Exam 1 - General Biology Cell - Menon
1/55
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
All matter is composed of ____.
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
All matter is composed of atoms.
The smallest unit of a chemical element is ____.
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
The smallest unit of a chemical element is an atom.
Atoms consist of a ____ and one or more ____ surrounding the nucleus.
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
Atoms consist of a nucleus and one or more electrons surrounding the nucleus.
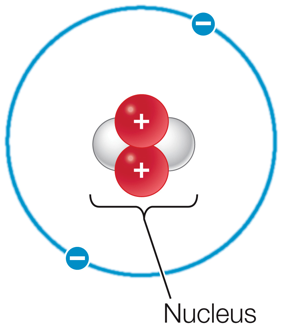
The nucleus of an atom is composed of ____ and ____ surrounded by ____.
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
The nucleus of an atom is composed of neutrons and protons surrounded by electrons.
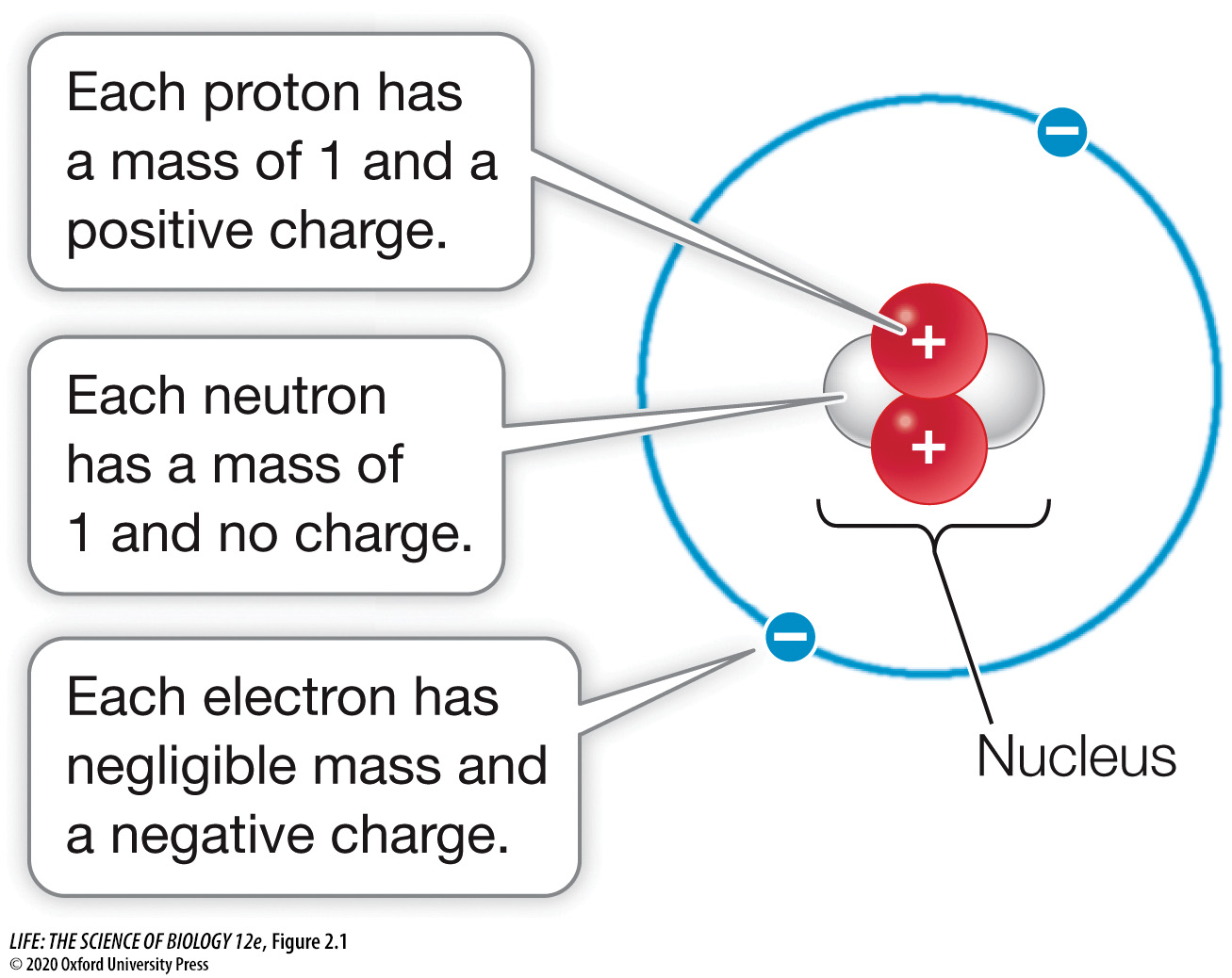
Electrons, neutrons, and protons are ____ particles.
