KIN 100 (L1-4 basic scapula) Midterm
1/173
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
174 Terms
what are the 4 subdivisions of anatomy
gross anatomy, neuroanatomy, histology and embryology
what is gross anatomy
the study of what you can see with the plain eye
what is neuroanatomy
the study of the brain and nervous system
what is histology
the study of tissue under a microscope
what is embryology
the study of human development
what are the two ways to study gross anatomy
1) systematically: studying system by system (e.g., skeletal, nervous, etc)
2) regionally: studying region by region (e.g., trunk, upper limbs, head, etc)
what is basal nomia anatomica
anatomical terminology
name the 8 regions studied in regional gross anatomy
1) head
2) neck
3) thorax: chest region covered by the ribcage
4) upper limbs: shoulders to hands
5) back
6) abdomen
7) pelvis/perinium
8) lower limbs: glutes to feet
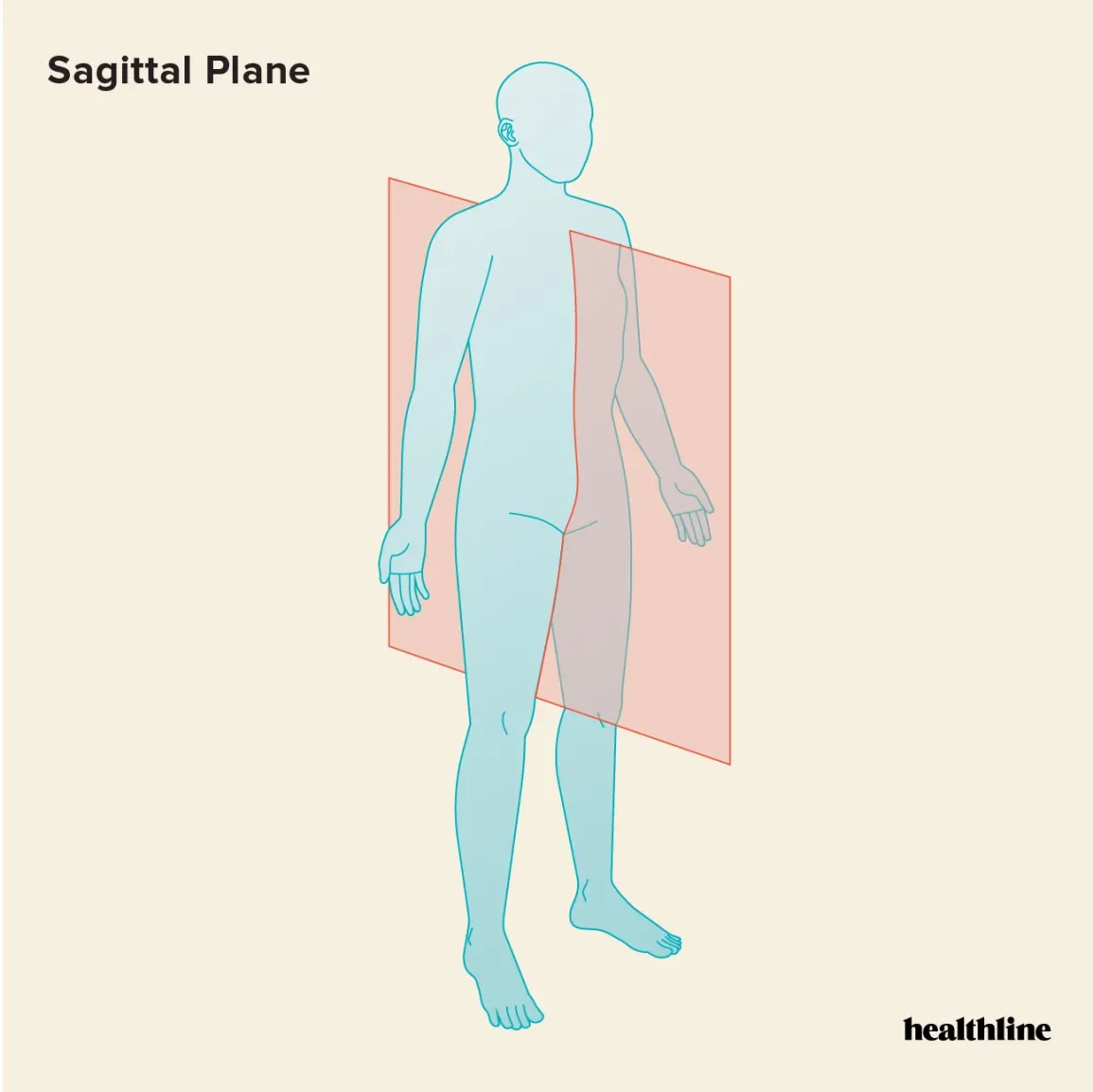
which plane is this
saggital plane
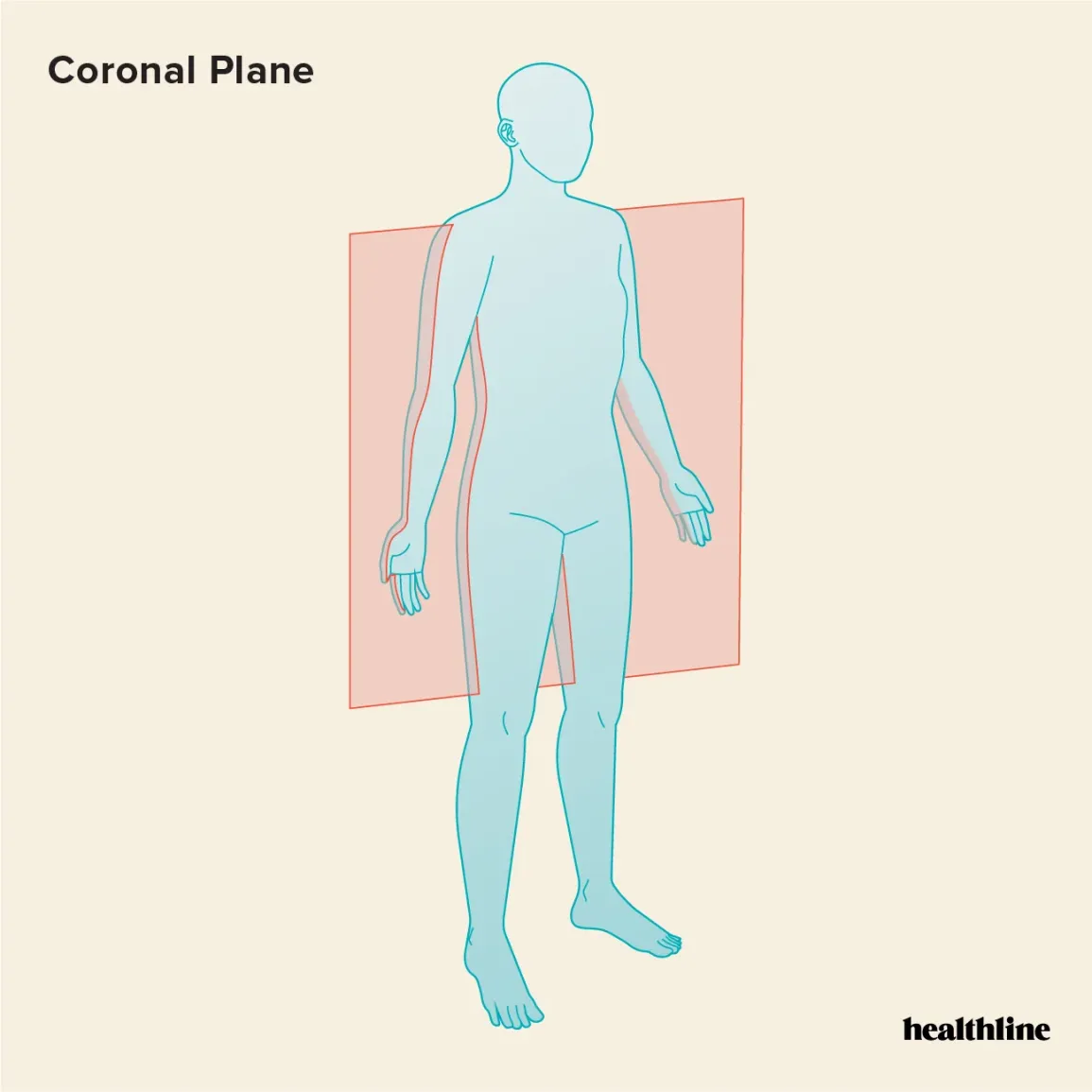
which plane is this
coronal/frontal plane
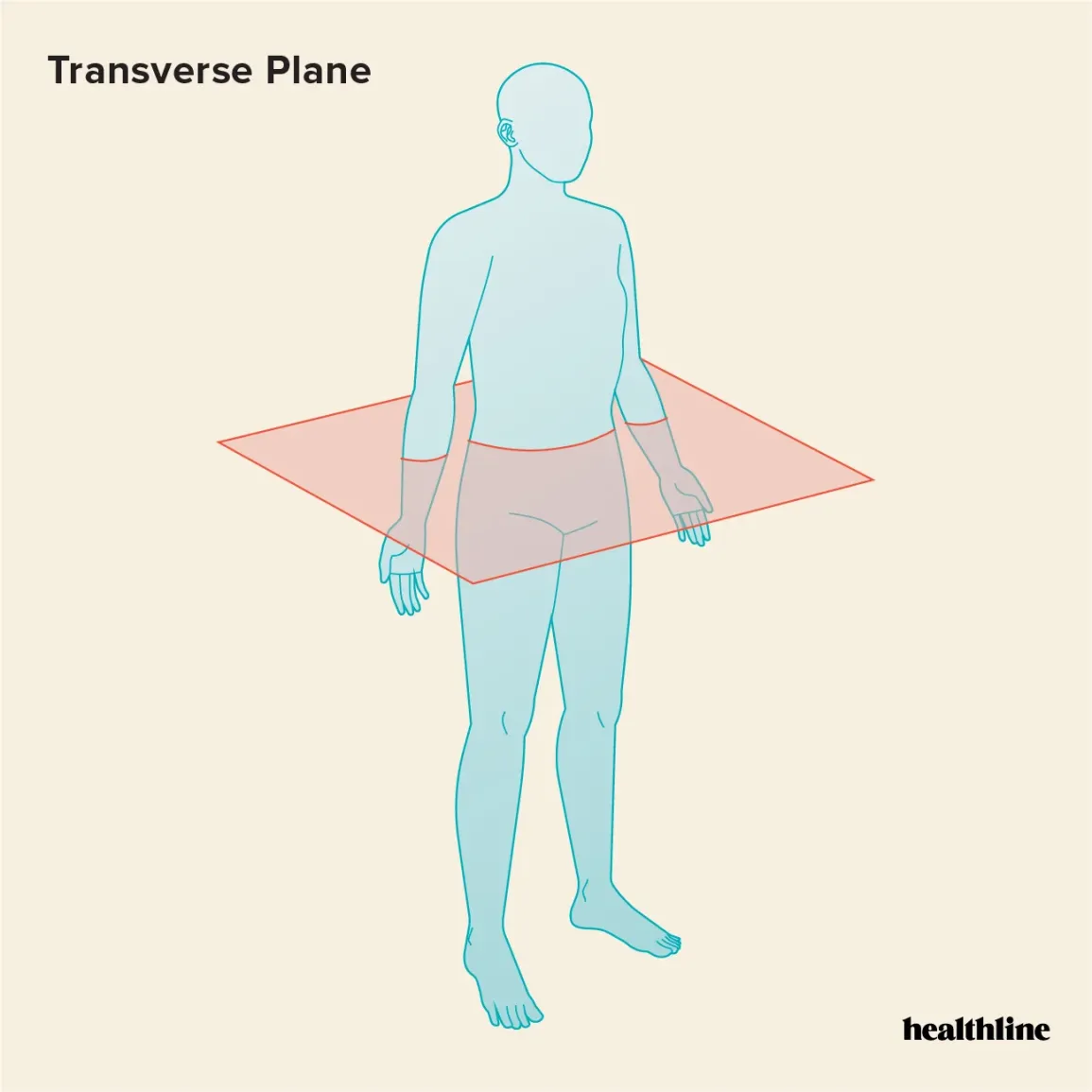
