Cognitive Psychology: Perceptual Constancy, Object Recognition, and Visual Cues
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
What is perceptual constancy?
The ability to perceive constant object properties (such as size and shape) despite changes in sensory information due to varying viewing circumstances.
What is brightness constancy?
The perception of an object's brightness remains stable regardless of variations in illumination.
What is size constancy?
The perception of an object's size remains constant despite changes in the size of its retinal image caused by changes in viewing distance.
What is shape constancy?
The perception of an object's shape remains constant despite changes in its shape on the retina.
What is unconscious inference?
The process by which the brain interprets sensory information based on relationships within the retinal image and distance cues.
What are binocular cues?
Depth cues that arise from the difference between each eye's view of a stimulus, aiding in depth perception.
What is binocular disparity?
The difference in the images received by each eye, which contributes to the perception of depth.
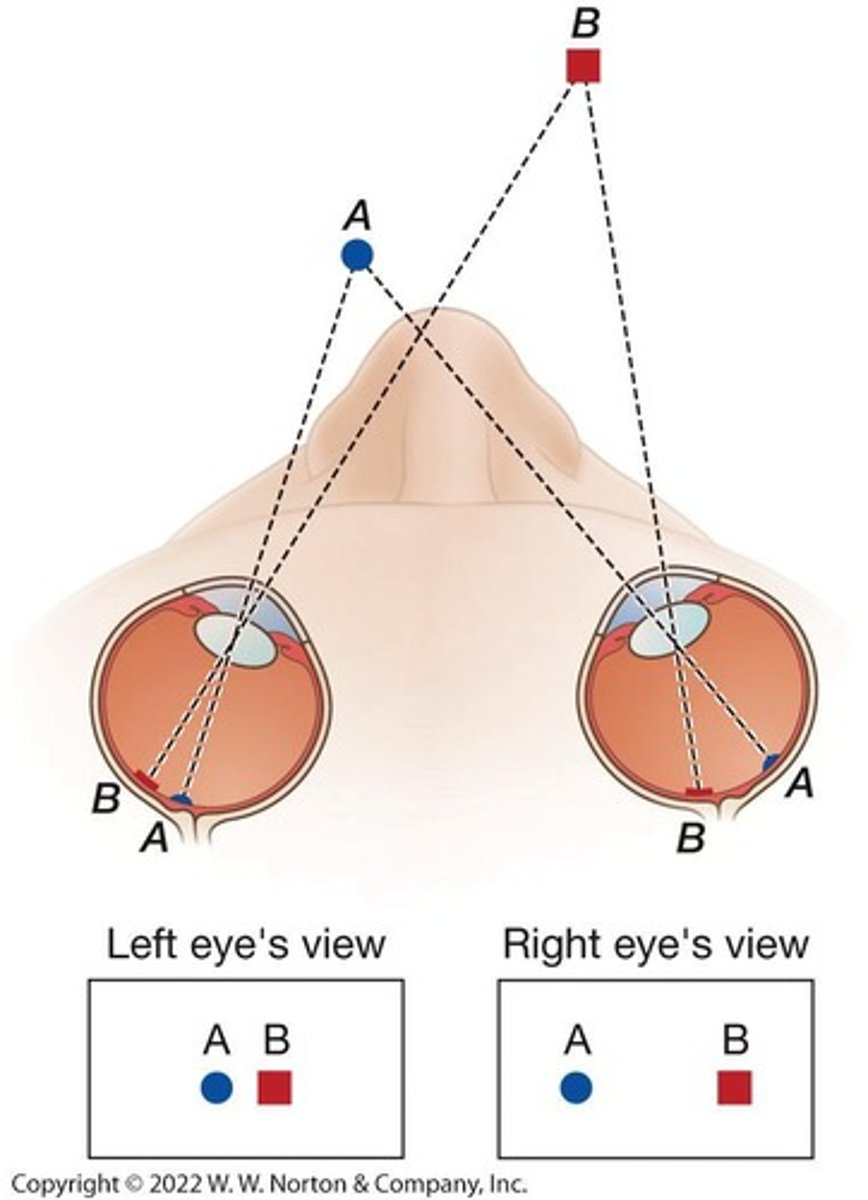
What are monocular distance cues?
Depth cues that depend on the information available from one eye alone, such as lens adjustment and pictorial cues.
What is motion parallax?
A depth cue where objects closer to the viewer appear to move faster across the visual field than objects that are farther away.
What is optic flow?
