Bio practical-4 pH and dilutions
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
bio 1107
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What are buffers made out of?
conjugate base and weak acid
What is a buffer?
are solutions that minimize change in pH
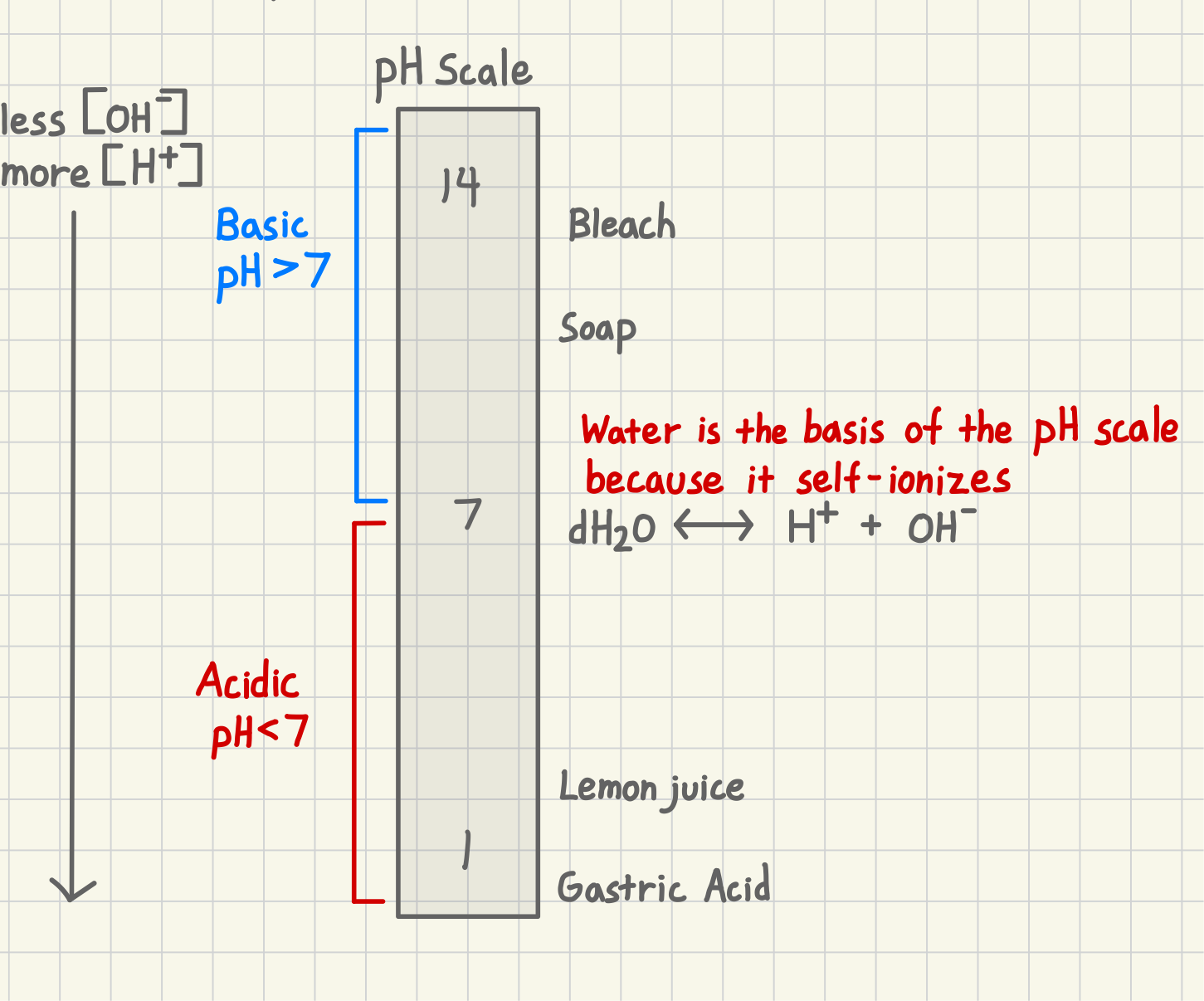
When a solution is more basic (alkalinity) what does it have a higher concentration in?