which plane is this
transverse plane
what does superior mean
above
what does inferior mean
below
what does anterior mean
in front/to the front
what does posterior mean
behind/to the back
what does lateral mean
away from the midline
what does medial mean
towards the midline
what does median mean
the exact midline
what does superficial mean
towards/on the surface
what does deep mean
away from/beneath the surface
what does external mean
outside, usually referring to hollow organs or a cavity
what does internal mean
inside
what does proximal mean
closer to the trunk
what does distal mean
further from the trunk
what does flexion mean
decreasing a joint angle
what does extension mean
increasing a joint angle
what is hyperextension
additional increase of a joint angle passed what is typical
what is lateral flexion
leaning of the trunk left or right
what is forward flexion
bending or folding of the trunk forward
what is apart of the axial skeleton
the skull, ribcage (ribs and sternum) and vertebral column
what is apart of the appendicular skeleton
everything not apart of the axial skeleton
what is a long bone, provide example(s)
bones that are longer than they are wide, work like levers for movement
e.g., the tibia and fibula
what is a short bone, provide example(s)
cube shaped bones that provide stability and some movement
e.g., carpals
what is a flat bone, provide example(s)
thin, flattened and often curved bones that provide surfaces for muscle attachment and protection for organs
e.g., hip, skull, scapula
what is an irregular bone
a bone with a unique shape that doesn’t fit other categories
e.g., vertebrae
what is a sesamoid bone
a small round bone embedded within tendons that protect tendons from stress
e.g., the patella
what is a tubercle bone marking
a small rounded projection, less rough than a tuberosity
e.g., greater and lesser tubercle of humerus)
what is a malleolus bone marking
a hammer shaped prominent protrusion
e.g., the bumps on the inside and outside of the ankle
what is a tuberosity bone marking
a large round and rough protrusion
e.g., the deltoid tuberosity where the deltoid muscle attaches to the humerus
what is a trochanter bone marking