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
Electrons, neutrons, and protons are subatomic particles.
Electrons have ____ charge.
a. no charge (0)
b. negative charge (-1)
c. positive charge (+1)
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
b. negative charge
Electrons have a negative charge (-1).
True or False? Protons have no charge (0).
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
False. Protons have a positive charge (+1).
Neutrons have ____ charge.
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
Neutrons have no charge.
Protons have ____ charge.
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
Protons have a positive charge.
True or False? Atoms and their component particles have volume and mass.
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
True. Atoms and their component particles have volume and mass.
The mass of one proton or neutron is equal to 1 ____ or 1.7×10⁻²⁴ grams.
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
The mass of one proton or neutron is equal to 1 Dalton (Da) or 1.7×10⁻²⁴ grams.
The mass of an electron is ____.
a. 1 Dalton
b. 1.7×10⁻²⁴ grams.
c. Negligible
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
The mass of an electron is negligible.
c. Negligible
For an atom to be neutral, the # of ____ must be equal to the # of ____.
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
For an atom to be neutral, the # of electrons must be equal to the # of protons.
A fundamental substance that contains only one kind of atom is an ____.
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
A fundamental substance containing only one kind of atom is an element.
Ex. The element Iron (Fe) consists only of Iron atoms.
(An element can’t be converted to a simpler substance.)
The # of ____ is the atomic number, which identifies an element.
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
The # of protons is the atomic number, which identifies an element.
The # of ____ + ____ of an element equals its mass number.
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
The # of protons + neutrons of an element equals its mass number.
The # of ____ and ____ determines the characteristics of an element and how an element behaves in chemical reactions.
