Mixed Economy: Key Concepts, Roles, and Global Examples
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
laissez faire
the doctrine that government generally should not intervene in the marketplace
private property
property that is owned by individuals or companies, not by the government or people as a whole
mixed economy
a market-based economic system in which the government is involved to some extent
economic transition
a period of change in which a nation moves from one economic system to another
privatization
the process of selling businesses or services operated by the government to individual investors, and then allowing them to compete in the marketplace
free enterprise system
an economic system in which investments in firms are made in a free market by private decision rather than by state control
characteristics of a mixed economy
A mixed economy is characterized by a market-based economy with some government intervention
government intervention in mixed economies
Government helps societies meet needs that would be too difficult for them to meet under a totally free market economy
fair marketplace
Government ensures that exchanges in the marketplace are fair
American government intervention
The American government intervenes in the economy by keeping order, providing vital services, and promoting general welfare
protection of private property
Federal and state laws protect private property
limited government regulation
The marketplace operates with a limited degree of government regulation
Adam Smith's view on government
Even free market thinkers like Adam Smith recognized the need for a limited degree of government involvement in the economic marketplace
government involvement in mixed economies
In a mixed economy, the market is free but has a certain degree of government control
Government Intervention
Actions taken by the government to influence the economy, including enforcing laws and providing services.
Economic Stability
A state where the economy experiences constant growth and low inflation, maintained by government regulations.
Infrastructure
The physical structures and facilities needed for the operation of a society, such as roads, bridges, and public transportation.
Public Safety
Services provided by the government to protect citizens, including police, firefighters, and military.
Social Services
Programs designed to support individuals and families, including education and healthcare.
General Welfare
The overall well-being of citizens, which the government aims to promote through various regulations and services.
Social Safety Nets
Government programs that provide financial support to individuals in need, such as Social Security and food assistance.
Economic Questions
The three fundamental questions of economics: What to produce? How to produce? Who has access?
Free Market
An economic system where prices and products are determined by unrestricted competition between privately owned businesses.
Continuum of Mixed Economies
A spectrum that illustrates the varying degrees of government intervention in different economies.
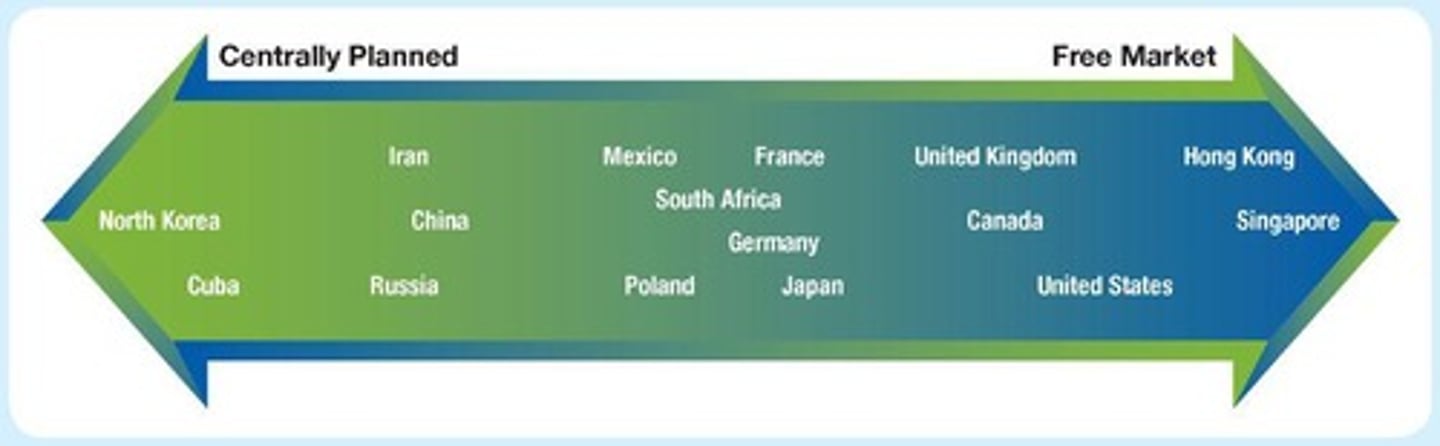
North Korea's Economy
An economy almost entirely controlled by the government, with limited foreign trade and ownership of all property.
China's Economic Transition
The shift towards privatization of state-owned firms since the 1970s, allowing individual investors to compete in the marketplace.
Hong Kong's Market
One of the world's freest markets, characterized by low taxation, limited government intervention, and no tariffs on foreign trade.
Economic Goals
The five objectives of an economy: Freedom, Growth, Security, Equity, and Efficiency.
Purchasing Power
The ability of consumers to buy goods and services, which influences access to products in an economy.
Consumer Demand
The desire of consumers to purchase goods and services, which largely determines what to produce.
Producers/Businesses
Entities that create goods and services, influencing how products are produced in an economy.
Government Preferences
The priorities set by the government that can influence access to goods and services in the economy.
Coal and Fish Exports
The main exports of North Korea, highlighting its limited trade activities.
Electronic Goods and Textiles
The primary exports of Hong Kong, reflecting its strong market presence.