The pattern of stimulation across the visual field that changes as an observer moves toward or away from an object.
What is the binding problem?
The challenge of understanding how the brain combines separate perceptual features, such as color and texture, into a coherent object.
What is the Mach bands illusion?
An optical illusion that demonstrates the effect of lateral inhibition on the perception of brightness at the edges of objects.
What is apperceptive agnosia?
A condition where patients can perceive an object's features but cannot recognize the object as a whole.
What is associative agnosia?
A condition where patients can see an object but cannot name it or link it to visual knowledge.
What is the role of context in perception?
Context helps the visual system determine the identity of ambiguous stimuli, supporting the idea that perception is influenced by the observer.
What is Gestalt psychology?
A theory that emphasizes the human ability to perceive patterns and wholes in visual stimuli, rather than just individual components.
What is linear perspective?
A monocular cue where parallel lines appear to converge in the distance, creating a sense of depth.
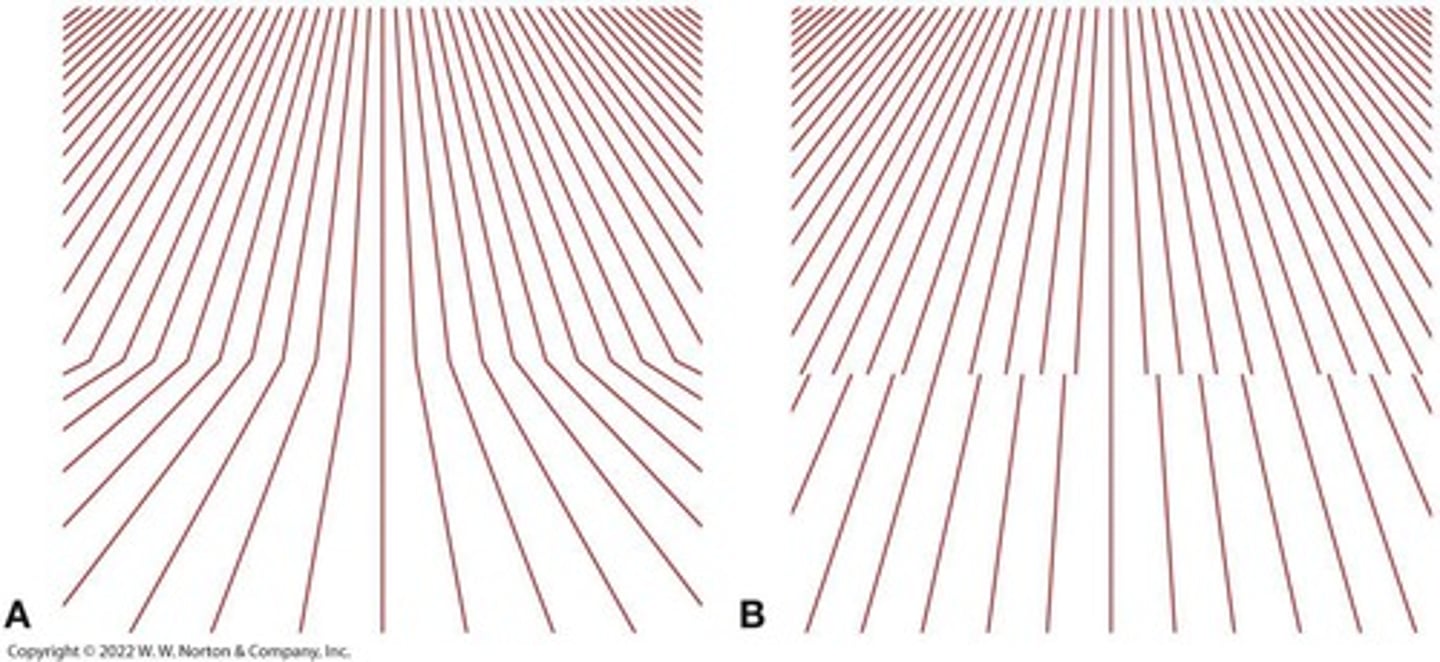
What are texture gradients?
Monocular cues that provide depth information based on the density and detail of textures as they recede into the distance.
What is interposition?
A monocular cue where one object obstructs the view of another, indicating that the obstructed object is farther away.
What is the significance of redundancy in perceptual cues?
Different cues can provide overlapping information about depth, but their importance may vary depending on the viewing circumstances.
What is the importance of distance cues in perception?
