Properties of Water ~ Study Guide [Review 2023 ~ Team O, Review 2024 ~ Team Y]
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
cohesion
The tendency of water molecules to stick together is called ___________.
(example: water dome on the waxed paper)
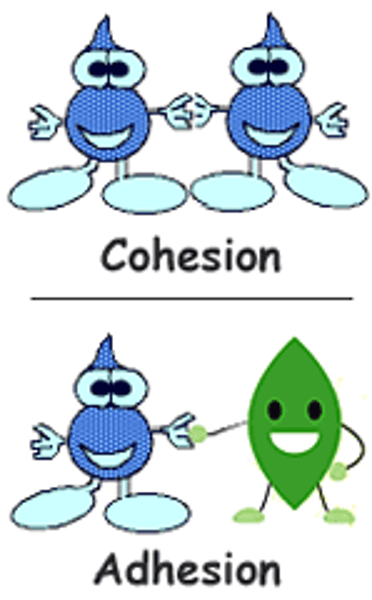
adhesion
The tendency of water molecules to stick to other objects is called __________.
(example: water sticks to the side of a graduated cylinder)

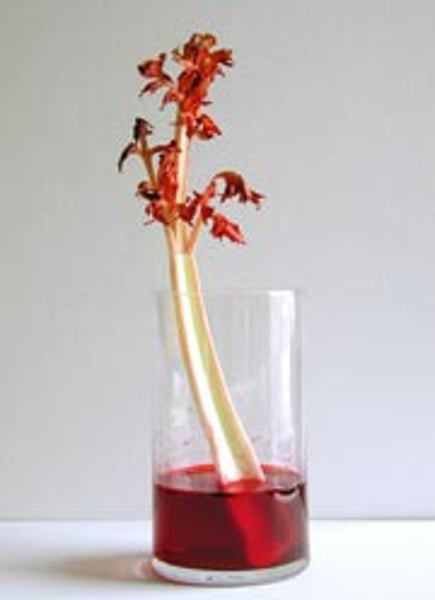
capillary action
The ability of water to move upward through narrow tubes is called _________.
The water properties of cohesion and adhesion work with water property.
(example: blood moves through the capillaries in our body or the flower experiment)

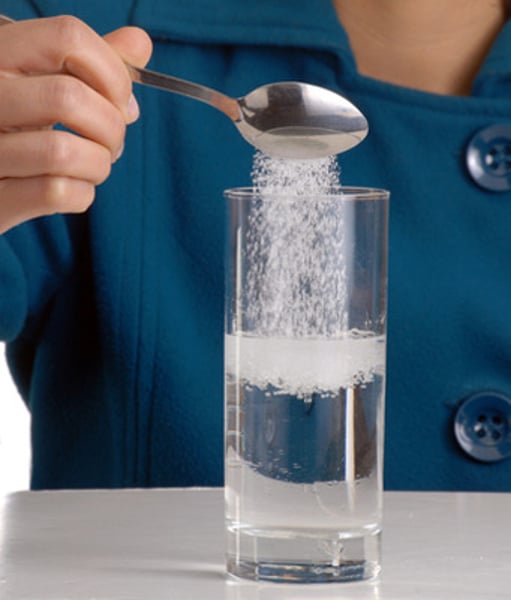
universal solvent
Water is known as the __________ __________ because it dissolves so many substances.
(examples: mixing salt or ice tea mix into a glass of water, making lemonade, making hot cocoa, etc.)

