5.2.3 Redox and electrode potential
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
what is redox reaction
reaction where both reduction and oxidation happens
what is the oxidation number of Hydrogen
+1 ( unless when bonded to a metal)
what is the oxidation number of Oxygen
-2 ( unless H₂O₂)
what is oxidation
losing e⁻
what is reduction
gaining e⁻
what does OILRIG stand for

what is it when a ion becomes more positive
Oxidation ( losing electrons )
what is it when a ion becomes less positive & negative
reduction ( gains electrons)
when balancing half equations where do e⁻ go when element is reduced
the + e⁻ goes to the REACTANTS side when oxidation number gains e⁻
( Reduced Reactants )
when balancing half equations where do e⁻ go when element/ion is oxidised
the + e⁻ goes to the PRODUCTS when oxidation number loses electrons
method to balancing half equations
Work out the oxidation number /state for element/ion
balance the elements
work out if electrons were lost or gained
add to reactants side ( gained) or product side ( lost)
balance O₂ with H₂O
balance hydrogens with H⁺
method to combine half equations
work out the half equation
balance the e⁻ ( same on each equation) / whatever you do to e⁻ do to equation
cancel out the same species on both equations ( e⁻ / H₂O)
add the reactants then add the products
what are the conditions for metal ion cells
25°C
101 kpa
1 mol dm⁻³
what factors does electrode potential depend on
Temperature
Pressure
concentration
in the metal/metal ion cells what is the function of the salt-bridge
regulates neutrality
metal/metal ion cells how do e⁻ and ions carry charge ?
e⁻ → charge carriers through the wire
ions → charge carriers through the solution/ salt bridge
when working out P.D which cell is always oxidised
the more negative E⁰ is always oxidised
when working out P.D which cell is always reduced
the more positive E⁰ is always reduced
why is the redox system oxidised
in a more negative reaction the equilibria moves to the left
why is the redox system reduced
the more positive reaction = equilibria moves to the right
In a P.D reversible reaction what direction does the more E⁰ negative go
goes left ( oxidation)
how to work out the E⁰ cell
E⁰ ( Positive) - E⁰ ( Negative)
Standard electrode potential defintion
the difference in potential difference between a standard electrode potential and a standard hydrogen half-cell.
what is the best oxidising agent in half-cell equations
the half-cell equation with the most positive E⁰/V
Metal/metal ion cell ( Image)
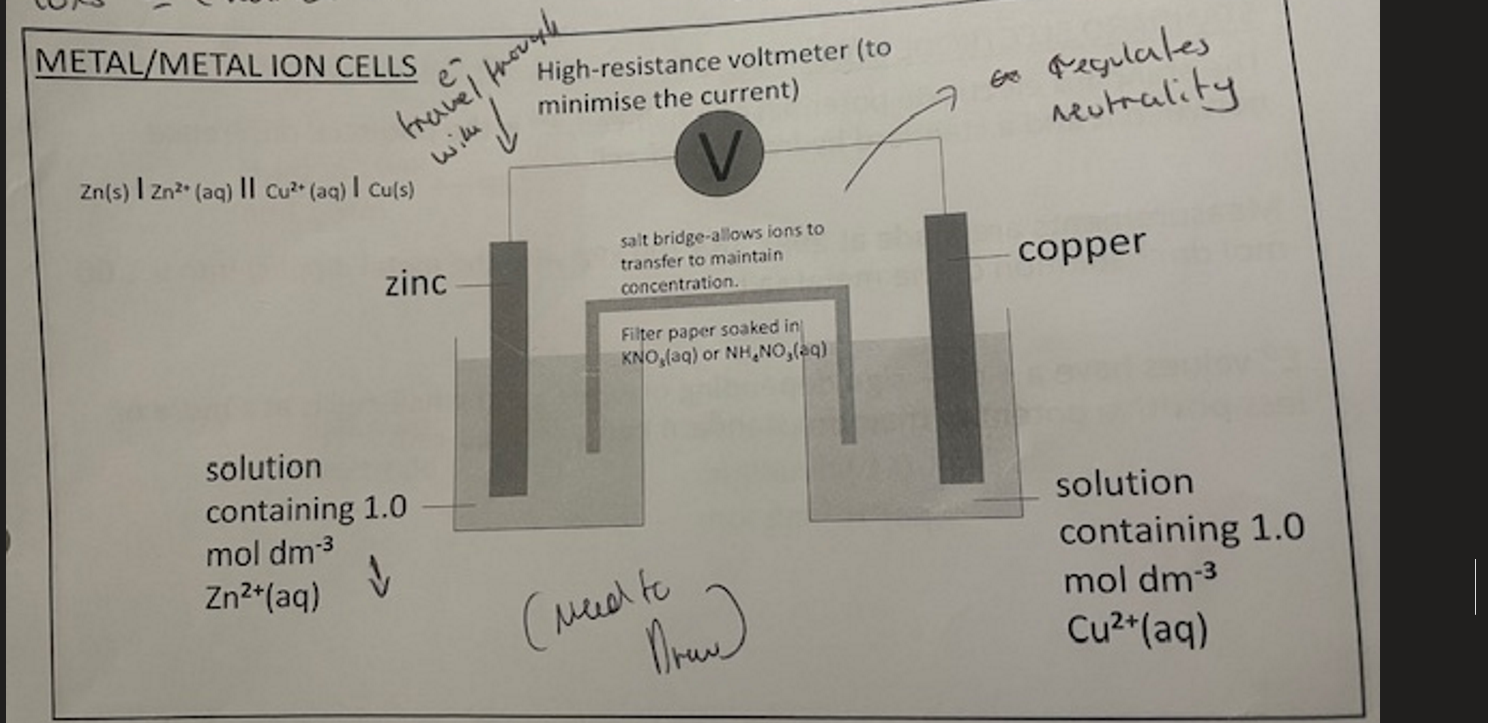
Why may results be different in a E° reaction
Not standard conditions
Rate of reaction too slow
Ea too high