a large blunt projection on the femur
what is a epicondyle bone marking
a projection above or on a condyle, only at the knee or elbow
what is a crest bone marking
a prominent ridge of a bone
e.g., iliac crest
what is a spine bone marking
sharp, slender process aka spinous process
what is a condyle bone marking
a large, rounded knuckle like process for articulation
e.g., occipital condyles (where skull sits on first vertebra)
what is a trochlea bone marking
a pully-like surface
e.g., portion at elbow that articulates with the ulna
what is a head bone marking
a rounded enlargement at the end of a bone
e.g., head of humerus that fits into the shoulder socket
what is a facet bone marking
a flat or slightly curved articular surface of a synovial joint
e.g., articular facets where adjacent vertebrae connect
what is a foramen bone marking
a round opening where blood vessels, nerves, ligaments, etc can pass through
e.g., vertebral foramen for the spinal cord
what is a meatus bone marking
a tube like passageway through a bone
e.g., ear canal
what is a sinus bone marking
air filled cavity within a bone
what is an alveolus bone marking
a deep narrow pit
e.g., tooth socket
what is a groove/sulcus bone marking
a grove that accommodates a soft structure
e.g., intertubercular groove
what is a notch bone marking
an opening along the edge of a bone to accommodate a soft structure
e.g., trochlear noth on ulna at elbow
what is a fossa bone marking
a borad depression
e.g., glenoid fossa (shoulder socket)
what is a fovea
a small fossa
e.g., costal fovea (small vertebra depression for rib articulation)
what is a process
a projection from the main part of a bone
e.g., spinous process
what is a fibrous joint
fibrous tissue uniting two articulating bones, allowing little to no movement
e.g., syndesmosis between radius and ulna
what is a cartilaginous joint
primary: hyaline cartilage uniting bones allowing temporary growth
e.g., growth plates
secondary: fibrocartilage uniting bones that are strong and slightly moveable
e.g., intervertebral discs
what is a synovial joint
a joint cavity between two bones containing synovial fluid, freely moveable
e.g., where the patella and femur meet