True
True or False: Water is made up of atoms bonded to form molecules.
H₂O
The chemical formula for water is _______. There are two (2) hydrogen atoms & one (1) oxygen atom that make up water.
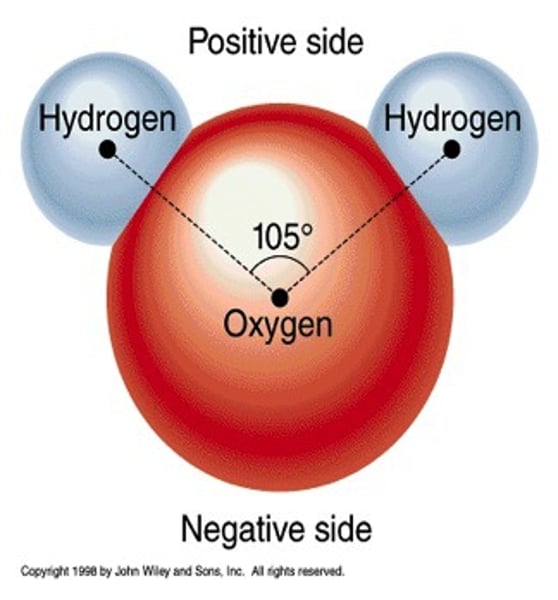
polar
A molecule that has electrically charged areas is called a ____________ molecule. Water is a ________ molecule.
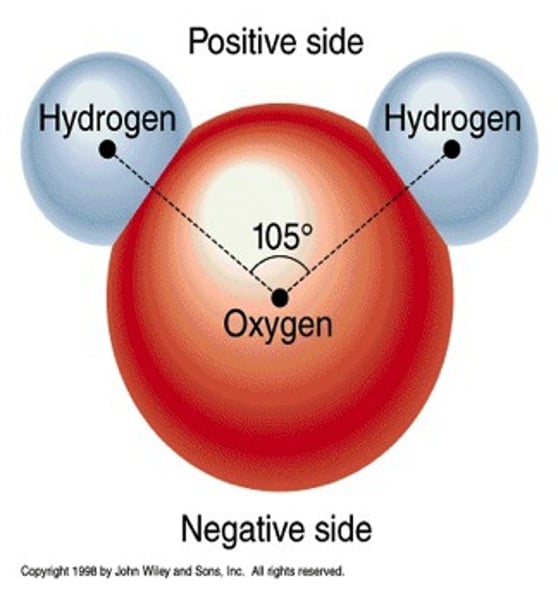
positive
Each hydrogen atom has a slight __________ charge.
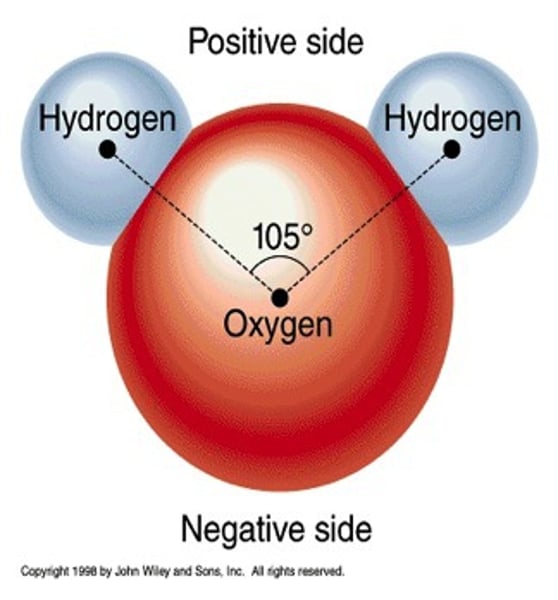
negative
A oxygen molecule has a slight _________ charge.
specific heat
___________ __________ is the amount of heat it takes to raise the temperature of a substance by one degree Celsius.

slowly
Because of specific heat, large bodies of water heat up/cool off more ___________ than nearby land [ex. sand].
quicker
In comparison to water's specific heat, land (sand) will heat up and cool down much ____________ than water.
1 g/cm3 or 1 g/mL
The density of water is ___________.
float
When an object’s density is less than water, the object will _______.
sink
When the object’s density is greater than water, the object will ________.
less
Ice is _________ dense than water and as a result, ice will float/stays on the surface.

oxygen
As water temperature decreases, the weaker hydrogen bonds begin to hold the negatively-charged ________ atoms apart, forming a rigid crystal honeycomb structure we call ice.
Since ice has more volume, it has a lower density than liquid water. This causes ice to float in water!

