The Central Nervous System
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
151 Terms
brain and spinal cord
what does the central nervous system consist of
interpretation and coordinate appropriate responses
functions of central nervous system
cerebral hemispheres, diencephalon, brain stem, cerebellum
four major regions of the human brain
thalamus and hypothalamus
major parts of the diencephalon
midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
major parts of the brain stem
gyri (gyrus)
ridges (twisters)
sulci (sulcus)
shallow depressions/ furrows
fissures
deeper depressions
longitudinal fissure
separates the two cerebral hemispheres
transverse fissure
separates the cerebral hemispheres from the cerebellum
frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital lobes
four bilateral cerebral lobes
central sulcus
blue line
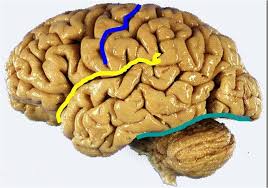
lateral fissure
yellow line
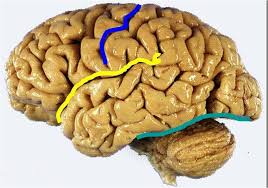
transverse fissure
green line
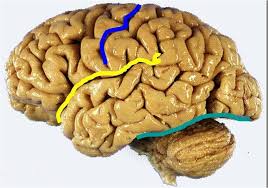
frontal lobe
lobe that is anterior to the central sulcus and superior to the lateral fissure
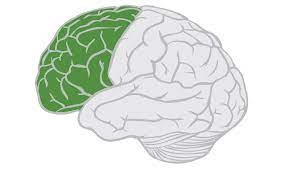
frontal lobe
lobe that deals with reasoning, planning, aspects of speech, movement, emotions, problem solving, memorizing, talking, analyzing, meaning of a word
parietal lobe
lobe that is posterior to the central sulcus and superior to the lateral fissure