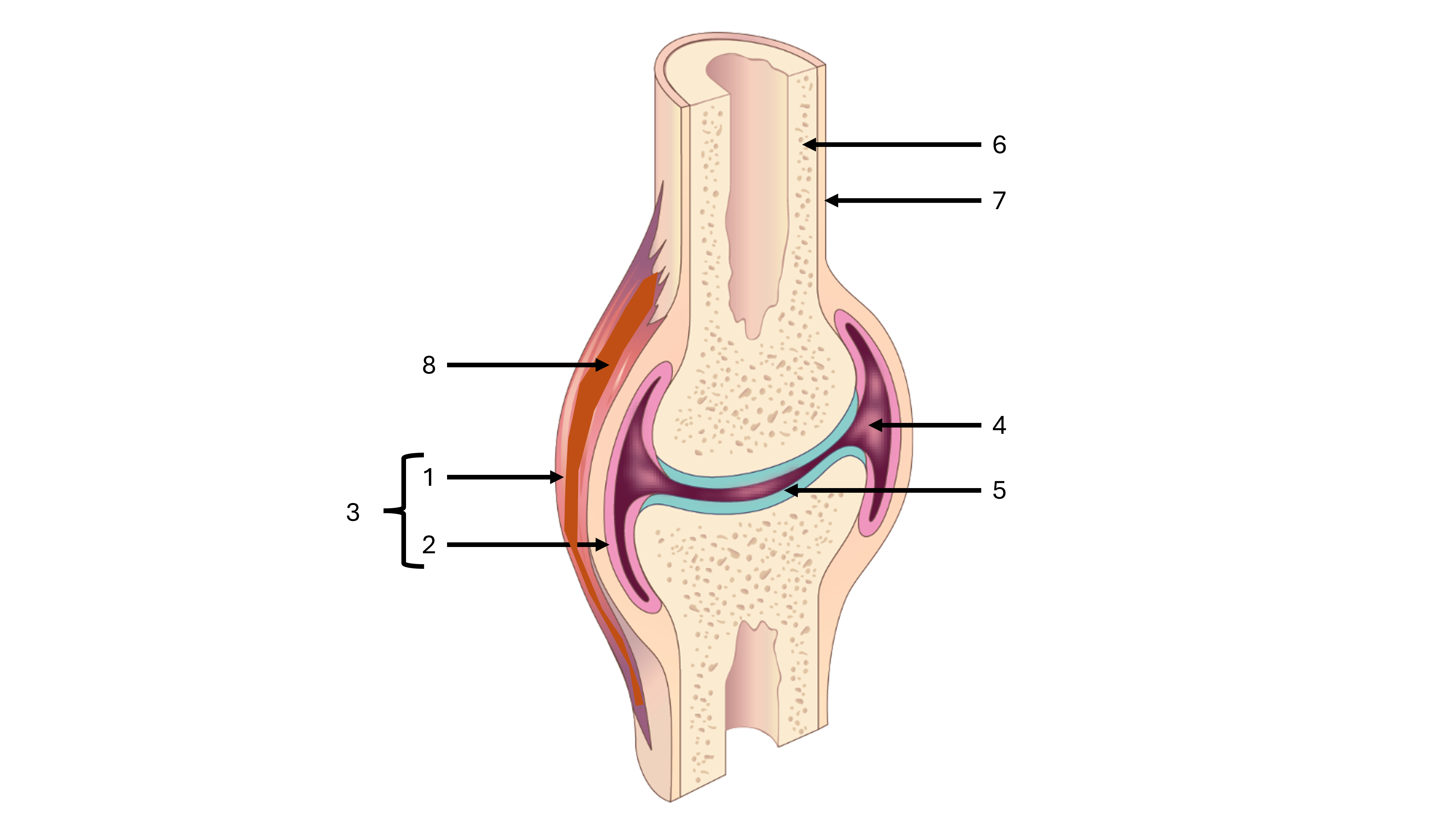
what is label #1
fibrous capsule
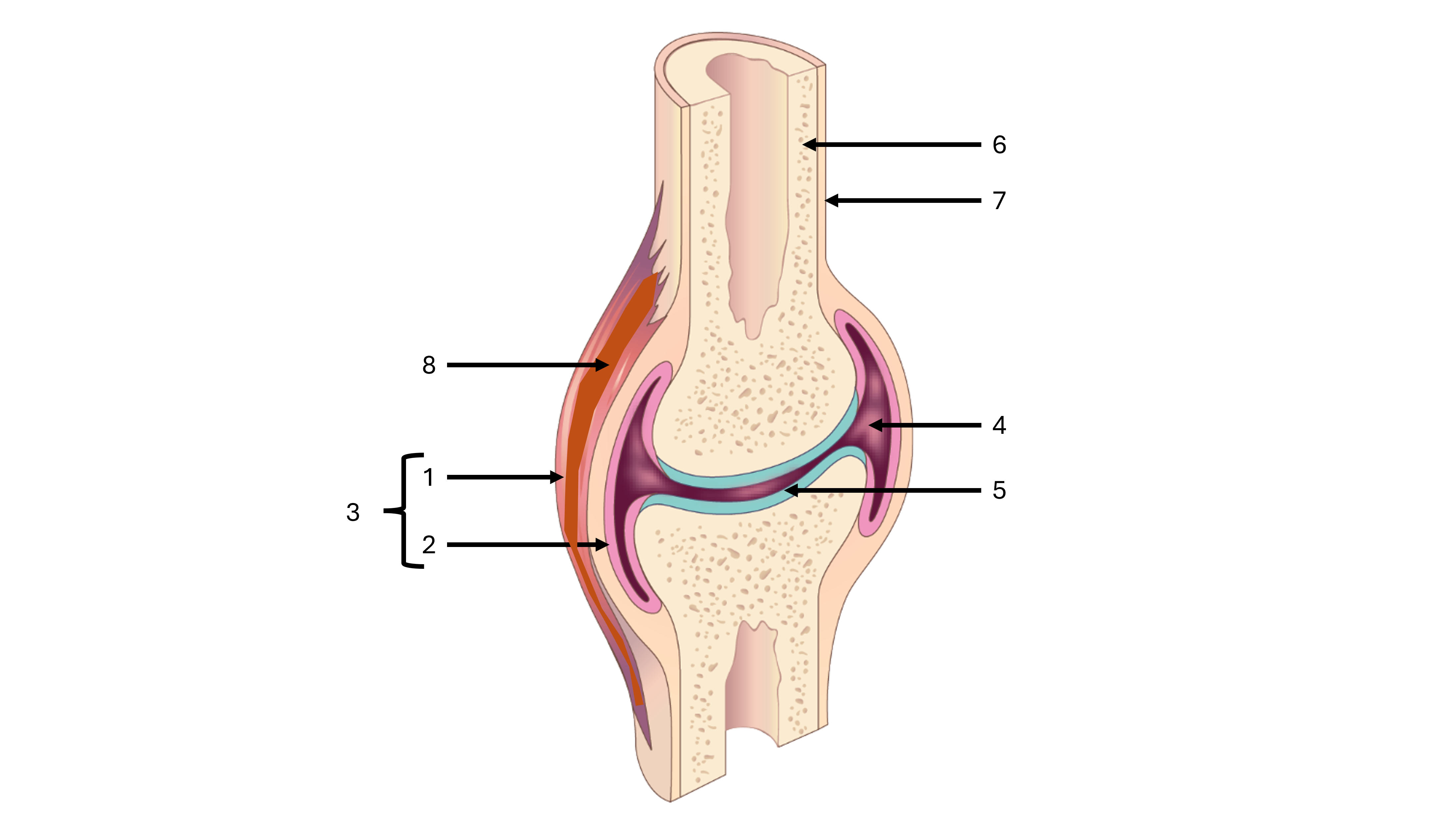
what is label #2
synovial membrane
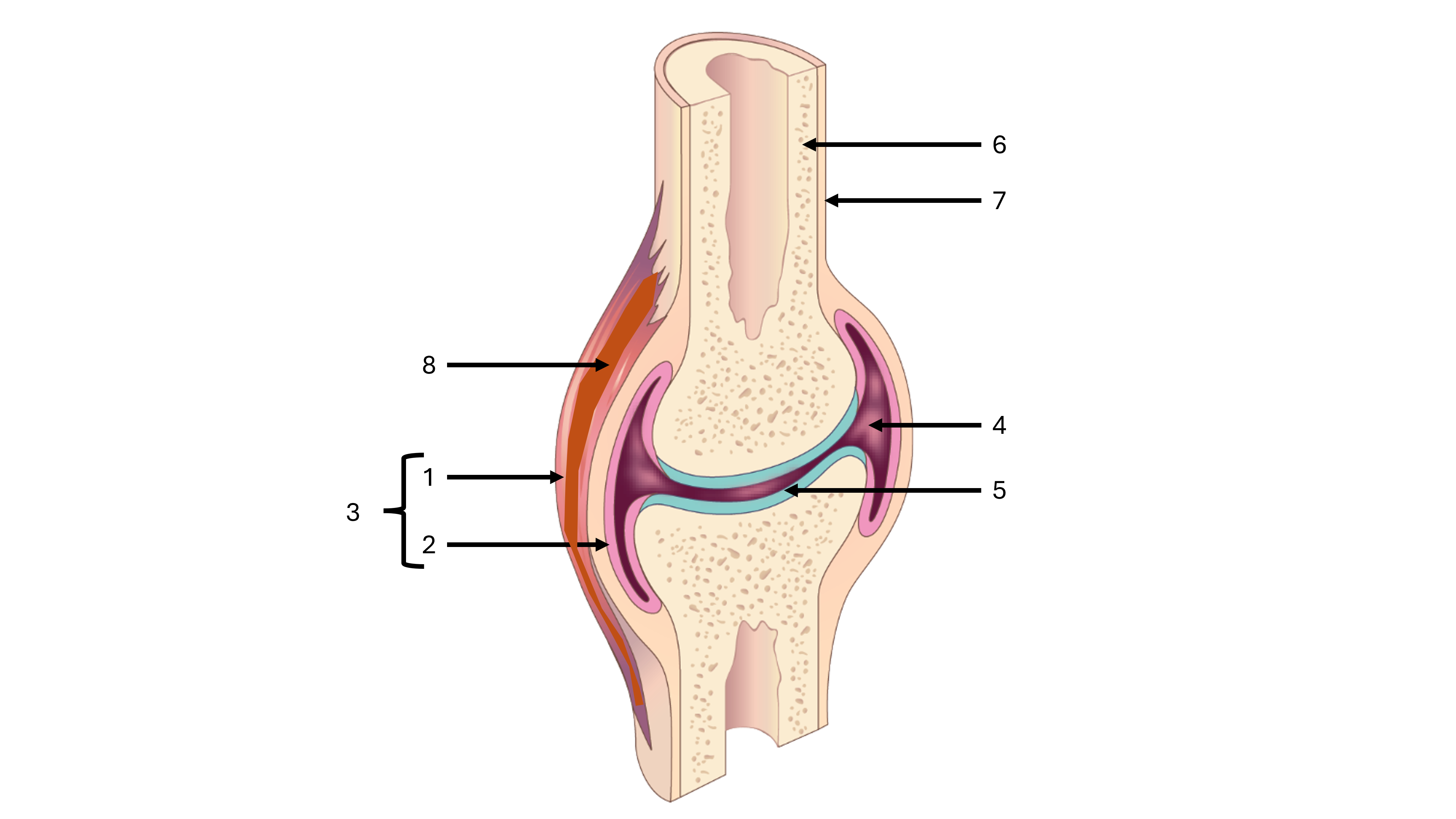
what is label #3
joint capsule
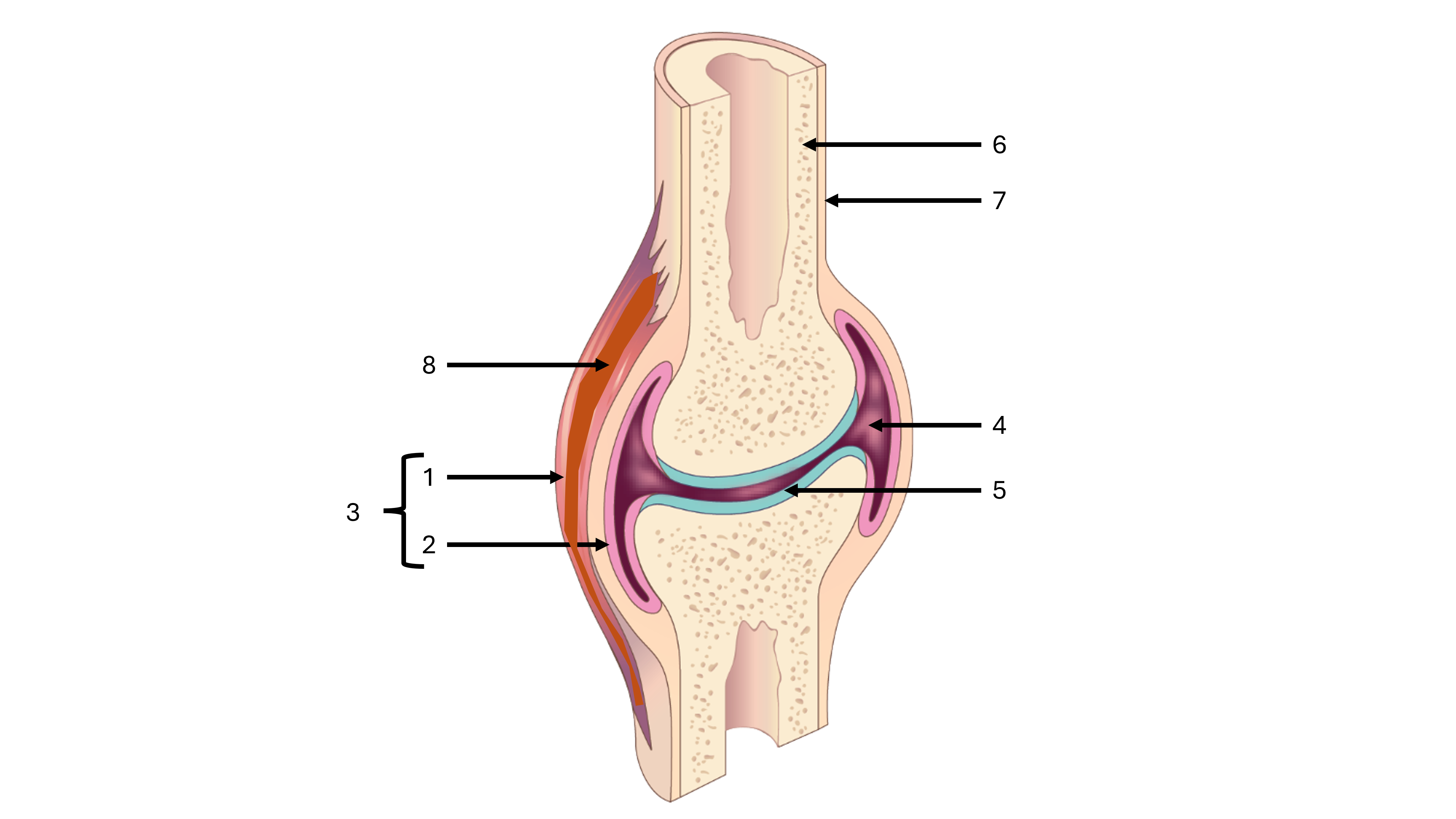
what is label #4
joint cavity containing synovial fluid
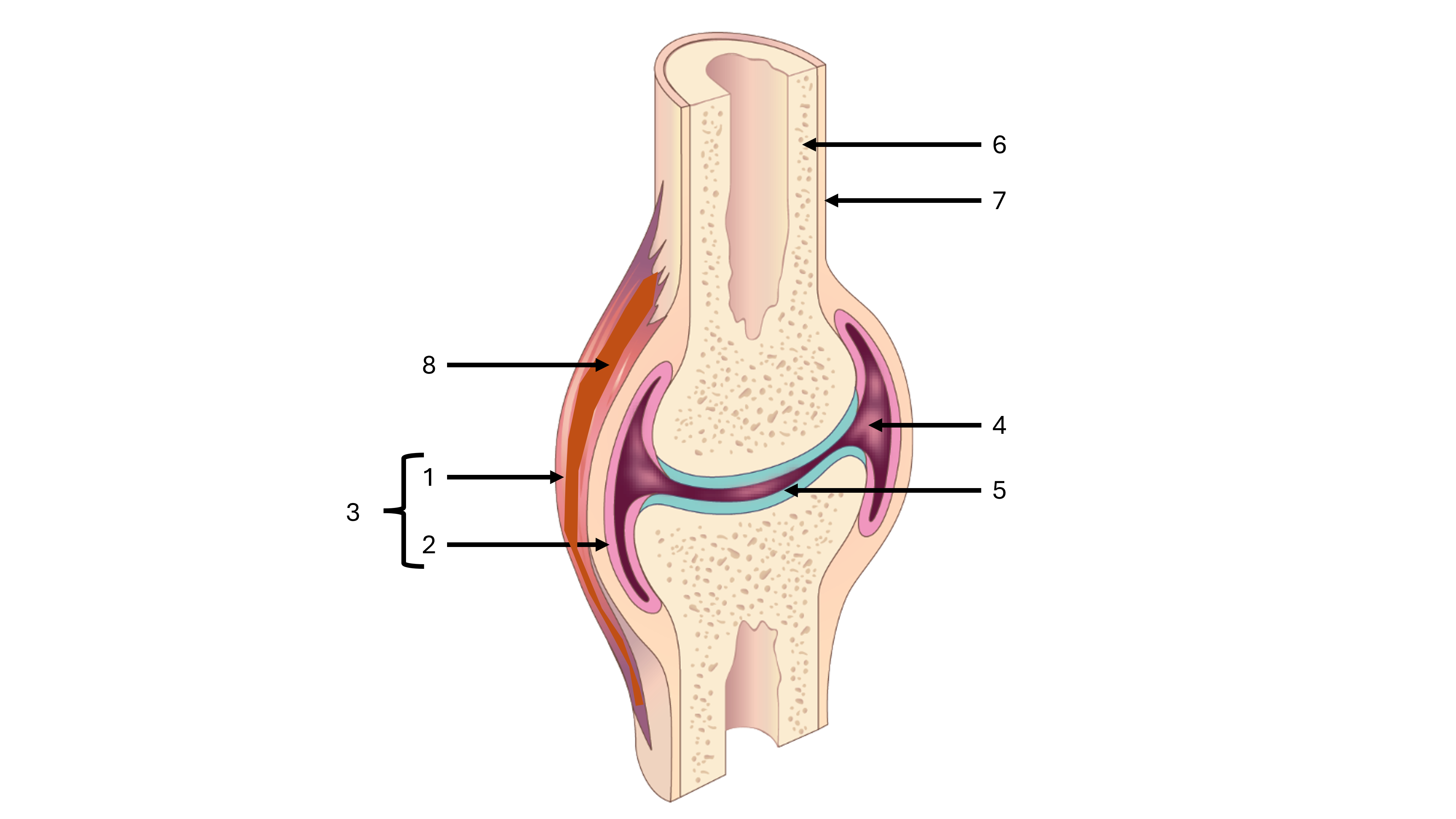
what is label #5
articular cartilage
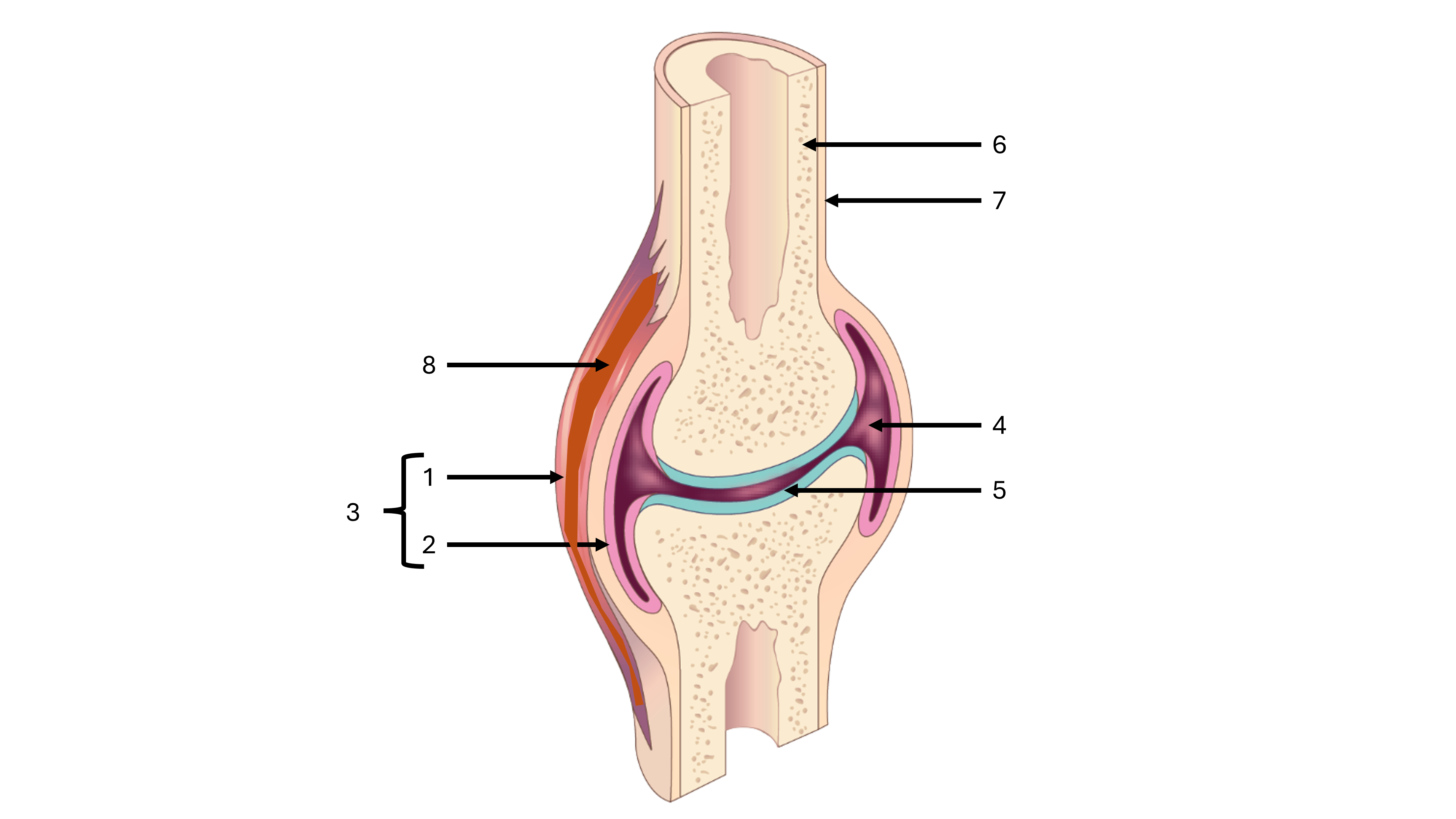
what is label #6
compact bone
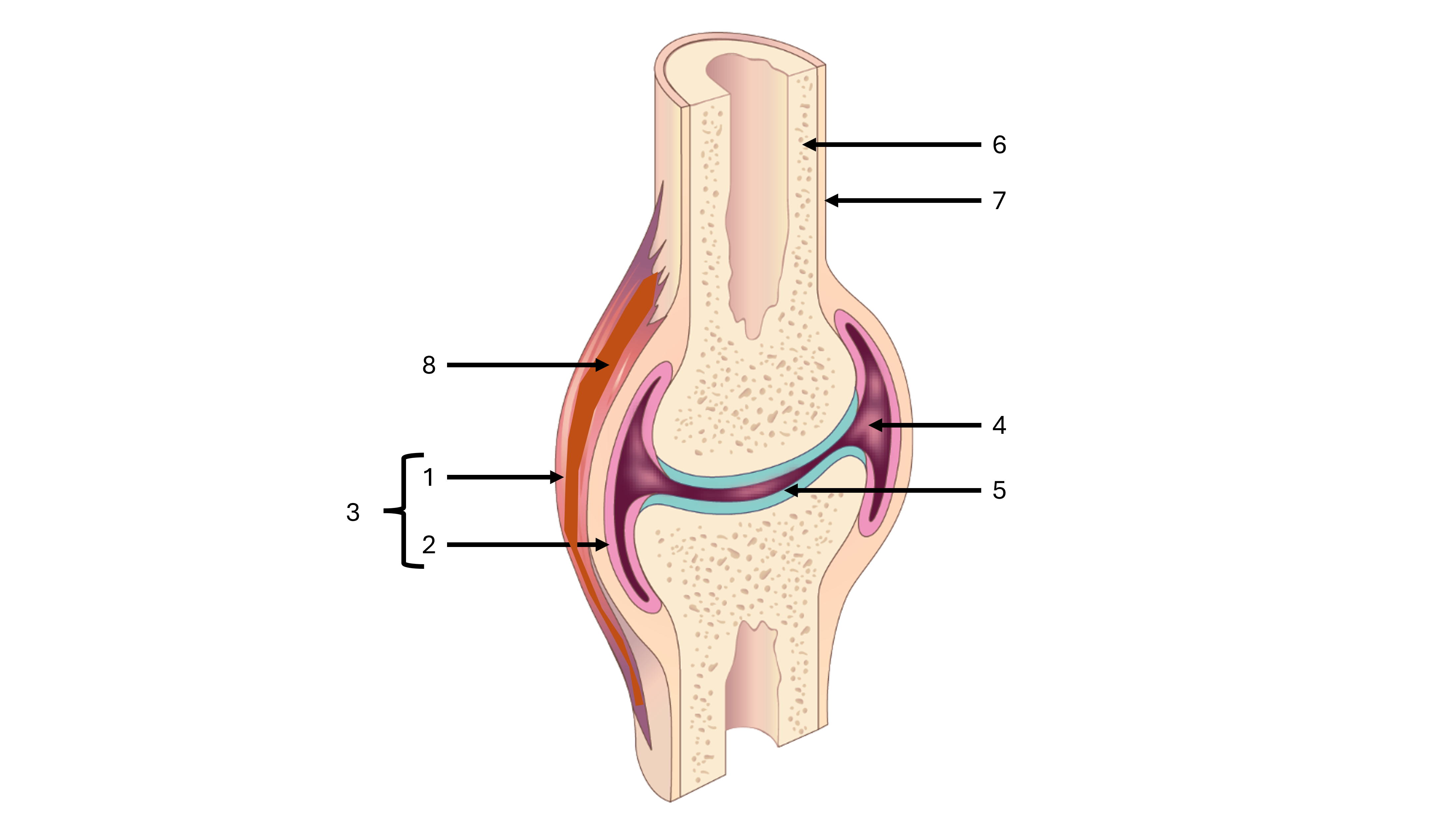
what is label #7
periosteum
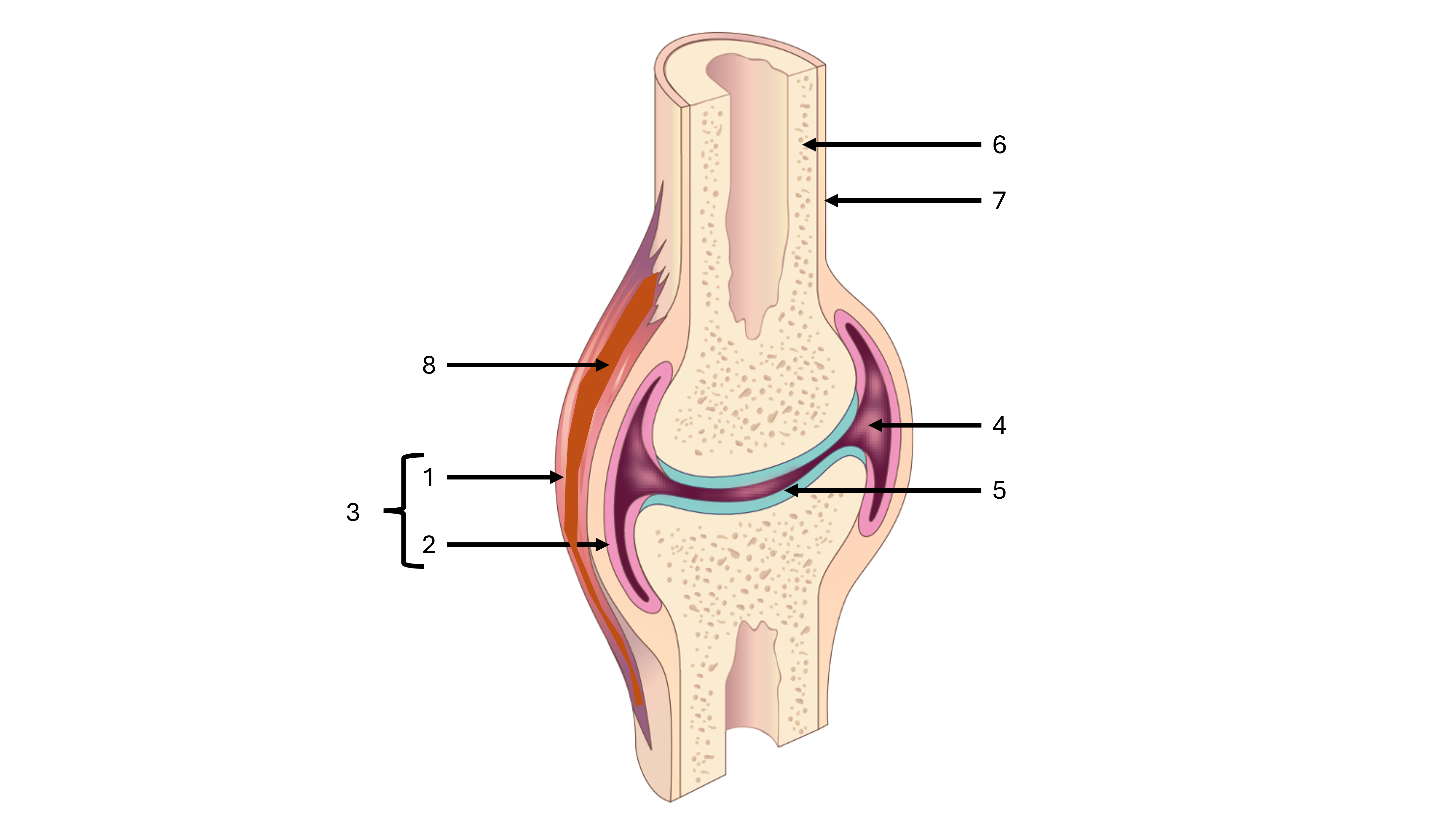
what is label #8
intrinsic ligament
what is an intrinsic ligament
a thickening of the fibrous joint capsule
what is a plane/gliding synovial joint
typically uniaxial joints permitting gliding and sliding movements
e.g., intercarpal
what is a condyloid synovial joint
biaxial joint allowing flexion, extension, abduction, adduction and circumduction
e.g., metacarpophalangeal
what is a saddle synovial joint
a biaxial joint allowing movement in two planes
e.g., carpometacarpal joint of thumb
what is a hinge synovial joint
