Histology Quiz 4
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/90
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
1
New cards
cell body, nucleus, nucleolus, nissil body
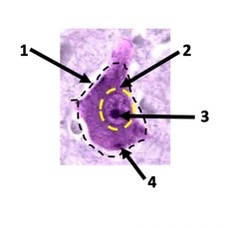
2
New cards
satellite cells
What type of glial cells?
3
New cards
astrocytes
What type of glial cells?
4
New cards
Oligodendrocytes
What type of glial cells?
5
New cards
schwann cells
What type of glial cells?
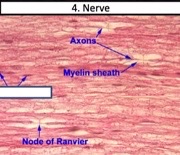
6
New cards
Epnendymal cells
What type of glial cells?
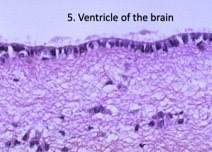
7
New cards
Oligodendrocytes
myelin-producing cells that ensheathe axons for protection and to increase signaling efficiency
8
New cards
Astrocytes
abundant cells that support and protect neurons while also assisting with neuron function
9
New cards
Ependymal cells
cells that line the brain ventricles and spinal cord central canal; produce and circulate CSF
10
New cards
Microglia
migratory cells that act as immune cells in the CNS
11
New cards
contraction
key function of muscle tissue
12
New cards
skeletal, cardiac, smooth
3 types of muscle
13
New cards
move body parts, pump blood, drive involuntary movement
what is contraction used for?
14
New cards
quick, forceful and voluntary contractions
function of skeletal muscle
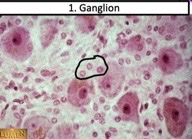
15
New cards
myofibrils
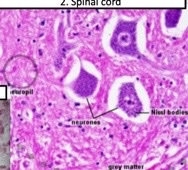
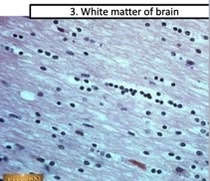
long protein fibers that dominate skeletal muscles cells
16
New cards
mitochondria, acidophilic
skeletal muscle is abundant in ____ making them ______
17
New cards
sarcomeres
\-basic contractile structure of skeletal muscle
\-repeating units that make up myofibrils
\-repeating units that make up myofibrils
18
New cards
myofilaments
what are the proteins that make up sarcomeres called?
19
New cards
myosin
what are thick myofilaments made of?
20
New cards
actin
what are thin myofilaments made of?
21
New cards
A band
intensely staining region in sarcomere where thick and thin filaments overlap
22
New cards
I band
Near Z-discs, no overlap, only contains less dense thin filaments so this is the lightest staining region of the sarcomere
23
New cards
one z disc to the next
where does a sarcomere extend from
24
New cards
z-discs
where are sarcomeres anchored on each end?
25
New cards
acetylcholine
what crosses the neuromuscular junction to initiate contraction
26
New cards
inward towards M line
in contraction, myosin heads pivot to pull actin fibers _____
27
New cards
full
in skeletal muscle, every contraction is _____ meaning if a fiber contracts, then every sarcomere in that muscle fiber contracts
28
New cards
controlling how many muscle fibers are contracting
how do skeletal muscles control strength of contraction?
29
New cards
I band, A band, Z-disc
name these structures in skeletal muscle
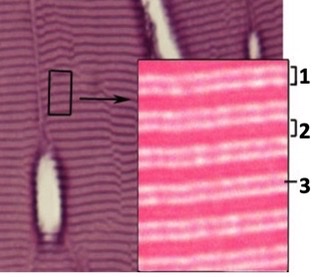
30
New cards
fascicles
what are muscle fibers bundled into?
31
New cards
endomysium
\n Individual muscle fibers are surrounded by a thin ECM of \n reticular fibers called….
32
New cards
perimysium
\n Muscle fibers assemble into fascicles, what are fascicles bound together by?
33
New cards
epimysium
what binds multiple fascicles together to form an muscle?
34
New cards
myofilaments, sarcomere, myofibril, muscle fiber, fascicle, muscle
Organize from smallest unit to largest unit: \n – Myofibril \n – Fascicle \n – Myofilaments \n – Muscle fiber \n – Muscle
\-sarcomere
\-sarcomere
35
New cards
muscle fiber, fascicle, endomysium, perimysium
identify these muscle structures
black circle, red circle, small arrow, big arrow
black circle, red circle, small arrow, big arrow
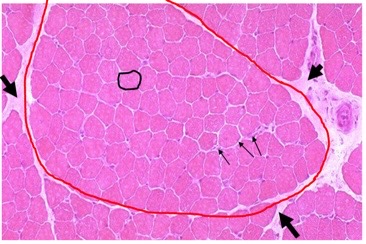
36
New cards
myoglobin
what does red/slow fibers contain to give its color?
37
New cards
oxidative phosphorylation
what is the function of myoglobin?
38
New cards
red/slow
what type of muscle fiber would stain most intensely in an NADH or myosin ATPase antibody?
39
New cards
existing muscle fibers increase in size
how do skeletal muscles grow?
40
New cards
no, they have multiple nuclei
can muscle fibers divide? why?
41
New cards
undifferentiated satellite cells, myoblasts
\n During hypertrophy, _________ divide, differentiate into ______, and then fuse with existing muscle fibers to drive cell growth
42
New cards
atrophy
decrease in muscle size due to disuse or disease that can result in weakness or loss of function
43
New cards
cardiomyocytes
cardiac muscle cells
44
New cards
coordinated
what type of contractions do cardiac muscles generate?
