Unit 1 gr 11 Molecules and Water
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
147 Terms
the sum of all chemical reactions in a cell or organis
metabolism
the ability to do work (move an object against an opposing force)
energy
series of reactions involved in metabolism processes
metabolic pathways
what type of metabolic pathways can there be
linear or cyclic
what do u cells use to control metabolic reactions
enzymes
whats an example of a linear pathway
glycolysis (part of respiration) l
whats an example of cyclic pathway
urea cycle
anabolism
join small molecules, make big ones NEED ENERGY
Catabolism
Break large molecule, make small RELEASE ENERGY
whats an example of anabolic reaction
dehydration synthesis
whats an example of catabolic reaction
hydrolysis
Enzymes Biological catalysts
speed up chem reactions without being consumed
what type of proteins are enzymes
globular proteins
examples of enzymes
lactase, amylase
active site
where an enzyme specifically binds the substract
substrate
reactant (starting substances)
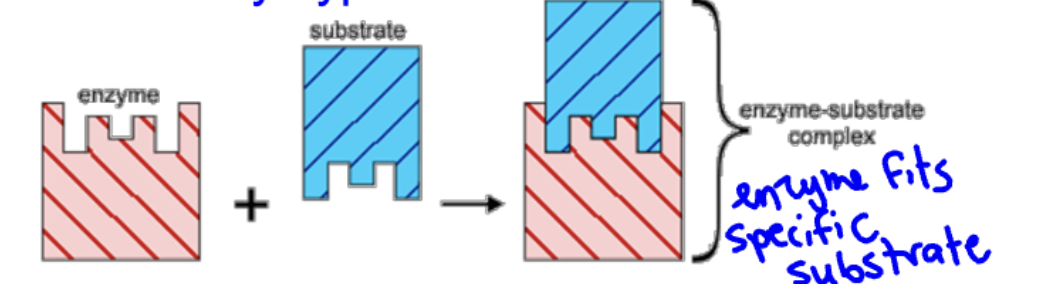
what is this
lock and key hypothesis
induced fit hypothesis
enzymes and substrates change to slightly better fit
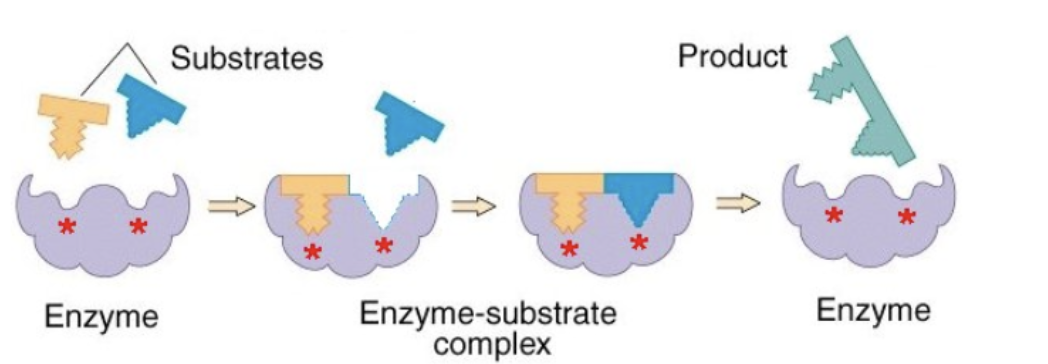
what hypothesis is this
induced fit
collision theory
E and S collide in correct orientation for reaction
when will there be more collisions
high temps and higher concentration w
when will there be fewer collisions
low concentration and low temp
what is DNA replication an example of (idea)
that some large substrate molecules need enzyme to move
what is cell membrane an example of
that some enzymes are immbolilized
what is the problem with denatured active sites
prevents substrate from binding
what 4 factors effect enzyme activity
enzyme concentration
substrate concentration
temperature
pH
what type of increase is enzyme concentration (assuming high of substrate)
linear increase assuming high of substrates and more active sites
what type of increase would substrate concentration cause
initally increase (PLATEAU) , more substrate = more likely to collide with enzymes
plateau
all enzyme active sites are taken
what happens when pH is further from optimal
active site is denatured more
why temp matter?