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
The # of protons and electrons determines the characteristics of an element and how an element behaves in chemical reactions.
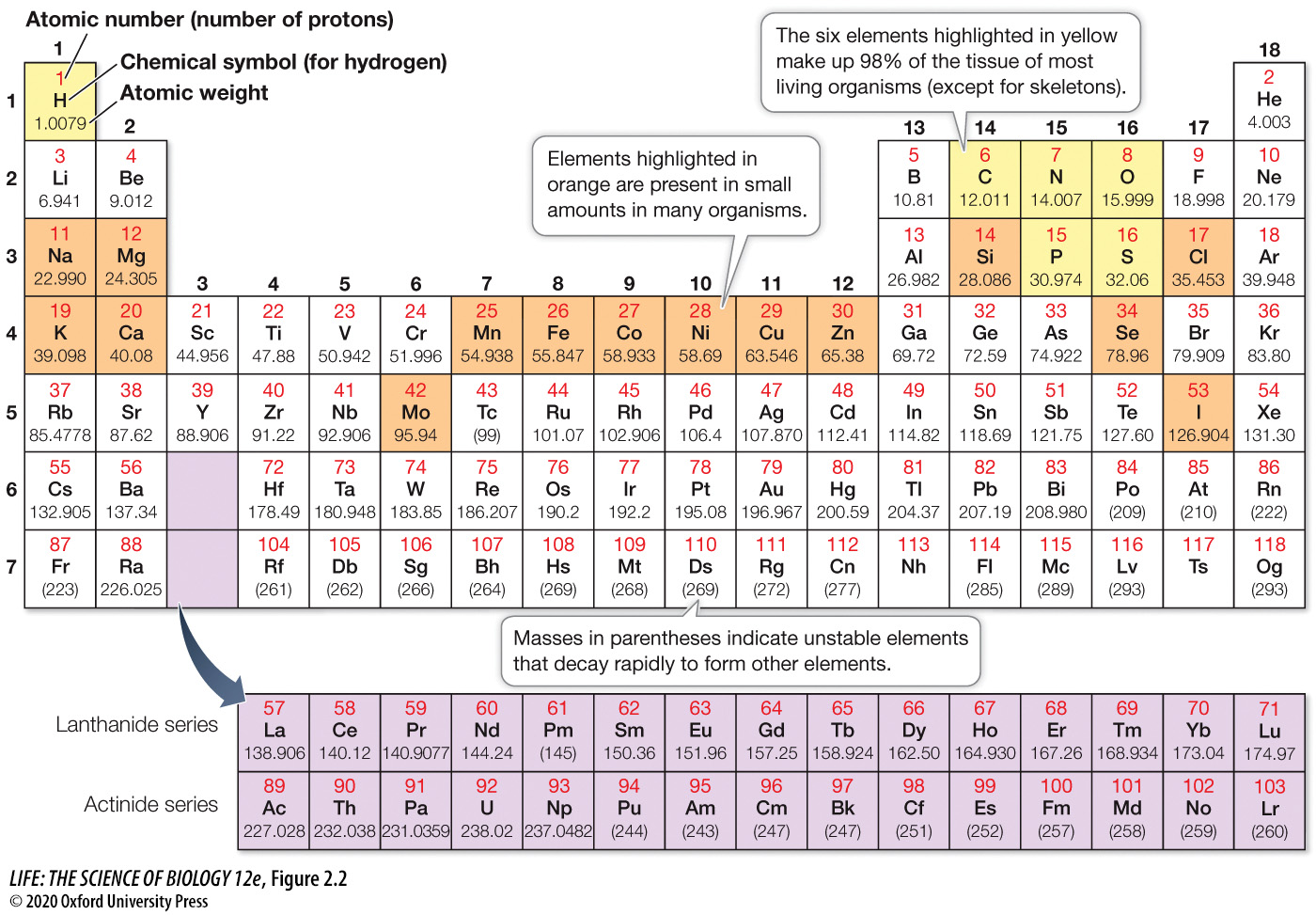
98% of tissue in living organisms (except for skeletons) is made up of these 6 elements: ____, ____, ____, ____, ____, and ____.
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
98% of tissue in living organisms (except for skeletons) is made up of these 6 elements: Hydrogen, Carbon, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, and Sulfur.
(A mnemonic to remember these 6 elements is CHNOPS)
Forms of an element with different numbers of neutrons are referred to as ____.
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
Forms of an element with different numbers of neutrons are referred to as isotopes.
(Isotopes have different mass numbers and the # of protons remains the same and unchanged in each.)
The average of the mass numbers of a representative sample of atoms of an element (with all naturally occurring isotopes) is an element’s ____ ____.
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
The average of the mass numbers of a representative sample of atoms of an element (with all naturally occurring isotopes) is an element’s atomic weight.
Unstable isotopes are called: ____
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
Unstable isotopes are called: Radioisotopes
True or False? Radioisotopes release energy/radiation from the nucleus.
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
True. Radioisotopes release energy/radiation.
(This release of energy is referred to as radioactive decay)
Radioisotopes release ____ from the nucleus in three different forms:
1. α ____
2. β ____
3. γ ____
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
Radioisotopes release energy from the nucleus in three different forms:
1. α Alpha radiation
2. β Beta radiation
3. γ Gamma radiation
A chemical substance made up of two or more atoms joined by covalent bonds or ionic bonds is a ____.
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
A chemical substance made up of two or more atoms joined by covalent bonds or ionic bonds is a molecule.
