Chemistry 3.9- Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
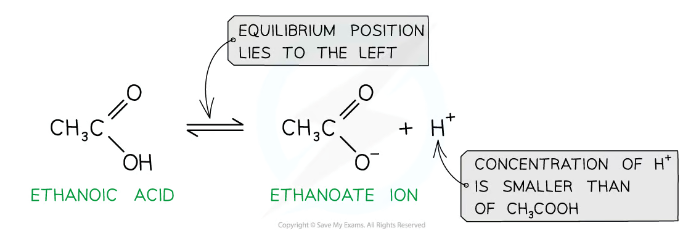
Why are carboxylic acids weak?
They only partially dissociate in aqueous solution (to form carboxylate and hydrogen ions)
Are carboxylic acids soluble?
Carboxylic acids with fewer than five carbon atoms are completely soluble because the OH group can form hydrogen bonds with water
How do carboxylic acids react with carbonates?
Carboxylic acids react with metal carbonates to produce carbon dioxide and a carboxylate salt:
2RCOOH + Na2CO3 → 2RCOONa + CO2 + H2O
Carboxylic acids react with metal hydrogen carbonates in the same way:
RCOOH + NaHCO3 → RCOONa + CO2 + H2O
This is why sodium carbonate is used to test for carboxylic acids, because it produces CO2 bubbles
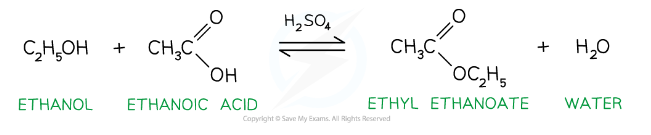
How can esters be produced?
Esters can be formed (esterification) by:
The condensation reaction between an alcohol and carboxylic acid in the presence of an acid catalyst e.g. sulfuric or hydrochloric acid (nucleophilic addition-elimination, reversible reaction)
The acylation of an alcohol by acyl chloride or acid anhydride (nucleophilic addition-elimination, not reversible)
How do we name esters?
The group attached to the O is the alkyl group, which goes first
The group including the C=O is given the suffix -oate, which goes second
(The alkyl group is the one which replaced the H in the condensation reaction forming the ester)

What are esters used for?
They are naturally occurring in triglycerides (fats and oils)- ester bonds link 3 fatty acids to glycerol (propane-1,2,3-triol), but they are also used in industry:
Fragrances and flavourings- fruity and sweet smell
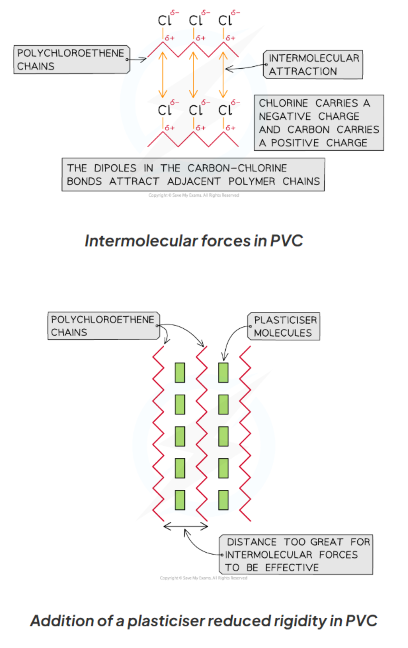
Plasticisers- added into polymers eg. poly(chloroethene), to increase their flexibility (by disrupting the polymer chains and weakening the C-Cl bond)
Solvents- used in glue and nail polish
Biodiesel- vegetable oils are converted into methyl esters and combined with long-chain carboxylic acids, creating renewable fuels
Soaps- hydrolysing triglycerides in alkaline conditions produces glycerol and salts of long-chain carboxylic acids, which are soap
How do we make biodiesel?
Vegetable oils are reacted with methanol, using a strong acid catalyst, to form methyl esters, usually combined with long-chain carboxylic acids to make biodiesel
How do we make soap?
