Pathophysiology of Major Depressive Disorder (MDD): Neurotransmitters, Inflammation, and Hormonal Dysregulation
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
What are common symptoms of Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)?
Fatigue, loss of interest, social withdrawal, feelings of emptiness, suicidal ideation, and unyielding sadness.
Which neurotransmitters are typically decreased in MDD?
Serotonin, dopamine (DA), and norepinephrine (NE).

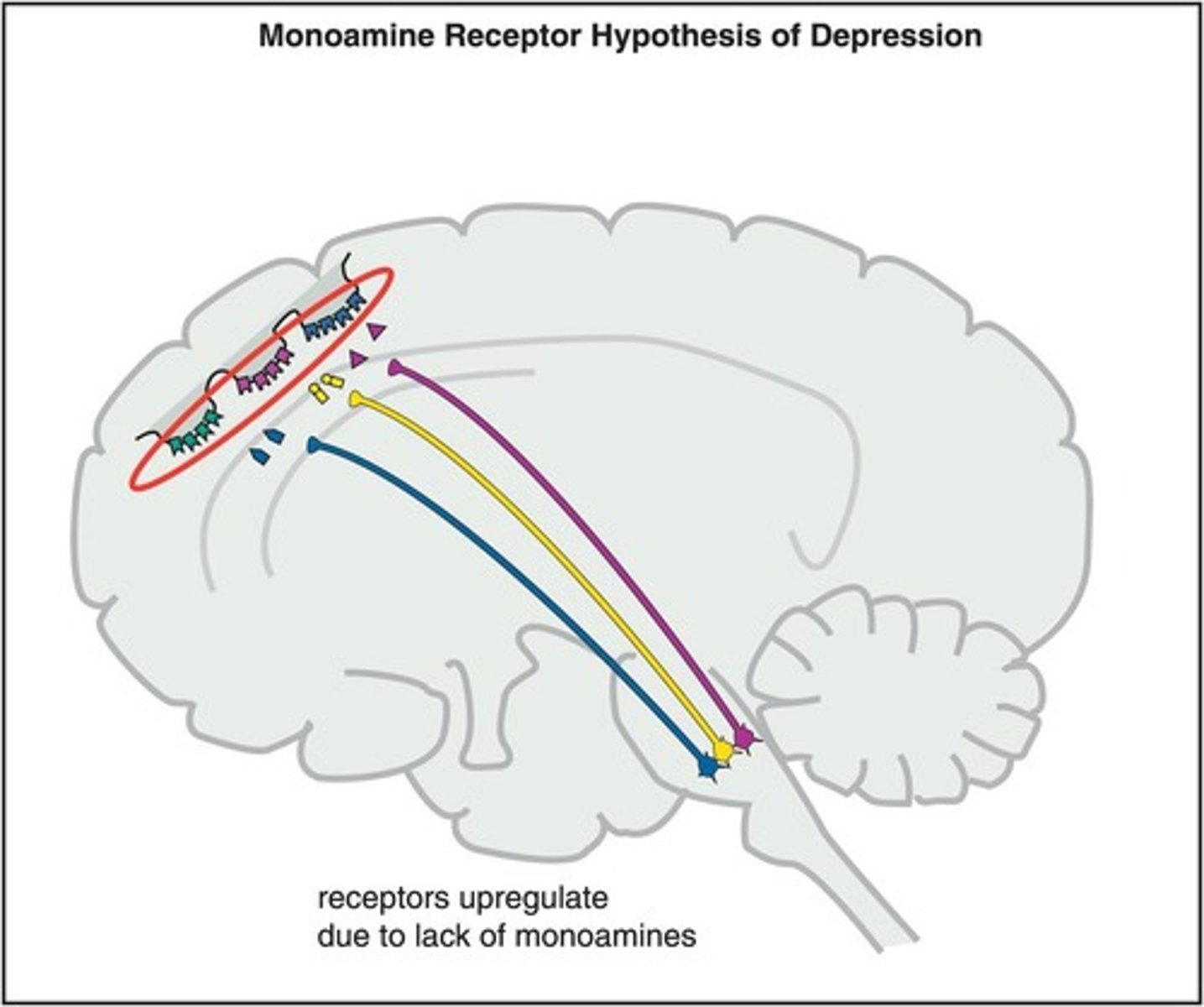
What is the Monoamine Hypothesis of MDD?