Distance cues are essential for making accurate size judgments and interacting effectively with the environment.
What is the relationship between perception and stimulus?
Perception can vary based on the observer's interpretation, suggesting that it is influenced more by the observer than by the stimulus itself.
What is the role of the ventral visual stream?
The ventral visual stream, also known as the 'what' pathway, is responsible for object recognition and perception of object properties.
What is bottom-up processing?
Processes that are directly shaped by the stimulus, also known as data-driven processing.
What is top-down processing?
Processes shaped by knowledge and expectations, also referred to as concept-driven processing.
What are feature detectors?
Neural mechanisms in the visual system that identify basic visual features such as lines, curves, and angles.
What is the significance of visual search tasks?
They demonstrate how recognition efficiency varies based on whether a target is defined by simple or complex features.
What is the repetition priming effect?
The phenomenon where words that have been seen recently are recognized more easily.
What is the word-superiority effect?
The tendency to recognize letters more easily when they are part of a word than when they are presented in isolation.
What is well-formedness?
The degree to which a letter sequence conforms to typical spelling patterns in a language, affecting recognition ease.
How does well-formedness influence errors?
More well-formed sequences are likely to be misread as other well-formed sequences, while less well-formed sequences lead to unlikely errors.
What is a feature net?
A model that describes how visual recognition occurs through a network of detectors that respond to specific features.
What factors influence a detector's activation level?
Recency and frequency of prior activation; detectors recently or frequently activated have higher activation levels.
What is the role of priming in recognition?
Priming increases the likelihood that a detector will respond to an ambiguous input based on previous exposure.
What is the McClelland and Rumelhart model?
A model that emphasizes the role of inhibitory connections among detectors in the recognition process.
What is the recognition by components (RBC) model?
A model that applies the feature net concept to the recognition of three-dimensional objects.
What is the impact of efficiency versus accuracy in recognition?
The mechanisms that allow for quick recognition can also lead to errors, sacrificing perfect accuracy for efficiency.
What is the effect of stimulus presentation time on recognition?
Brief presentations of stimuli (20-30 ms) can affect recognition accuracy, often requiring techniques like tachistoscopes.
What is the relationship between word frequency and recognition?
Higher frequency words are recognized more easily than lower frequency words, demonstrating the influence of familiarity.
What are context effects in recognition?
The influence of surrounding information or context on the recognition of a stimulus.
What is the role of a post-stimulus mask?
A visual interruption that can hinder continued processing of a stimulus after its presentation.
What is the significance of the two-alternative, forced-choice procedure?
A method used to demonstrate the word-superiority effect by comparing recognition accuracy between words and single letters.
What is the difference in reaction time (RT) in visual search tasks?
RT is faster when a target is defined by a simple feature compared to when it is defined by a combination of features.
What is the importance of feature analysis in recognition?
Feature analysis is a crucial step that occurs before combining detected features to recognize complex objects.
What are excitatory and inhibitory connections?
Excitatory connections increase the likelihood of a neuron firing, while inhibitory connections decrease it.
What is the recognition-by-components (RBC) model?
The RBC model suggests that objects are recognized by identifying their basic shapes, called geons, which serve as building blocks for three-dimensional forms.