Hydrolysing triglycerides in alkaline conditions produces glycerol and salts of long-chain carboxylic acids, which are soap
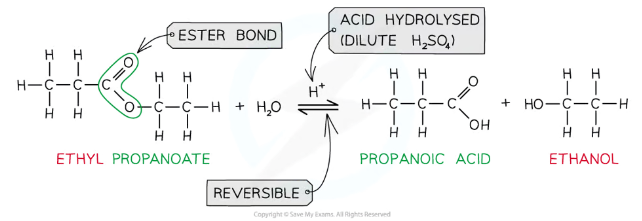
How are esters hydrolysed in acidic conditions?
Heating an ester under reflux with dilute acid reforms the original carboxylic acid and alcohol in a reversible reaction
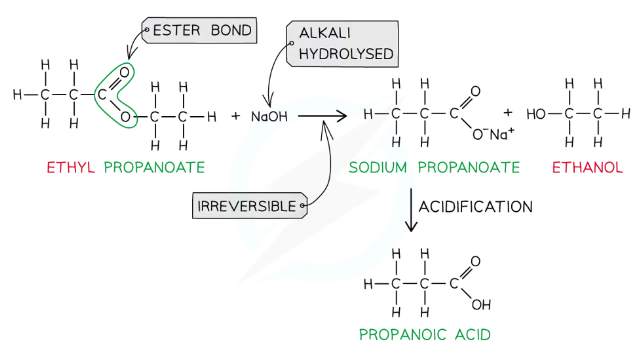
How are esters hydrolysed in alkaline conditions?
Heating an ester under reflux with dilute alkali produces the original alcohol and a carboxylate salt (which requires further acidification to turn into the original carboxylic acid) in an irreversible reaction
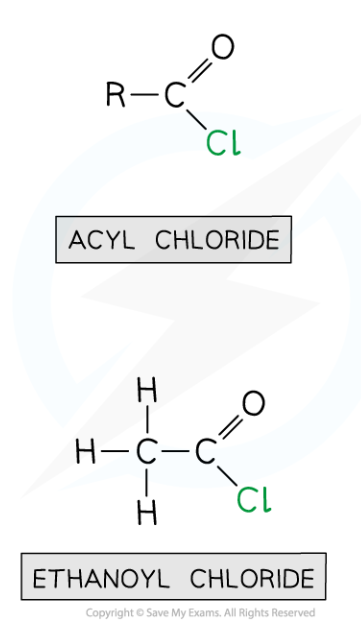
What are acyl chlorides and how do you name them?
They are named by adding -oyl chloride to the end of the parent hydrocarbon chain- eg. ethanoyl chloride has a two carbon chain, including the C=O
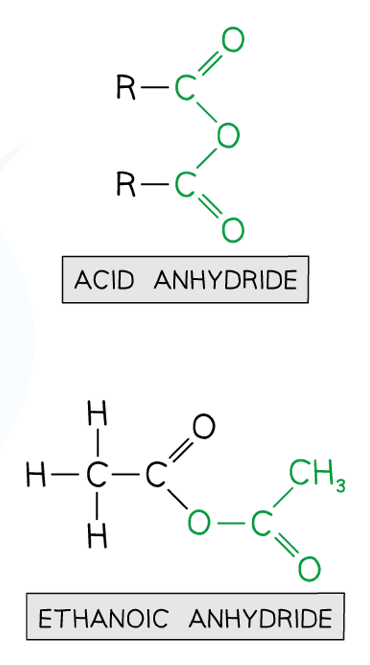
What are acid anhydrides and how do you name them?
They are named by adding -oic anhydride to the end of the parent hydrocarbon chain- eg. ethanoic anhydride has a two carbon chain (including the C=O) on either side
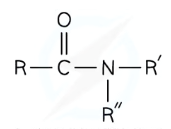
What are amides, and how can they be classed?
