Lecture 20: Signal Transduction – Part 1
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Cells need to respond how often to changes in external environment?
constantly
What detectd and respond to changes in nutrients, chemicals, light, heat,mechanical forces, etc.
cells
Which organisms must coordinate these responses to different external signals across different cell types
Multicellular
Order of Signal Transduction
1. Receive Signal ---------> 2. Transduce Signal -----------> 3.Respond to Signal
The complex process by which a cell converts a signal from outside (or from inside the cell) to a functional change within the cell
Signal Transduction
Location of Signal Transduction
Signaling Cell ---------> Signal ---------> Receptor ---------> Target Molecule ---------> Response
whereby a protein in the signal transduction pathway (S5) or an effector protein modifies either the receptor or an early protein in the pathway
feedback controls
Ex: hormones (insulin secreted by pancreatic cells travels through blood and acts on target cells in liver, muscles, etc)
Endocrine signaling
Ex: neuron releasing a neuro transmitter, growth factors et
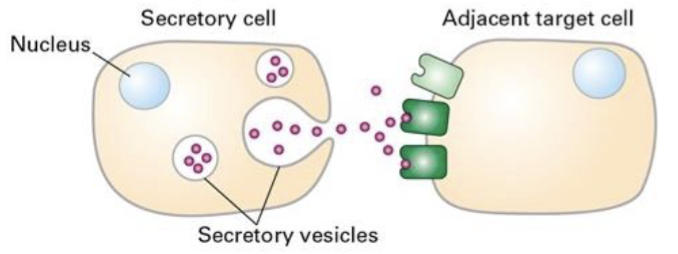
Paracrine signaling
Ex: tumor cells secrete growth factors that act on itself
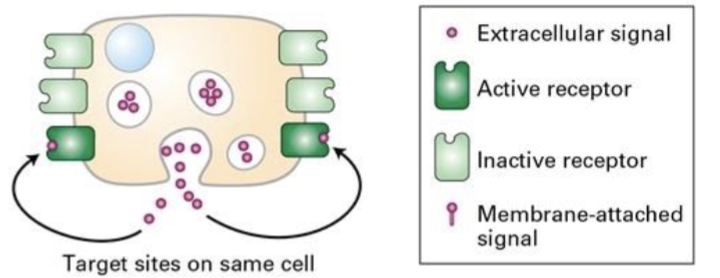
Autocrine signaling
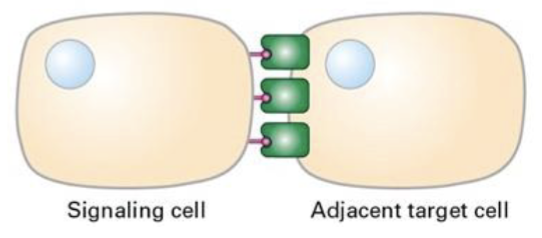
Ex: notch signaling pathway
Signaling by plasma membrane attached proteins
typically consequences of modifications to specific preexisting enzymes and other proteins that alter their activity or function
Rapid changes
effector proteins are typically transcription factors and results in
changes in gene expression
Slower, long-term changes
Often initiated by covalent modifications such as phosphorylation or ubiquitination or by binding of ions or molecules such as Ca2+ or cAMP
Rapid changes
Induces changes in cell proliferation, cell differentiation, and organismal development
Slower, long-term changes
Such modifications can induce changes in cellular metabolism, secretion of hormones, firing of action potentials in nerve cells etc
Rapid changes
Diffuse through the plasma membrane
Bind to cytosolic receptors
Hydrophobic signaling molecules
Cannot diffuse across the cell membrane
Bind to specific cell-surface receptor proteins
Hydrophilic signaling molecules
Receptor-signal complex moves into the nucleus – binds
promoter regions in DNA to regulate gene expression
e.g., Estrogen – Estrogen Receptor
Hydrophobic signaling molecules
triggers receptor conformational change that activates the receptor
Ligand receptor interaction can be extracellular or intracellular
small molecules [adrenaline, acetylcholine], peptides [yeast
mating factors, glucagon], and proteins [insulin, growth
hormone]
Hydrophilic signaling molecules
Same ligand can induce different cells to respond in a different ways
Effector Specificity of the Receptor – Ligand Complex
small molecules and ions in signaling pathways
Second Messengers
bind to and activate or inhibit specific intracellular proteins
Second Messengers
Plays important role in signal amplification
Second Messengers
a reversible post-translational modification
Protein phosphorylation
covalently attaches phosphate groups to other proteins (substrates) at serine, threonine and tyrosine residues
Protein kinases
Blank activity of protein kinases can be regulated by:
o Binding to other proteins
o Intracellular concentrations of small molecules
o Phosphorylation by other protein kinases
Catalytic
enzymes that removes phosphate groups from substrate proteins
Protein Phosphatases
GTP bound
On Form
GDP bound
Off Form