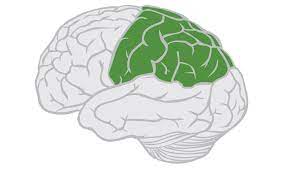
parietal lobe
lobe that deals with the perception of stimuli related to touch, pressure, temperature, and pain
temporal lobe
lobe that is inferior to the lateral fissure and anterior to the occipital lobe
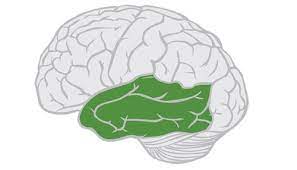
temporal lobe
lobe that deals with the perception and recognition of auditory stimuli (hearing) and memory, both this and frontal lobe give complex memories
occipital lobe
lobe that is posterior and inferior to the parieto-occipital sulcus, and is posterior to the temporal lobe
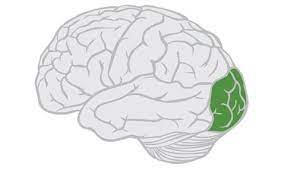
occipital lobe
lobe that deals with many aspects of vision, like driving
cerebral cortex
outermost layer of the cerebrum, about 2-4mm thick, and composed of gray matter
gray matter
matter made up of neuron cell bodies, dendrites, short and unmyelinated axons
white matter
matter located beneath the cortex and is made up of longer, myelinated axons
-connect different regions of the central nervous system
-composed of fiber tracks carrying impulses to, from, or within the cortex
prefrontal cortex
problem-solving, emotion, complex thought, takes a long time to develop
primary motor cortex
initiation of voluntary movement, walking
motor association cortex
coordination of complex movement, playing drum set, walking/talking at the same time
primary somatosensory cortex