Amides can be primary, secondary or tertiary:
Primary amide - one carbon bonded to the nitrogen (and two hydrogens)
Secondary amide- two carbons bonded to the nitrogen (and one hydrogen)
Tertiary amide- three carbons bonded to the nitrogen (and no hydrogens)
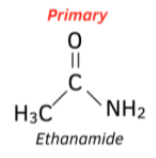
How do we name primary amides?
Adding -amide to the carbon stem of the acyl group
Eg. two carbon acyl group → ethanamide
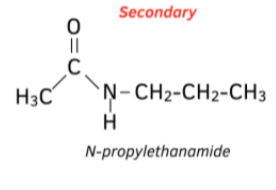
How do we name secondary amides?
The alkyl group (not containing the carbonyl) is put at the start, prefixed with N-
The carbon stem of the acyl group (containing the carbonyl) is suffixed with -amide
Eg. a propyl group and a two carbon acyl group → N-propylethanamide
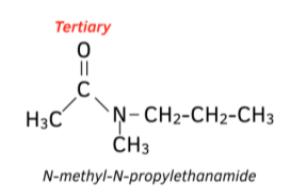
How do we name tertiary amides?
The alkyl groups (not containing the carbonyl) are put at the start in alphabetical order, each prefixed with N-
The carbon stem of the acyl group (containing the carbonyl) is suffixed with -amide
Eg. a propyl group, a methyl group, and a two carbon acyl group → N-methyl-N-propylethanamide
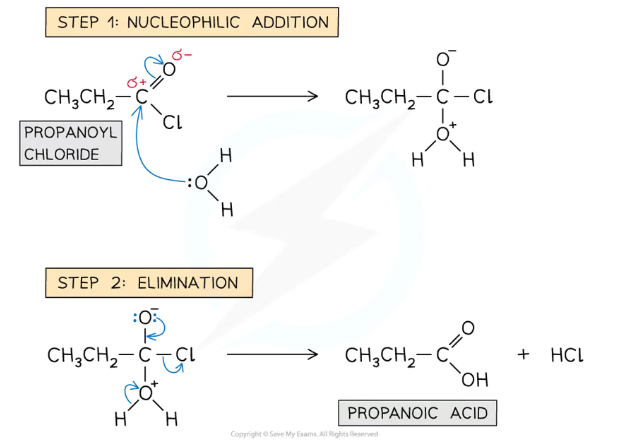
Give and name the mechanism for the reaction between water and acyl chlorides
The reaction is a two-part nucleophilic addition-elimination mechanism, where an OH from the water molecule replaces the Cl of the acyl chloride, producing a carboxylic acid and hydrogen chloride
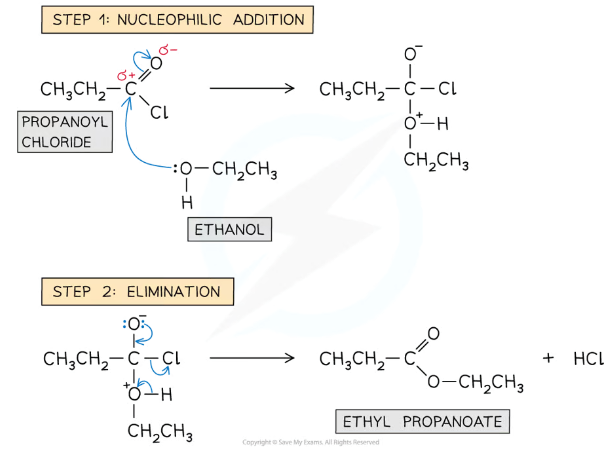
Give and name the mechanism for the reaction between alcohols and acyl chlorides
The reaction is a two-part nucleophilic addition-elimination mechanism, where the OH from the alcohol replaces the Cl of the acyl chloride, producing an ester and hydrogen chloride
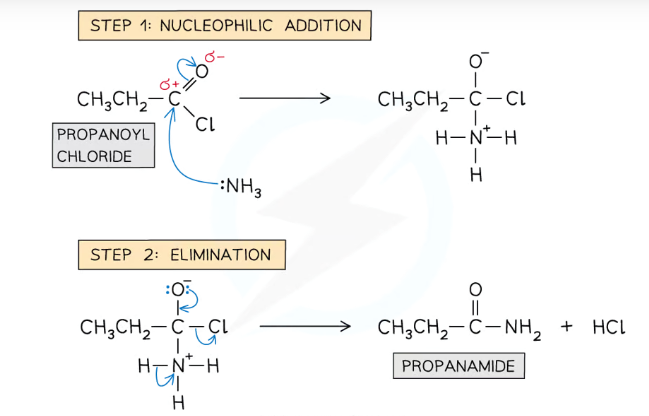
Give and name the mechanism for the reaction between ammonia and acyl chlorides
The reaction is a two-part nucleophilic addition-elimination mechanism, where the NH2 from the ammonia replaces the Cl of the acyl chloride, producing a primary amide and hydrogen chloride