more
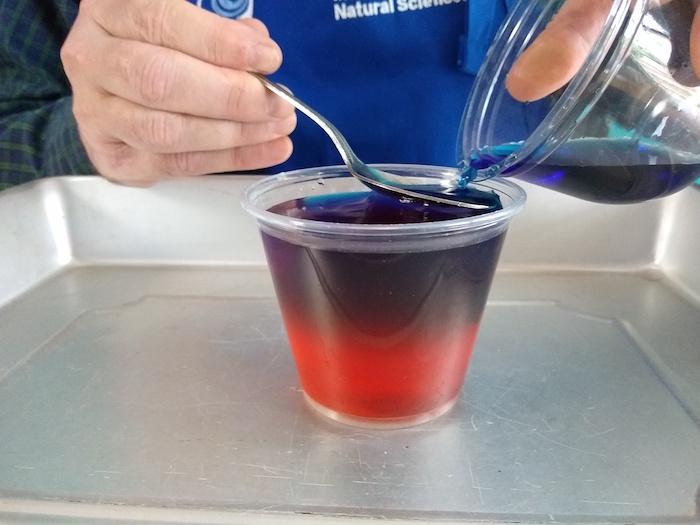
When mixing the blue salt water and the red freshwater, we learned freshwater is able to “float” on saltwater because saltwater is _______ dense.

solute
The substance that dissolves [ex. sugar] to form a solution is called a __________.
![<p><span>The </span><u><span>substance that dissolves</span></u><span> [ex. sugar] to form a solution is called a __________.</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f4453851-a9bb-48e6-97bf-77617cf24815.jpeg)
solution
A mixture that forms when one substance dissolves another is called a _________.

solvent
The substance that does the dissolving [ex. water] is called a __________.
![<p><span>The substance that</span><u><span> does the dissolving </span></u><span>[ex. water] is called a __________.</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5a883e44-48d2-47ef-bf56-d6a0db3d24e2.jpeg)
evaporation [boiling]
Which type of change occurs when the starting state is a liquid and the ending state is a gas? This happens around 100 degrees Celsius.
condensation
Which type of change occurs when the starting state is a gas and the ending state is a liquid?
absorb
Evaporation occurs as water molecules __________ energy and it occurs at the surface of a liquid. Water is changing from a liquid to a gas.
An example of evaporation is air drying your wet hair.
Condensation
________________ occurs as water molecules slow down changing from a gas to a liquid.
An example is when your breath clouds up a cold window.
Water
____________ is the only substance on Earth that commonly exists in all of its different states (solid, liquid, or gas).
3%
The percentage of the Earth's water that is fresh water is ______?
sun
The energy for the water cycle originally comes from the ____________.
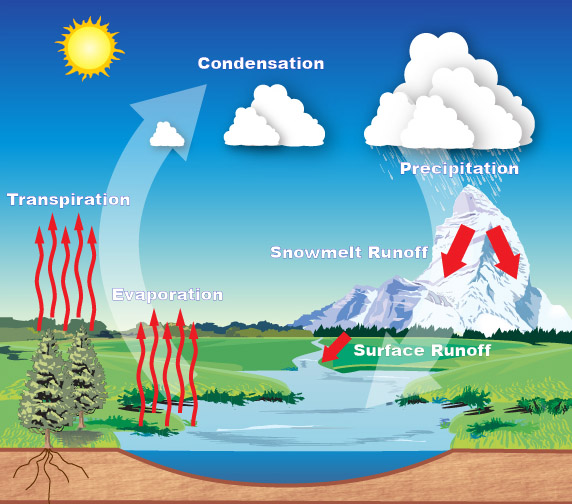
water cycle
Water that falls to the Earth as rain, snow, sleet , or hail is called ______________. Water is returned to the Earth's surface from the atmosphere.
evaporation
The four factors that affect the rate (speed) of ___________ are temperature, surface area, humidity, and wind speed.
increases
The rate of evaporation ______________ with an increase in temperature.
decreases
The amount of water vapor present in the air is called humidity. The rate of evaporation ____________ with an increase in humidity.
increases
The rate of evaporation ______________ with an increase in surface area.
increase
Evaporation increases with an ______________ in wind speed.
water cycle
The process(es) of evaporation, precipitation, and condensation are involved with the _____________.
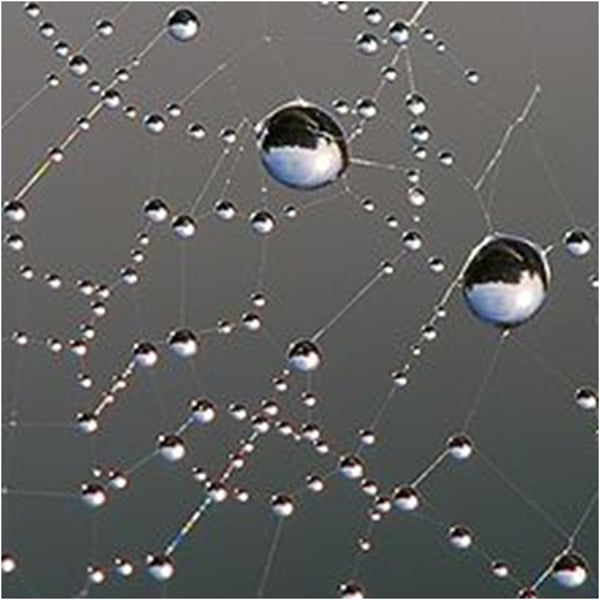
surface tension
An effect where the surface of a liquid is strong is called ___________. As a result, water molecules bond tightly to one another.