receives tactile information from the body, touch, pain, pressure, temperature
sensory association area
processing of multisensory information, how hot/heavy something is
visual cortex
detection of simple visual stimuli
visual association area
complex processing of visual information
auditory cortex
detection of sound quality
auditory association area
complex processing of auditory information, too loud/too soft/ what type of sound
wernicke’s area
language comprehension, meaning of words and sounding out words- one hemisphere
broca’s area
speech production and articulation, can’t speak off the top of your head, one hemisphere, left side- can’t say words properly if damaged
homunculus
visualizes the connection between different parts of the primary motor cortex
-large parts have more sensory/motor connections to the brain
corticospinal or pyramidal track
axons of motor neuron that form the major voluntary motor track which descend to the spinal cord
insula
-layer of cortex that lies beneath the parietal and temporal lobes
-formed from parts of the frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes
-perception, motor control, self-awareness, cognitive functioning, and interpersonal experience
contralateral
opposite/acting in unison part on other side
ipsilateral
situated on the same side
basal ganglia
islands of gray matter located deep within the white matter of the cerebrum
-work together with the cerebellum to produce smooth, coordinated movements
-regulate voluntary motor activities by modifying instructions, particularly to stopping or starting movement
-include caudate nucleus, putamen, and globus pallidus
caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus
parts of the basal ganglia
limbic system
ring of cortex deep within the cerebrum which encircles the ventricles
-center of emotions related to behavior
-formation of memories
-”emotional visceral brain”
-”roid rage”
cerebral white matter
-located beneath the cortex
-longer, myelinated axons
-connect different regions of the central nervous system
-different areas of the cerebral cortex must be able to communicate with each other and with the brain stem/spinal cord
-myelinated axons are usually bundled into tracts
commissures, association fibers, and projection fibers
types of white matter tracts
commissures
type of white matter tract that allows communication between the cerebral hemispheres
-the Corpus Callosum is the largest ______
-little to no corpus callosum results in cerebral palsy
corpus callosum
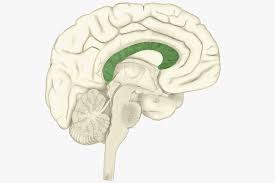
association fibers
type of white matter tract that allow communication between different parts the same hemisphere
projection fibers
type of white matter tract that run vertically and allow communication between the cerebral cortex and lower brain regions of the central nervous system