(The hydrogen chloride would then react with excess ammonia, producing ammonium chloride)
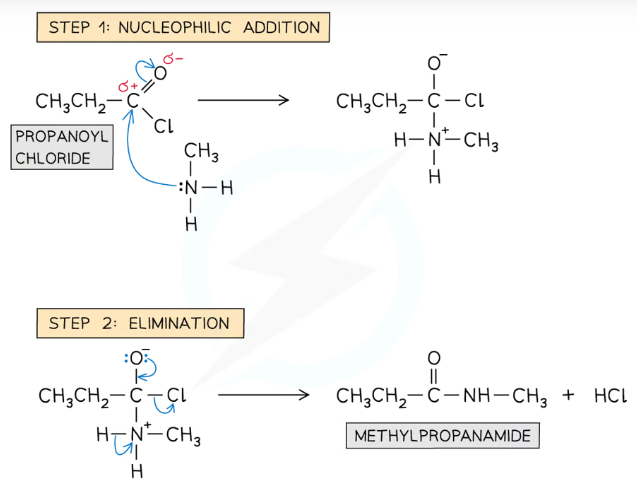
Give and name the mechanism for the reaction between primary amines and acyl chlorides
The reaction is a two-part nucleophilic addition-elimination mechanism, where the amine group replaces the Cl of the acyl chloride, producing a secondary amide and hydrogen chloride
(The hydrogen chloride would then react with excess amine, producing an ammonium salt)
Give the reaction between water and acid anhydrides
The reaction is a nucleophilic addition-elimination mechanism, where the water splits the acid anhydride, producing 2x a carboxylic acid
Give the reaction between alcohols and acid anhydrides
The reaction is a nucleophilic addition-elimination mechanism, producing an ester and a carboxylic acid
Give the reaction between ammonia and acid anhydrides
The reaction is a nucleophilic addition-elimination mechanism, producing a primary amide and a carboxylic acid
(The carboxylic acid would then react with excess ammonia, producing an ammonium salt)
Give the reaction between a primary amine and acid anhydrides
The reaction is a nucleophilic addition-elimination mechanism, producing a secondary amide and a carboxylic acid
(The carboxylic acid would then react with excess amine, producing an amide)
What is the reaction to produce aspirin?
Salicylic acid + ethanoic anhydride → aspirin + ethanoic acid (more commonly used)
OR
Salicylic acid + ethanoyl chloride → aspirin + hydrogen chloride
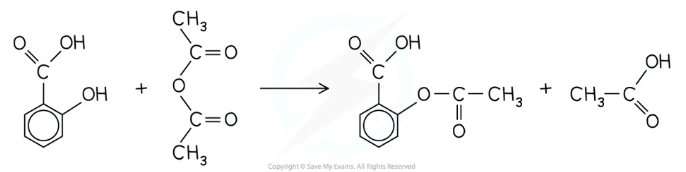
What are the industrial advantages to producing aspirin using acid anhydrides instead of acyl chlorides?
Cheaper
React less violently, so it easier to control the reaction and prevent side reactions
The carboxylic acid by-product is less corrosive and dangerous than hydrogen chloride