a uniaxial joint allowing flexion and extension
e.g., elbow
what is a pivot synovial joint
a uniaxial joint where a round projection fits in a socket allowing rotation
e.g., proximal radioulnar
what is a ball and socket synovial joint
a multiaxial joint where a round head fits in a concavity allow movement in several axes
e.g., shoulder
what does aponeurosis mean
a thin flat sheet of tendon
what is a concentric contraction
muscle shortening
what is an eccentric contraction
muscle lengthening
what is an isometric contraction
muscle length stays the same
what system is the spine apart of
the central nervous system
what is the difference between the spine and the vertebral column
spine = vertebrae
vertebral column - collection of vertebrae and intervertebral discs
how many of each vertebrae does an adult have total, and per type
total: 33
cervical: 7
thoracic: 12
lumbar: 5
sacral: 5
coccygeal: 3-5 fused
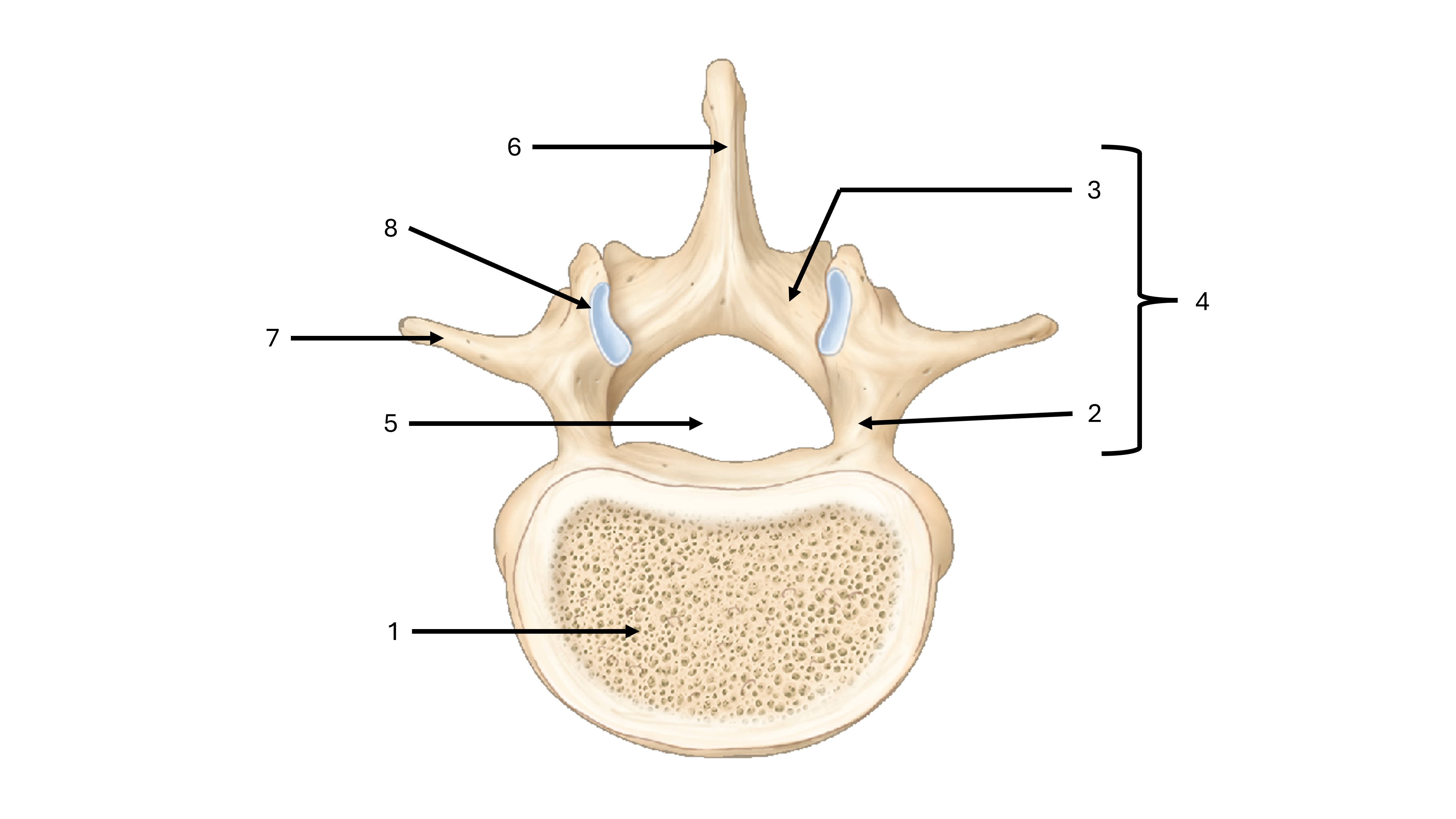
what view are we seeing this vertebrae from
superior
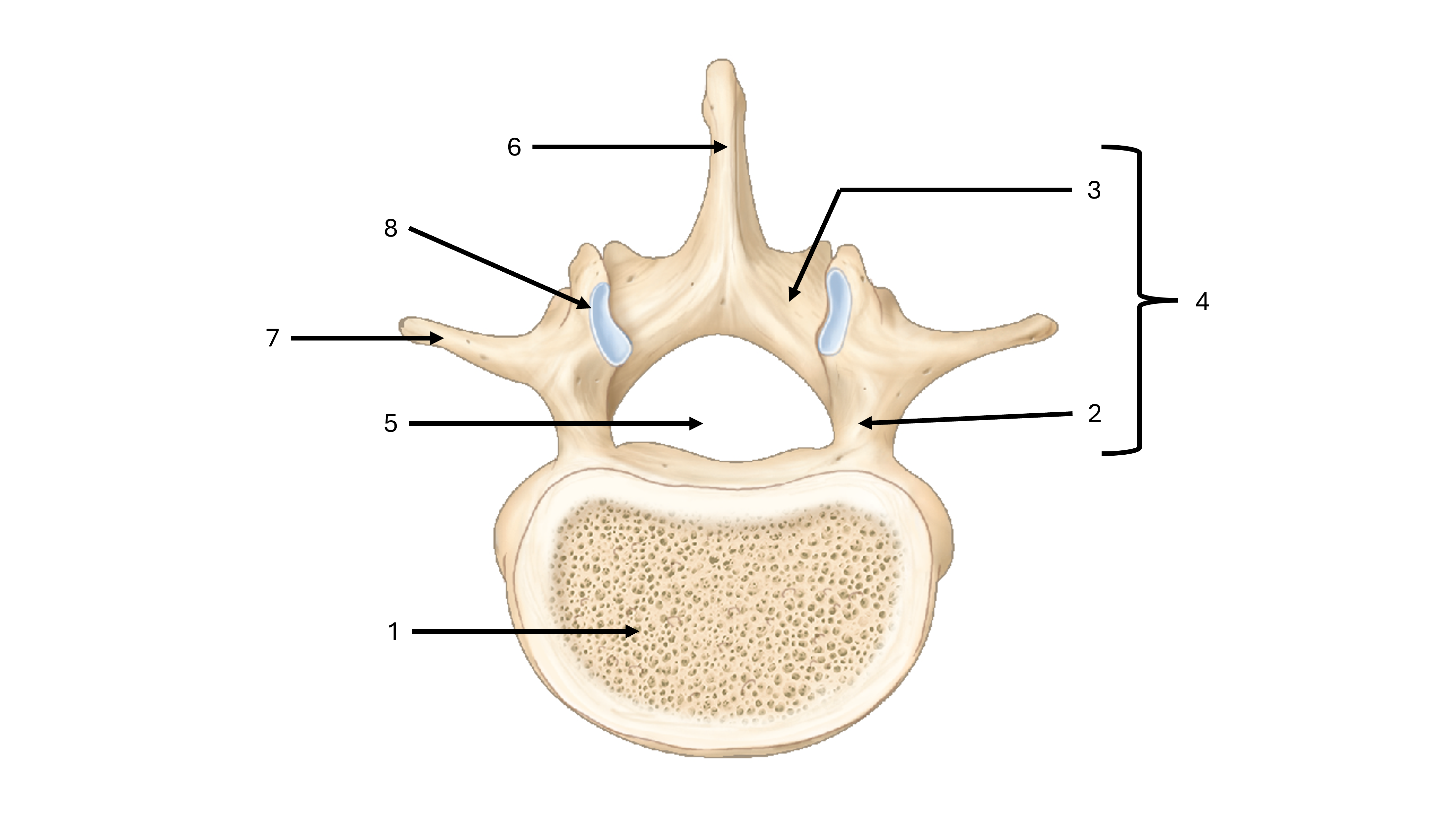
what is label #1
body
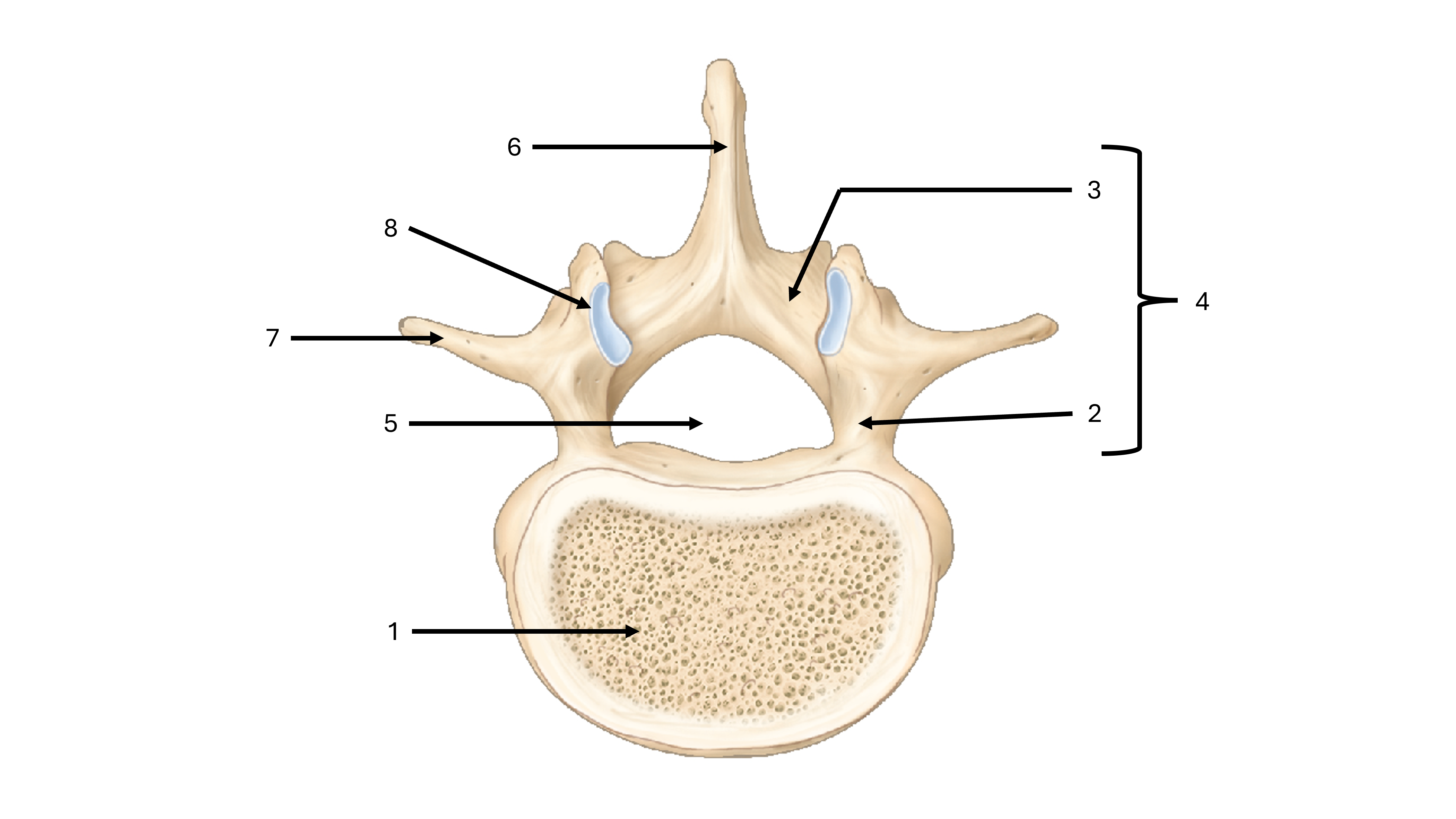
