(b) cell structure
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
cell wall (2.2 / 2.3)
boundary more resistant that the cell membrane; not found in animal cells; made of cellulose in plant and bacteria cells; made of chitin in fungus cells
cell membrane (2.2 / 2.3)
boundary between the cytoplasm of a cell and its surroundings
cytoplasm (2.2 / 2.3)
thick watery liquid in which most chemical reactions occur in the cell
nucleus (2.2 / 2.3)
organelle found in eukaryotic cells that contains the genetic information of the cell in the form of DNA
mitochondrion (2.2 / 2.3)
very small organelle found in all cells other than bacteria where key reactions of aerobic respiration take place
ribosome (2.2 / 2.3)
organelle responsible for the synthesis of proteins; so small that it can only be seen with an electron microscope; there are millions of ribosomes per cell
vacuole (2.2 / 2.3)
mostly found in plant cells (can sometimes be found in animal cells); filled with cell sap (a watery solution) that gives the cell rigidity
chloroplast (2.2 / 2.3)
where photosynthesis occurs in plant cells and some protoctist cells; green due to the presence of chlorophyll
plasmid (2.2 / 2.3)
present in bacteria cells; small circle of DNA that stores the genetic information of the cell as bacteria cells do not contain nuclei
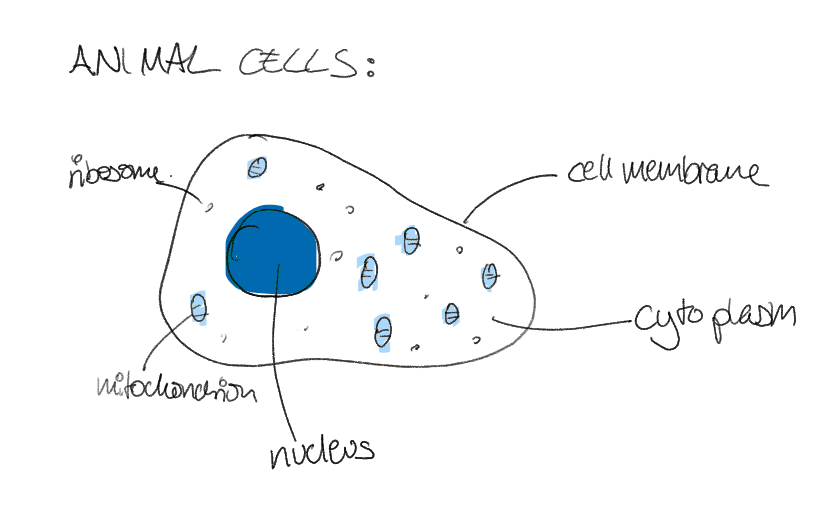
animal cell (2.4)
contains:
nucleus
cell membrane
cytoplasm
mitochondria
ribosomes
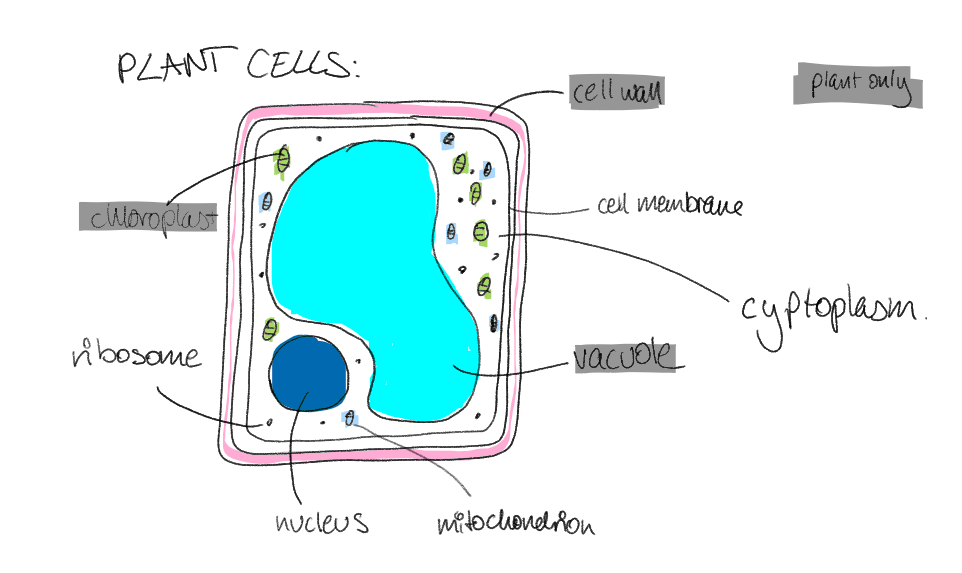
plant cell (2.4)
contains:
nucleus
cell wall
cell membrane
cytoplasm
mitochondria
ribosomes
chloroplasts
cell differentiation (2.5B)
organisms begin life as a single cell (fertilised egg aka zygote)
this cell divides to form two daughter cells, then they divide etc.
eventually one organism is made up of several billion differentiated cells
as new cells develop, specific genes are active and inactive inside each cell, which cause a cell to begin differentiation
there are 250 possible types of cells in an adult human body
stem cell (2.5B)
undifferentiated cell of an organism that is capable of dividing an unlimited number of times, giving rise to other cell types
advantages of using stem cells in medicine (2.6B)
provides medical benefits in the fields of therapeutic cloning + regenerative medicine, providing great potential for discovering treatments and cures to a variety of diseases e.g. parkinson’s, alzheimer’s, cancer, diabetes etc.
disadvantages of using stem cells in medicine (2.6B)
most adult stem cells are pre-specialised i.e. blood stem cells only make blood and brain stem cells only make brain cells. these stem cells are derived from embryos that are not a patient’s own, which means the patient’s body may reject them