less kinetic energy, fewer collisions
2 things to measure reaction rate
fixed time
time of completion
First Law of Thermodynamics
energy not destroyed or created, just converted
activation energy (Ea)
minimum amount to break bonds in reactants T
transition state
intermediate condition where bonds in reactants are breaking and bonds in products are forming
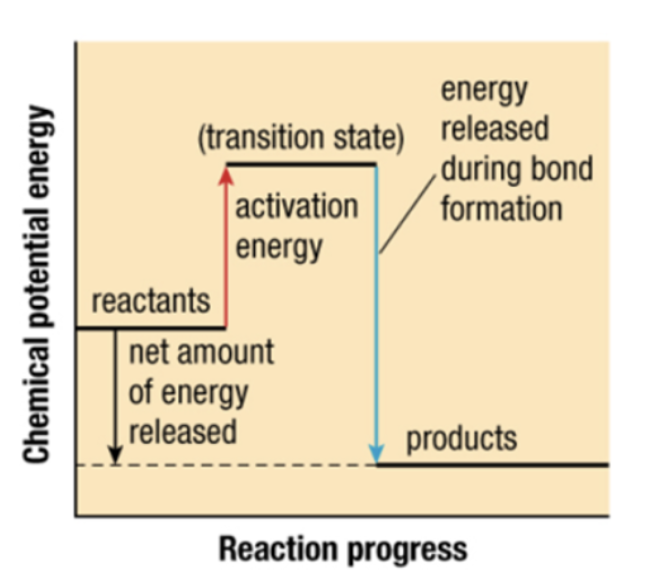
what type of reaction
exothermic
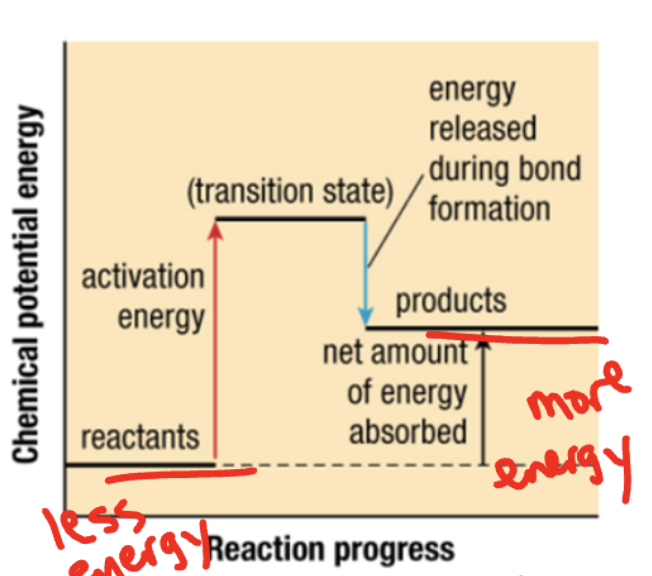
what reaction energy
endothermic
after enzymes bind to reactant molecules what hpappens to transition state
lower the energy
what does enzyme lower activation energy mean
less energy to start reaction, more likely reaction will occur
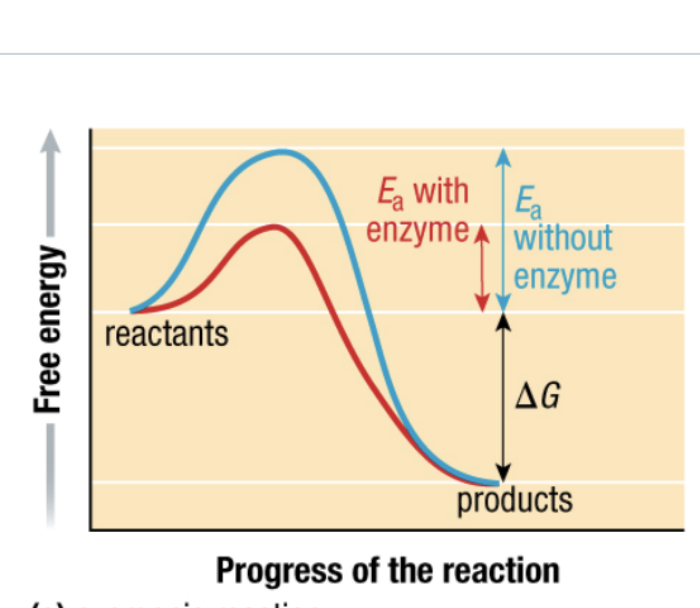
what type of reaction
exergonic
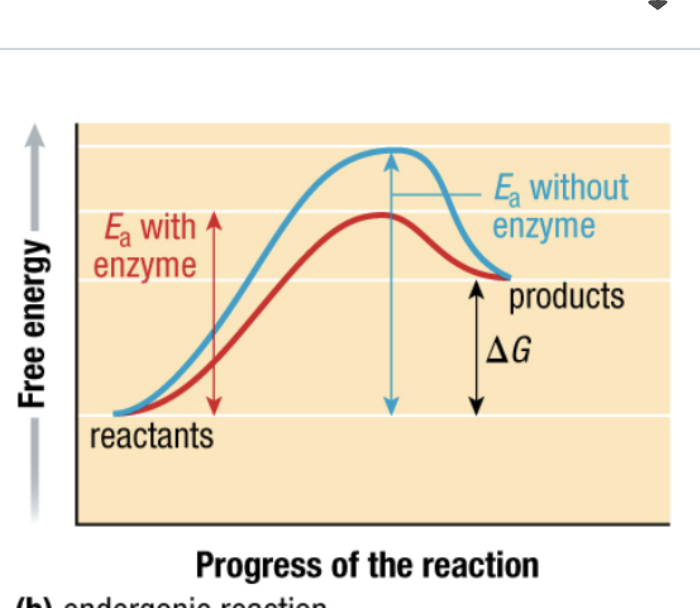
what type of reaction
endergonic reaction
2 ways enzymes lower activation energy
bring molecules together in the correct orientation
change shape of substrate
heat is a byproduct of…
metabolism
what is brown adipose tissue
humans produce more heat during respiration and less ATP
allosteric site
binding site for regulatory molecules
allosteric regulation
enzyme changes shape when allosteric molecule bound
what does the allosteric site do
control when enzyme is active
what may the allosteric regulation do
may allow or prevent substrate from binding
what is.a competitive enzyme inhibition
inhibitor binds to active sit and blocks substrate
what is a noncompetitive enzyme inhibition
inhibitor binds to allosteric site
which inhibitor has a higher inital rate of reaction
competitive inhibitor
allosteric (non-competitive inhibition)
end product of a pathway inhibits an earlier enzyme
negative feedback
controls levels within a set range like body temp
mechanism-based inhibition
inhibitor is permanentaly bound to active site and enzyme is inactivated
penicillin
blocks active sit on transpeptidase enzyme in bacteria
what happens to cells ways in penicillin
cells walls cannot be built properly, cell bursts
what carries genetic information
is dna deoxyribonucleic acid
whats nitrogenous base + pentose sugar +phosphate group
nucleotide
whats the difference between DNA vs RNA
DNA has one less oxygen on carbon 2
whats the difference between purines and pyriidines
purines = 2 rings
pyrmidiries = 1 ring
at the groupchat mmenoic
AT GC
ACTG vs ACUG
DNA vs RNA
whats the bond between nucleotides (sugar and phosphorus)
phosphodiester