what is label #2
pedicle
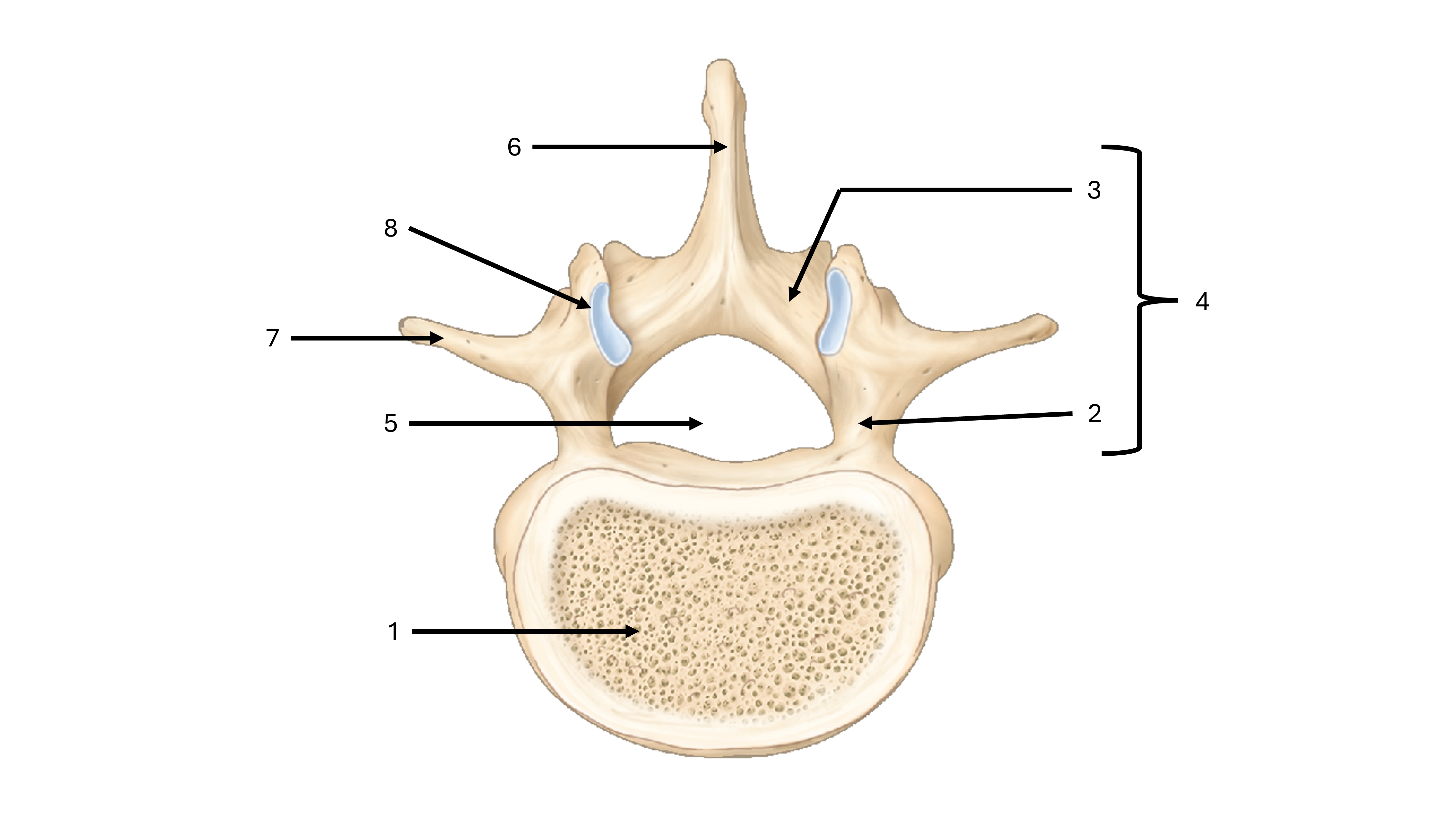
what is label #3
lamina
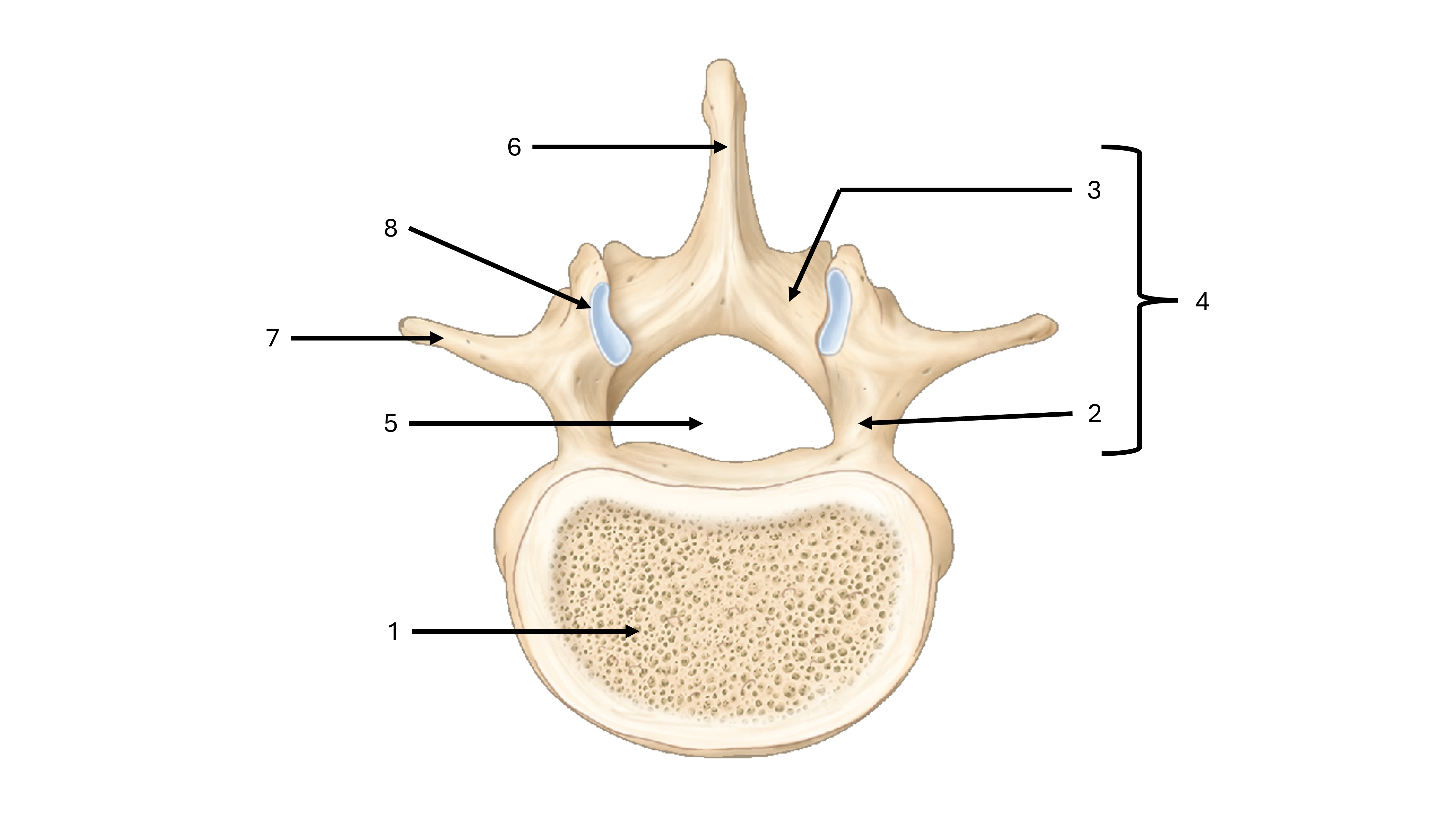
what is label #4
vertebral arch
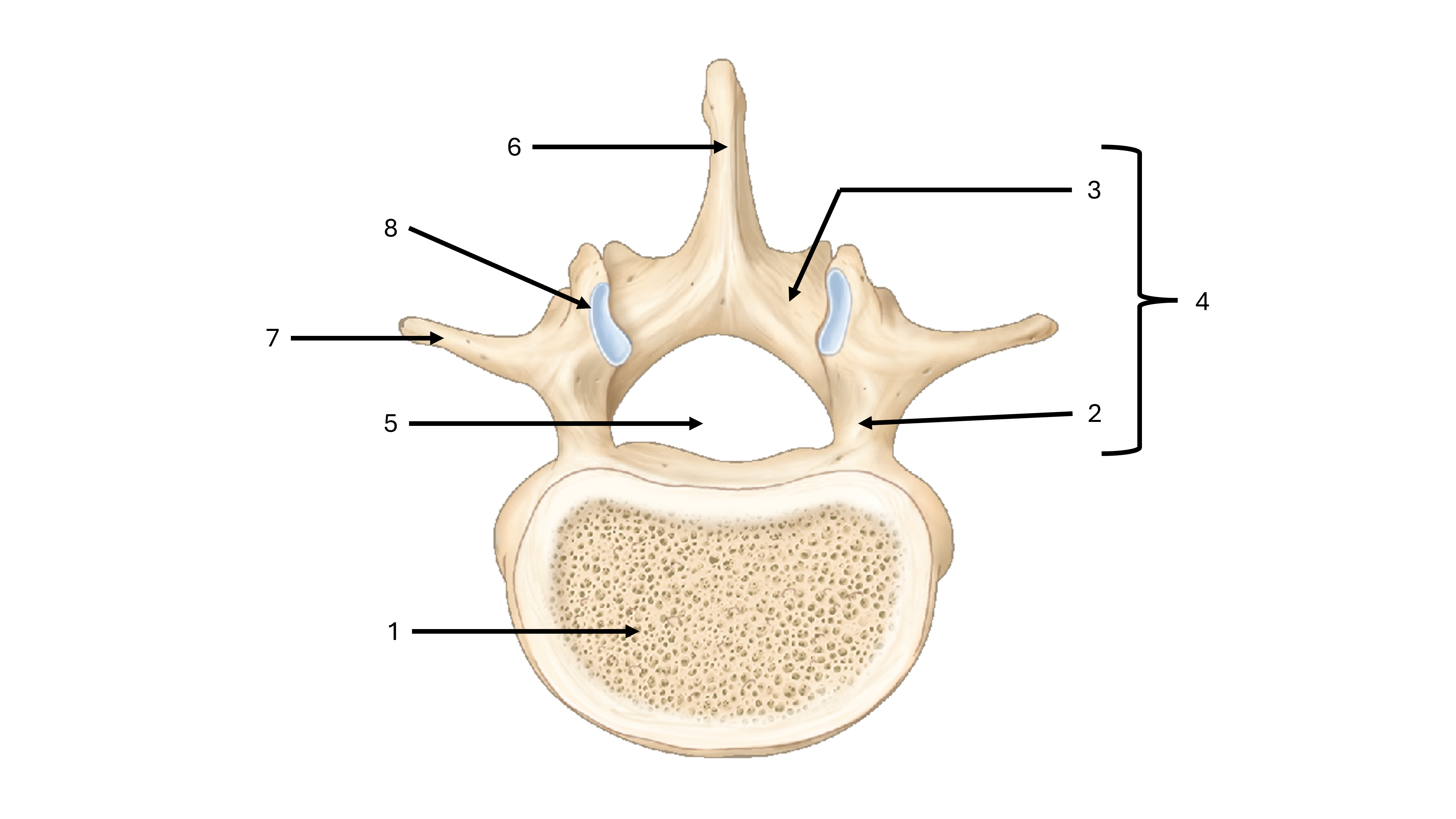
what is label #5
vertebral foramen
what passes through the vertebral foramen
the spinal cord
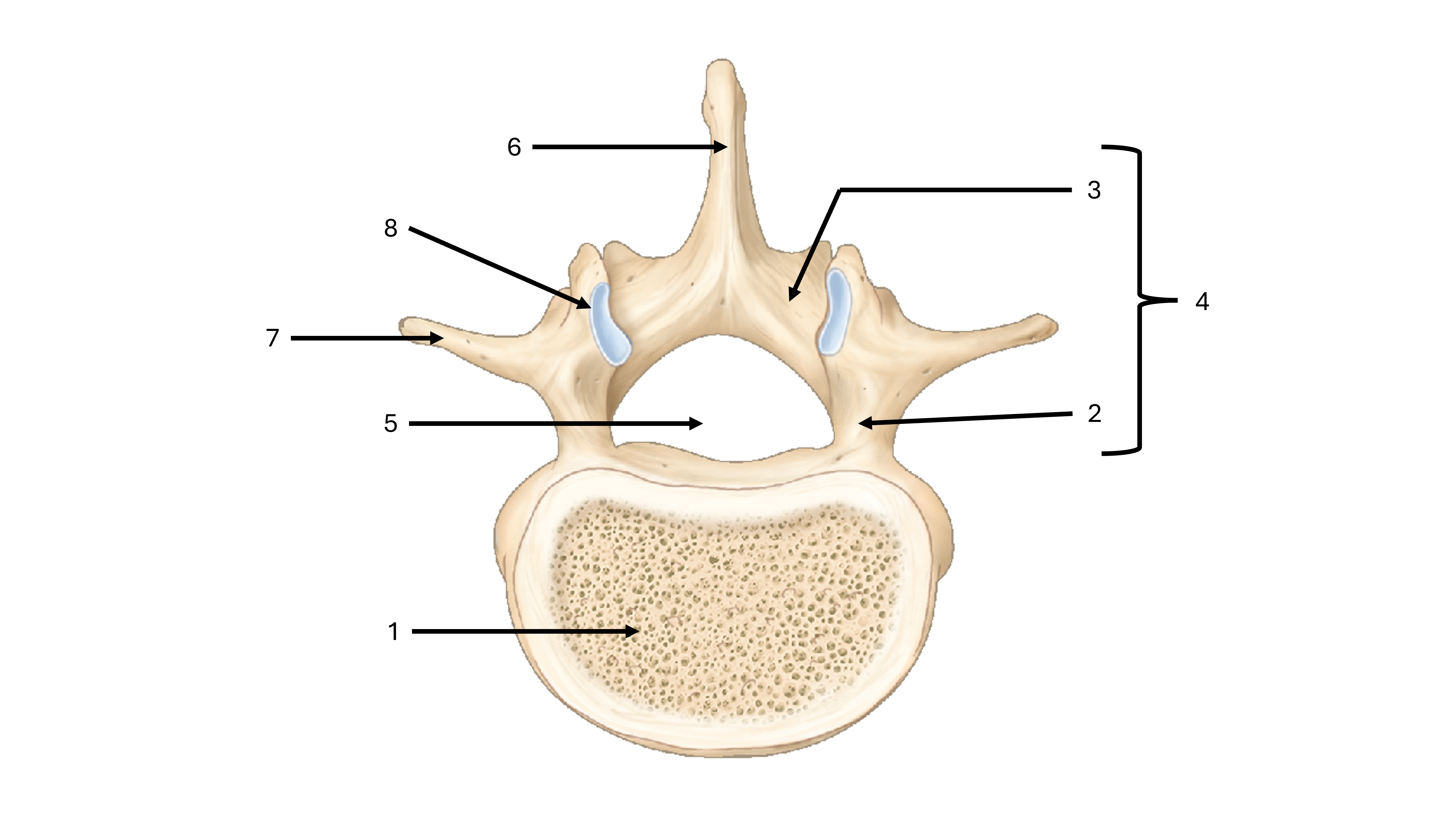
what is label #6
spinous process
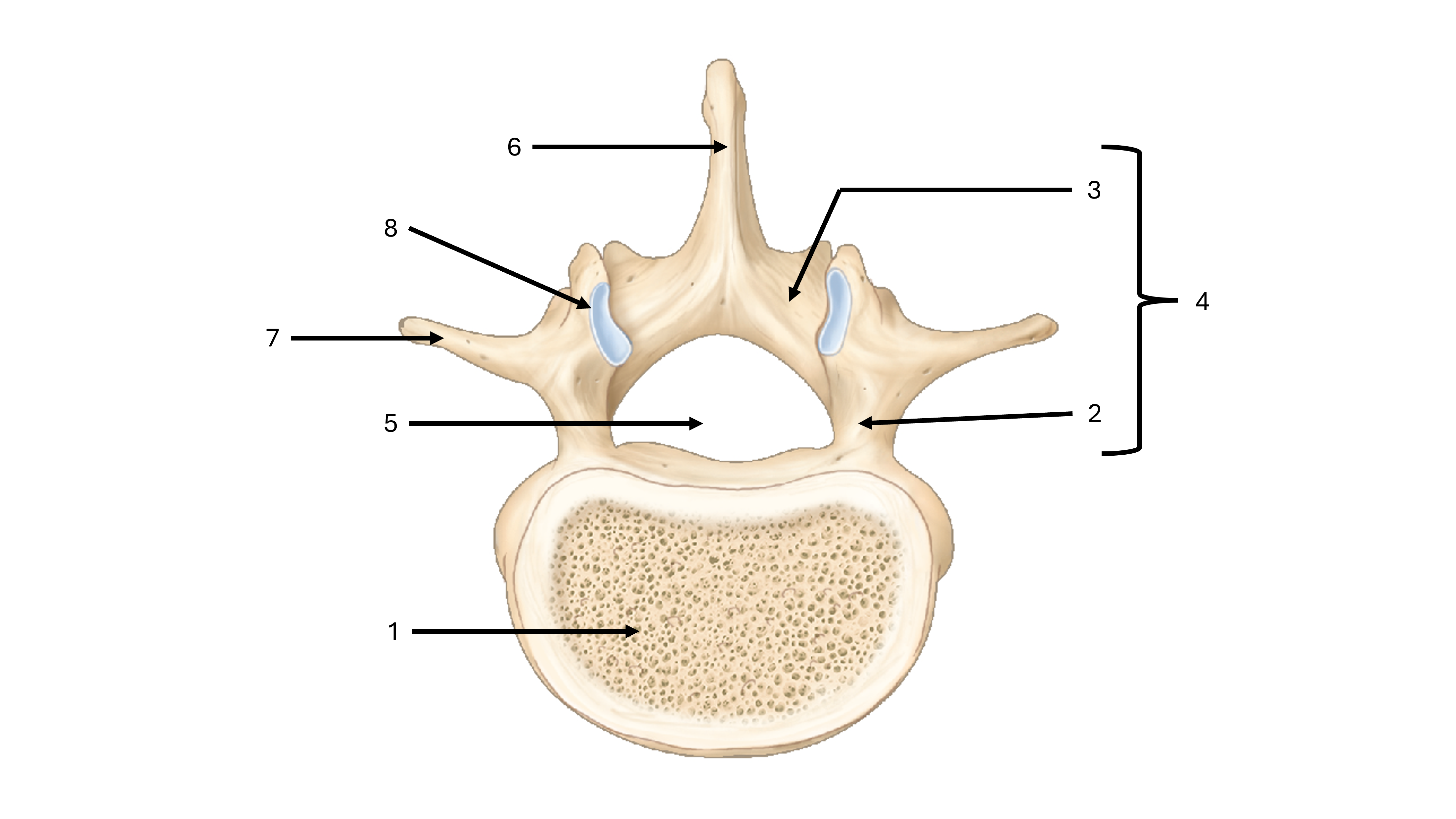
what is label #7
transverse process
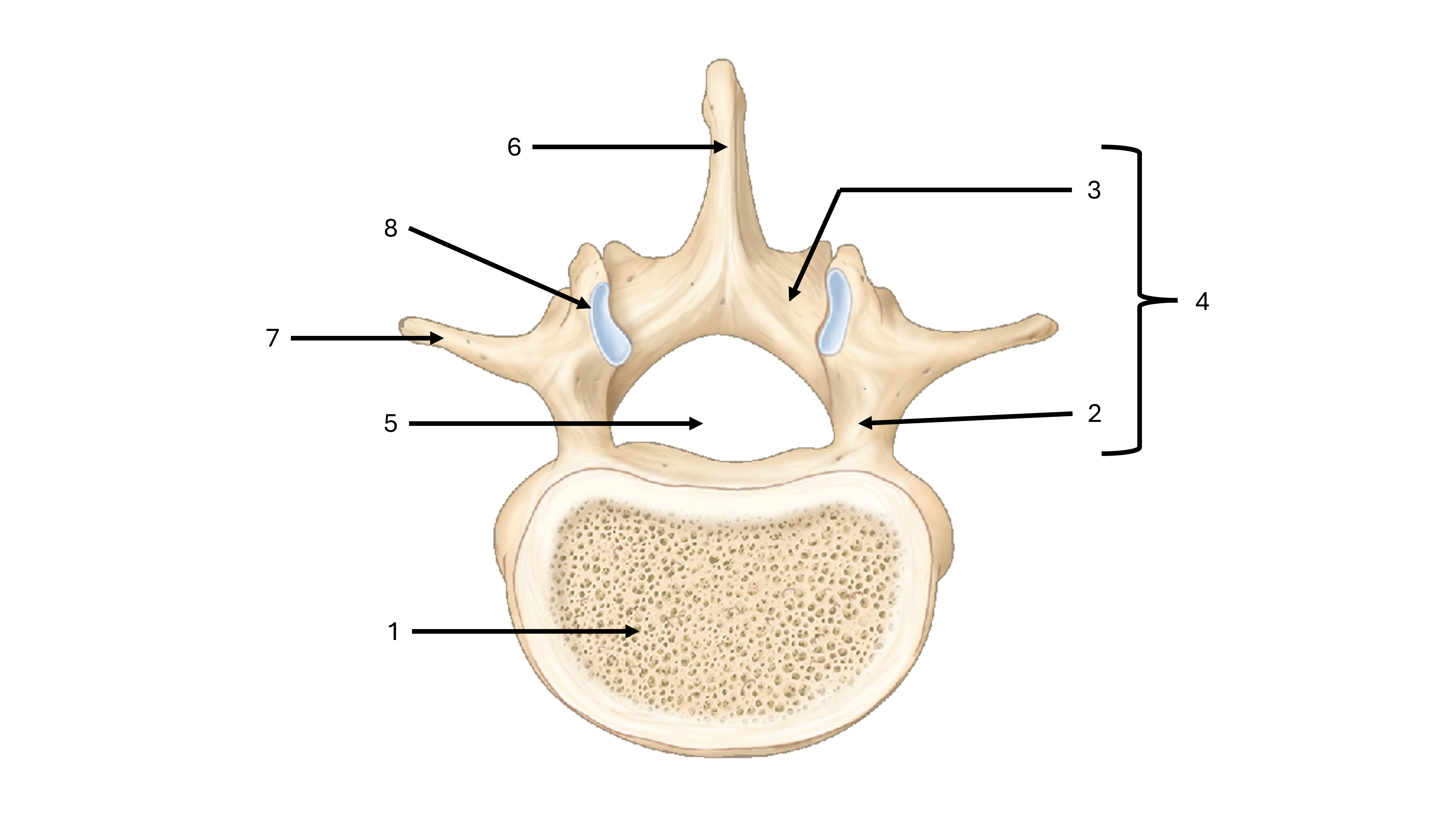
what is label #8
superior articular process/facet
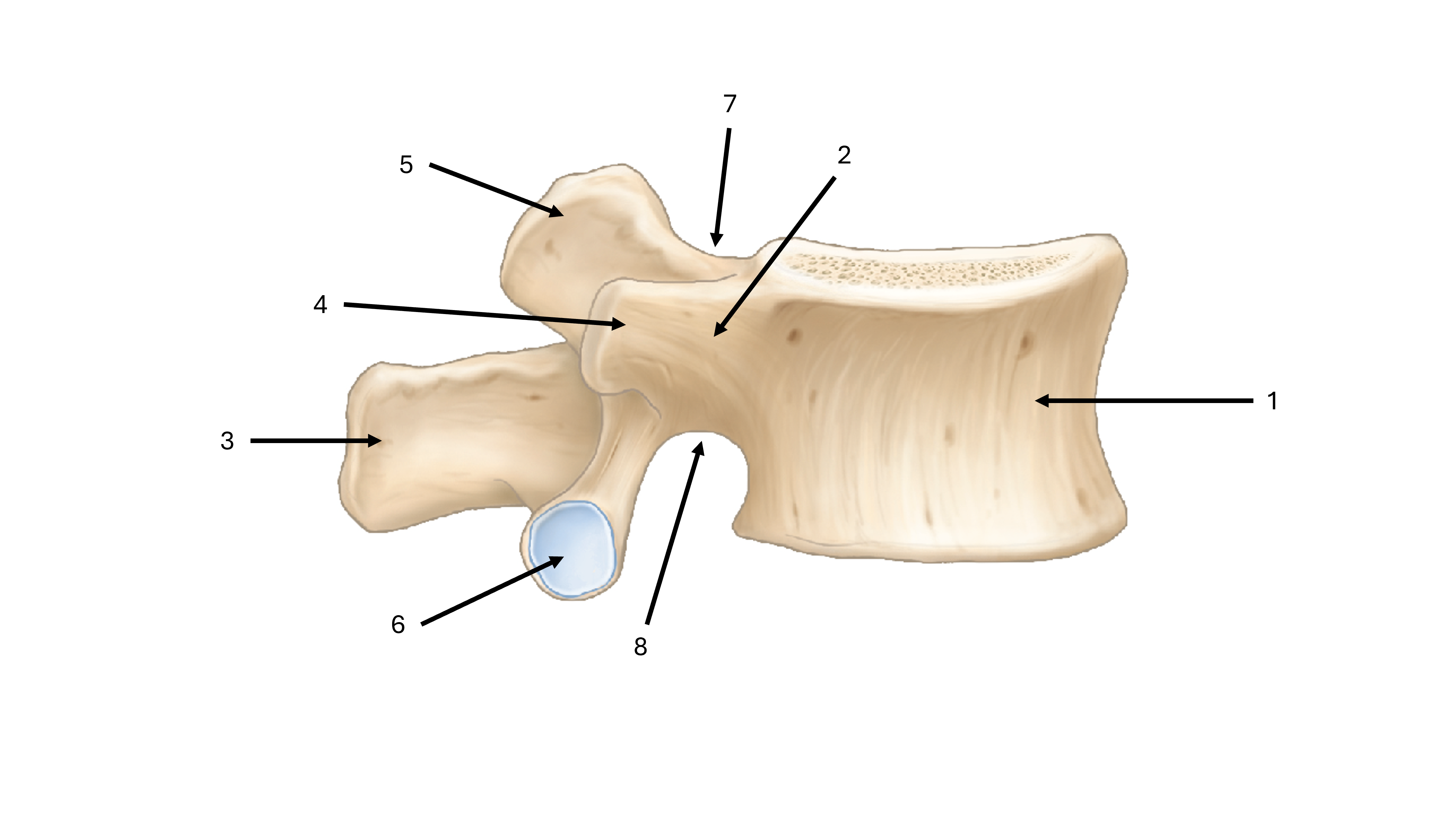
what is label #1
body
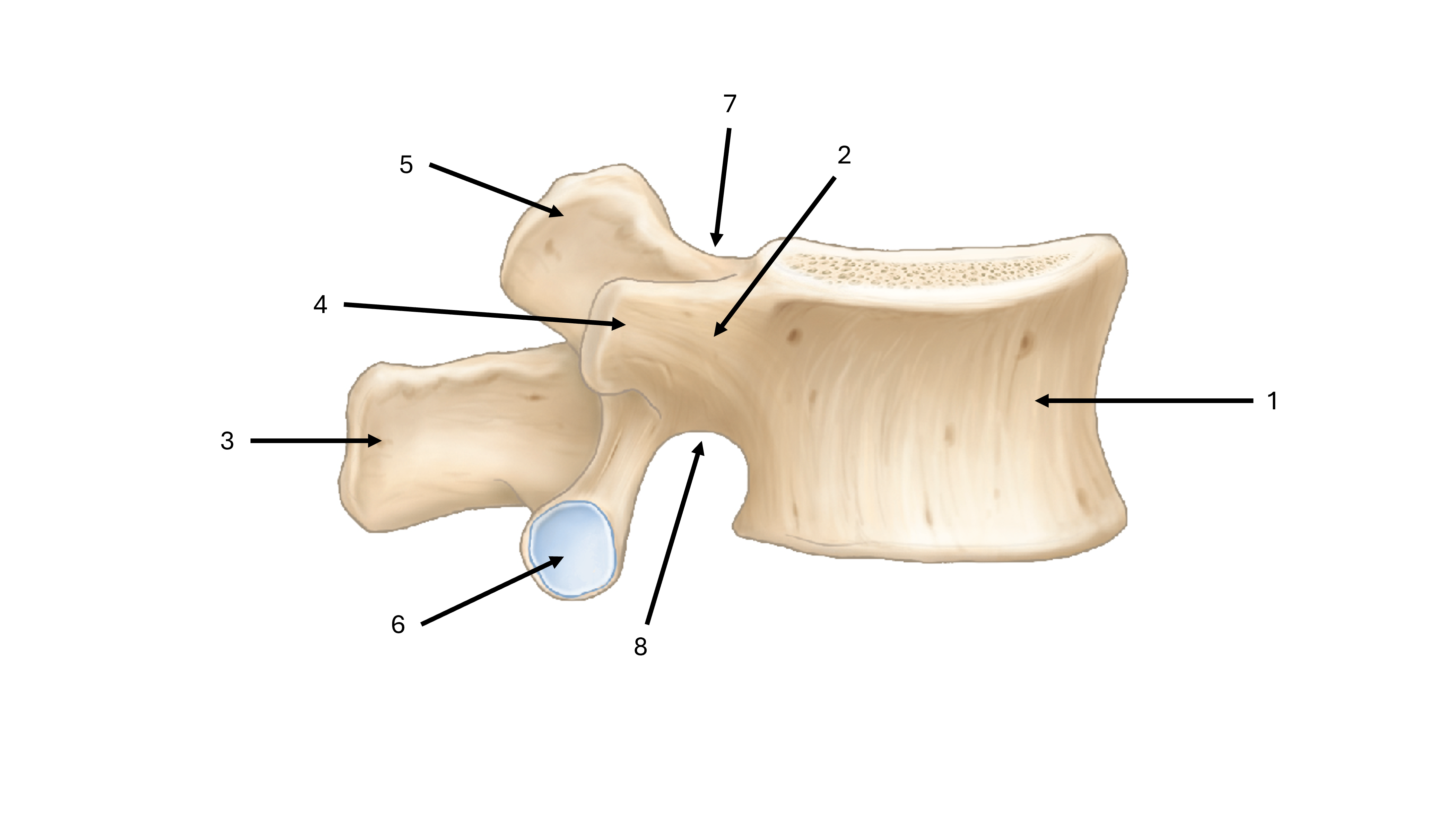
what is label #2
pedicle
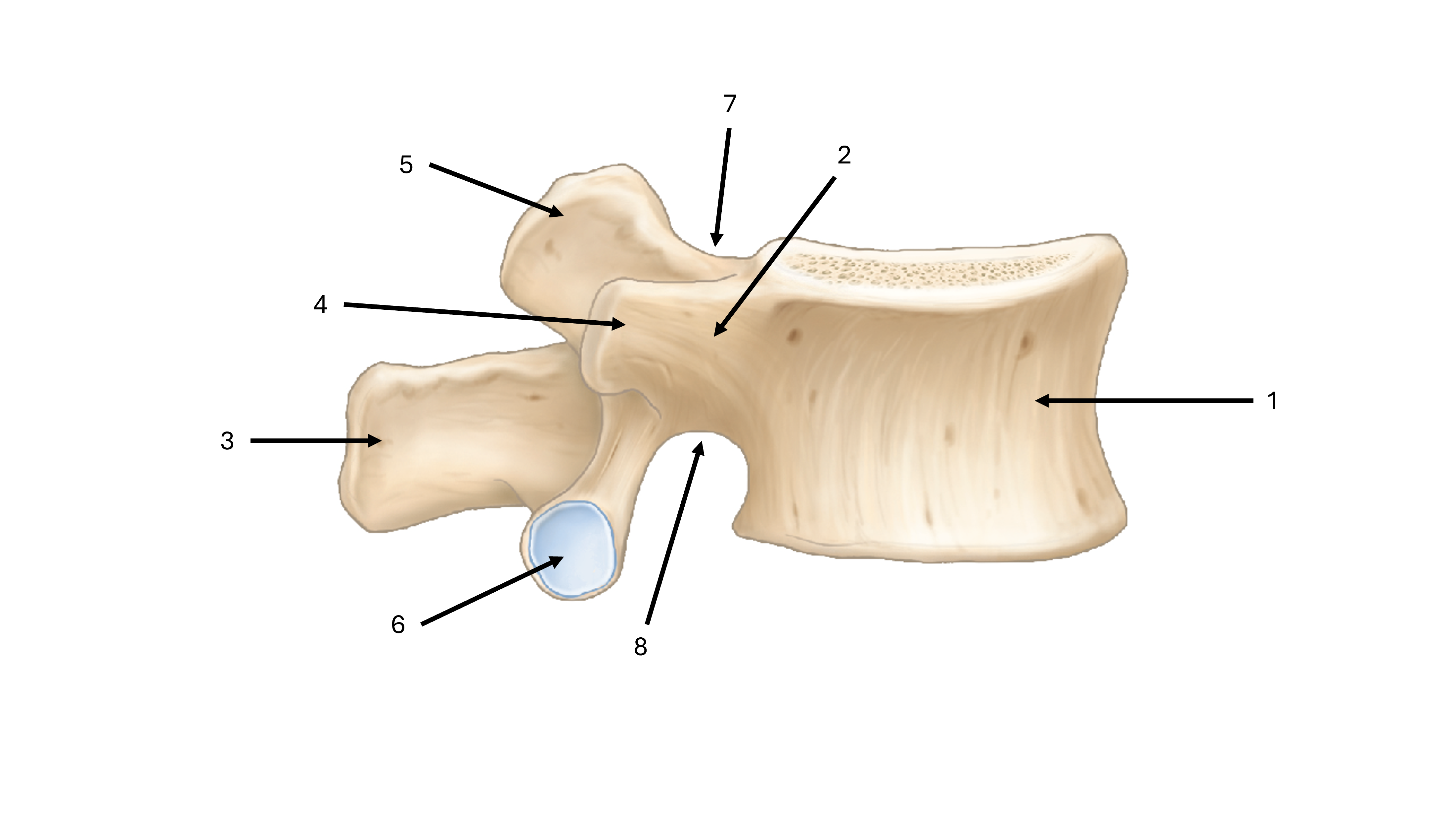
what is label #3
spinous process
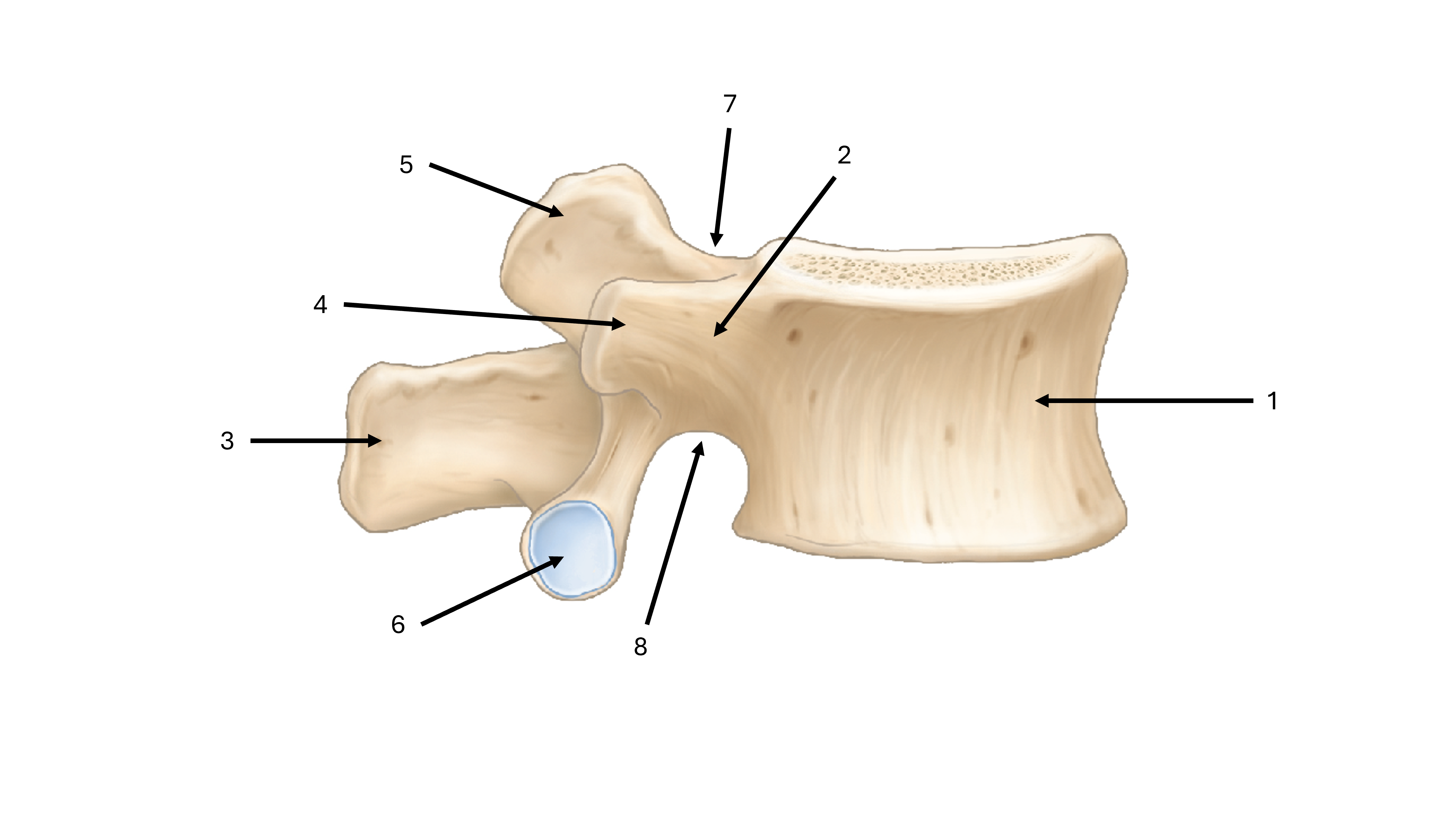
what is label #4
transverse process
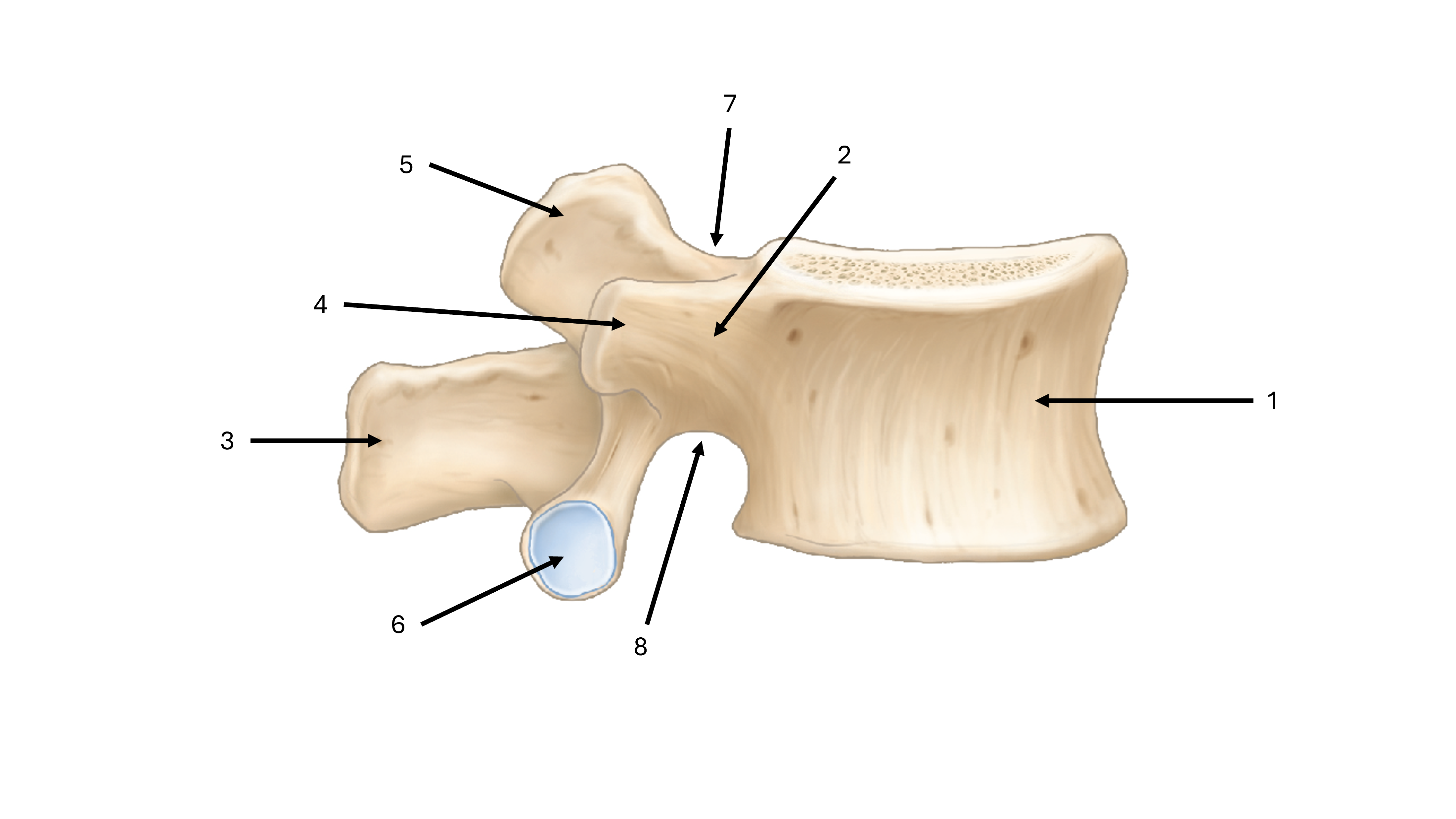
what is label #5
superior articular process/facet
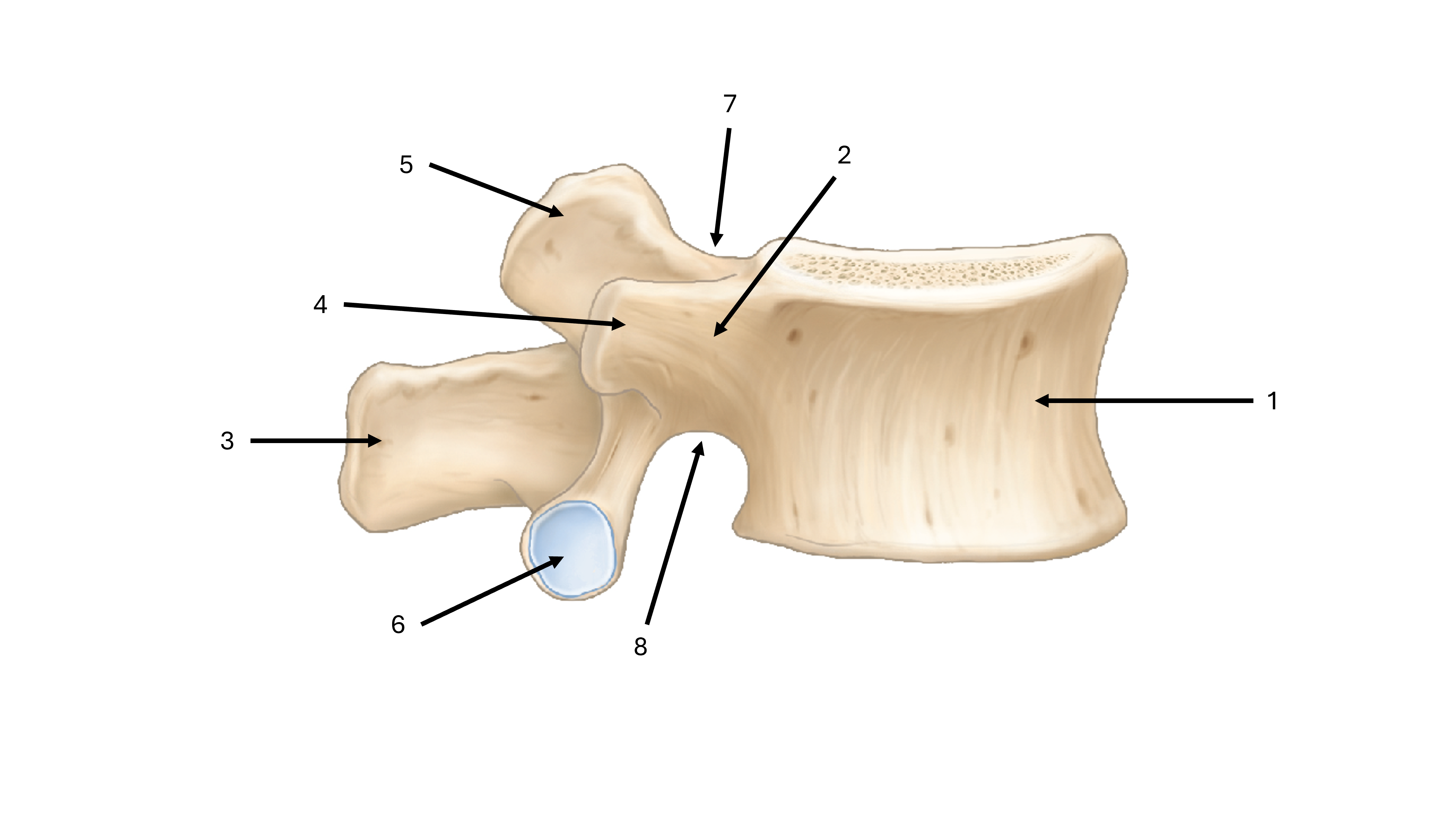
what is label #6
inferior vertebral process/facet
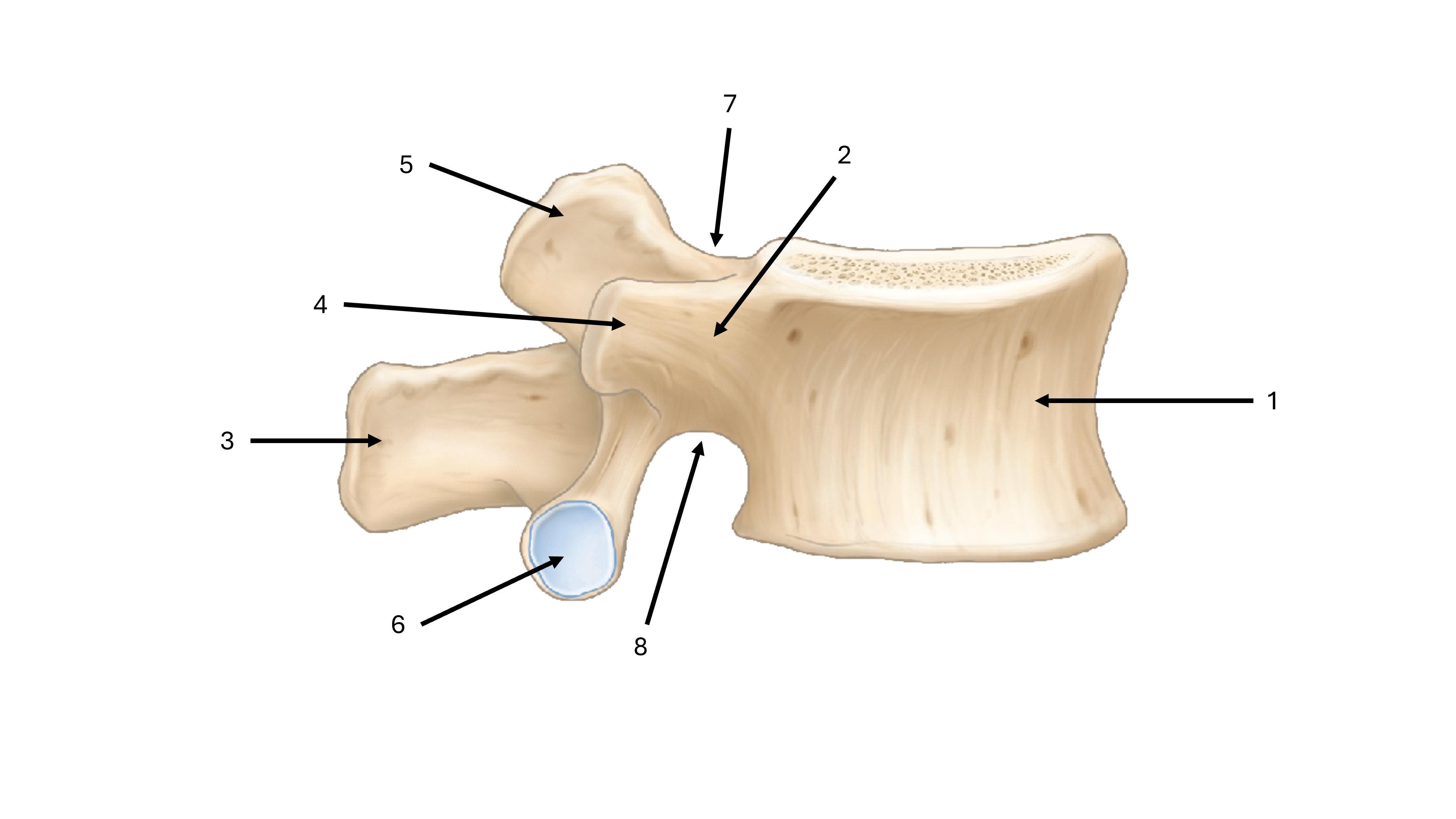
what is label #7
superior vertebral notch