MODULE 2 – EQULIBRIUM CHEMISTRY
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Mole
Even the smallest samples we deal with in the laboratory contain enormous numbers of atoms, ions, or molecules.
mol
abbreviated as mol
Avogadro’s number
6.022 x 10²³
atomic weight
an element in atomic mass units is numerically equal to the mass in grams of 1 mol of that element.
molar mass
is numerically equivalent to the sum of the atomic weights of all the atoms present in a compound, and has the unit g/mol.
solution
is a homogenous mixture of two or more substances whose composition may be varied within certain limits.
solute
comprises one substance
solvent
dissolved in another substance
solute
is the substance that is present in the smaller amount.
solvent
is the substance that is present in the larger amount.
water
Most chemical reactions encountered in analytical chemistry take place in aqueous solutions, those whose solvent is ?
ionic compounds and polar compounds
Because water is polar, the solutes that can dissolved in it are ? and ?.
electrolytes
Ionic compounds form ? when they dissolve in water, while polar compounds do not.
Concentration
is a general measurement unit stating the amount of solute present in a known amount of solution.
molar
symbolized by M, which has the dimensions of mol/L.
Percent Composition
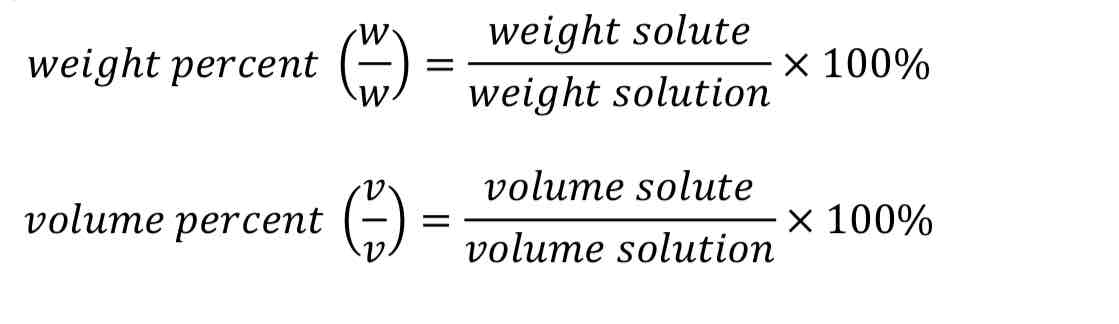
parts per million
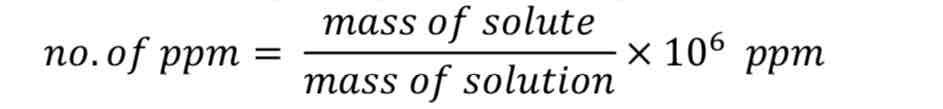
parts per billion
Density and specific gravity
are related terms often found in the analytical literature.
density
of a substance is its mass per unit volume
specific gravity
the ratio of its mass to the mass of an equal volume of water at 4°C.
kilograms per liter or grams per milliliter
Density has units of
irreversible
Most chemical reactions are
microscopic scale
On a ______________, most chemical reactions are reversible which means it can occur both in the forward and backward directions.
reversible
Many reactions used in analytical chemistry never result in complete conversion of reactants to products ?
chemical equilibrium
Reversible reactions often proceed to a state of _____________ in which the ratio of concentrations of reactants and products is constant.
mass-action effect
An equilibrium shift brought about by changing the amount of one of the participating reactants or products is called a
equilibrium-constant expression
The influence of concentration on the position of a chemical equilibrium is conveniently described in quantitative terms by means of an ?
equilibrium constant
The constant K in in the equilibrium constant expression is a temperature-dependent numerical quantity called the
Kw
Ion-product constant
Ka or Kb
Dissociation constant
Slightly soluble compounds
are those that has a solubility in water of less than 0.020 mol/L.
solubility product expression
for a compound is the product of the concentration of its constituent ions, each raised to the power that corresponds to the number of ions in one formula unit of the compound.
Solubility
amount of compound that dissolves in a specified volume of solution. This is
usually expressed as g/L or g/100 mL.
Molar solubility
number of moles of a compound that dissolve to give 1 L of saturated solution. This is expressed as mol/L.
common ion effect
When a solution of a slightly soluble salt is added with one of its ions from another source, the solubility of that salt is reduced. This is known as the ?
solubility product constant (Ksp)
a constant that describes the extent to which a slightly soluble salt dissolves in water, by expressing the concentration of the ions in a saturated solution (at equilibrium).
fractional precipitation
We sometimes wish to remove selected ions from solution while leaving others with similar properties in solution. This separation process is called ?
The reaction shifts to the left.
Backward reaction is favored; thus, more reactants are produced.
The reaction shifts to the right.
Forward reaction is favored; thus, more products are produced.
mass-action effect
An equilibrium shift brought about by changing the amount of one of the participating reactants or products
thermodynamics
They are important because they allow us to predict the direction and completeness of chemical reactions.
less than
If K is small, (K<1) like ________ 10^-3 a reaction yields very small products before equilibrium is reached.
like above
If K is large, (K>>1) ________ 103 very few reactants are left before equilibrium is reached.
solubility product (Ksp)
most useful in the qualitative analysis of cations.
Slightly soluble compounds
are those that has a solubility in water of less than 0.020 mol/L.