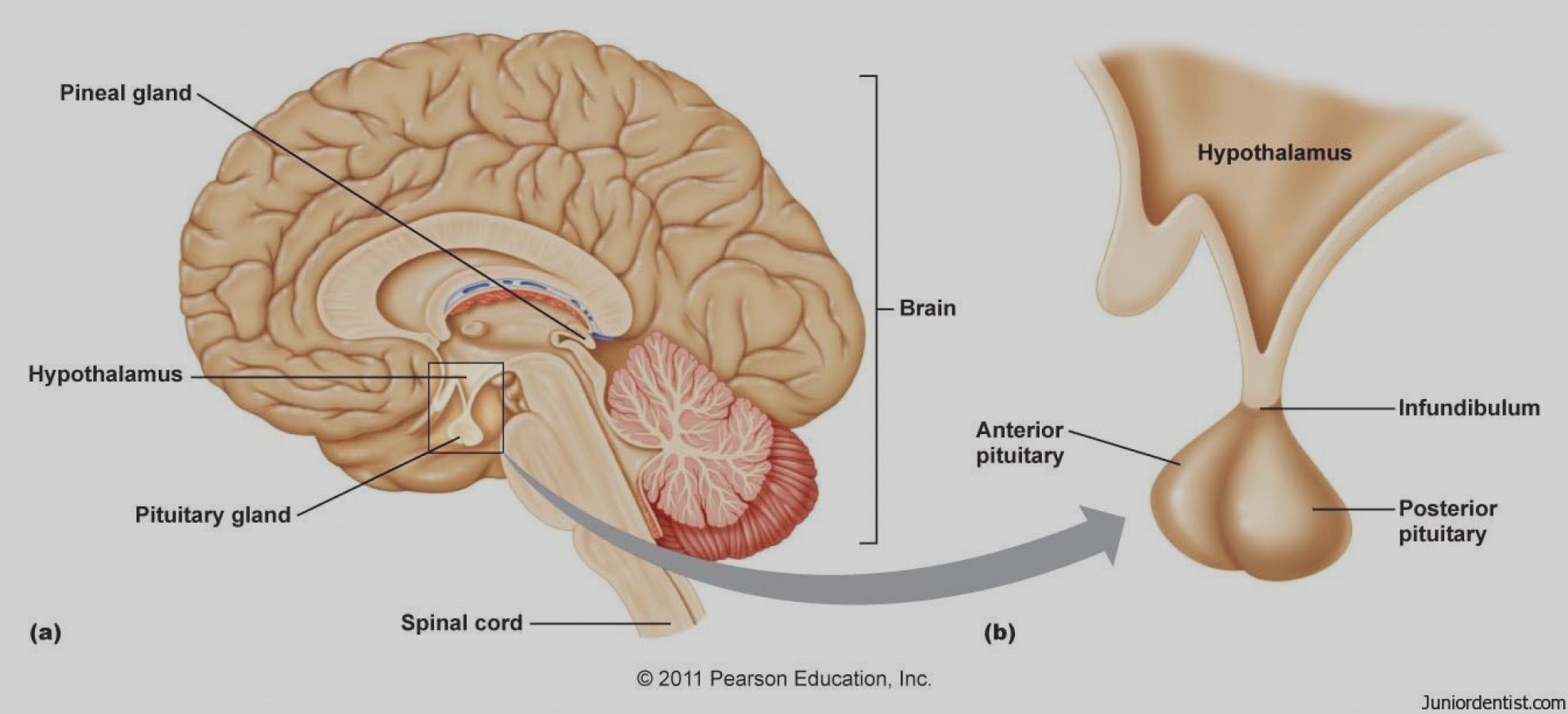
diencephalon aka: interbrain
sits on top of the brain stem
-primarily composed of two structures: thalamus and hypothalamus
diencephalon
red and pink area
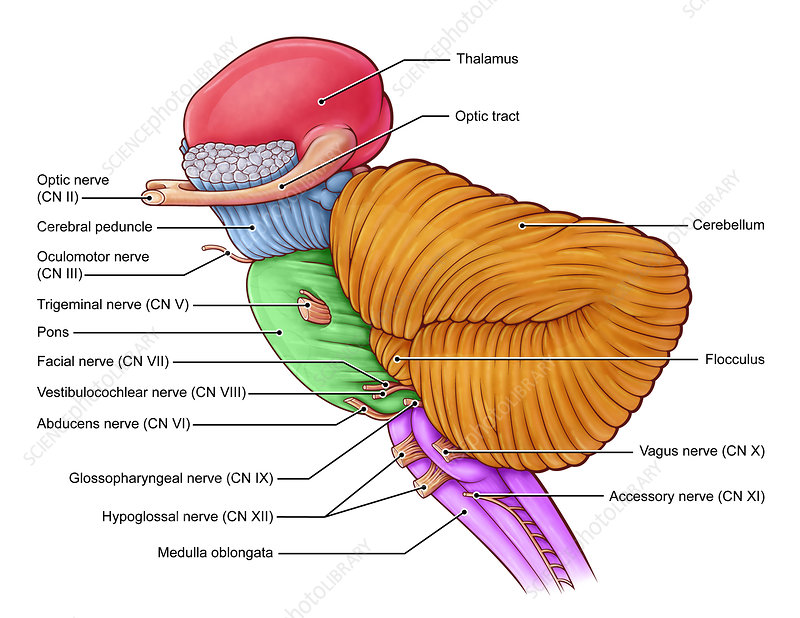
thalamus
receives sensory information and relays this information to the cerebral cortex, which also sends information here then transmits the information to other areas of the brain and spinal cord
thalamus
what is the green
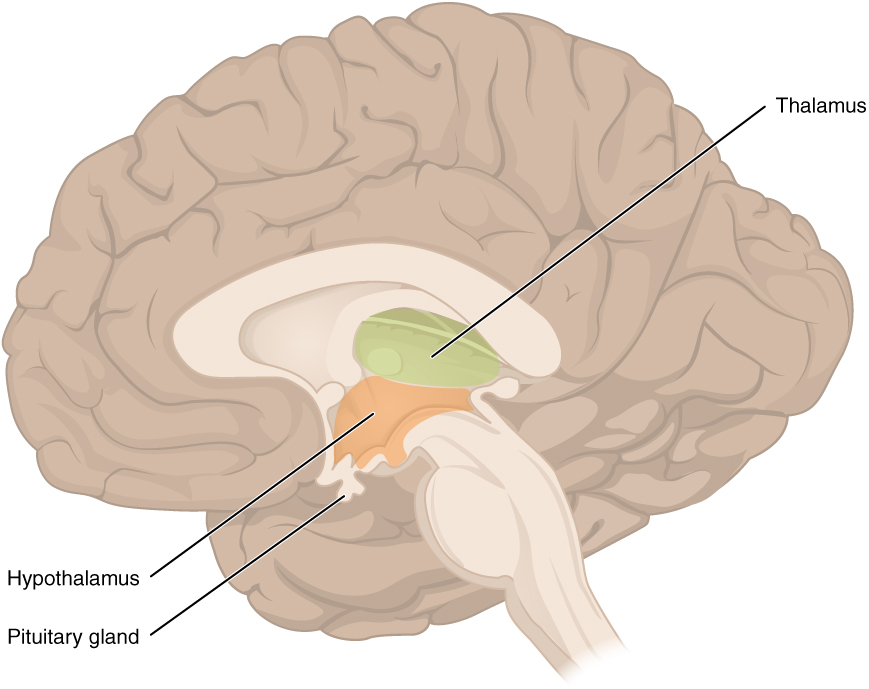
hypothalamus
what is the orange
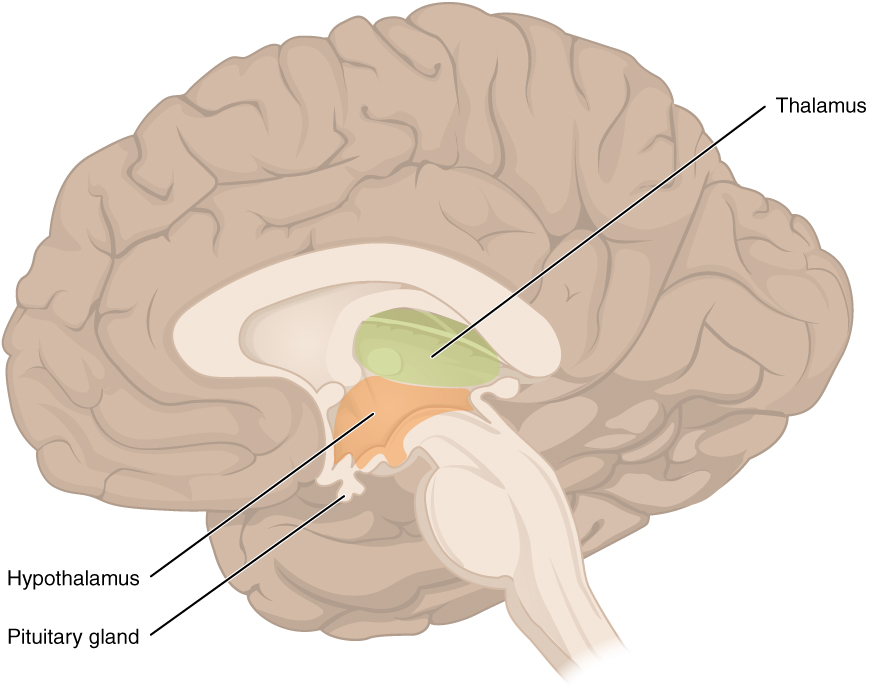
hypothalamus
regulates body temperature, controls hunger and thirst, involved in emotions, and controls the pituitary gland, part of the limbic system
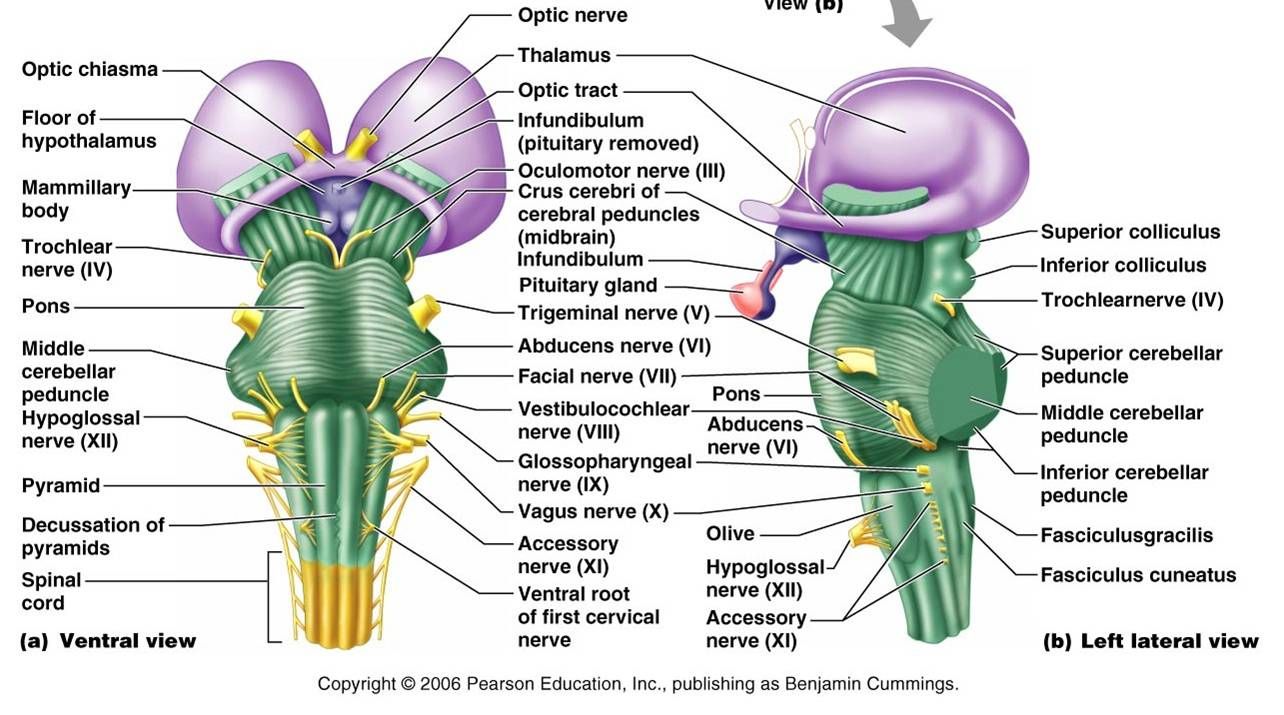
brain stem
area of the brain between the thalamus and spinal cord, contains the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata
brain stem
responsible for basic life functions, like breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure
-passageway for all fiber tracts running between the cerebrum and spinal cord
-contains the origins of 10 of the 12 cranial nerves
brain stem
without the yellow and light green what is this
pons
what is the blue
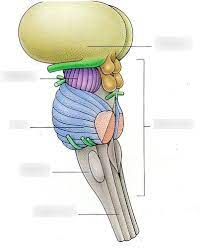
medulla oblongata
what is the gray
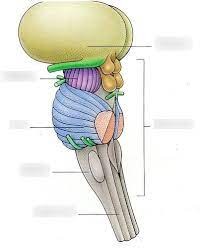