True or False? Molecules can be tagged and tracked in an experiment if a radioisotope is incorporated into it.
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
True. Scientist use radioisotopes to track and label molecules in experiments.
The # of which subatomic particle in an atom determines how it will combine with other atoms.
a. Protons
b. Neutrons
c. Electrons
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
The # of electrons in an atom determines how it will combine with other atoms.
c. Electrons
The region in space surrounding the atomic nucleus in which an electron is found at least 90% of the time is the electron’s ____.
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
The region in space surrounding the atomic nucleus in which an electron is found at least 90% of the time is the electron’s orbital.
Orbitals have characteristic shapes and orientations, and a given orbital can be occupied by a maximum of ____ electrons.
a. 2 electrons
b. 4 electrons
c. 6 electrons
d. 8 electrons
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
An orbital can be occupied by a maximum of 2 electrons.
a. 2 electrons
Orbitals are filled in a specific sequence, in a series known as ____ ____, or energy levels, around the nucleus.
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
Orbitals are filled in a specific sequence, in a series known as electron shells, or energy levels, around the nucleus.
The innermost electron shell (s-orbital) consists of ___ orbital(s) and can hold up to ____ electrons.
a. 1 orbital, 2 electrons
b. 1 orbital, 8 electrons
c. 4 orbitals, 8 electrons
d. 4 orbitals, 2 electrons
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
The innermost shell (s-orbital) consists of 1 orbital and can hold up to 2 electrons.
a. 1 orbital, 2 electrons
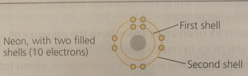
The second shell (1 s-orbital, 3 p-orbitals) consists of ____ orbital(s) and can hold up to ____ electrons.
a. 2 orbitals, 4 electrons
b. 4 orbitals, 8 electrons
c. 1 orbital, 2 electrons
d. 3 orbitals, 6 electrons
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
The second shell (1 s-orbital, 3 p-orbitals) consists of 4 orbitals and can hold up to 8 electrons.
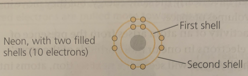
The farther a shell is from the nucleus, the ____ the energy level of electrons in that shell.
a. lower
b. higher
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
The farther a shell is from the nucleus, the higher the energy level of electrons in that shell.
b. higher
The outermost electron shell, ____ ____, determines how the atom behaves.
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
The outermost electron shell, valence shell, determines how the atom behaves.
Reactive atoms have ____ electrons in their outermost shell and can share or gain/lose electrons.
a. unpaired
b. paired
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
Reactive atoms have unpaired electrons in their outermost shell and can share or gain/lose electrons.
a. unpaired
If the outermost shell is full, the atom is ____ and won’t react with other atoms.
Concept 2.1 An Element’s Atomic Structure Determines Its Properties
If the outermost shell is full, the atom is stable and won’t react with other atoms.
Chemical bonds are attractive forces that link atoms together to form molecules. The different types of chemical bonds and interactions are:
1. ____ bonds
2. ____ bonds
3. ____ bonds
4. ____ interactions
5. ____ ____ ____ forces
Concept 2.2 Atoms Bond to Form Molecules
Chemical bonds are attractive forces that link atoms together to form molecules. The different types of chemical bonds and interactions are:
1. Covalent bonds
2. Ionic bonds
3. Hydrogen bonds
4. Hydrophobic interactions
5. Van der Waals forces
Match the bond/interaction with its description.
Bonds/Interaction
a. Covalent bond
b. Ionic bond
c. Hydrogen bond
d. Hydrophobic Interaction
e. Van der Waals Forces
Description
1. Attraction of opposite charges
2. Interaction of electrons of nonpolar substances
3. Sharing of electron pairs
4. Electrical attraction between a covalently bonded H atom and an electronegative atom
5. Interaction of nonpolar substances in the presence of polar substances (especially water)
Concept 2.2 Atoms Bond to Form Molecules
a3 - Covalent bond - Sharing of electron pairs
b1 - Ionic bond - Attraction of opposite charges
c4 - Hydrogen bond - Electrical attraction between a covalently bonded H atom and an electronegative atom
d5 - Hydrophobic interaction - Interaction of nonpolar substances in the presence of polar substances (especially water)
e2 - Van der Waals Forces - Interaction of electrons of nonpolar substances
In covalent bonds, atoms ____ one or more pairs of electrons so that the outer shells are filled.