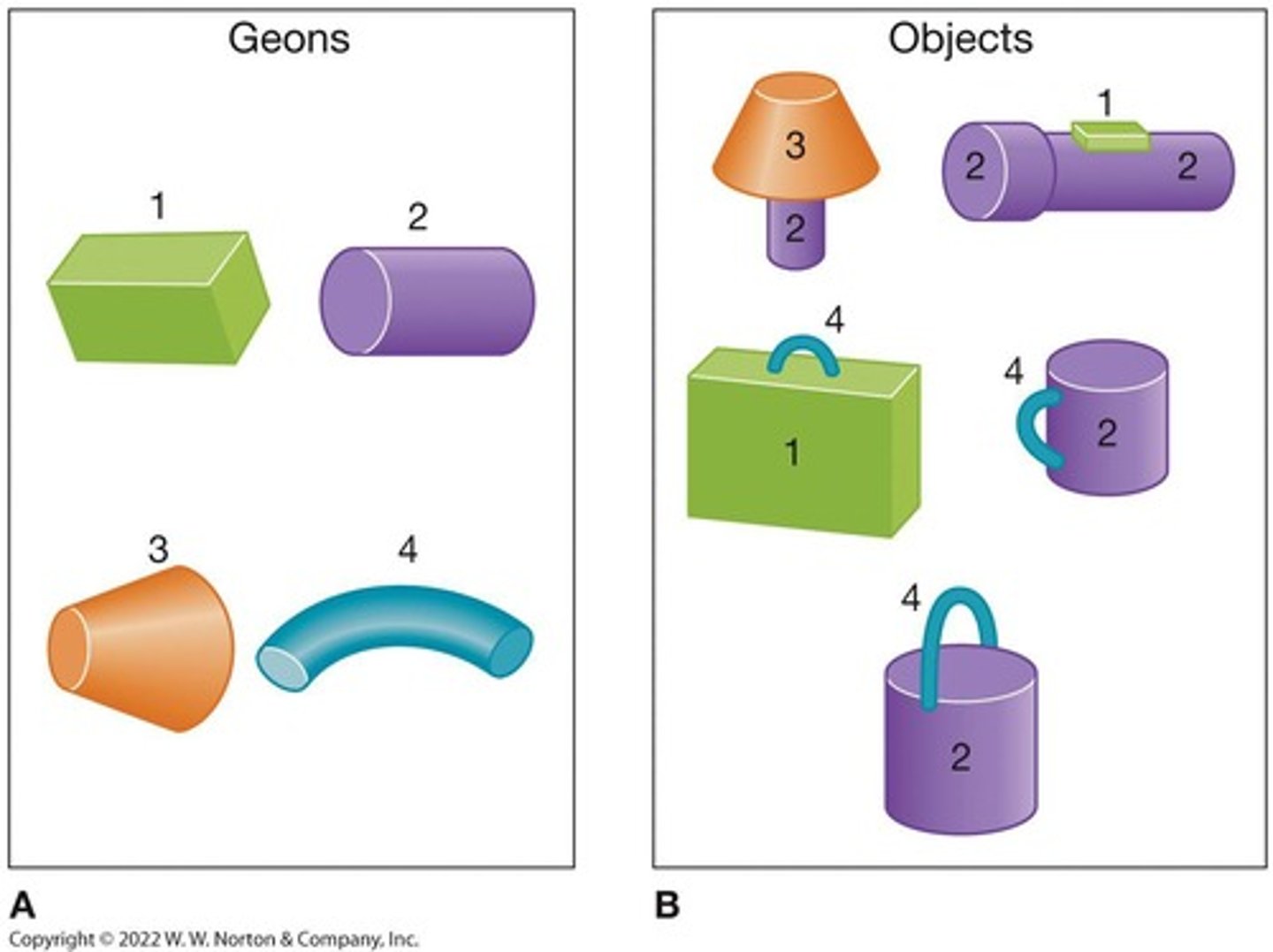
How many geons are suggested to describe any object?
It is suggested that 30 geons are sufficient to describe any object in our world.
What is an object model in the context of the RBC model?
An object model is a representation of the complete, recognized object formed by the assembly of geons.
What is a geon?
A geon is a basic shape that can be identified from virtually any angle and is used in the recognition of three-dimensional objects.
What is prosopagnosia?
Prosopagnosia is a condition characterized by the inability to recognize individual faces, including one's own, despite having normal vision.
What is the fusiform face area (FFA)?
The fusiform face area (FFA) is a region in the brain that is particularly responsive to faces and is involved in facial recognition.
What is holistic perception?
Holistic perception refers to the understanding of an object as a whole rather than as a collection of individual parts.
What is repetition priming?
Repetition priming is a phenomenon where exposure to a word or stimulus influences the response to the same word or stimulus when encountered again.
What is integrative agnosia?
Integrative agnosia is a condition where a person can perceive parts of an object but cannot integrate them into a whole object.
What is viewpoint-dependent recognition?
Viewpoint-dependent recognition refers to the idea that recognition of objects can be influenced by the angle from which they are viewed.
What is the composite effect in face recognition?
The composite effect demonstrates that it is easier to recognize faces when the two halves are misaligned, highlighting the holistic nature of face perception.
What is the significance of the inferotemporal cortex (ITC)?
The inferotemporal cortex (ITC) is involved in object recognition and may house cells that act as biological detectors for specific objects or words.
What happens during tachistoscopic presentation?
During tachistoscopic presentation, people may make recognition errors that are influenced by their knowledge of spelling and common letter pairings.