cerebral peduncles
what is the purple
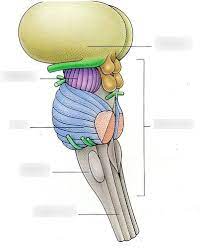
midbrain
all the colored parts make up the what
cerebral peduncles and corpora quadrigemina
what two things make up the midbrain
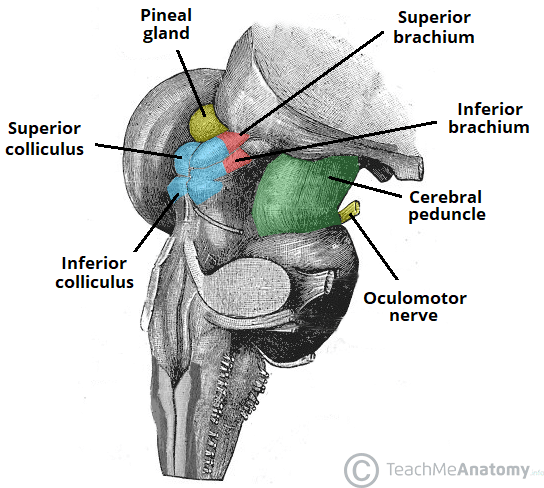
cerebral peduncles
bundles of fiber tracts that transport impulses from the cerebral cortex to the pons
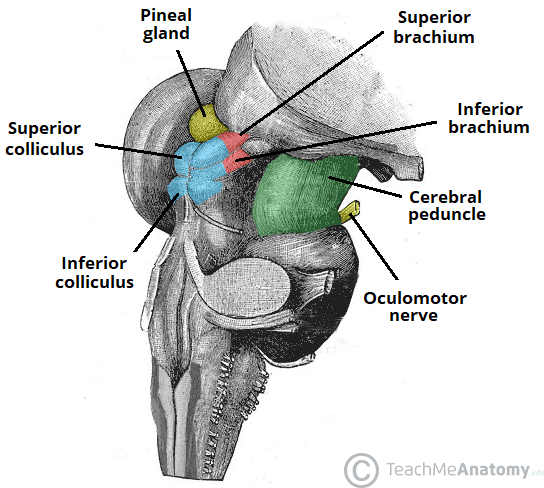
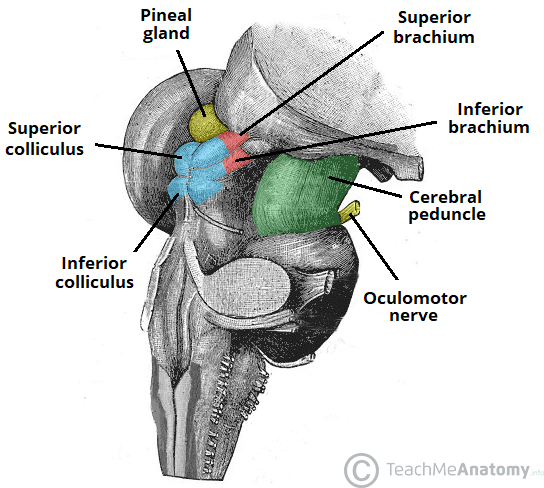
corpora quadrigemina
4 rounded protrusions that are reflex centers
superior colliculi
visual reflex center
inferior colliculi
auditory reflex center
corpora quadrigemina
what is the blue
choroid plexus
blood vessels in the thalamus
choroid plexus in the roof of the fourth ventricle
inferior blood vessels in the brain stem
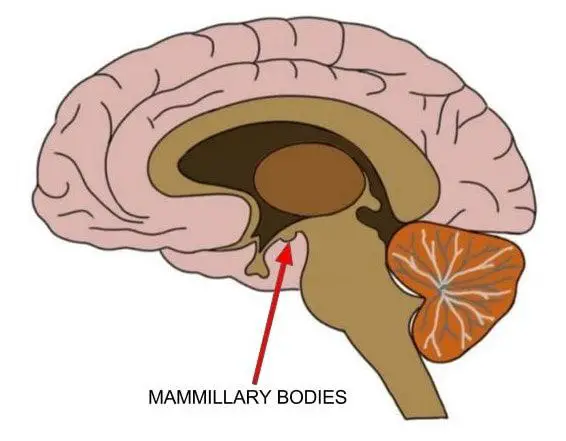
mammillary bodies
reflex centers involved in smell (olfactory), and bulge from the hypothalamus, posterior to the pituitary gland
pineal gland
what is the yellow
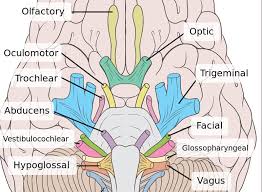
cranial nerves
what are these
pons
mostly bundles of fiber tracts and is a rounded structure that protrudes just below the midbrain
-has important nuclei involved in the control of breathing
infundibulum
space between the hypothalamus and pituitary gland
no answer just to study
medulla oblongata
most inferior part of the brain stem that merges into the spinal cord, and contains fiber tracts that conduct impulses between the brain and spinal cord (basic functions)