It suggests that a decrease in monoamine neurotransmitter signaling is associated with the symptoms of depression.
How long does it typically take for the clinical effects of antidepressants to manifest?
2 to 6 weeks.
What is the role of monoamine receptors in depression according to the Monoamine Receptor Hypothesis?
A high number of receptors with low levels of monoamines leads to increased presynaptic transporters, which return more neurotransmitters back to the neuron.
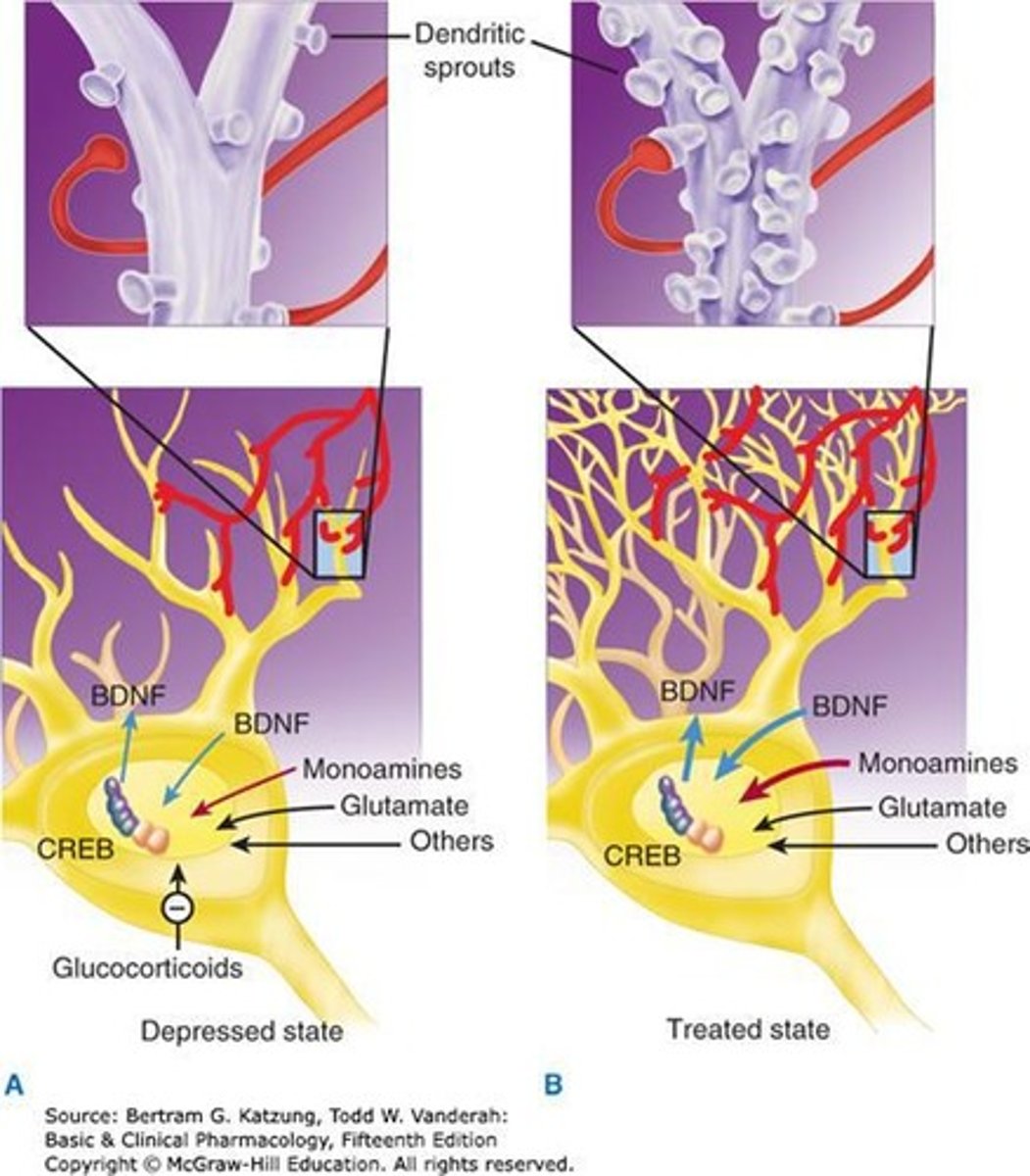
What does the Neurotrophic Hypothesis of MDD suggest?
