Introduction to Virology
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What is a virus?
An obligate intracellular parasite of translation.
What is the approximate size of viruses compared to bacteria?
Viruses = 20-300nm
Bacteria = 1-10um
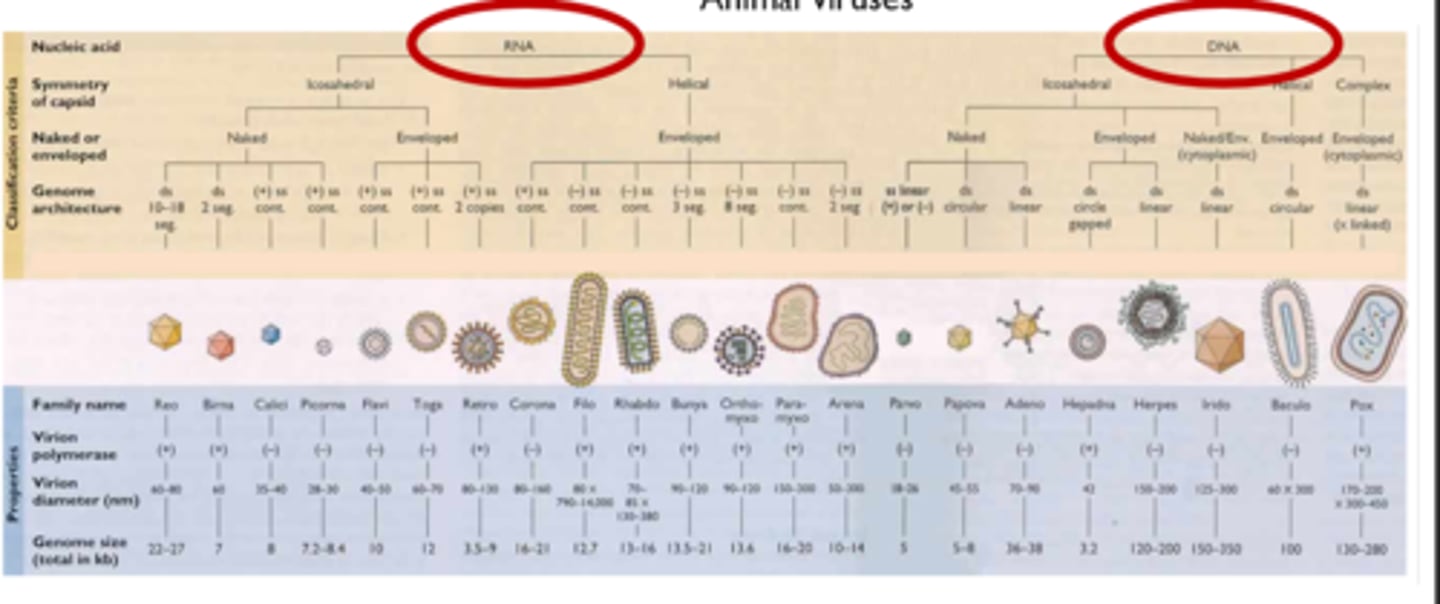
How are viruses classified?
-Genome: RNA or DNA
-Number and sense of RNA/DNA strands
-Morphology
-Genome sequence similarity
-Ecology
What is positive or negative sense RNA?
-mRNA is positive sense as it codes for protein
-If the genome codes for the complementary strand to the code that codes for proteins it is negative sense
What are the typical viral symmetries?
-Helical
-Icosahedral
-Poxviruses (complex symmetry)
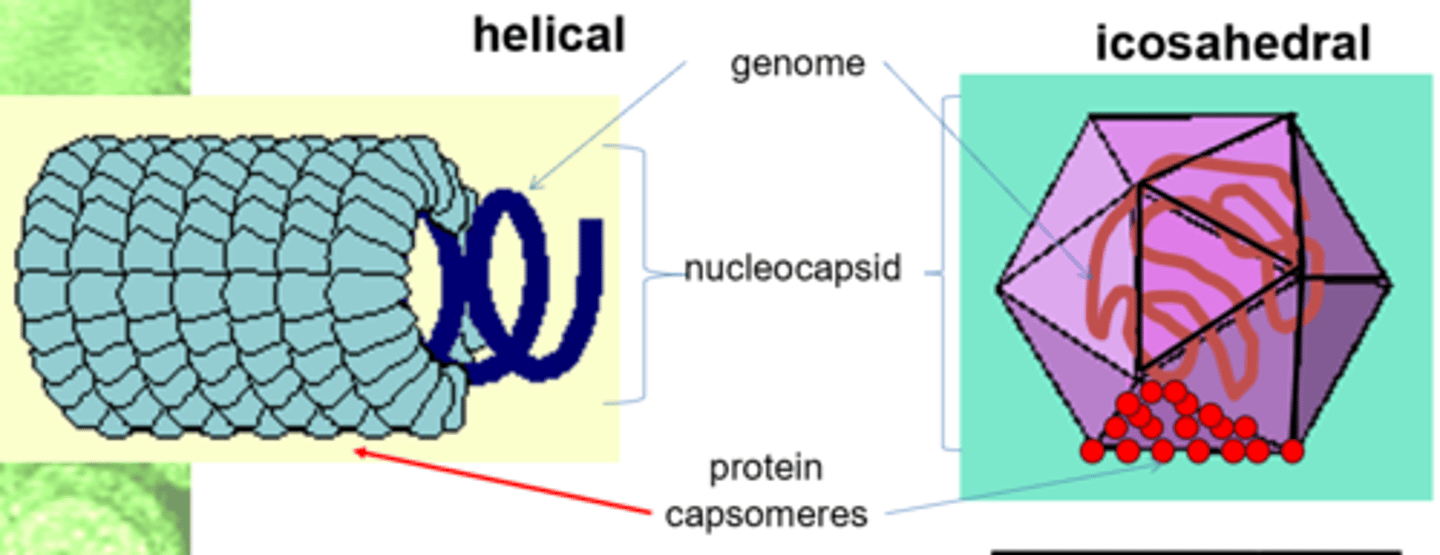
What is a viral capsid?