-contains 3 important nuclei (olivary nucleus, cardiovascular center, and respiration center)
olivary nucleus
located in the medulla oblongata; relays information from the spinal cord, brain stem, and cerebrum to the cerebellum
cardiovascular center
located in the medulla oblongata; controls heart rate, and the constriction and dilation of blood vessels
respiration center
located in the medulla oblongata; controls the rate and depth of breathing, allows for swallowing and vomiting
cerebellum
-projects from under the occipital lobe of the cerebrum
-has 2 hemispheres and a convoluted surface, connected by a constricted area called the vermis
-precise timing for skeletal muscle activity and controls our balance and equilibrium; does job less well when sedated by alcohol
cortex
gray matter of cerebellum
arbor vitae
inner layer of white matter (bush)
cerebellum
functions:
-smoothes and coordinates body movements
-controls balance and equilibrium
-maintains posture/trapezius
-autopilot
-compares body’s “intentions” with actual body performance
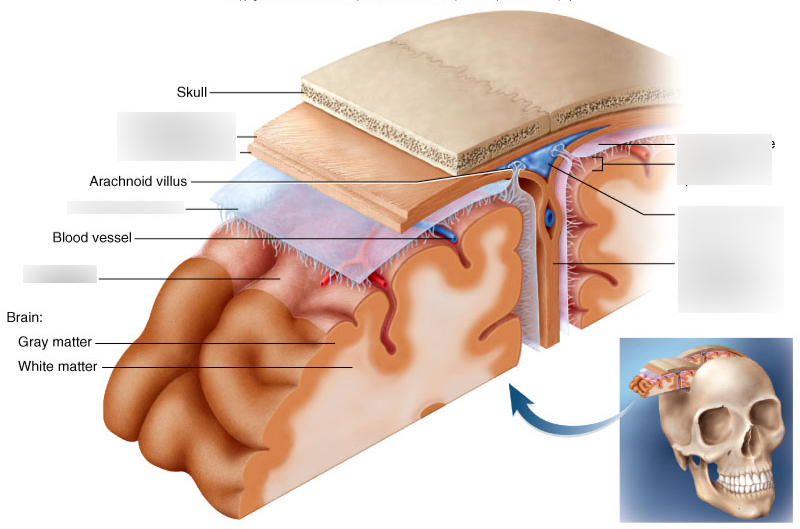
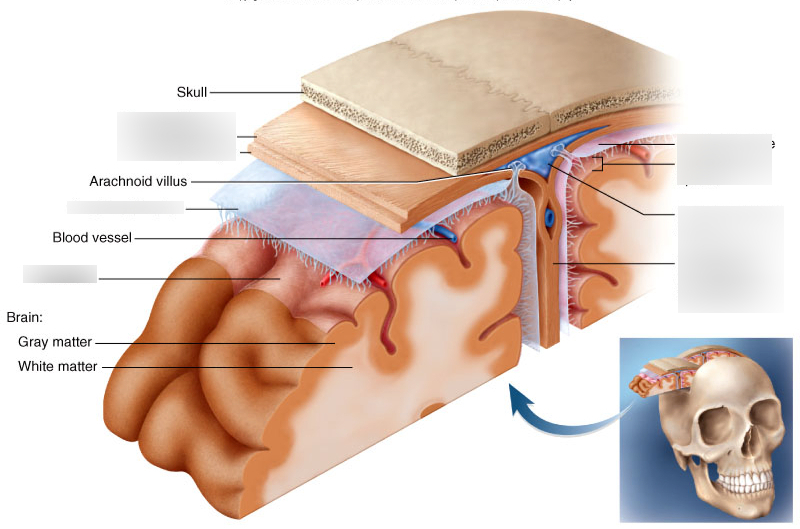
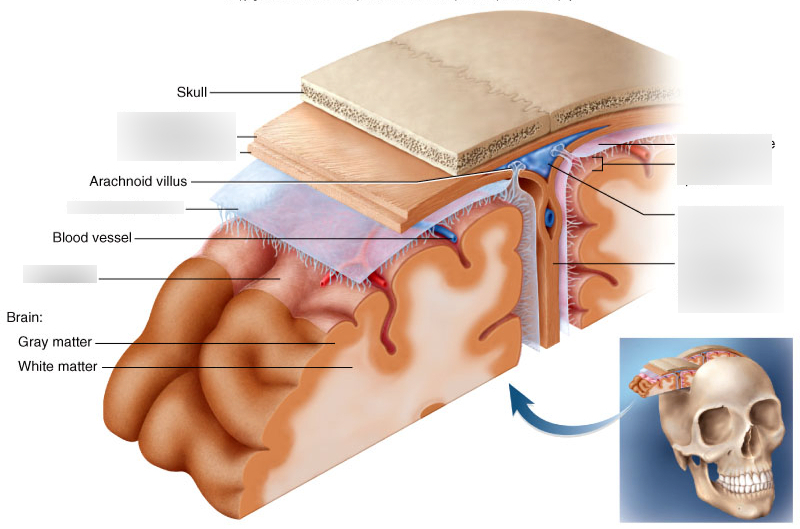
cranial meninges
set of three protective membranes that surround the brain
-include the dura mater, arachnoid membrane, and pia mater
dura mater
first blank on left