OH-
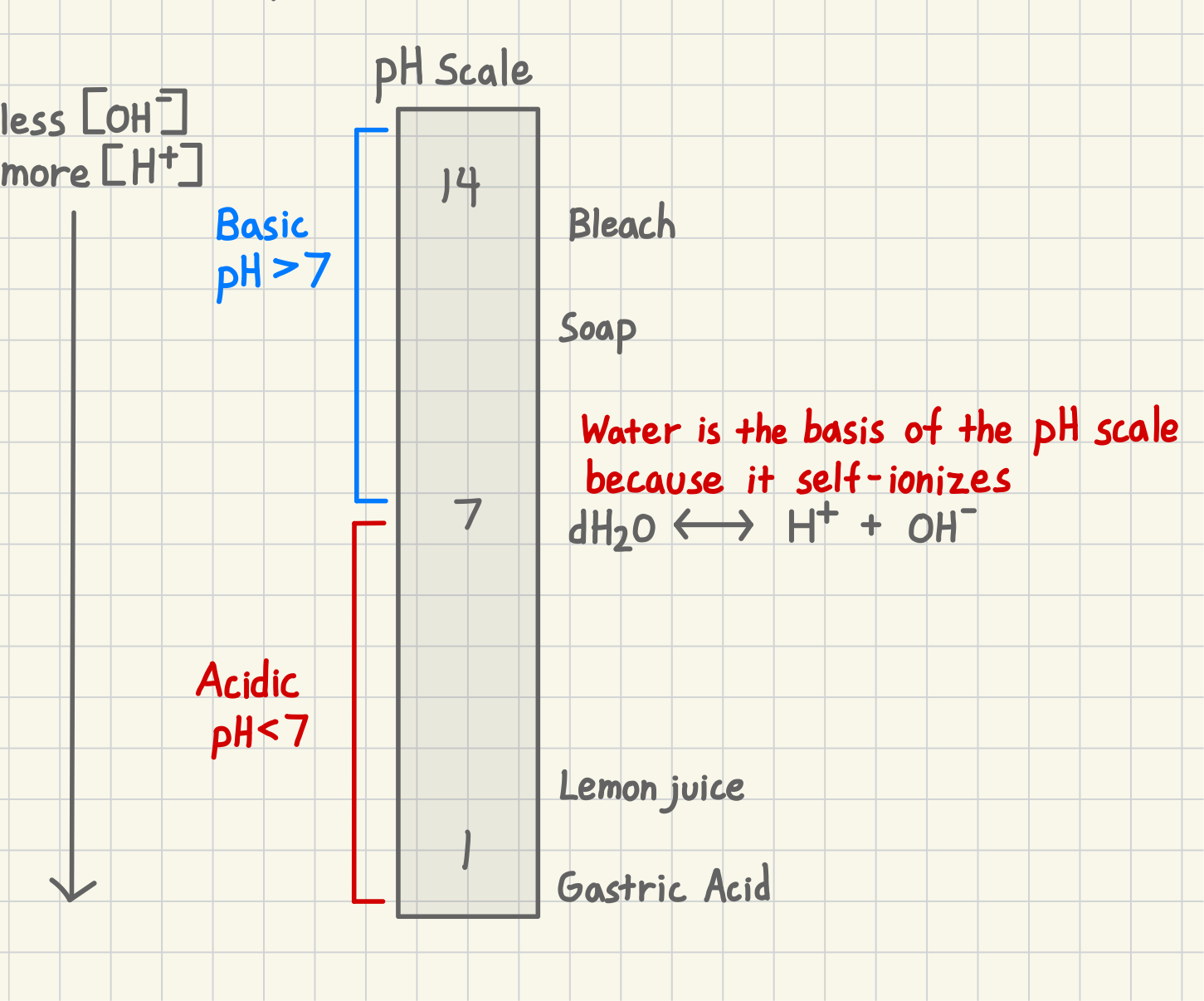
When a solution is more acidic, it has a higher concentration in…what?