45
New cards
collecting and analyzing info from environment/body, overseeing voluntary/involuntary actions
nervous system functions
46
New cards
neurons
–Cells that transmit, process, integrate, and respond to signals within the nervous system \n –Large cell bodies with large, euchromatic nuclei and often abundant ribosomes and RER in cytoplasm; long processes for signal reception and transmission
47
New cards
glial cells
Cells that support and protect neurons \n –Structure varies depending on specific function
48
New cards
information processing and message transmission/reception
function of neurons
49
New cards
synapses
sites of contact between adjacent cells in neuron for signal transmission
50
New cards
nissl bodies
clusters of ribosomes and RER – dense, basophilic cytoplasmic structures, common in neurons since they carry out such abundant protein production
51
New cards
dendrites
–Receive signals \n –Typically branched
52
New cards
axons
–Send signals \n –Often very long
53
New cards
ion channels
necessary for message transmission throughout the nervous system
54
New cards
6
how many total types of glial cells
55
New cards
oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, ependymal cells, microglia
what glial cells are found in the CNS?
56
New cards
schwann cells and satellite cells
what glial cells are found in the PNS?
57
New cards
myelin
Most axons in the nervous system are ensheathed in a lipid-based material called ______
58
New cards
protects axons and increases efficiency of nerve impulses
function of myelin
59
New cards
oligodendrocytes
\n -Produce myelin and ensheath axons within the CNS to protect axons and improve efficiency of signal transmission \n -have pale-staining cytoplasm due to abundant myelin
60
New cards
astrocytes
\-Provide metabolic support for neurons, as well as protecting, repairing damage, and assisting with neuron function \n •Very abundant throughout CNS \n •In H&E, only small basophilic cell body is apparent; with specialized stains, cellular processes are also apparent
61
New cards
ependymal cells
\-Line surfaces of brain ventricles and spinal cord central canal, \n where they produce CSF; also ciliated to circulate CSF \n •Columnar, ciliated cells resemble epithelial cells, but are not – note absence of basement membrane
62
New cards
microglia
\-Act as immune cells without the CNS; can clean up cellular debris, recognize cellular damage, and recognize pathogens \n •Relatively small and rare, so difficult to identify without \n specialized stains
63
New cards
schwann cells
\-Ensheath axons within nerves of PNS for protection and increased signal efficiency \n •Cells themselves have poorly stained, streaky cytoplasm due to abundant myelin
64
New cards
nodes of ranvier
Small gaps between adjacent Schwann cells
65
New cards
satellite cells
\-Support and protect neuronal cell bodies in ganglia \n •Small, round, basophilic cells surrounding neuronal cell \n bodies in ganglia
66
New cards
brain and spinal cord
what does the cns consist of
67
New cards
meninges
connective tissue that ensheaths entire cns
68
New cards
gray matter
\-Neuronal cell bodies and dendrites – not much myelin \n -Abundant astrocytes
\-more intensely stained, more nuclei, often organized into layers with large neuronal cell bodies
\-more intensely stained, more nuclei, often organized into layers with large neuronal cell bodies
69
New cards
white matter
\-Bundles of myelinated axons \n -Abundant oligodendrocytes and astrocytes
\-stains more poorly (myelin); often ‘streaky’ in appearance due to parallel axonal tracks and myelin
\-stains more poorly (myelin); often ‘streaky’ in appearance due to parallel axonal tracks and myelin
70
New cards
ganglia and nerves
2 general types of structures in the PNS
71
New cards
ganglia
clusters of PNS neuronal cell bodies
72
New cards
nerves
bundled axons throughout the PNS
73
New cards
endoneurium
delicate layer of ECM that ensheaths each individual axon with its accompanying schwann cells
74
New cards
nerve fiber
consists of axon, schwann cell, and endoneurium
75
New cards
fascicle
bundle of nerve fibers and its surrounding perineurium
76
New cards
perineurium
layer of CT that hold multiple nerve fibers together
77
New cards
epineurium
holds fascicles together in larger nerves
78
New cards
79
New cards
cerebellar cortex
Outer layer of highly folded gray matter
80
New cards
cerebellar medulla
Inner layer of white matter
81
New cards
brain stem
Heart rate, breathing, sleeping, eating
82
New cards
cerebellum
Fine motor control; cognitive processing
83
New cards
cerebrum
\n Movement, sensory processing, language, learning and memory
84
New cards
molecular layer
small cortex layer, sparsely distributed neurons as well as the dendrites of Purkinje neurons
85
New cards
granular, purkinje, molecular
layers of the cerebellar cortex from closest to farthest from inner medulla
86
New cards
pyramidal neurons
Most identifiable neurons w/ distinctive triangular cell bodies
87
New cards
cerebellum
what part of the brain?
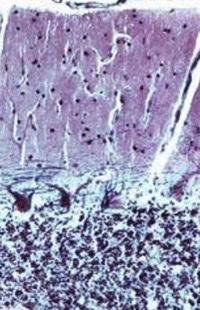
88
New cards
cerebrum
what part of the brain?
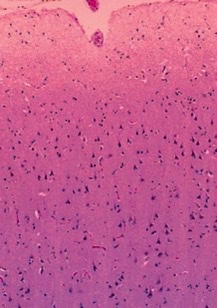
89
New cards
sensory, motor
in the spinal cord, dorsal “horns” of gray matter enriched in ____ neurons, while ventral “horns” are enriched in strikingly large ______ \n neurons
90
New cards
dura mater, arachnoid layer, pia mater
3 layers of meninges from exterior to interior
91
New cards
efferent
types of neurons like pyramidal that extend axons away from CNS towards body