vision and hearing
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
hearing
happens when something vibrates, hits eardrum and turns into electrical signals
outer ear
which part of ear catches sound?
auricle
outer part of ear where sound waves are collected and directs them into ear canal
auditory canal
carries sound from auricle to the eardrum
auditory canal
has hairs to keep dirt and bugs out; earwax to protect ear
tympanic membrane
the auditory canal leads through temporal bone to>
middle ear
what part of ear: functions to pass vibrations from eardrum to inner ear
middle ear
what part of ear is air filled
tympanic membrane
what part of ear: separates outer ear from middle and vibrates when sound hits it
tympanic cavity
small air space behind eardrum and contains auditory ossicles
auditory ossicles
what are these called: malleus, incus, stapes
tiny muscles
what r these called: stapedus & tensor tympani
tiny muscles
these things help protect ear from very loud sounds by: tightening and reducing mvmnt of bones
auditory tube
connects the middle ear to the back of the throat
auditory tube
helps equalize air pressure on both sides of the eardrum (when eardrums pop)
otitis media
what is the middle ear infection also called?
otitis media
this happens when: germs from throat travel to middle ear through eustachian tube
eustachian tube
childrens _ is shorter and flatter than older adults
meningitis
infection of the membranes around brain and SC
inner ear
what part of ear: functions for hearing and balance
labyrinth
the inner ear is made of bony _
bony labyrinth
hard outer shell and filled w/ fluid
membranous labyrinth
soft, tube like system that fits inside of bony labyrinth where sensory cells for hearing and balance are found
perilymph
fluid between bony and membranous labyrinth
endolymph
fluid inside membranous labyrinth
inner ear
