The Horses Foot and Distal Limb
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Horse
Structures of the distal limb
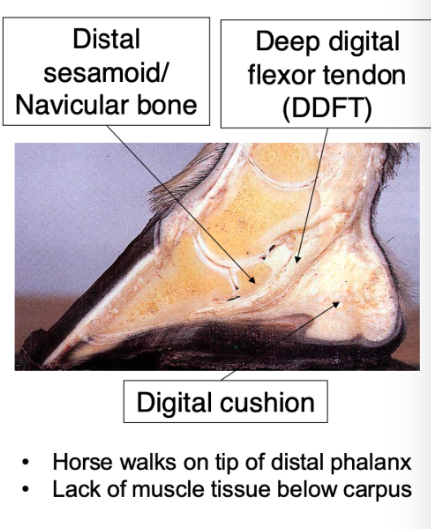
horse (unguligrade) walks on tip of distal phalanx
lack of muscle tissue below carpus (long tendons)
hoof contracts and expands with loads imposed
dynamic NOT STATIC strucuture
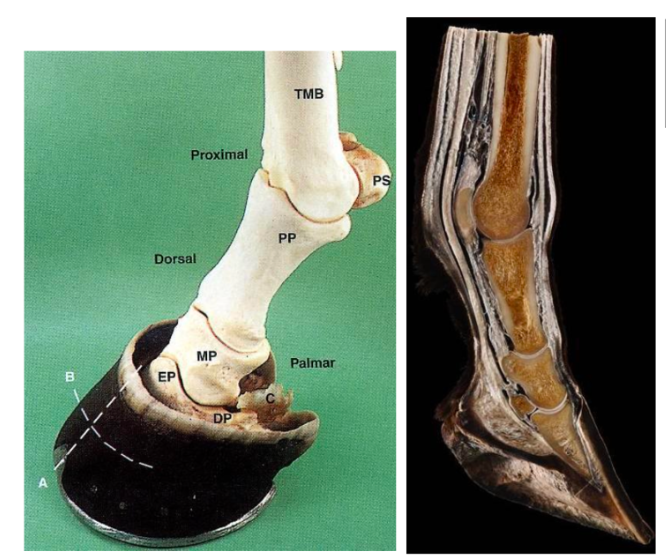
elongated 3rd metacarpal (with proximal sesamoid bones → Proximal phalanx → middle phalanx → distal phalanx (sits in the hoof capsule)
note extensor process of distal phalanx
navicular (distal sesamoid bone) - palmar/plantar aspect + sits inbtw DP and MP
DDFT inserts on the distal phalanx
cranial to caudal
navicular bone → DDFT → digital cushion
Distal phalanx (pedal bone)
Mirrors shape of hoof
Bound to hoof wall via lamellae
Collateral cartilages
projections of distal phalanx
Shock absorptive, blood flow role
Calcify with age in larger heavier breeds → fracture
Synovial structures
Large joint spaces with dorsal and palmar recesses
Very large dorsal + palmar recesses
Easy access for synovial fluid sampling or injection
Inject corticosteroids → arthritis treatment
Located at distal interphalangeal joints
Digital cushion
Role: shock absorption and circulation
Hydrostatic cushion- minimises pressure changes in navicular apparatus
Complex loading env: Compressed by middle phalanx and DDFT (via collateral ligaments)
Monitors load in navicular region via pain and pressure receptors
Tissue: myxoid tissue + fibrocartilage
collagen
elastic tissue
fat
Extends under distal sesamoid bone
Provides support for navicular bone and palmar pedal bone
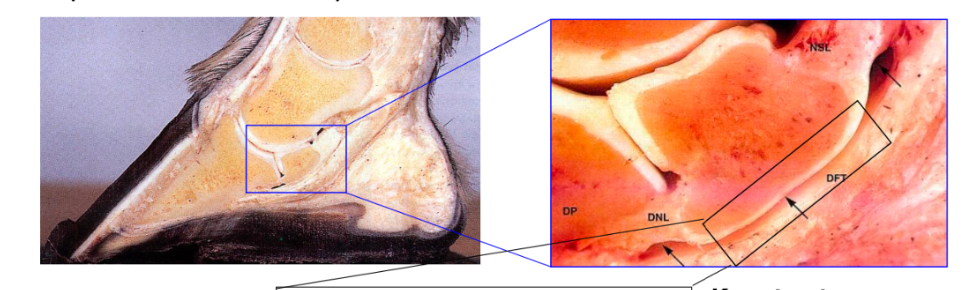
Navicular bursa
Plus navicular ligaments
Visible when DDFT reflected
Filled with synovial fluid
Navicular bone has fibrocartilage where it meets the bursa
hyaline cartilage when meeting phalanx
navicular suspensory ligament (collateral sesamoidean ligament)
suspends navicular bone
attaches proximal border to distal second/middle phalanx
distal navicular ligament
(distal sesamoidean ligament)
suspends navicular bone