Made up of alpha (α), beta (β) and gamma (γ) subunits
bind to the cell surface receptors called the G-proteins coupled receptors (GPCR)
Heterotrimeric G-proteins
“low molecular weight G proteins”
Do not directly bind to receptors
Monomeric G Proteins
acts as guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF)
G-proteins coupled receptors (GPCR)
binds to G proteins and triggers release of GDP from the Gα subunit
G-proteins coupled receptors (GPCR)
Gα subunit then spontaneously binds GTP inducing conformational change that activates
G-protein
GTPase activity of the Gα subunit hydrolyses GTP to GDP returning the G protein to “which” position
Off
β and γ subunits are closely bound to one another and are referred to as
Gβγ complex
Acts as intermediate proteins in signal transduction pathways
Monomeric G Proteins
Plays important roles in many pathways that modulate cell
division and cell motility
Monomeric G Proteins
Activation of a relatively small number of receptors to
trigger major changes in cell metabolism, movements, or
gene expression
SIGNAL AMPLIFICATION
Effector protein modifies and inhibits an early protein in the pathway, blocking an early step in that pathway
(feedback responses are sometimes referred to as adaptation)
FEEDBACK REPRESSION
How can we quantify the number of receptors on a cell surface
and determine how tightly they bind to a ligand?
Receptor–Ligand Binding Assays
Detect how much ligand is bound
Receptor–Ligand Binding Assays
Proportional to total number of receptors (ligand is in excess)
Maximal amount of binding (Bmax)
the ligand concentration that results in half the receptors being bound at equilibrium
Dissociation constant (Kd)
Lower the K the what the binding
tighter
Binds to receptor, induces conformation change that activates downstream signaling pathway
AGONISTS
Binds to receptor at normal ligand binding site
ANTAGONISTS
Most synthetic analogs bind more tightly to the receptor than natural hormone
AGONISTS
Does not induce conformation change leading to receptor activation
Block binding of ligand or agonists
Inhibits receptor signaling by ligand
ANTAGONISTS
largest superfamily of proteins and are highly conserved
GPCRs
Human genome encodes ~# GPCR
800
G protein–coupled receptors orientation
N-terminus outside, C-terminus in cytosol
All G protein–coupled receptors have # transmembrane α-helices
7
All G protein–coupled receptors have # extracelular segments and # cytosolic segments
4
Blank activates adenylate cyclase via ß2-adrenergic receptor
Epinephrine
Adenylate cyclase activates what via second messenger “cyclic AMP”
Protein Kinase A (PKA)
what activates PKA via GPCR signal transduction pathway
Epinephrine
what induces release of glucose from glycogen
Protein Kinase A (PKA)
releases glucose from
glycogen
Glycogen phosphorylase
incorporates glucose into
glycogen
Glycogen synthase
PKA activation results in what of glycogen phosphorylase
Activation
PKA activation results in what of glycogen synthase
Inhibition
cAMP is converted to what by cAMP phosphodiesterase
AMP
control the cellular levels of the second messenger cAMP and
the rates of their degradation (Repression)
cAMP phosphodiesterase
converts ATP into cAMP
Adenylate cyclase
what is stimulated by different Receptor–Ligand Complexes
Adenylate cyclase
When demand for glucose is high (low blood sugar (hypoglycemia)
or during exercise), what is released by the α cells of the
pancreatic islets
glucagon
polypeptide hormone that
induces glycogen breakdown
in liver and muscles
glucagon
Presence of what pathway in same cell – provides fine-tuned
control of the cAMP level and downstream cellular responses
both activation and inhibition