what is the special thing about DNA structure
its double stranded, so they’re anti parallel, so flipped
what carbons does. the dehydration synthesis/condensation join at
C5 (phosphorus) and C3 (OH)
what type of bond is a phosphodiester
a strong covalent one
what type of bond is the hydrogen bond
weak
main difference between DNA and RNA
DNA = genetic info
RNA is the process of transcribing genetic info from DNA into proteins
how else is the DNA double stranded helix called
complementary base pairing
what type of strand is RNA
single
type of enzymatic protein
acceleration of chemical reactions
structural proteins
collagen & elastin, keratin (hair and nails)
transport proteins
transport of other substaces
hormonal proteins
cellular communication
contractile
movement
defensive
protect against disease
what 4 type of amino acids are there
nonpolar
polar
charged/acidic
charged/basic
LUCA
last universal common ancestor
whats the bond in the sulfhydye group
disulfide bridge
primary structure
sequence of amino acids joined by polypeptides
whats the possibilites of amino acids
20^n
whats the H2N- called
N-terminus
whats the carboxylic acid side called
c terminus
secondary structure
hydroge bonding between amino acid backbone
whats the 2 important things in 2nd structure
alpha helix and beated sheets
tertiary structure
interactions between side chains (R groups)
what type of tertiary structures are there (4)
charged ionic bonds
polar hydrogen bonds
non polar hydrophobic
disulfide bridge (cysteine)
where is the hydrophilic interaction (outside or inside)
the outside (exposed to cytoplasm/water)
where is the hydrophobic interaction (outside or inside)
inside (amino acids fold into middle)
whats the thing about phospholipids
polar on the outsides and non polar on the inside
quaternary structure
two or more folded polypeptides come together to make a functional proteins
how can polypeptides may be held together together
ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds, etc
non conjugated protein
only poplypetide (insulin and collagen)
conjugated proteins
one or more non polypeptide unit (hemoglobin has heme)
example of globular protein
hemoglobin or insulin
example of fibrous protein
collagen
what causes denaturation
heat and pH changes
what is denaturation
protein unfolds, breaks 2nd, 3rd or 4th structure p
proteome
all proteins produced by cell, tissue or organism
proteomics
study of which proteins are active in certain cell at certain time