Concept 2.2 Atoms Bond to Form Molecules
In covalent bonds, atoms share one or more pairs of electrons so that the outer shells are filled.
A pure substance made of two or more different elements bonded together in a fixed ratio is a ____.
a. Molecule
b. Atom
c. Element
d. Compound
Concept 2.2 Atoms Bond to Form Molecules
A pure substance made of two or more different elements bonded together in a fixed ratio is a compound.
d. Compound
Every compound has a ____ weight that is the sum of the atomic weights of all atoms in the molecule.
Concept 2.2 Atoms Bond to Form Molecules
Every compound has a molecular weight that is the sum of the atomic weights of all atoms in the molecule.
Covalent bonds have four features:
1. ____
2. ____
3. ____
4. ____
Concept 2.2 Atoms Bond to Form Molecules
Covalent bonds have four features:
1. Strength and stability (these bonds require lots of energy to break)
2. Orientation
3. Multiple bonds (You can have a single, double, triple, or quadruple bond)
3. Unequal sharing of electrons
When two atoms of the same element are covalently bonded, electrons in the bond are shared ____.
a. Equally
b. Unequally
Concept 2.2 Atoms Bond to Form Molecules
When two atoms of the same element are covalently bonded, electrons in the bond are shared equally.
a. Equally
(When two diff atoms bond, the sharing may not be equal. One nucleus will exert a greater attractive force on the electron pair so the pair tends to be closer to that atom.)
The attractive force that an atomic nucleus exerts on electrons is called its ____.
Concept 2.2 Atoms Bond to Form Molecules
The attractive force that an atomic nucleus exerts on electrons is called its electronegativity.
What two factors does electronegativity depend on?
Concept 2.2 Atoms Bond to Form Molecules
Electronegativity depends on the # of protons an atom has and the distance between the nucleus and electrons (in the valence shell).
When atoms are shared unequally, the covalent bond is ____.
a. polar covalent bond
b. nonpolar covalent bond
Concept 2.2 Atoms Bond to Form Molecules
When atoms are shared unequally, the covalent bond is polar.
a. polar covalent bond
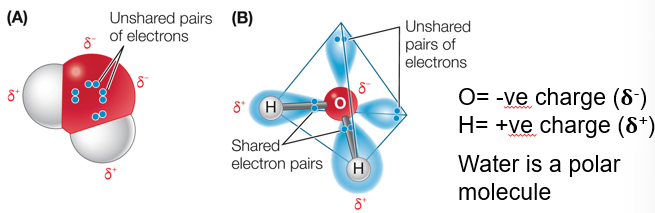
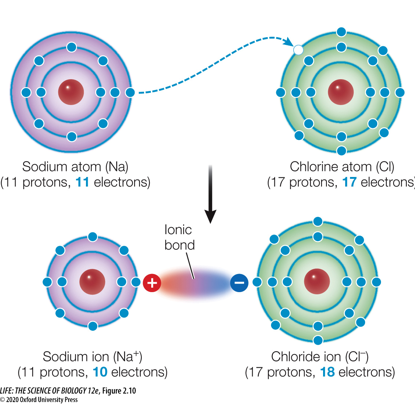
Info Card
When one atom is much more electronegative than the other, a complete transfer of electrons may occur.
This results in two ions with full outer shells.”
