Coagulation Cascade
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
for BIOE 3020 Exam 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
where are endothelial cells found
lining all cardiovascular system
what is released when platelets are damaged
granule contents: ADP, thromboxane, small thrombin
what is a zymogen
enzymes in an inactive form
protease/proenzyme definition
enzymes that activate macromoelcules with enzymatic cleavage or conformational change
MMPs
zinc dependent protease for ECM proteins
draw out the intrinsic coagulation cascade
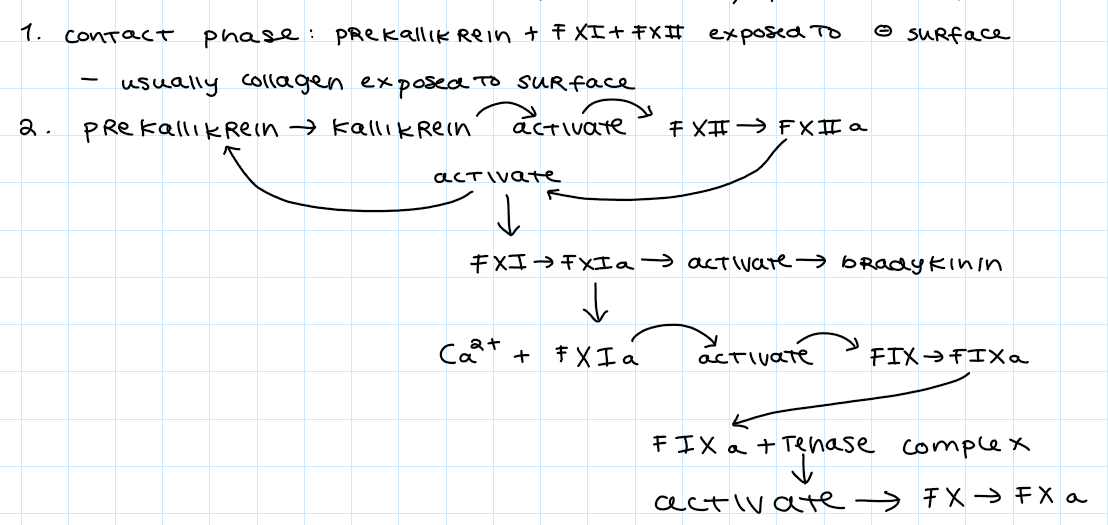
what does the intrinsic coagulation cascade require
factors (VIII,IX,X,XI,XII), prekallikrein, calcium ions, phospholipids
what is in the tenase complex
calcium ions, FVIIIa, FIXa, FX
purpose of tenase complex
localized clotting at the surface
tenase complex formation
phospholipids exposed during platelet activation, cause formation
what is required for the extrinsic coagulation cascade
factor VII, thrombin, tissue factor (FIII)
draw out the extrinsic coagulation cascade

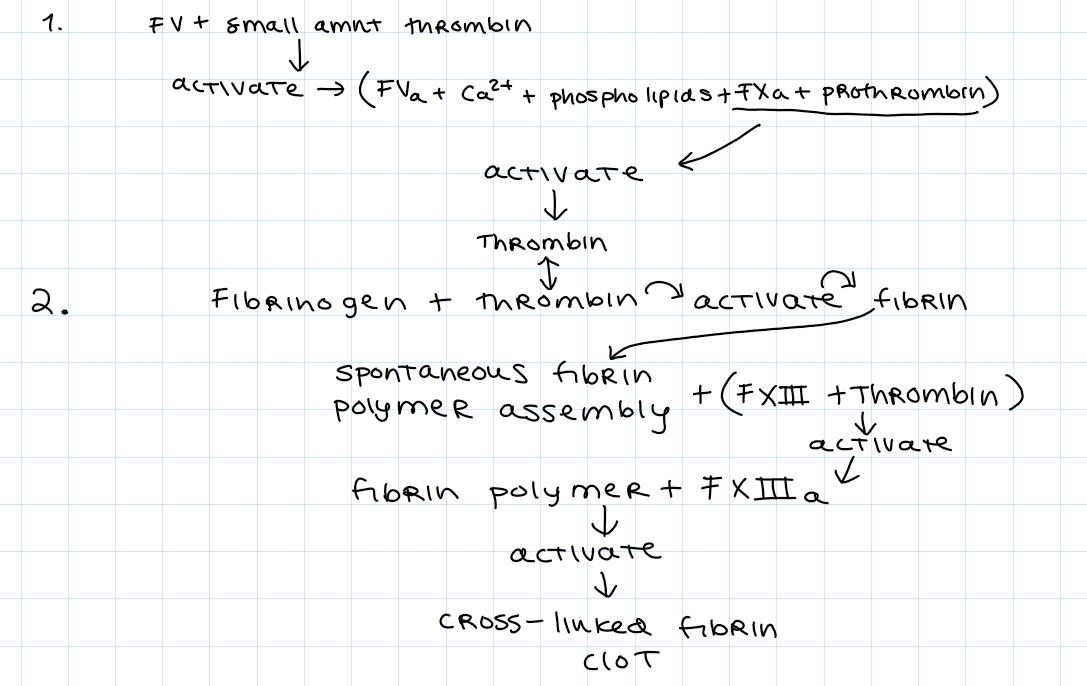
what is required for the common coagulation cascade
prothrombinase complex:(platelet phospholipids, calcium, FXa,FVa, prothrombin), fibrinogen(FI)
draw out the common coagulation cascade
2 ways coagulation is controlled
surface localization thru thrombin and FX, and blood flow dilution of activated factors
coagulation inhibitors
antithrombin III + heparin
what does fibrinolysis require
plasmin, tPA, urokinase, plasminogen-activator inhibitors 1&2, macroglobulin, antiplasmin
fibrinolysis process
urokinase + tPA activate during injury, bind to fibrin with plasminogen (inhibited by plasminogen-activator inhibitors)→ turned into plasmin & eat fibrin clot (inhibited by macroglubin + antiplasmin)
fibrin monomers become…
gel-like, signal end of APTT and PT