these are structures of which part of the ear: bony labyrinth, membranous labyrinth
cochlea
hearing part of inner ear (turns vibrations into merve signals)
fluid filled chambers
what are these called: scala vestibuli, scala media, scala tympani
scala vestibuli
top chamber, filled with perilymph
scala media
middle chamber filled with endolymph
scala tympani
bottom chamber, filled with perilymph
vestibular membrane
separate scala vestibuli from cochlear duct
basilar membrane
separates cochlear duct from scala tympani
basilar membrane
spiral organ sits on top of
spiral organ
turns vibrations into nerve signals; this is the actual hearing sensor
hair cells
special sensory cells with stiff little hairs called stereocilid (hairs bend when the fluid moves)
supporting cells
help hold hair cells in place
tectorial membrane
gel-like layer that rests on top of the sterocilia; when fluid moves, the stereocilia bends against tectorial membrane
outer hair cells
adjust the cochleas sensitivity to dif sound frequencies and makes hearing more precise
inner hair cells
sends info to brain, main cells for hearing
conjunctiva
what accesory of the eye: is the clear mucous membrane (covers white of eye and inside eye lid) keeps eye moist, prevents dryness
lacrimal apparatus
makes,spreads, drains tears; functions to clean and lubricate eye and tears include lysosome
extrinsic eye muscles
6 muscles that move the eyeball
rectus muscles
muscles that are: superior,inferior,lateral,medial
oblique muscles
help rotate the eyes slightly when u tilt your head, keeps vision straight
fibrous tunic
outer layer of eyeball
fibrous tunic
layer of the eyeball: includes cornea and sclera
vascular tunic
middle layer of eyeball
vascular tunic
layer of eyeball that includes: iris, ciliary body, choroid
inner tunic
layer of eyeball: includes retina
retina
contains photoreceptors that detect light
optic nerve
carries visual signals to brain
sclera