soluble
Something that will dissolve in water (ex. sugar or salt).

insoluble
Something that will not dissolve in water (ex. pepper or oil).

meniscus
The curved surface at the top of a column of liquid is called the ________.

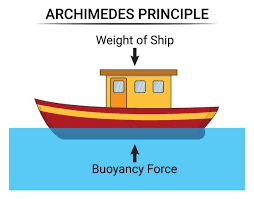
buoyancy
The ability of an object to float in a liquid (like water) because of an upward force that pushes against it is called ________.
precipitation
Water that falls from clouds to Earth’s surface as rain, freezing rain, sleet, snow, or hail is known as ___________.

transpiration
Plants release water vapor through their leaves through __________.
percolation
The movement of water through soil itself is called ____________.
sublimation
The process when a solid changes directly to a gas is referred to as _____________.

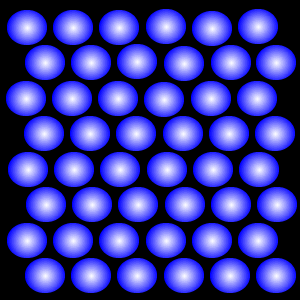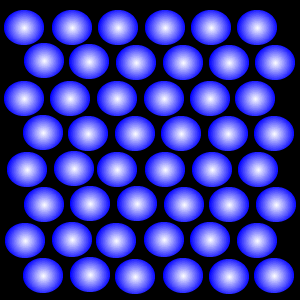
solid
This state of matter has molecules vibrate in fixed positions.
A ________ has definite shape and definite volume.
liquid
This state of matter does not have a definite shape since it takes the shape of a container.
It does have a definite volume.
The particles are free to move over each other, but are still attracted to each other.

gas
This state of matter does not have a definite shape since it takes the shape of the container.
There is no definite volume and the particles move in random motion with no attraction to one another.
A _______ is highly compressible.

boiling point
The __________ is the temperature where a liquid turns into a gas.
freezing point
The ____________ is the temperature at which water changes from a liquid to a solid.
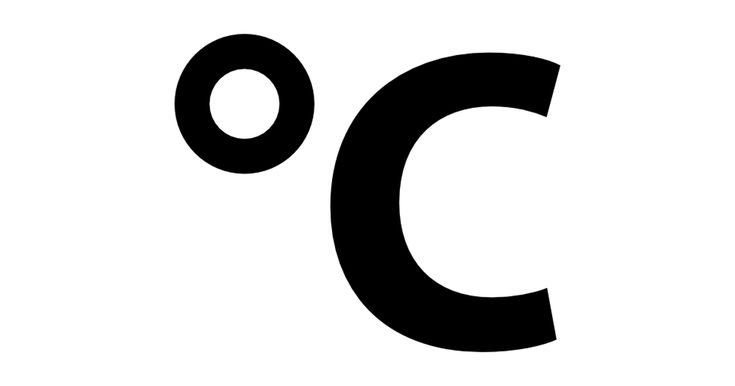
Celsius
The system of measuring air temperature/heat used throughout most of the world.
In _______, water freezes at 0 degrees and boils at 100 degrees.

Fahrenheit
The system of measuring air temperature/heat used in the United States. In ___________, water freezes at 32 degrees and boils at 212 degrees.