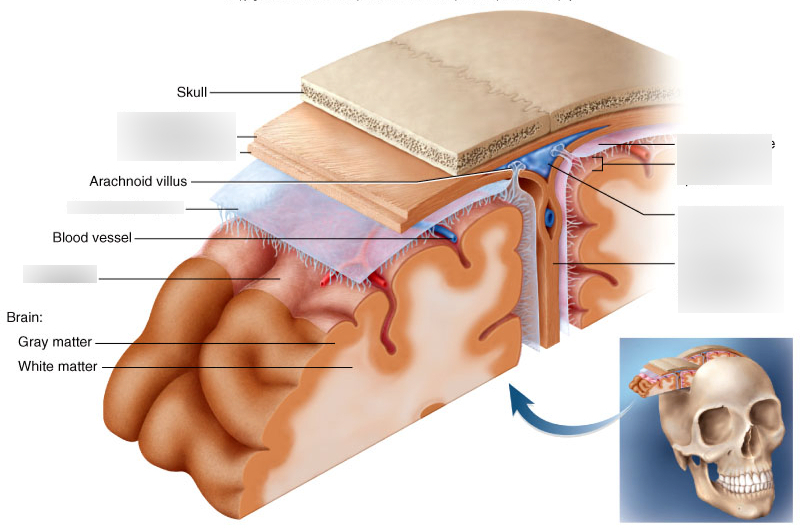
arachnoid membrane
second blank on left
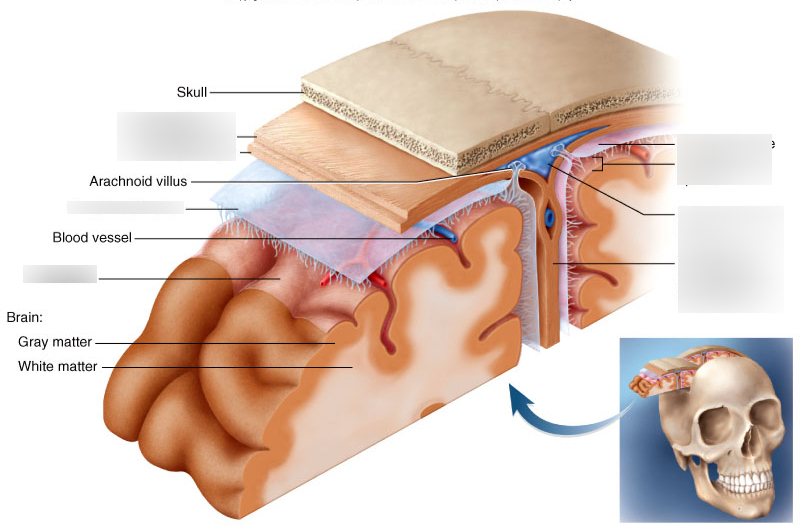
pia mater
third blank on left
superior sagittal
first line of second blank on right
falx cerebri
second line of second blank on right
dura mater
outermost meninx/ double layered membrane
-periosteal layer and meningeal layer
periosteal layer
layer of the dura mater that attaches to the inner surface of the skull
meningeal layer
layer of the dura mater that forms the outermost covering over the brain
-continues as the dura mater in the spinal cord
-falx cerebri
-at the longitudinal fissure only
-one of two folds that attaches the brain to the cranial cavity
falx cerebri
deep fold that projects between the cerebral hemispheres along the midsagittal plane
tentorium cerebelli
separates cerebellum from cerebrum
arachnoid membrane
-middle meninx
-cobweb appearance
-threadlike extensions (arachnoid space) attach it to the pia mater
pia mater
-innermost meninx
-clings tightly to the surface of the brain and spinal cord
-has glistening appearance/ follows every single fold of the brain
subarachnoid space
-lies between the arachnoid membrane and pia mater
-contains cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
brain ventricles
cavities in the brain- lateral ventricles, third ventricle, fourth ventricle
-filled with CSF and lined with Ependymal cells