attaches distal border to distal/third phalanx
Navicular syndrome/disease (palmar foot pain)
Common cause of lameness
Involves navicular bone + surrounding structures
Lesions formed in navicular bursa → friction with DDFT → pain
No reversal just management
shoeing horse advantages
protection against penetration of sharp objects
less likely to slip on wet/muddy surfaces
feet unlikely to wear unevenly
shoeing horse disadvantages
farriers regulated by farriers regulation council
expensive
potential to increase lameness
entirely dependent on horse activity
unnatural → barefoot has greater contact area with ground
shoe bears most of weight peripheral through hoof wall
nails placed into white line → between sensitive lamellae + dermis and insensitive hoof wall
nail ends are bent outwards to side of hoof → secures nails in place
Barefoot hoof care
Bearing weight through solar surface and hoof wall
Correct diet and environment important for good hoof growth
Hoof boots → provide protection (e.g. stony ground)
Effect of barefoot trimming V shoeing
Studies have shown:
Shoeing changes hoof shape
Shoeing decreases digital cushion thickness and increases stride length
Shoeing decreases hoof temp
Shoeing improves lameness scores
Epidermal and dermal structures
Hoof is specialised skin
Epidermis (outer → inner)
Stratum externum
Stratum medium
Stratum internum (interdigitates with dermis)
Dermis (corium) [inner vascularised and innervated]
Peri-oplic corium (above the coronary band)
Coronary corium
Lamellar corium (majority)
Solar corium
Epidermal/Primary lamellae
Projections from dermis and epidermis
Primary lamellae- interdigitate
provides high surface area to bind dermis and epidermis
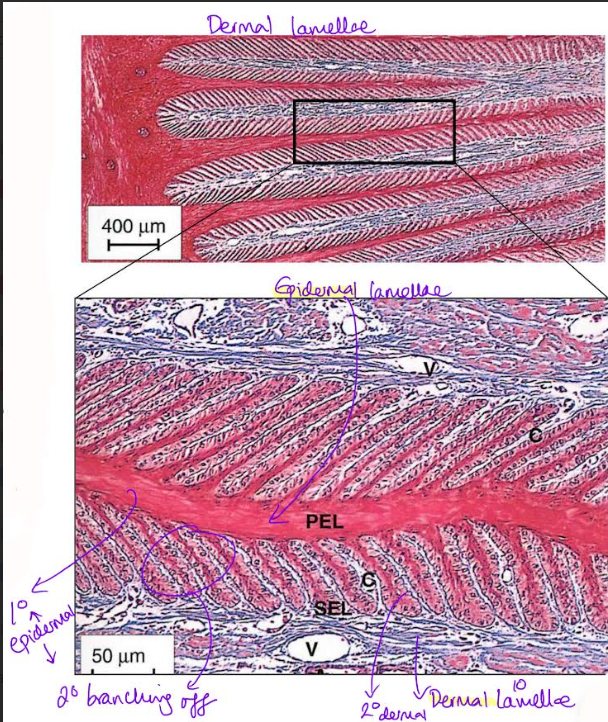
Dermal/Secondary Lamellae
Cross-section
hoof wall (stratum internum of epidermis)→ lamellae → dermis → distal phalanx
Each primary lamellae have secondary lamellae
Highly vascularised
Surface friction prevents lamellae pulling apart
Hoof wall growth
Growth to replace hoof lost to wear
Regeneration occurs at coronary band