H+
How to determine a hydrogen conjugate base
1 hydrogen
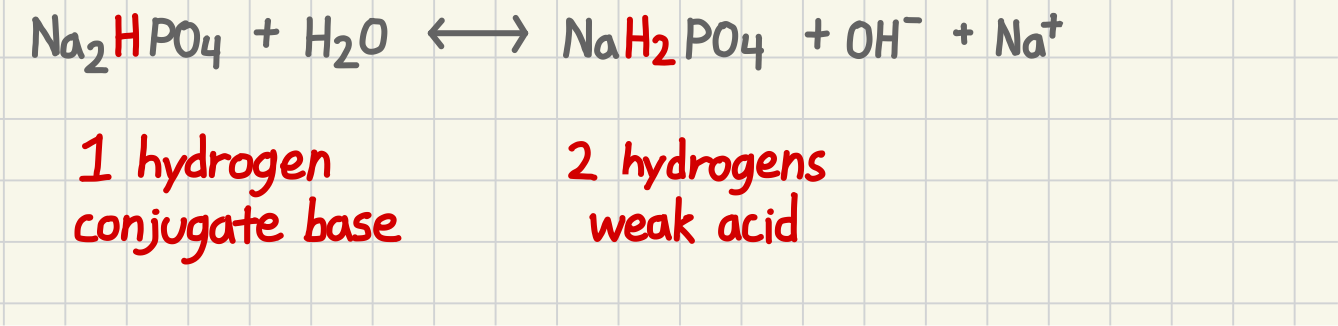
How do determine weak acid
2 hydrogens
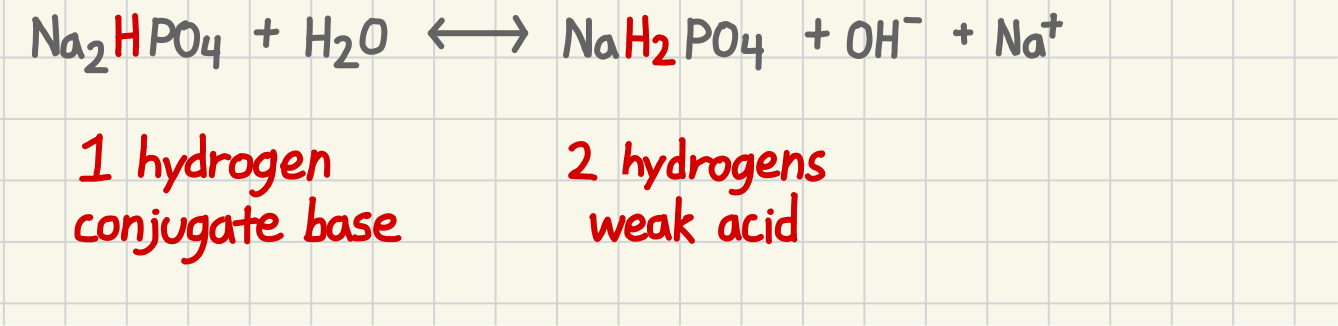
Cohesion
attraction between like molecules
ex: surface tension
Adhesion
Attraction between different substances
ex: water droplets sticking to glass
what is very good solvent?
water
why is water a good solvent?
water self-ionizes o yield H+ ions
H₂O (l) → H+ (aq) + OH- (aq)
what does [H+] mean and what does it determine?
molarity of hydrogen ion
how acidic or basic a solution is
How do you find pH?
pH =-log[H+]
How do you find hydrogen ion concentration
[H+]= 10^-pH
What unit must [H+] be in before finding pH?
Molarity (M)
pH meter reminders
pH meters must remain submerged at all times
Keep the pH meter in the holding solution if not being used, or in the experimental solution
Remember to rinse the base of the meter with distilled water over the liquid waste container before and after each use
Make sure the correct one is connected to your iPad
Use the ID number on the back of the pH meter
What is the pH of a solution with a concentration of 0.7 M hydrogen ions?
pH = -(log(0.7))
pH = -(-0.15)
pH = 0.15
What is the concentration of [H+] present in a solution with a pH of 11.0?
[H+] = 10-11 = 1.0 x 10-11
What does weak acid absorb?
excess OH-
Conjugate base absorbs what?
excess H+
What are the 3 main buffers in human body
Carbonic Acid-Bicarbonate Buffer
Phosphate Buffer
Protein BUffer
What is the purpose of Dilutions?
Make a less concentrated solution from a more concentrated stock solution
How are dilutions done?
adding more solvent (typically water)
What can dilutions NOT do
can NEVER increase the concentration
What formula can you use for dilutions?
C₁ x V₁ = C₂ x V₂
C₁ - initial concentration (of the stock solution)
V₁ - initial volume (of the stock solution needed to make the diluted solution)
C₂ - final concentration (of the diluted solution)
V₂ - final volume (of the diluted solution)
How would you prepare 400 mL of a 0.2 M hydrochloric acid from a concentrated stock of HCl with a concentration of 8.0 M?
(8.0 M)(?) = (0.2 M)(400 mL)
(8.0 M)(?) = 80
V₁ = 10 mL of HCl is needed to make the dilution
How much 0.5 M sodium chloride solution can you prepare if you start with 150 mL of a 2.0 M NaCl stock solution?
(2.0 M)(150 mL) = (0.5 M)(?)
300 = (0.5)(?)
V₂ = 600 mL of the NaCl solution can be prepared