white part of eye; tough, made of collagen to protect
cornea
clear front part of eye; lets light enter and helps focus it
choroid
dark, blood rich layer (eye)
ciliary body
ring of muscle around lens; holds lens, helps focus it
iris
color part of eye, controls size of pupil and light entering
retina
turns light to nerve signals
optic nerve
carries nerve signals to brain so we can see
aqueous humor
clear watery fluid made by ciliary body
aqueous humor
fills space between iris and lens (keeps eyes shape and gives nutrients to cornea and lens)
lens
changes shape to focus light on retina (held in place by tiny fibers)
vitreous body
thick, jelly like fluid that fills space between lens and retina (helps keep eye round and holds retina in place)
cataracts
clouding of lens
cataracts
mostly caused by aging and treated by replacing normal lens w/ plastic ones
glaucoma
happens when pressure inside eye gets too high (aqueous humor can’t drain properly) can cause death and damage of retinal cells (blind)
action potentials
retina turns light energy into _ that travel to the brain
pigmented
what layer of retina; back layer & absorbs stray light so image stays clear
photoreceptor
what cells: absorb light and create electrical signals
rods
used for night vision; shades of grey
cones
work in bright light; allows color vision
bipolar
what cells: receive signals from rods & cones; passes signal forward to ganglion cells
ganglion
what cells: make the optic nerve, which sends vision to the brain
rhodopsin
visual pigment in rods (made of 2 parts)
opsin
the protein (part of rhodopsin) triggers signal
retinal
made of vitamin A (part of rhodopsin)
photopsin
visual pigment in cones (each type absorbs dif wavelength of light) allows us to see colors
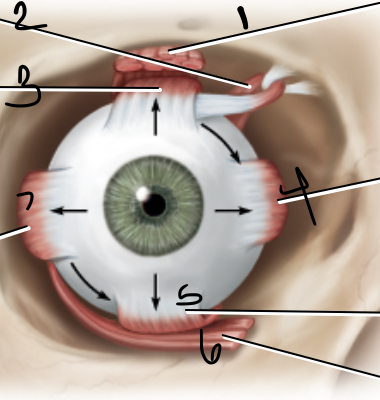
medial rectus
1
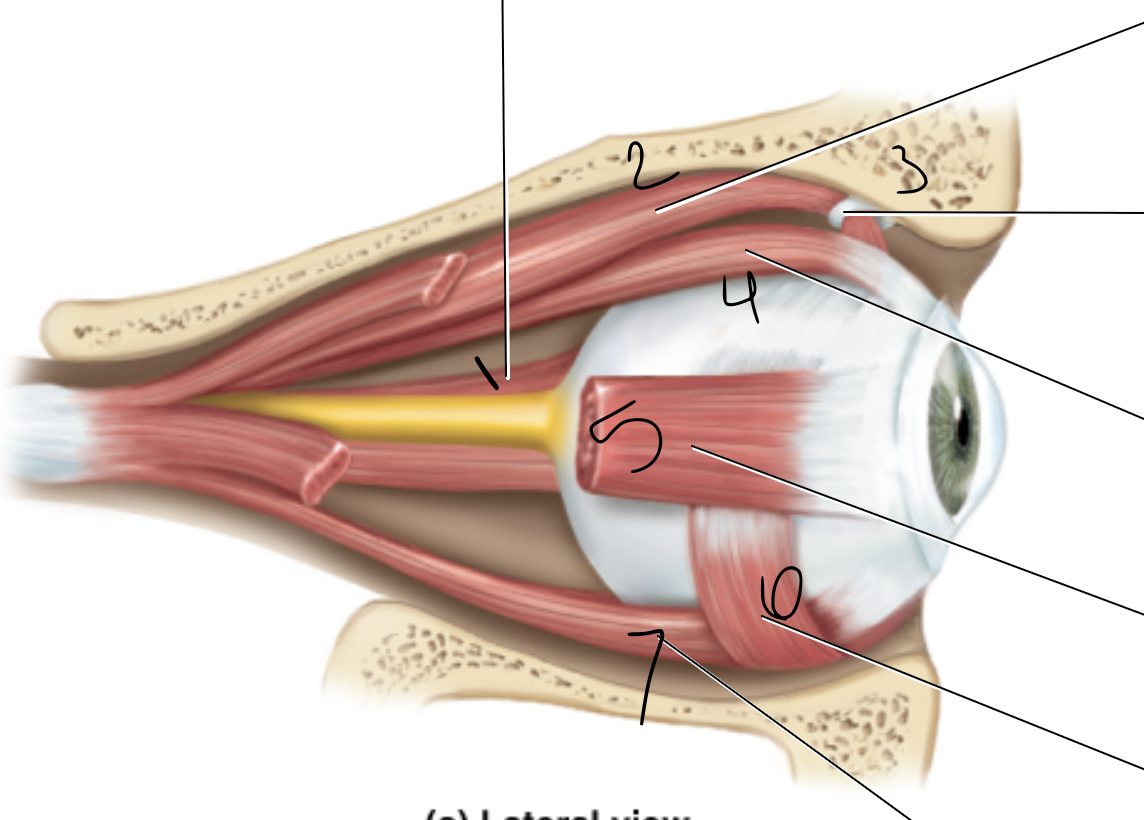
superior oblique
2
trochlea
3
superior rectus
4