Germinal cells in epidermis → daughter cells → mature + keratinise, add to proximal (deepest) hoof wall
More proliferative cells in proximal V distal lamellae
New hoof wall moves past stationary distal phalanx via remodeeling in epidermal lamellae
Horse foot blood supply (inside)
Extensive blood supply: palmar digital arteries
Drainage: lateral & medial digital veins
Horse blood supply (outside)
Hoof wall → epidermis → lamellae [axial veins and arteries] → sublamellar dermis
[sublamellar venous plexus + parietal branches of palmar/plantar digital arteries]
sublamellar venus plexus drains dermis/corium
supplies by parietal braches of terminal arch of palmar/plantar digital arteries
Axial veins and arteries are within the primary dermal lamellae ABOVE the sublamellar dermus
Dermal microcirculation
Capillary beds in 2ndary dermal lamellae
Arteriovenous anastomoses (AVA) regulate blood supply
Directly connect arteries and veins
Normally closed → forces blood into capillary network
open→ bypasses capillary network
Laminitis- loss of lamellar integrity
Stretching of white line
Sole prolapse
Mostly front limb condition
Rocked back position → shift limbs from front to hind limb
Recognition
Heat within hoof wall
Strong digital pulse
Change in behaviour
reluctance to turn
reluctance to walk on hard ground
Chronic laminitis
Divergent lines on hoof wall
Wider in quarters (proximally) vs toe
Laminitis causes
Underlying endocrine condition + high sugar intake (lush grazing → bouts of laminitis)
Equine metabolic syndrome
Pituitary Pars Intermedia disorder
degeneration of dopmine producing neurones in pars intermedia
Less inhibition of ACTH
leads to excessive cortisol production → hyperadrenocorticism
Sepsis associated (systemic infection)
Supporting limb laminitis
Overuse of healthy limb to compensate of an injured limb for weight bearing (overwork)
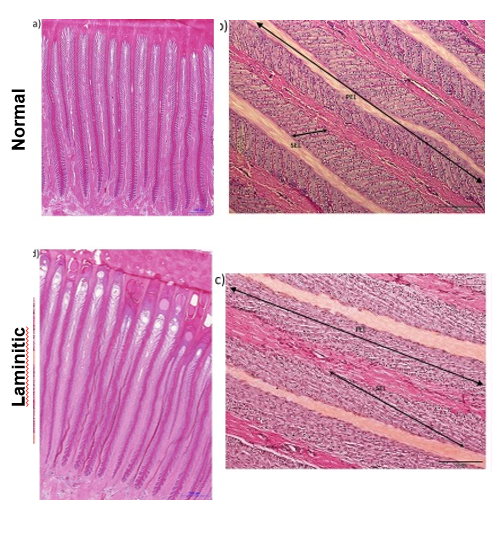
Laminitis histopathology
Lesions form at tips of primary (epidermal lamellae)
Loss of secondary lamellae OR secondary lamellae may become longer
Primary lamellae pulled apart
Underlying mechanisms unclear- endothelial cell dysfunction?
