Diagnostic Imaging (weeks 1-7)
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
What helps dissipate heat and allow for higher exposure setting?
the rotating anode
Heel Effect
describes the variation in x-ray beam intensity due to anode angle
Cathode
emits electrons when heats
What is the relationship between wavelength and frequency?
It is inverse
high wavelength means low frequency
X-rays are produced when high-speed electrons strike what?
the anode
mA
controls the quantity of electron produced during x-ray exposure
The higher the ____, the more x-rays that are produced
what will increasing the mA do
it will darken the image
kVp
The energy of the electrons as they reach the anode.
This controls the quality of the x-ray beams.
The higher the _____, the more penetrating power the beam will have.
will 100 mA and 1/10 second and 200 mA and 1/20 seconds result in 10mAs
yes they both do
how to reduce blur in radiographs
use high mA and the lowest exposure time
Exposure light
notifies the technician that x-rays can be released
Intensifying screens
can be used to reduce the amount of radiation needed to produce an image
Cassette
hold the film and intensifying screens in place during exposure
Types of intensifying screen
rare earth(green)
calcium tungstate(blue)
blue sensitive
green sensitive
Speed of intensifying screen
affects image detail and exposure time
Disadvantage of fast screens
lower image detail
How often should proper cleaning of intensifying screens be done
weekly
Label should include what?
name of veterinary practice
date of exposure
patient name
owner first and last name
Methods to label
lead marker
graphite tape
light flasher
Latent image
invisible image created on the film after exposure
Film storage
Dark, cool, dry place
Should be upright
emulsion layer contains what?
silver halide crystals
Developer solution
converts the latent image into a visible image
Part of the film development process
developing
fixing
washing

Safelight
should be in the dark room to help prevent film fogging
Fixer solution
hardens the film emulsion
DR
Direct Digital Radiography
after exposure the detector plate automatically sends the digital image to the computer for viewing
CR
Computed Radiography
Uses photostimulable plate to capture the image
After exposure the PSP is places into a reader that scans the interior screen and produces a digital image
DICOM
Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine
This is the universal format for storing and sending medical images.
Includes:
● Patient name and ID
● Study date and time
● Modality and description
● Series and image metadata
PACS
Picture archiving and communication system
Digital artifacts
ghosting
dust
fogging
What are intensifying screens used for
they are used to reduce the amount of radiation needed to produce an image
What is part of the film development process
Developing
fixing
washing
drying
What are some benefit of digital imaging
Immediate image preview
reduced radiation dose
easy image storage
Does patient signalment need to be included on radiographic labels
NO they don’t
What does need included is:
Name of vet practice
date of exposure
owner first and last name
patient name
Radiographic density
The degree of blackness on the image
Air(gas) --> Fat --> Soft tissue --> Fluid --> bone --> contrast media --> metals
What affects the contrast of a radiographic image
kVp
(Higher kVp the higher the scale of contrast so, more greys)
Increasing mAs
this will result in a darker, denser radiographic image
Sante’s rule
kVp = 40 + (2 x thickness in cm)
What absorbs the least x-rays
air (gas)
what absorbs the the most x-rays
metal
Recommended exposure time for thoracic radiographs to minimize motion blur
1/30 - 1/120 second
Caliper
tool used to measure the widest portion of the body that will be within the radiograph
If the radiograph is too dark but not over-penetrated, what adjustment should be made
decrease mAs by 30-50%
What does the technique chart do?
helps determine ideal settings for kVp, mAs, and exposure time for different anatomical regions
Inverse-square law
states that the intensity of the x-ray beam is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source
What are X-rays
x-rays are ionizing form of electromagnetic radiation
Stationary X-ray machine
Tube head, control center, table, bucky tray, transformer, generator
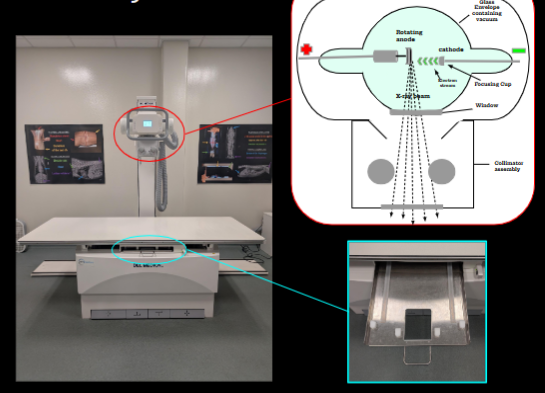
Portable X-ray Machine
Control panel, Exposure switch, Battery, Various stand and table options

Film-Screen Radiography
The image is produced by exposing film contained within a cassette that must then be developed using wet-processing