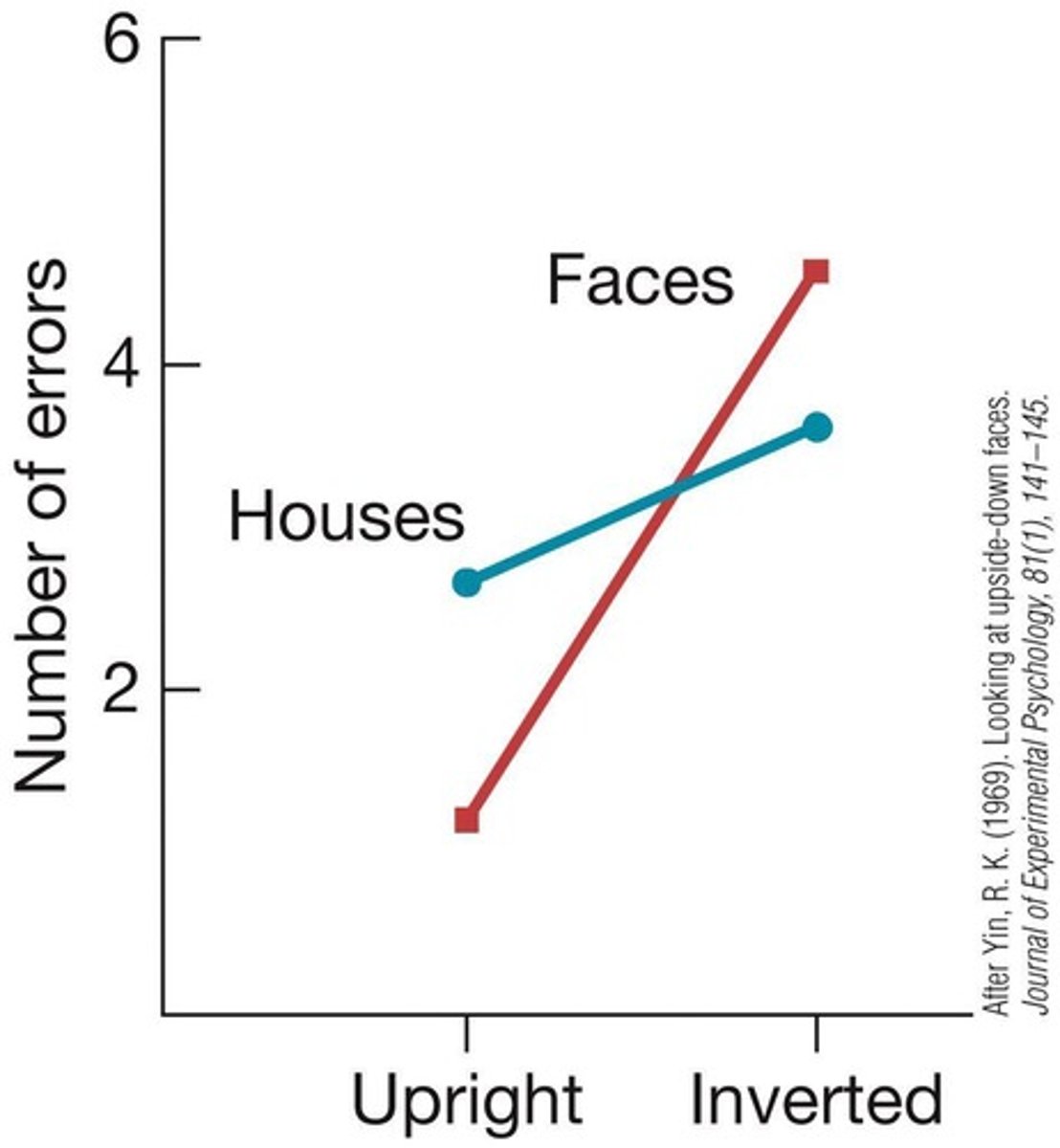
What is the inversion effect in face recognition?
The inversion effect refers to the phenomenon where faces are more difficult to recognize when they are upside down compared to other objects.
What is the role of context in object recognition?
Context can significantly influence object recognition, as expectations and surrounding information can affect how stimuli are perceived.
What is the relationship between geons and object recognition?
Geons are integral to the recognition-by-components model, as they serve as the basic shapes that combine to form recognizable objects.
What is the biological basis for word and object detectors?
Evidence for biological word and object detectors includes specific cells in the IT cortex that respond strongly to particular objects or words.
What is the effect of partial occlusion on object recognition?
Partial occlusion of objects does not necessarily prevent recognition, as the brain can often fill in missing information.