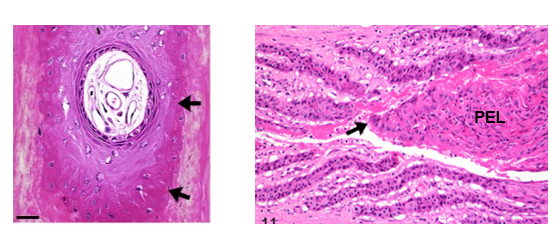
lesion formation at tip of the epidermal lamellae
pulling apart of primary lamellae due to secondary elongation
Complete epidermal and dermal lamellar separation when lamenitis progresses
Lack of connection btw hoof and underlying dermis
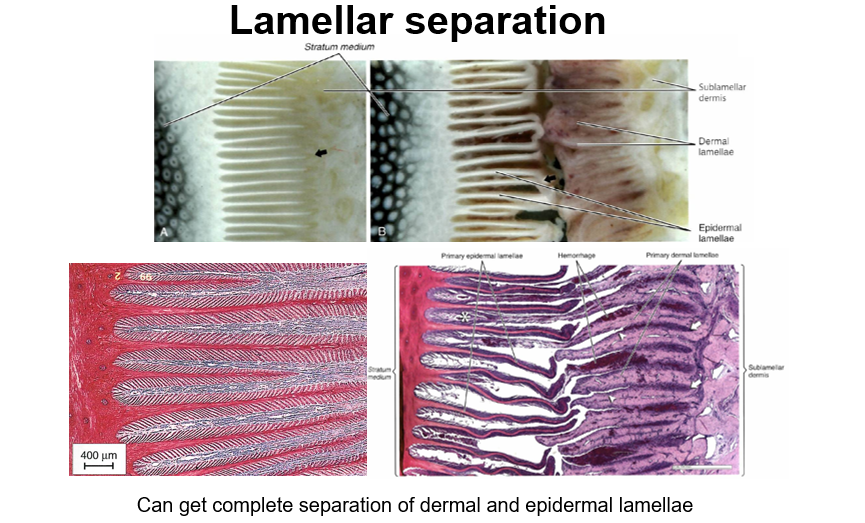
Pedal bone rotation and solar penetration
DDFT pulls on pedal bone
Pedal bone pulled away from hoof wall
Pedal bone penetrates sole
Can be reversed by careful trimming and management (but takes long time)
Diagnostic nerve blocks
Localises site with pain → lameness
Sequential local anaeshesia of sensory nerves from distal → proximal (upwards)
Nerves part of neurovascular bundle
palmar to vein and artery
dorsal → palmar/plantar = VAN
surface → underside
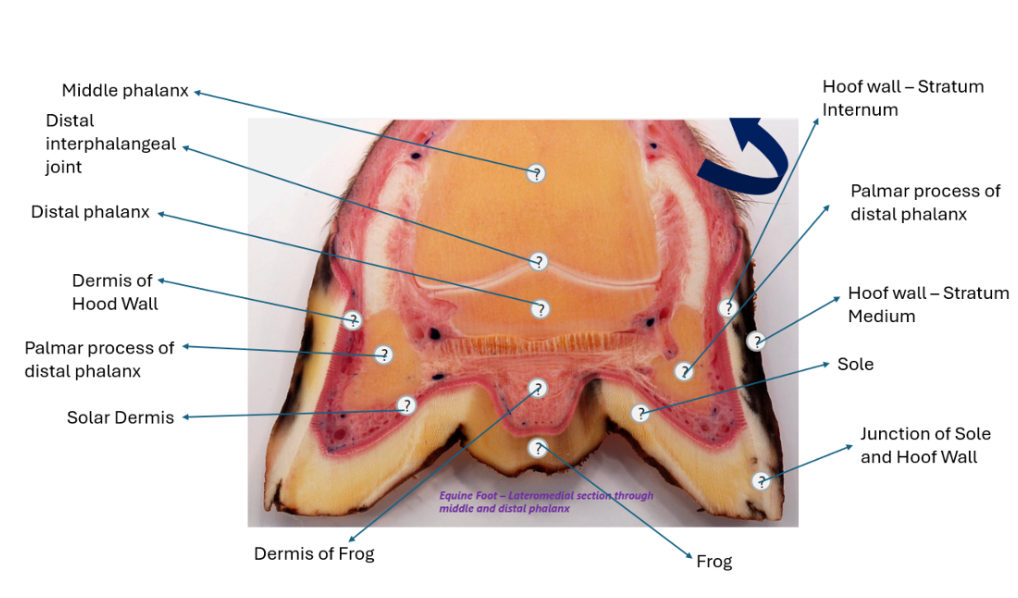
Hoof
- lateromedial section through middle
and distal phalanx
Ventral to the synovium of dorsal recess of interphalangeal joint = middle phalanx
coronary dermis/band (coronet) → proximal ring around the hood where stratum medium and stratum internum mmet
