Biology Exam #2: Fungi
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
When did fossilized fungal evidence arise?
Silurian Period
1 Billion years ago
Hyphae fossilizes
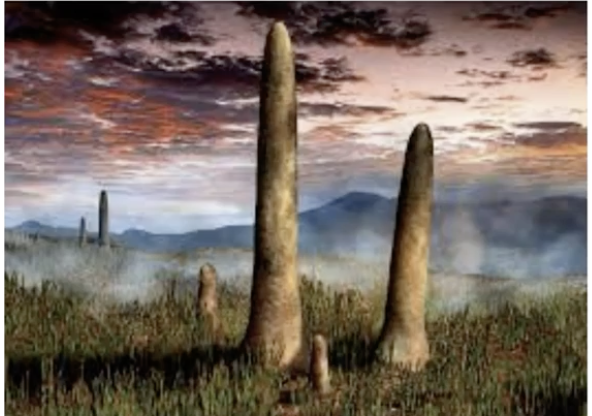

What are prototaxites?
one of the first fungal bodies to exist
was much more humid back then
What is ploidy?
Plants and fungi have multiple copies of chromosomes
Fungi characteristics
Characteristics similar to animals
Heterotrophic- Derive energy from organic compounds
Cells walls made of chitin
Produce pigments
store carbs as glycogen
can absorb nutrients from environment across cell surface
Characteristics similar to bacteria
They are decomposers
Cell structure and function
Contain a complex cell structure like other eukaryotic cells
Membrane bound nucleus (DNA within)
DNA wrapped around histones
Mitochondria
golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum
DONT HAVE CHLOROPLASTS
Thick cell walls like plants
Anatomy of fungi
Mycelium- network of hyphae
obtains nutrients, produces fruiting body, mostly underground
Reproductive structure
fruiting body (The mushroom)
produces spores
spores
Involved in fungal reproduction
produced in fruiting body
HAPLOID
They germinate when they hit damp soil
Fungal reproduction
Both sexual and Asexual
most produce haploid spores that go through mitosis
form multicellular haploid organisms
Asexual fungal reproduction
Budding
buldge forms and nucleus divides by mitosis
Fragmentation
Fragment of hyphae grow new colonies
producing spores
genetically IDENTICAL to parent
Sexual
Genetic VARIATION
conditions and environment have to NOT be great
or else asexual would occur
Homothallic= Self fertile
How do fungi get nutrients?
They are heterotrophic
They must take in organic molecules to generate energy they need
Digestion before ingestion
Exoenzymes secreted from hypha break down large organic molecules
obtain nutrients from organic decaying matter
saprobes
They can derive nutrients from host tissue (parasitic)
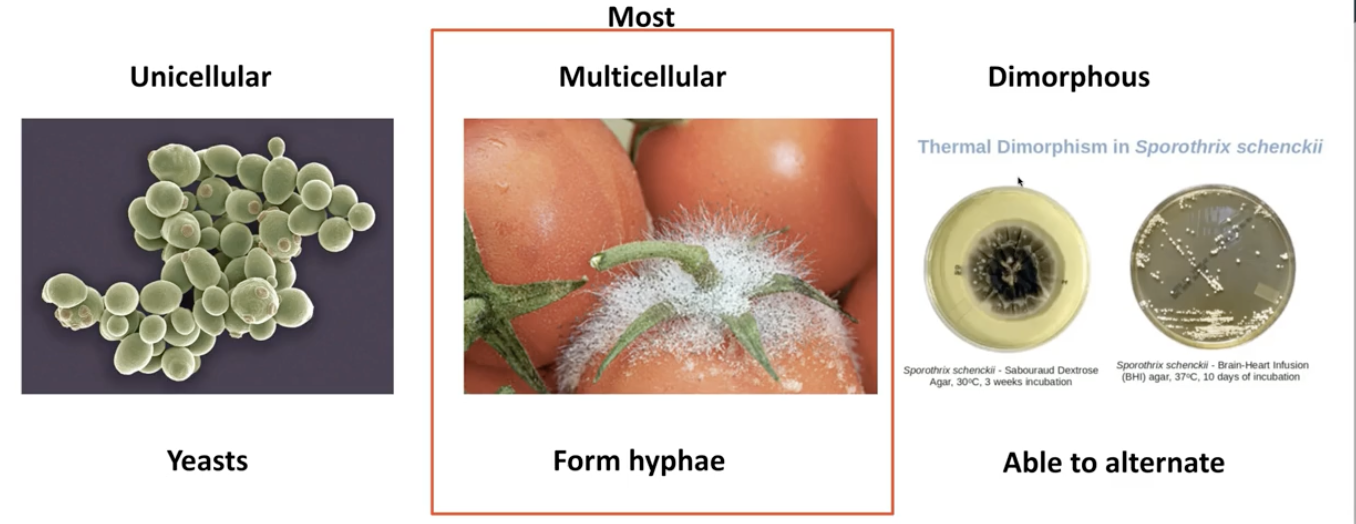
what type of growth do mose fungi have?
Multicellular
Form hyphae (This is the fuzz we see on tomatoes)
Which mushrooms have a bright red pigment, some of which are poisonous to humans?
Amanita Muscaria (Fly agaric)
Pigments are associated with cell wall
Protection against ultraviolet radiation (the pigment)
What habitats do fungi grow best in?
Moist
slightly acidic
both dark and light environments
Vary in O2 requirements
Most need O2
Some can be killed by O2
Most can live anywhere
What molecules are released when fungi breaks down organic material?
Nitrogen
Phosphorus
DIGESTION BEFORE INGESTION
Mutualistic Relationships
Mycorrhizae
about 90% of plant species
Ectomycorrhizae= wrap roots in a sheath of hyphae
Endomycorrhizae= fungi grow within roots
Endophytes= Live within a plant and secrete toxins that help prevent predation and resistance to environ. stress
Are fungi mutualistic?
YES
Most terrestrial plant roots connect w/ fungi and form mycorrhizae
Allows exchange of nutrients and H2O to benefit both organisms

Another example of mutualistic relationships
Lichen
A fungus that lives in a mutualistic relationship w/ a photosynthetic organisms
neither organisms can live without this relationship
Very sensitive to air pollution
Which means that if the species is there, the air quality is probably good
How do ants and fungi work together?
Ants maintain a fungal body within their ant colony
Ants collect leaves to feed the fungal body
Ants can eat portions of the fungus and byproducts of the fungus
What are fungivores?
Animals that unknowingly disperse fungal spores due to their diet
PIGS
How do humans benefit from fungi?
Nutrient cycling
pest control
Humans are heterotrophic as well
Mycorrhizae relationship to plant growth and agricultural goals
Foods for human consumption
Mushrooms
cheese
Alcohol
Bread
Medicine
Clothing