(1AA3) Chapter 7 - Current Liabilities
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Liabilities (according to IFRS)
Something your business already owes
Can be paid by:
Cash
Give another asset
Deliver goods or services you own (i.e unearned revenue)
Converted to shares (creditor accepts equity instead of cash)
Current liabilities
Obligation due within one year or within a company's operating cycle
Operating cycle
The time it takes for a company to convert its investments in inventory into cash flows from sales
Typically is one year
Types of current liabilities
Known amounts
Provisions (less certainty about timing or amount)
Types of known current liabilities
Accounts Payable
Accrued liabilities
Income tax payable
Unearned revenue
Current portion of long-term debt
Payroll liabilities
Sales tax payable
Short-term notes payable
Dividend Payable
Accounts Payable
Amounts owed to suppliers
Accrued liabilities
Expenses incurred (used), but not paid
insurance payable
Rent
payable
Interest payable
Unearned revenue / Deferred revenue
Cash advances from customers for services that have not been delivered yet
Current portion of long-term debt
Business has a debt that is due after 1 year
Long-term liability on the balance sheet
As time passes, the business must reclassify the portion of debt into a current liability
Payroll liabiliites includes;
Payroll deductions
Payroll expenses
Payroll deductions
Paid by employers to the government on behalf of employees
Income taxes
Canada Pension Plan (CPP)
Retirement fund
Employment Insurance (EI)
Security in case they lose their job at some future date
Payroll expenses
Salary expenses
Canada Pension Plan (CPP)
Employer's CPP contribution = Employee CPP contribution
Employment Insurance (EI)
Employee EI contribution x 1.4
Why are Income taxes, CPP and EI considered a liability?
The liabilities will remain in the books until the company pays the money to the government
Hence why they owe this, making it a liability
Sales tax payable
The tax added to purchases when shopping
3 Types of Sales Tax Payable
Goods and services tax (GST)
Provincial/regional sales tax (PST)
Harmonized sales tax (HST)
Harmoinized sales tax (HST)
Ontario only has HST
HST combines GST and PST = 13% in Ontario
Value-added sales tax
Businesses that buy a product and resell it for a profit will receive an input tax credit (ITC) for the HST they paid
Input tax (or Tax recoverable)
Tax paid when purchasing goods
Output Tax (or Tax payable)
Tax collected when selling goods or services
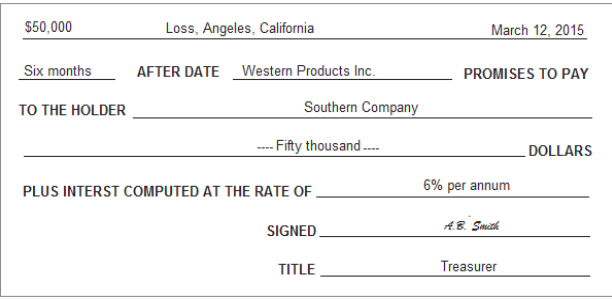
Notes Payable and Notes Receivable (OR promissory notes)
Written promise to pay a sum at the maturity date
Plus interest
Why are notes payable and notes receivable issued?
Gives the lender stronger legal protection
The borrower signs it, the lender keeps it as proof
Example of issues N/R/NP
Dates in which journal entries should be made for notes payable/receivable
Initial transaction
End of accounting period
First interest payment date
Final payment
Interest
The cost of borrowing money
Stated as an annual percentage date
Maturity date
The date at which the debtor must pay the note
Principal
The amount of money borrowe dby the debtor
Term
The length of time the debtor must repay the note