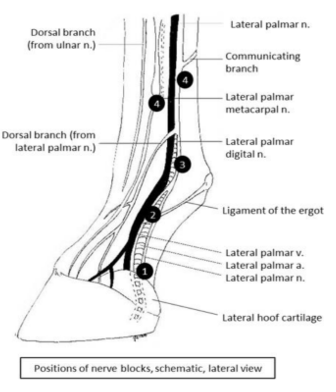
4 distinct targets of nerve blocks
(1,2,3,4a, 4b)
block 1 first (work distally → proximally)
nerve block both medial and lateral → communicating branch
Low palmar/plantar digital block → navicular bursa and distal phalanx
Midpastern palmar/plantar digital block → DIP joint + all deep structures EXCEPT lamellar corium
Abaxial sesamoid block → PIP joint, distal sesamoidean ligaments, lamellar corium
Low palmar/plantar block → MCP/MTP joints and proximal sesamoids
4a → distal ends of both splint bones
4b → distal to communicating branch
DP → DIP → PIP → MCP/MTP
Low digital → midpastern → abaxial sesamoid → low palmar/plantar
![<p><strong>Forelimb mid fetlock</strong></p><p>(dorsal to palmar)</p><p>Common + lateral extensor tendon</p><p>lateral joins common above the fetlock</p><p></p><p>Just before fetlock</p><ul><li><p>sdft wraps around ddft f<strong>orming flexor manica/manica flexoria → (bifurcated sdft)</strong></p></li><li><p>oblique ligaments adjacent and caudal to straight [distal