Grid
Made of alternating strips of radiodense and rediolucent material
Used to reduce radiation scatter and increase image contrast
Advantages to DICOM
it has tools that can be used to enhance images by reducing noise, changing brightness or contrast, and enhancing sharpness
Focus Film Distance (FFD)
The distance between the x-ray source and the cassette(plate)
As the distance increases, the intensity of the x-ray beam decreases
mAs
Controls the total quantity of x-rays produced per exposure.
As mA is increased, the exposure time will be decreased
Affect image density
Radiographic Detail
the sharpness of the image
Contrast
the degree of visual difference in densities between structures
Underexposure
the image appears too bright and/or grainy as a result of not enough beam reaching the detector
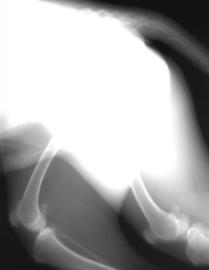
Overexposure
Image appears too dark as a result of too much radiation reaching the detector
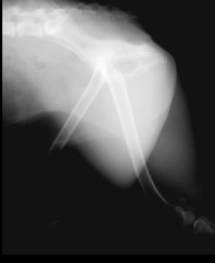
3 categories of artifacts
Pre-exposure, Exposure, Post-exposure
Developing a Technique Chart
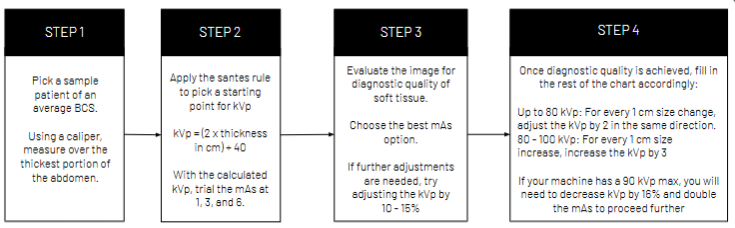
Exposure Latitude
Each setting correlates to a range rather than one specific measurement, becuase digital systems, because digital systems have contrast optimization software that allows a wider range of techniques to result in a diagnostic quality image
How x-rays are produced
an electrical current is applied to the cathode, which allows negatively charged electrons to enter the tube where they are attracted to the positively charged anode. Once they hit the anode this created heat and x-rays
ALARA
As Low As Reasonably Achievable
Minimum lead equivalence required for protective equipment
0.5mm
MPD
Maximum permissible dose
Maximum permissible dose for occupational personnel
5 REM per year
4 types of dosimeter Badges
1) Film Badges
2) Thermoluminescent Dosimeter (TLD)
3) Optical Stimulated Luminescence (OSL) dosimeter
4) Ion Chamber dosimeter
How often should you check lead aprons and thyroid collars for cracks?
every 12 months
How often should lead gloves be checked?
Every 6 months
First Trimester of Pregnancy
The most sensitive period for fetal radiation exposure
Sources of Scatter radiation
Table, Patient, floor
Where should your dosimeter be worn?
At thyroid level, OUTSIDE the lead
4 possible effects of radiation on living tissue
1) Can pass through with no effect
2) Repairable cell damage
3) Irreparable cell damage
4) Cell death
Somatic
Radiation effect within the individuals during their life time
Genetic
Radiation effects that affect future generations through damage of reproductive cells
What is the primary source of radiation exposure to personnel
Scatter radiation
4 ways to minimize radiation exposure
time, distance, shielding, and technique
Which of the following is NOT a required PPE in radiology
safety goggles
4 clinical applications of nuclear scintigraphy
Detections of bone trauma and disease
Evaluation of thyroid disease in cats
Evaluation of renal function
evaluation of cardiac perfusion
Limitation of nuclear scintigraphy
Long imaging time
Nuclear scintigraphy
Uses radioactive tracers to evaluate physiological function
Most common used isotope in nuclear scintigraphy
Technetium
Which organ is commonly evaluated using nuclear scintigraphy
Thyroid
Scintigraphy is useful for detecting what activity in bones
Metabolic activity
Gamma (scintillation) camera
The camera used to capture scintigraphy images
Ultrasound imaging is based on _____
sound waves
Which of the following is a common use of ultrasound?
Gastrointestinal imaging
Ultrasound is ideal for what type of monitoring during pregnancy
fetal monitoring
Can doppler ultrasound be used to assess blood flow
Yes
Curvilinear transducer
Used for abdominal ultrasound
What is ultrasound limited by
Gas (blocks the sound waves)
Which modality is safest for both patient and personnel
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is commonly used for what
Cardiac evaluations
CT
Computed tomography
What does CT us to produce cross-sectional images?
x-rays
How are CT scans are often enhanced
Iodinated contrast agents
What is a common clinical application of CT
Lung evaluation
3 Planes that CT produces images in
dorsal
axial (transverse)
Sagittal
What does MRI use
Magnetic fields and radio waves to generate images
What protection should you use with MRI
Ear protection due to scanner noise