It posits that atrophic factors and decreased glucocorticoids contribute to reduced neuronal survival.
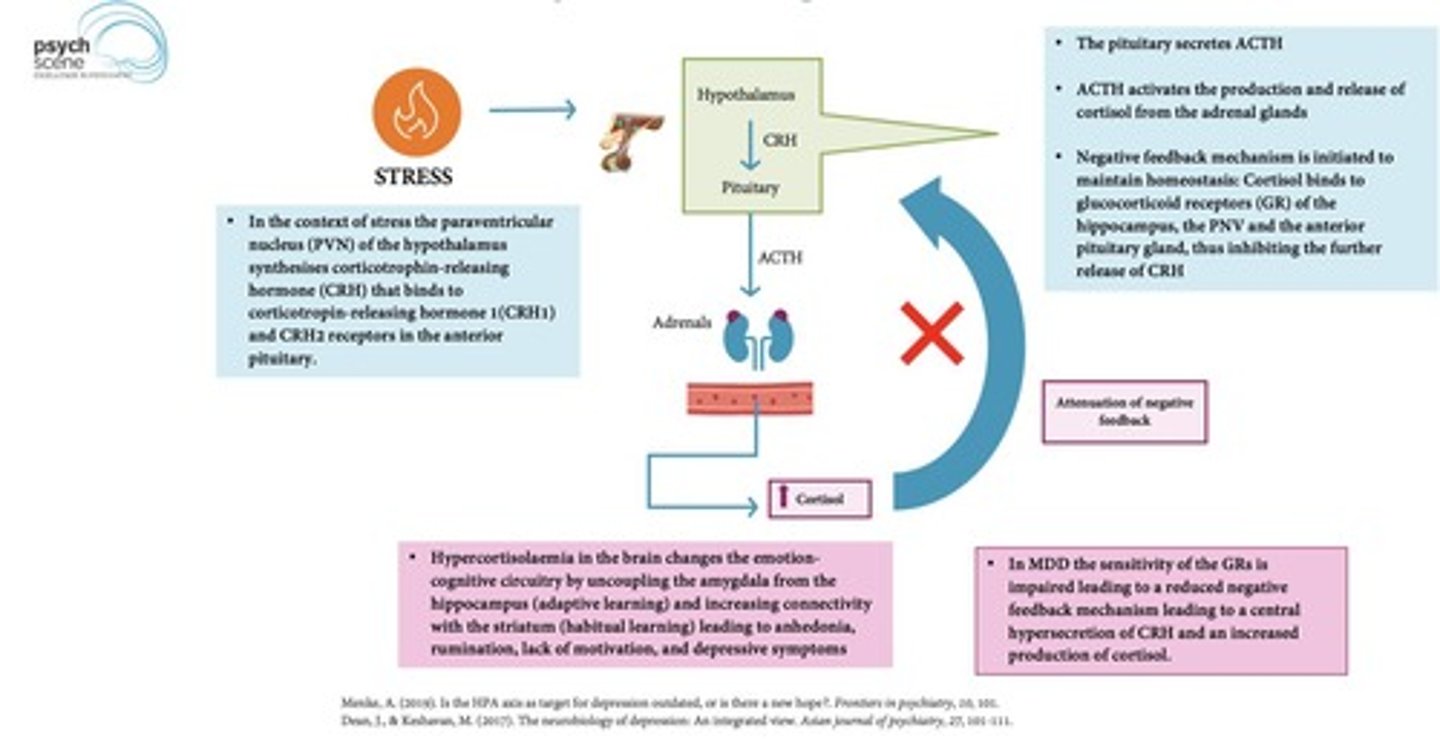
What is the Neuroendocrine Hypothesis of MDD?
It states that depressed patients lose negative feedback mechanisms, resulting in increased cortisol levels.
What is the significance of pro-inflammatory cytokines in MDD?
Increased pro-inflammatory cytokines are associated with the pathophysiology of MDD.