Disadvantages and advantages of electrochemical cells
Disadvantage: Use toxic chemicals /Chemicals are flammable
Advantages: cheap to make
what is the hydrogen half cell equation
2H⁺ + 2e⁻ ⇌ H₂
what is the E° for the hydrogen half cell
0v
In a redox system what is effect of increasing concentration of reactant
equilibria moves to the right → more products are made
E° → becomes more positive
in redox system what is the effect of increasing concentration of products
equilibria moves to the left/ more reactants are made
E° → becomes more negative
what is the salt bridge made out of ?
KNO₃ ( inert ions)
how to measure standard electrode potential of a half-cell
standard hydrogen electrode ( left) connected standard electrode potential of metal ( right)
how to work out equation when energy storage is recharging
full equation ( combine half equations ) in reverse
reactants →products / products → reactants
what is a fuel cell
cell that produces electricity by reacting a fuel with oxygen
how to work out half-equation at other electrode from overall equation + half equation ( from one electrode)
add anything that appears in overall equation but not half equation
to get rid of H⁺ and e⁻ →add to other side
2 differences between fuel cell and modern storage cell
fuel cell → fuel reacts with O₂ to give electrical energy
Refuel → constant supply of O₂ and fuel
one advantage of using ethanol over hydrogen fuel in a vehicle
hydrogen is flammable
ethanol is liquid its easier to store
method to working out formula of hydrated salt
use conc and volume ( mean titre) of given salt to work out mols of salt ions
if in 25cm³ x 10 → 250cm³ ( moles )
mass / mols —> mr of hydrated salt
mr ( hydrated salt) - mr of ions = mr of H₂O
then divide by 18 = •H₂O
volume to reach endpoint = mean titre
Thiosulfate titration what are the colour changes
tiitration solution brown → straw colour
when starch is added straw to blue
Thiosulfate titration what is the endpoint and isnt starch added initally
endpoint = blue colour to colourless
no sharp endpoint but gradual colour change if starch added initally
redox titrations how to go from 250cm⁻³ to 25cm⁻³ when diluting only
moles in 250cm⁻³ x 10 ( mention diluting with water only)
how to work out mass in (g dm⁻³)
conc x Mr
how to convert g → mg
x 1000
Advantages of fuel cells compared to combustion of fossil fuels
produce less CO₂
Fuel cells are more efficient
redox system when does cell potential change ?
Concentrations are changing
Ways of storing hydrogen as fuel in cars
absorption
Liquid under High pressure
How to know which redox system to use for each electrode
oxygen electrode is always more positive E°V ( reduction)
Hydrogen is more negative