Animal Biogeography
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Define Animal Biogeography
Study of distribution of animals in space
What are the two main types of Animal Biogeography?
Historical and ecological
History of Historical Biogeography. Who was involved?
Biogeographic patters gave rise to some of the eary anomalies leading people to think about evolution. Buffon, Darwin, and Alfred R. Wallace
Buffon
late 1700’s. Large cats in New and Old World
Darwin
1830’s. Galapagos animals.A
Alfred R. Wallace
Broad zoographic regions based largely on mammals and birds.
“Wallace’s Line” in Indonesia separates Oriendtal from Australian fauna
What does historical biogeography today look to?
evolutionary history and geology to explain species distribution
What is a vicariant event?
When ancestral populations are divided by a geographical barrier (mountains, river, sea, etc.), can split and diverge into 2 or more species.
Vicariance biogeography
combines phylogenetics based on past speciation with geographical distribution to produce area cladograms
If common geological events gave rise to splitting, we expect multiple groups to show _____________________.
The same patterns
Pangaea and Gondwanaland had continental Drift due to ……
plate tectonics explains otherwise puzzling distribution patterns
Pangaea
All continents united (210) mya, Upper Triassic)
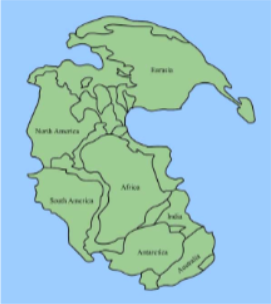
Gondwana
Aouthern continents still united (180 mya, Jurassic). Gondwanan distributions are common
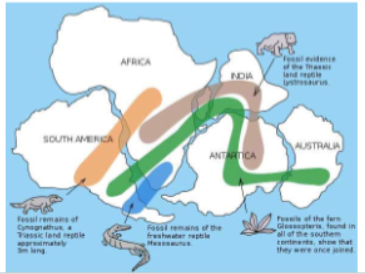
Dispersal
Animals can also move from one area to another
Examples of Dispersal
• islands
– oceanic vs. continental
– species/area curves
– balance between immigration and extinction
Great American Interchange
– ~3.5 mya Panamanian land bridge arose, allowing animals from N. America to go to S. America (& vice versa)
– (as we have seen, also a vicariant event for marine critters)
Climate Cycles & Vicariance
During Ice Ages (3 mya up until 10,000 years ago), animal & plant distributions very different (e.g., La Brea Tar Pits)
As climate warmed, many species retreated up mountains, became isolated
Are environmental conditions important in determining animal distributions?
Yes
What are the different kinds of environments?

How can environments be classified?
into broad biomes – typical plant & animal communities
What are the 10 major biomes?
Tropical Forest
Temperate Forest
Desert
Tundra
Taiga (boreal forest)
Grassland
Savanna/tropical grassland
Freshwater
Marine
Ice
Who first pointed out biomes?
Alexander von Humboldt
How do we classify marine zones?
Benthic
Intertidal
Subtidal
Pelagic
epipelagic
mesopelagic
bathypelagic
abyssopelagic
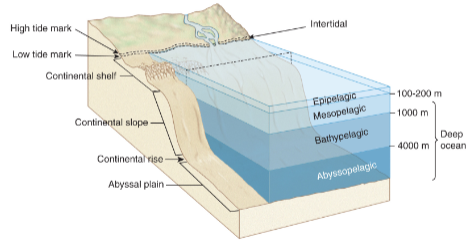
Most animals are ____, relatively few are _____. ______ and _________ _____ are richest in animal life. (marine zones)
benthic, pelagic, intertidal, nearshore subtidal
Intertidal Zonation
Rocky shores stratified based on tidal exposure:
spray zone
high tide zone
middle tide zone
subtidal
Integration of Historical & Ecological Biography
e.g., Anolis lizards in Caribbean
similar ecomorphs have repeatedly evolved on different islands
phylogeny reconstruction leads to understanding of _______ and ______ history of these forms
phylogenetic, ecological