sesamoidean] ligament</p></li><li><p>straight ligament deep to the ddft</p></li><li><p>cruciate sesamoid ligamants btw oblique ligaments deep to straight → resting on the palmar bone surface</p><p></p></li></ul><p></p><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/abc506cd-33c9-47ad-9a00-d9ec6c263bf9.png)
Forelimb mid fetlock
(dorsal to palmar)
Common + lateral extensor tendon
lateral joins common above the fetlock
Just before fetlock
sdft wraps around ddft forming flexor manica/manica flexoria → (bifurcated sdft)
oblique ligaments adjacent and caudal to straight [distal sesamoidean] ligament
straight ligament deep to the ddft
cruciate sesamoid ligamants btw oblique ligaments deep to straight → resting on the palmar bone surface
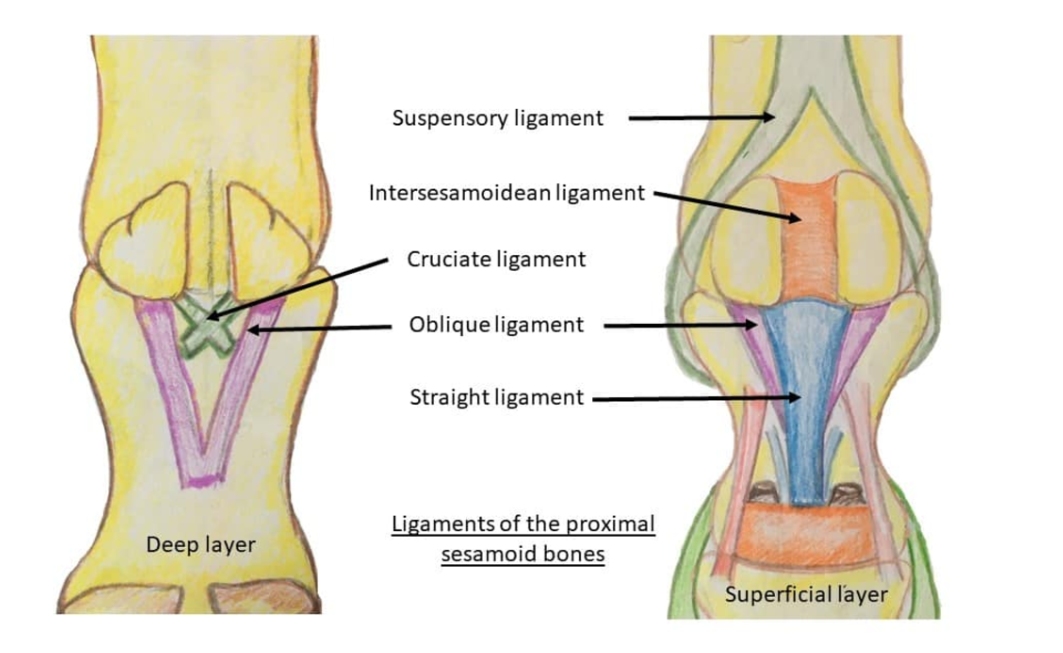
Common digital extensor tendon (lateral already inserted) → cannon bone
→ paired proximal sesamoid bones → intersesamoid ligament →
cruciate sesamoid ligaments (cross-shaped)
→ 2 oblique distal sesamoidean ligaments
→ straight distal sesamoidean ligament
