Circuits and Transistors
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Circuit
closed path where electrons flow from a source of voltage or current
Source
origin of electrons
Ground
return path of electrons
Voltage (volts, V)
difference in electric potential between source(origin) and ground(return path)
Current (I) (amps, A)
rate of electrons flowing through a circuit
Resistance (ohms, 𝛀)
opposition to electrons flowing through a circuit
ohm’s law - V=IR
Analog signal
takes any continuous value
Digital signal
takes one of a discrete set of values
Binary signal
0 or 1
Digital Circuit
connection of components that takes digital inputs and produces digital outputs (binary digital signal)
Switch
Source Input
Control Input
Output
Moore’s Law
number of transistors on an IC doubles about every 2 years
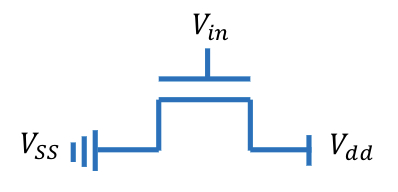
N - Channel MOSFET (nMOS)
Vdd = Source Input
Vin = Control input (apply 1 = circuit closed) (apply 0 = open circuit)
Vss = Output
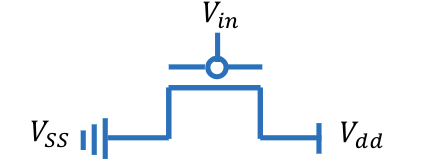
P - Channel MOSFET (pMOS)
Vin = Control Input (apply 1 = open circuit) (apply 0 = closed circuit)
CMOS
Complimentary Metal - Oxide - Semiconductor
integrated circuit made from pairs of nMOS and pMOS transistors