The protein coat surrounding a virus.
What is an enveloped virus?
A virus that, when exiting a cell, push out the host cell membrane and form a membrane around itself using the host cell membrane.
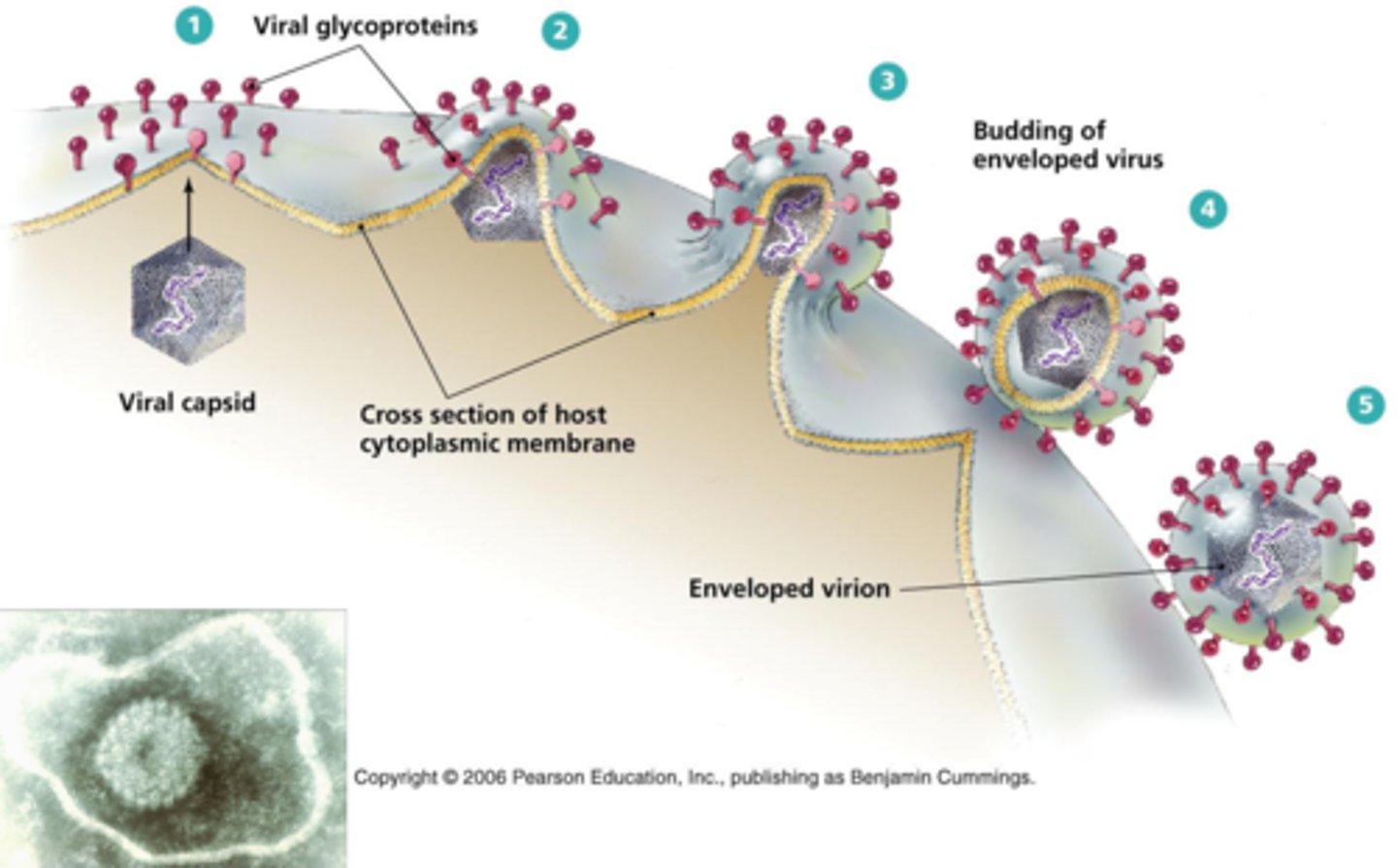
Why is the viral envelope important?
As the envelope is made of fat and proteins it increases the fragility of the virus meaning it is easier to be destroyed.
Which viruses are generally easier to destroy, enveloped or non-enveloped? Why?
Enveloped as they can be destroyed by destroying the envelope (which is typically destroyed by handsoap or sanitiser).
Do viruses have a narrow or wide host range?
Varies based on the family and species of the virus.
How can we control the spread of viruses?
-Antivirals
-Vaccination: Main approach
-Eradication: E.g. done for FMD, Rabies (in some areas)
-Biosecurity: Important to minimise contact between virus and the host
Give examples of viral diseases that have been eradicated
-Smallpox
-Rinderpest
-FMD
What makes controlling viruses difficult?
-Politics (e.g. war)
-Religion
-Culture
-Cost