Concept 2.2 Atoms Bond to Form Molecules
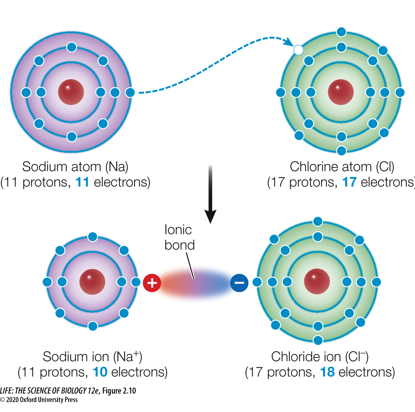
If two atoms have transferred the electrons, how do they form a bond?
Concept 2.2 Atoms Bond to Form Molecules
The bond is formed by the charge difference. This bond is referred to as an ionic bond.
Electrically charged particles that form when atoms gain or lose one or more electrons are ____.
a. cations
b. ions
c. anions
Concept 2.2 Atoms Bond to Form Molecules
Electrically charged particles that form when atoms gain or lose one or more electrons are ions.
b. ions
An ion with one or more positive charges is a ____.
a. anion
b. cation
Concept 2.2 Atoms Bond to Form Molecules
An ion with one or more positive charges is a cation.
b. cation
(A positive charge is gained when an atom gives away an electron since it will then have one less electron than it has proton.)
A negatively charged ion is a ____.
a. anion
b. cation
Concept 2.2 Atoms Bond to Form Molecules
A negatively charged ion is an anion.
a. anion
(A negative charge occurs when an atom takes an electron since the atom will then have more electrons than protons)
Groups of covalently bonded atoms that carry an electric charge are referred to as ____ ____.
Concept 2.2 Atoms Bond to Form Molecules
Groups of covalently bonded atoms that carry an electric charge are referred to as complex ions. (ex. SO₄²⁻)
Ionic bonds are formed by the electrical attraction of ____ and ____ ions.
a. positive and positive ions
b. negative and negative ions
c. positive and negative ions
Concept 2.2 Atoms Bond to Form Molecules
Ionic bonds are formed by the electrical attraction of positive and negative ions.
c. positive and negative ions
Info Card
In solids, ionic bonds are stronger since the ions are closer together.
Ions can also interact with polar molecules because of polarity.
Concept 2.2 Atoms Bond to Form Molecules
The attraction between a negatively charged atom to a positively charged hydrogen atom is referred to as a ____ bond.
Concept 2.2 Atoms Bond to Form Molecules
The attraction between a negatively charged atom to a positively charged hydrogen atom is referred to as a hydrogen bond.
(Ex. Water molecules use hydrogen bonds to interact with one another.)
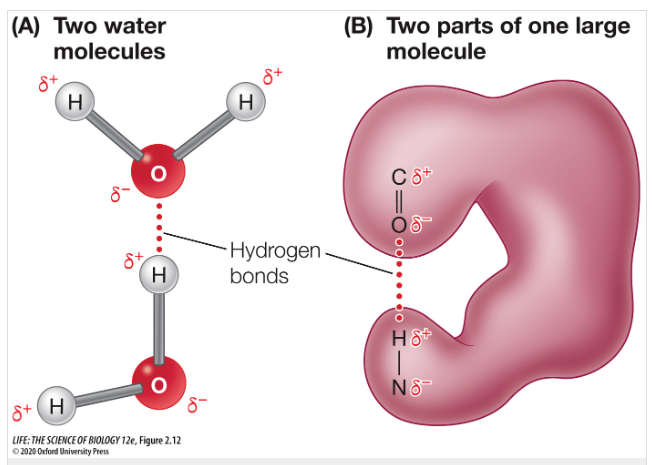
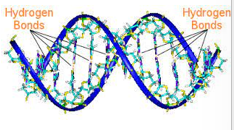
Info Card
Hydrogen bonds are weaker than ionic and covalent bonds. Despite this, if you have MANY hydrogen bonds like in the structure of DNA then it can be strong.
Concept 2.2 Atoms Bond to Form Molecules
Polar molecules that form hydrogen bonds with water are ____.
a. Hydrophilic
b. Hydrophobic
Concept 2.2 Atoms Bond to Form Molecules