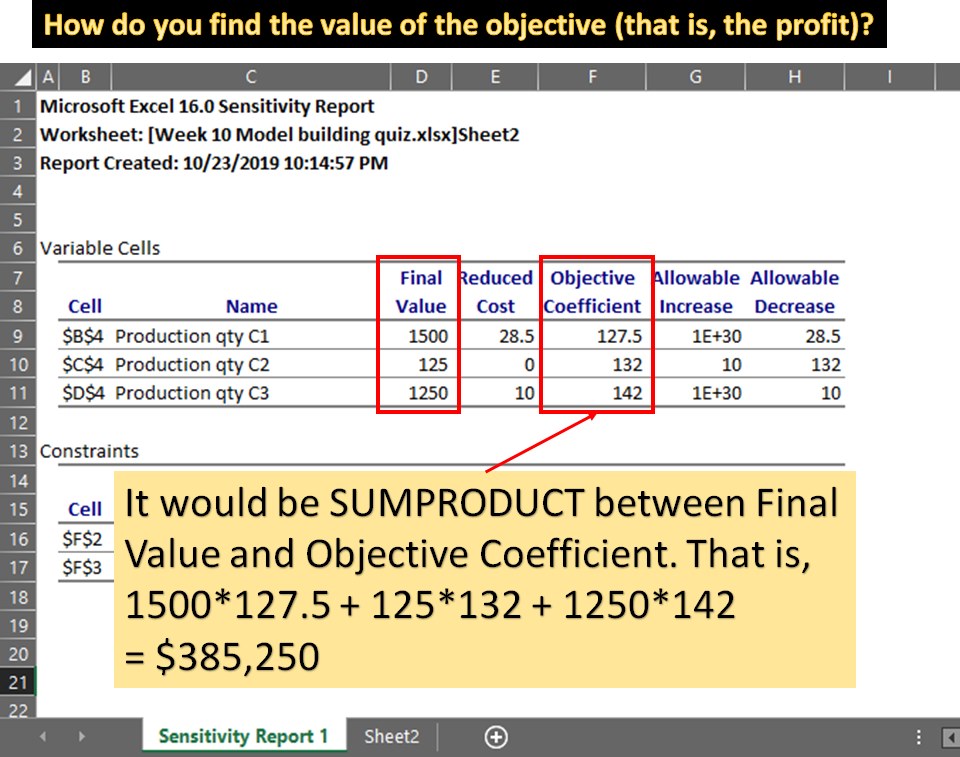
how do you find the value of the objective
SUMPRODUCT between the final value and objective coefficient
7
New cards
what is the reduced cost?
amount of loss when they deviate from the optimal solution by 1 unit
8
New cards
the reduced cost is always zero when?
the optimal solution is not at its limits
9
New cards
the reduced cost is positive when?
the optimal solution is at the upper limit
10
New cards
the reduced cost is negative when?
the optimal solution is at the lower limite
11
New cards
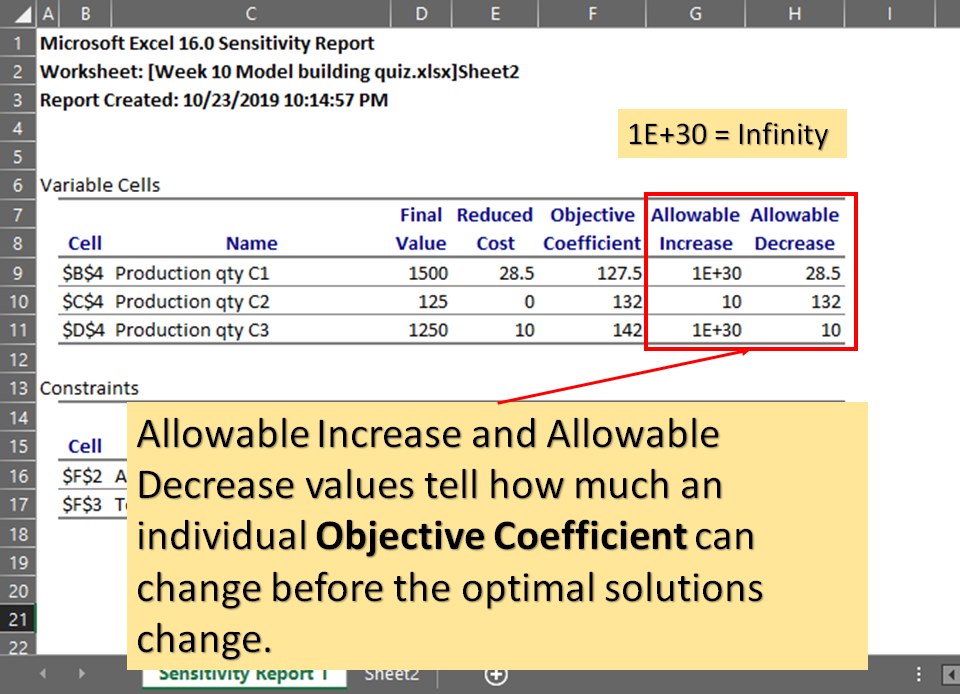
what do allowable increase and allowable decrease values tell?
how much an individual objective coefficient can change before the optimal solutions change
12
New cards
if the allowable ranges are large,
then reasonable errors in estimating the coefficients will have no effect on the optimal policy (although they will affect the value of the objective function)
13
New cards
tight allowable ranges suggest?
that more effort might be spent ensuring that correct data or estimates are used in the model
14
New cards
what is the constraint R.H. side?
values of available amount of each resource
15
New cards
what is the finale value?
amount used for each resource
16
New cards
when all available amount of resource is used, that resource is called
a binding constraint
17
New cards
when a resource is no completely used up, it is called a
non-binding constraint. the unused amount is called a slack
18
New cards
the shadow price is?
amount of contribution to the objective by each additional unit’s in the available amount. it will always be zero for non-zero binding constraints
19
New cards
for binding constraints, the shadow price is
non-zero. any change in the available amount (Constaint R.H. Side) will cause optimal values of the decision variables as well as the objective value to change
20
New cards
allowable increase and decrease togethe form a ange in which?
the current shadow price remains valid