AP U.S. Government & Politics - Course Vocabulary Unit 5
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary terms for AP U.S. Government & Politics.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Suffrage
The right to vote in political elections.
Rational Choice voting
A voting theory where voters act in their own self-interest.
examines the issues/ candidates and votes in a way you believe benefits you/America the most.
Retrospective voting
Voting based on the past performance of a candidate or party. (accomplishments or shortcomings)
Prospective voting
Voting based on predictions of future performance. (potential actions/promises)
Party line voting
Voting for candidates of the same political party.
straight ticket voting- individuals who vote for everyone from one party.
encourages party loyalty
Demographics
Age, gender, race, marital status, education, employment
most likely to vote: educated, married, older white woman who work in the government.
Political Efficacy (engagement)
The belief that your vote matters, if you don’t believe your vote will make a difference, you probably won’t vote.
Gender Gap
The differences in political views and voting behavior between men and women.
Linkage Institution
channels or structures that connect people to government/communicate their preferences to policy-makers such as
political parties
interest groups
elections
media
Data Management Technology
Technological tools used for collecting, storing, and analyzing data.
pinpoints who gets what political messages, effective target marketing during campaigns
Psychographic Segmentation
Using data about citizens; personality, lifestyle, and social class to categorize voters
explains why voters vote the way they do by examining likes
parties use info of to tailor their messages (hobbies, interests, and personality)
Third Party
A political party other than the two major parties.
omnipresent (always exist but the likelihood of success is low )
Winner-Take-All System
An electoral system where the candidate with the most votes wins all electoral votes.
Interest Group
An organization that seeks to influence public policy. May represent very specific or more general interests, and can educate voters and office holders, draft legislation, and mobilize membership. (influence judicial decisions)
Free Rider
Someone who benefits from resources or services without paying or any effort ( like a clean park or successful lobbying) without contributing
Incumbent
The current holder of a political office who will run for another term.
Closed Primary
must register with a part ro vote, encouraged party loyalty.
Open Primary
A voter does not have to register with a specific party to vote. In theory, could participate in either party’s primaries. A primary election in which any registered voter can participate, regardless of their declared political party affiliation.
Caucus
A gathering of party members and voice their preference for a particular candidate to win the nomination. (very few states use this method.)
Coattail Effect
A popular presidential candidate can impact other candidates running for various offices and issues down the ballot within the same party.
Bandwagon Effect
A phenomenon where individuals adopt certain behaviors or beliefs because others do.
Electoral College
536 total delegates, delegates cast their vote in December for president; winner take all system except Maine and Nebraska. 270 needed to win.
Federal Election Commission (FEC)
an independent U.S gov agency created to administer and enforce federal campaign finance laws for presidential, House, and Senate elections.
Hard Money
Money provided directly to candidate.
Soft Money
Money that is not given directly to candidate but still benefits them.
Bipartisan Campaign Reform Act (BCRA)
An effort to ban soft money and reduce attack ads with “Stand by Your Ad” provision. “I’m [name] and I approve this message.”
Political Action Committee (PAC)
Regulated by FEC, money given by PACs is regulated donate limited amount of money.
Super PACs
Are allowed to donate unlimited amount of money w/o restriction.
Dark Money
Contributions to political causes that is difficult to track
source of income is not disclosed
Investigative Journalism
Reporters deeply investigate a single topic of interest over a period of months/years.
ex. Watergate
Horse Race Journalism
Focusing on who’s ahead in the polls instead of like what their primary issues are, what’s their past etc. But what’s more entertaining who’s more popular.
Political Reporting
Fact based reporting (congress, president, courts)
Plea Bargain
A negotiated agreement in criminal law where a defendant pleads
Political Analysis
Expert opinion/explanation, still opinion, so not free from bias, can explain causes/effects/implications of legislation, court ruling, econ policy
Commentary
Opinion based reporting and often becomes the focus of pollings because it is the most entertaining (if political→opinion reporting, inherently based.)
Confirmation Bias
Can be created through ideologically oriented programming
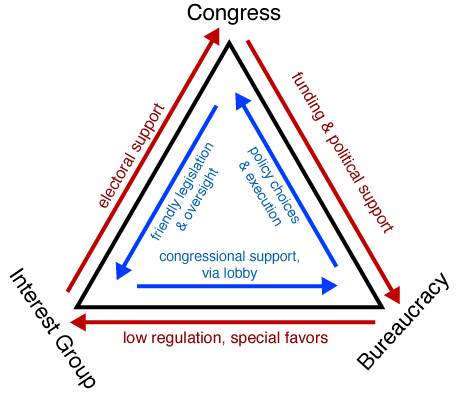
iron triangle
Pluralism
Brings representation to all
Elitism
Elite run the government
Hyperpluralisim
Too many groups demand government’s attention.