→ DDFT → SDFT (@ level of fetlock it has bifurcated and surrounds DDFT)
Mid metacarpal
(from dorsal to palmar)
before fetlock
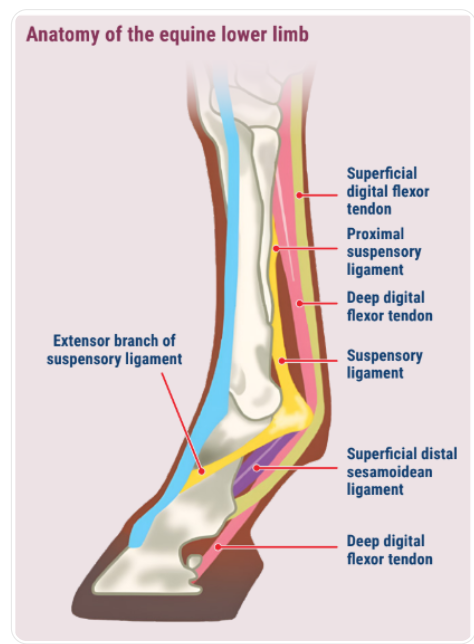
Lateral & common digital extensor tendon → cannon bone → splint bones
→ suspensory ligament
→ Accessory/inferior check ligament → DDFT → SDFT
check ligament = accessory/branch of ddft
plantar + proximal to suspensory ligament
fuses with ddft before origin of the suspensory ligament
Above the MCP
deep → superficial
check/accessory → ddft → sdft
Below MCP but proximal metacarpal (add suspensory)
suspensory → check/accessory → ddft → sdft
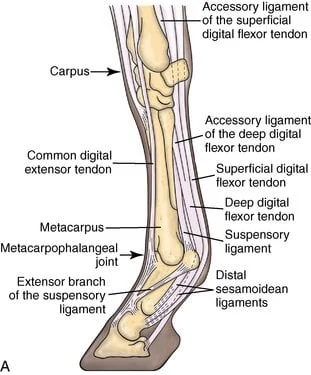
What wraps around the SDFT and DDFT
Palmar annular ligament wraps over SDFT and DDFT superficially and mediolaterally
Intersesamoid ligament continuous but deep to S/DDFT = straight distal sesamoidean ligament = straight ligament
Hindlimb - dorsal to plantar
Mid Fetlock
(lateral fuses with the long digital extensor tensor)
Long digital extensor tendon → cannon bone → paired proximal sesamoid bones → intersesamoid ligament