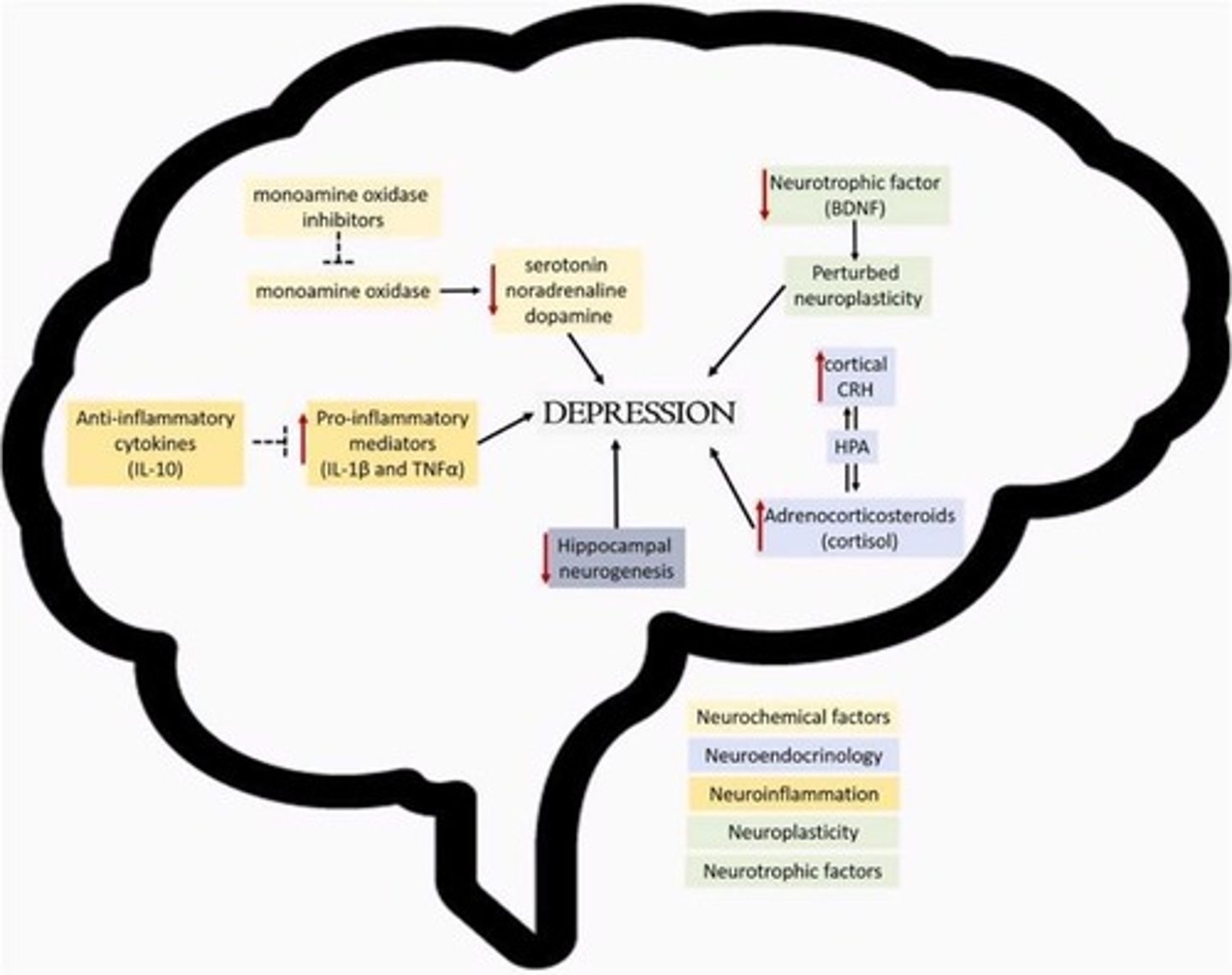
What is the impact of antidepressants on homeostasis in MDD?
Antidepressants help restore homeostasis by affecting monoamine signaling.
What physiological changes occur in the neuroendocrine system in depressed patients?
Depressed patients experience a loss of negative feedback in the neuroendocrine system, leading to dysregulation.
What is the relationship between neurotrophic factors and neuronal survival in MDD?
Decreased neurotrophic factors are linked to reduced neuronal survival, contributing to the pathology of MDD.