lateral rectus
5
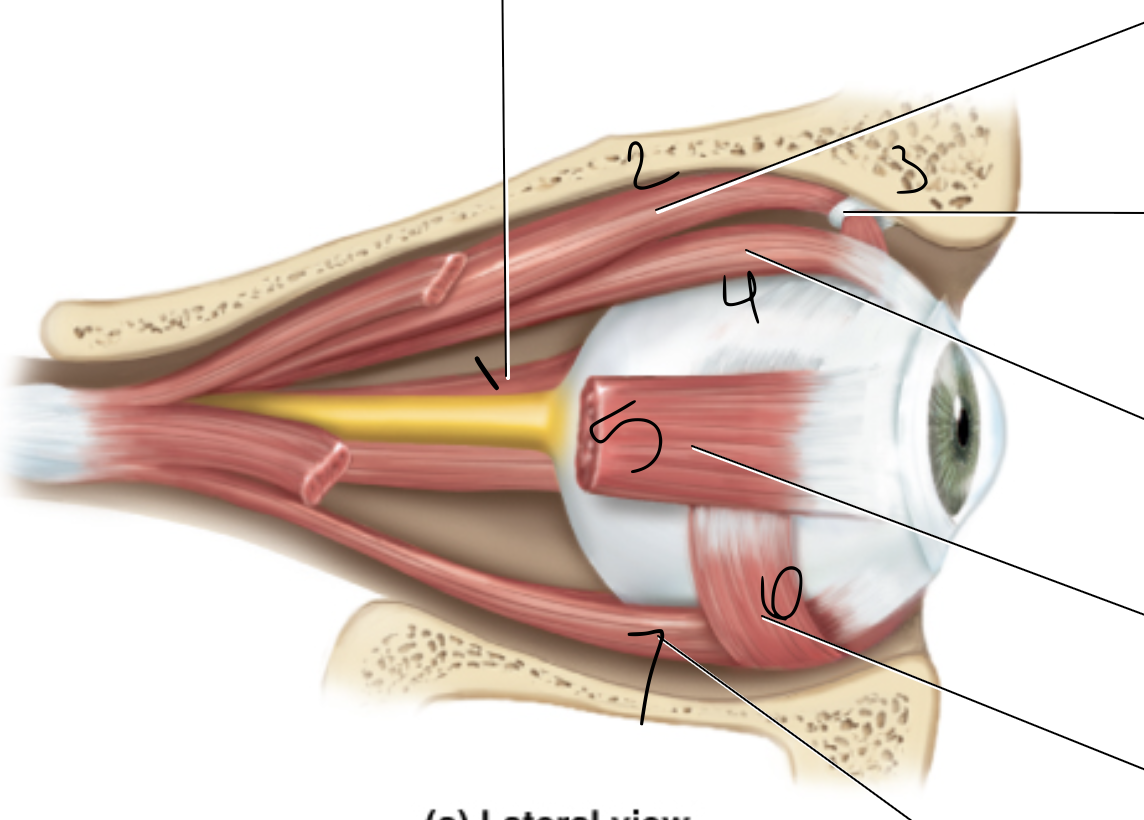
inferior oblique
6
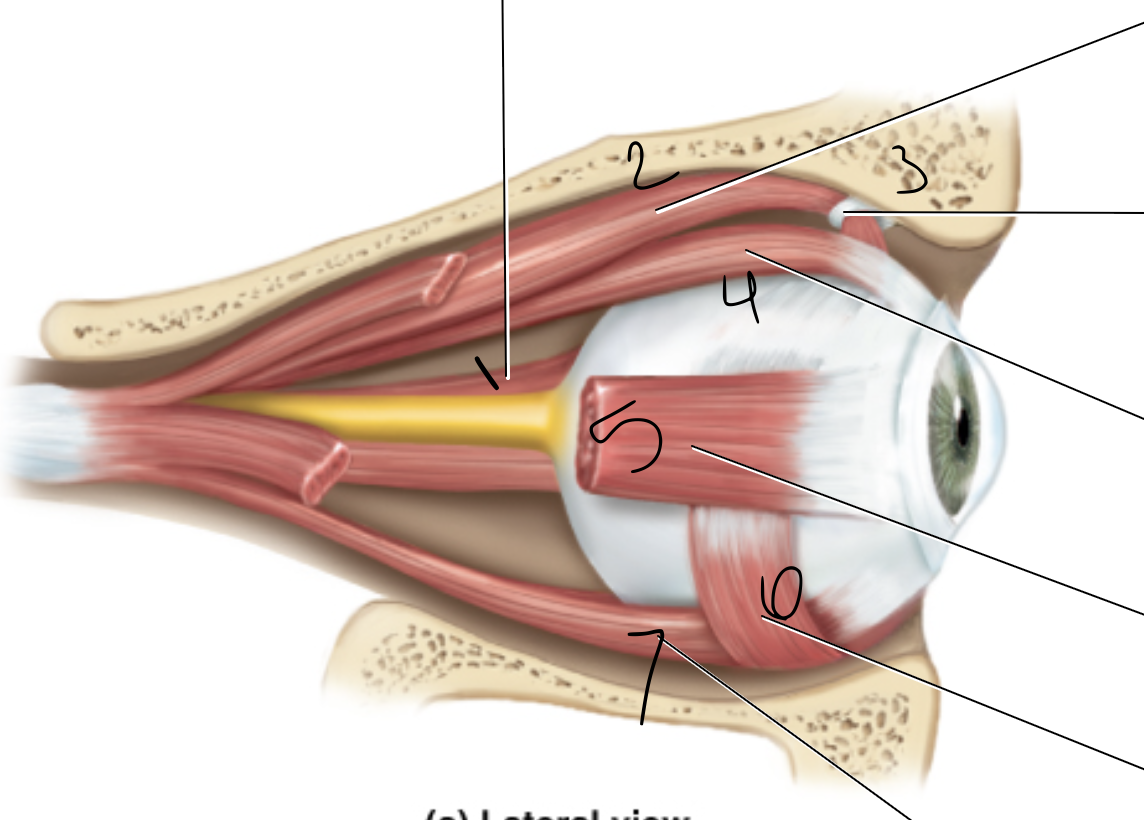
inferior rectus
7
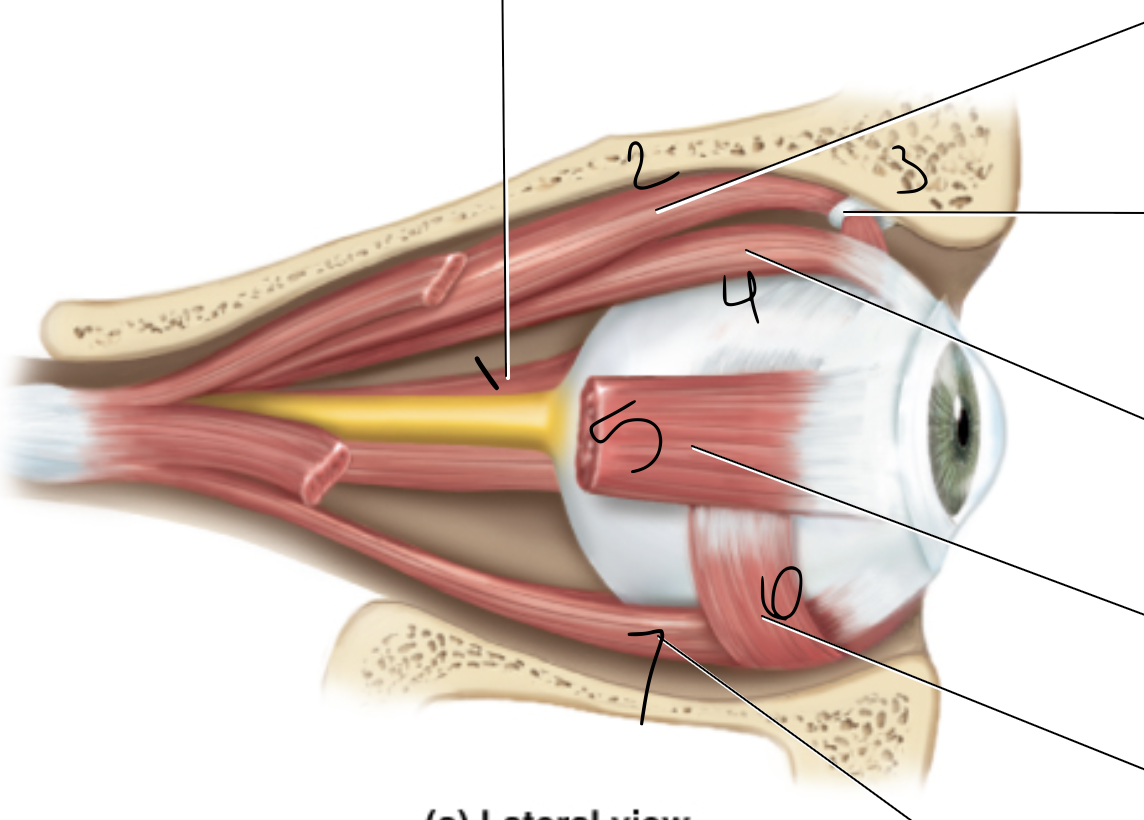
levator palpebrae
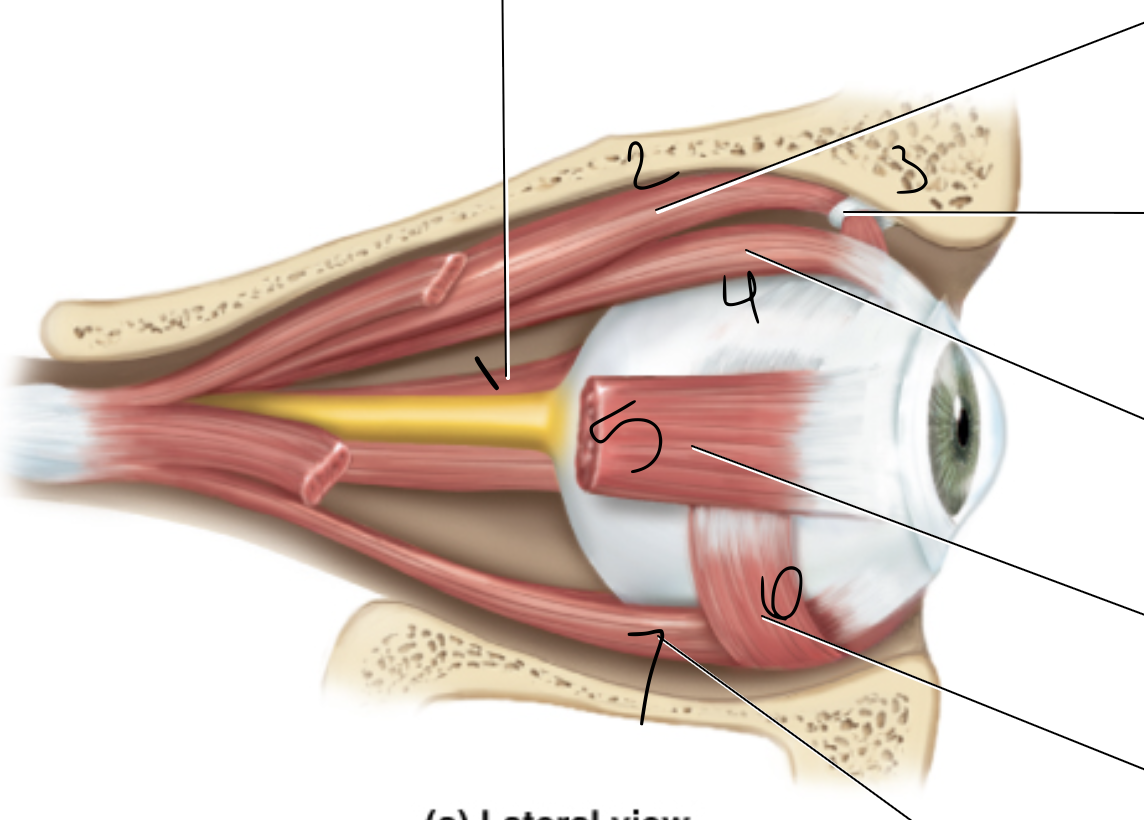
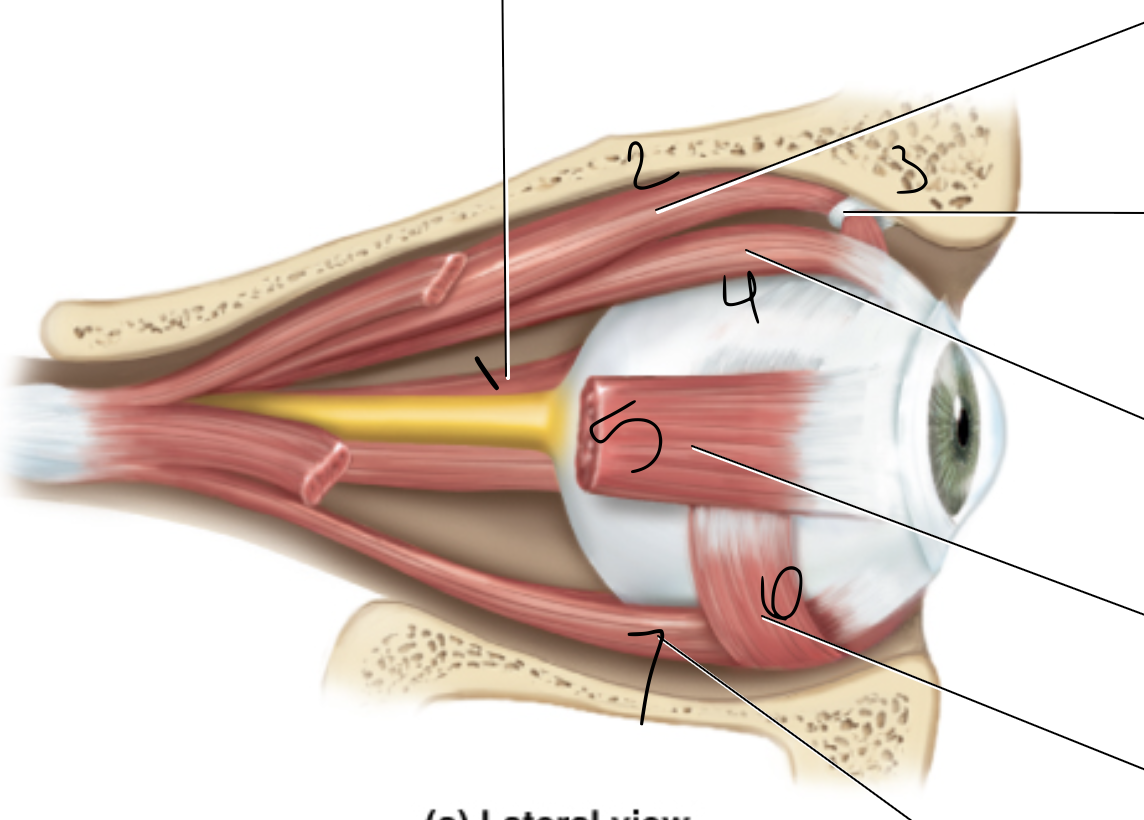
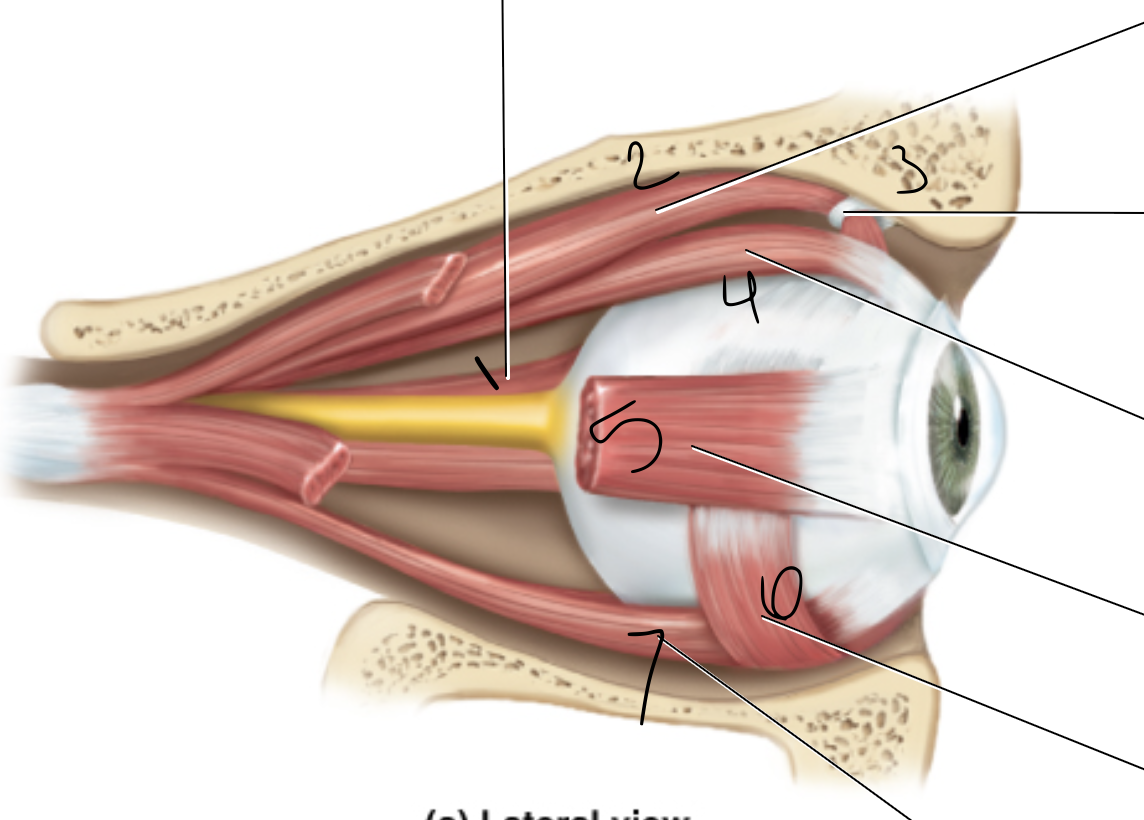
1
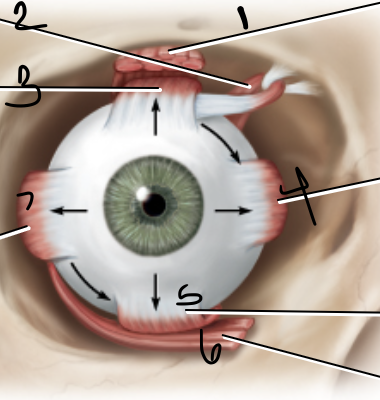
superior oblique muscle
2
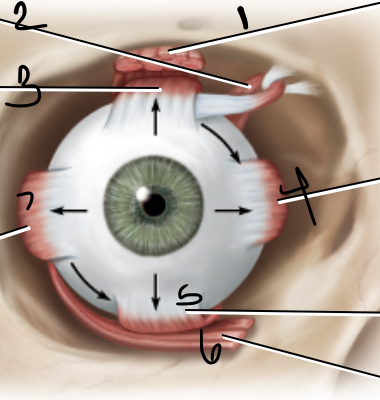
superior rectus muscle
3
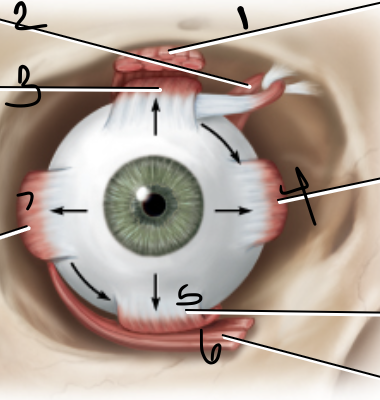
medial rectus muscle
4
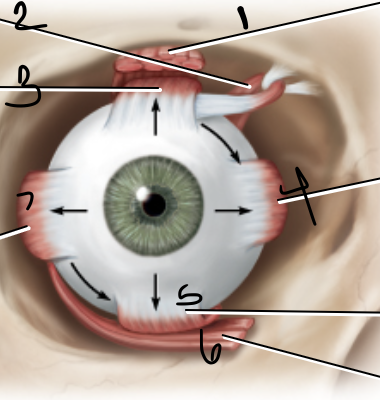
inferior oblique muscle
6
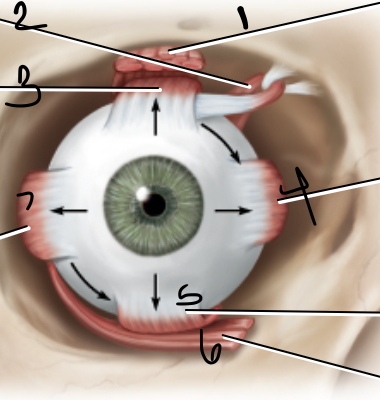
lateral rectus muscle
7
convergence
the eyeballs rotate inward to focus on an object so its image falls on each fovea centralis for sharp vision
accommodation
the lens changes shape (curvature) to bend light so it focuses on retina
presbyopia
reduced ability to accomodate for near vision due to age related stiffening of the lens