cruciate sesamoid ligaments (cross-shaped) → 2 oblique distal sesamoidean ligaments → straight distal sesamoid ligament → DDFT → SDFT
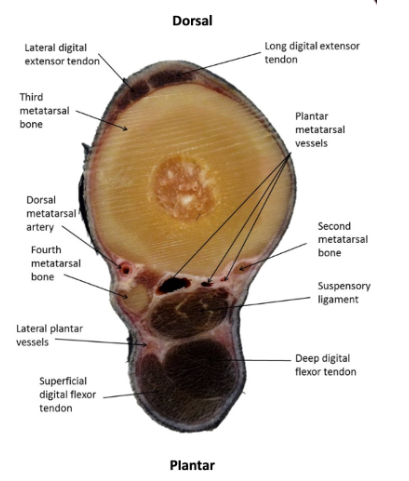
Mid-metatsal - dorsal to plantar
Lateral & common digital extensor tendon → cannon bone
→ splint bones → suspensory ligament
→ Accessory/inferior check ligament → DDFT → SDFT
Forelimb
Before fetlock:
lateral & common digital extensor tendons
After fetlock
fuses } common digital extensor tendon
(PTO for hindlimb)
HINDLIMB
Before fetlock:
lateral and LONG digital extensor tendons
After fetlock
fuses } LONG digital extensor tendon
Forelimb vs hindlimb - metacarpal/tarsal differentiation
PART 1
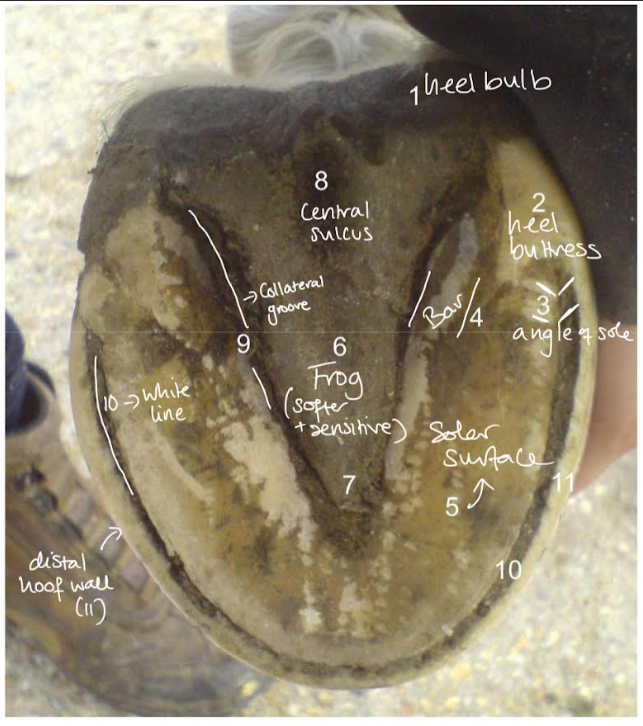
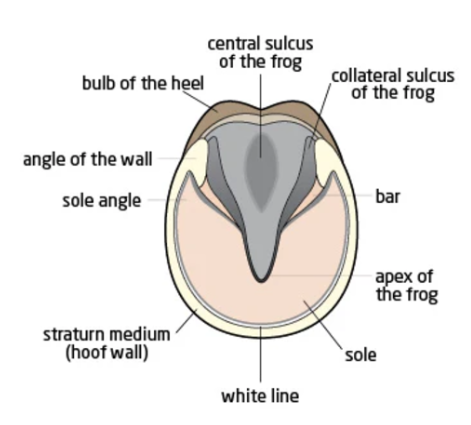
Solar surface of hoof
central sulcus (of the frog)
collateral sulcus
heel bulb
bars
white line
hoof wall
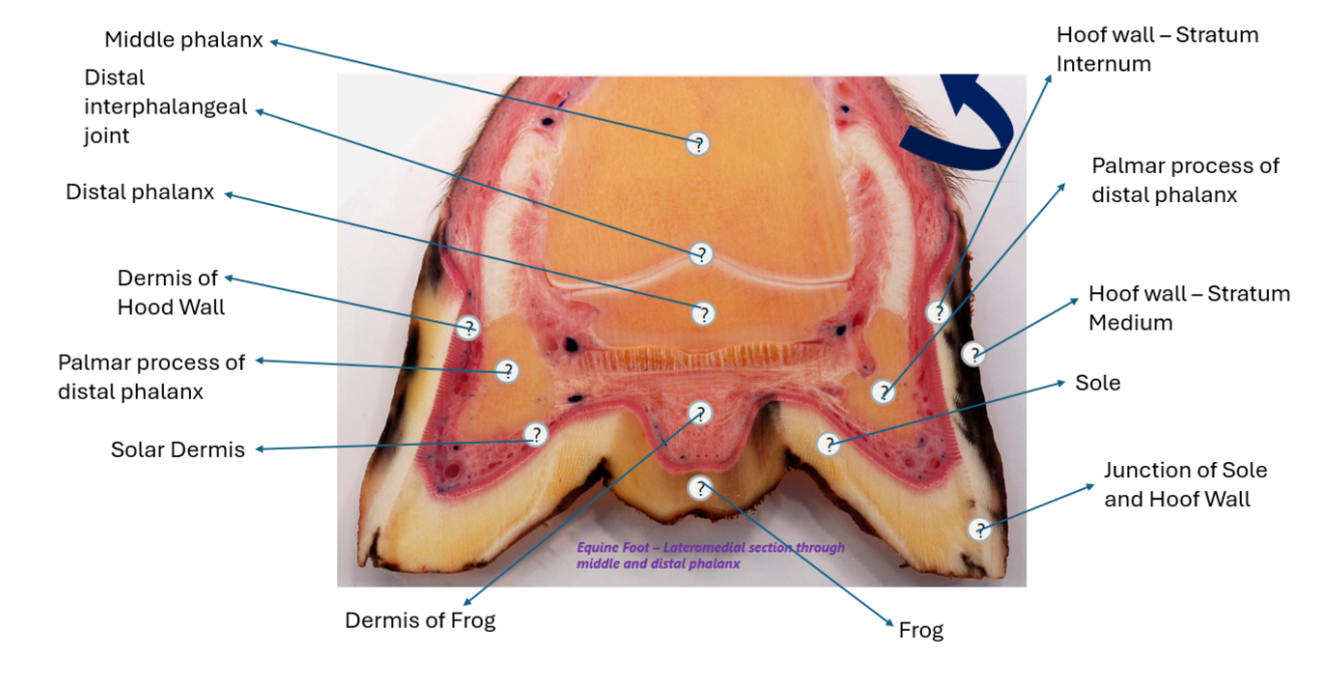
Other key hoof terms
coronary band/corium
digital cushion
lamellar and solar dermis (corium)
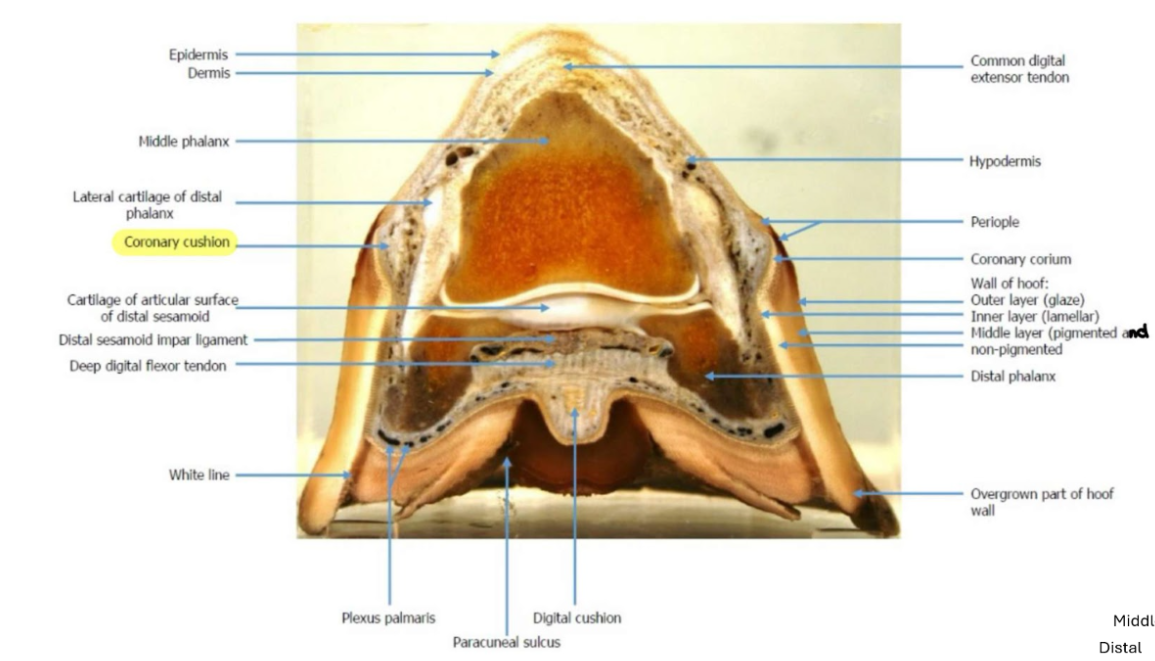
More important external hoof structures