Anatomy and Physiology Lab Exam 1
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Anatomical Position
Universally accepted standard position. Body is erect, feet slightly apart, head and toes pointed forward, and arms hanging at the sides with palms facing forward.
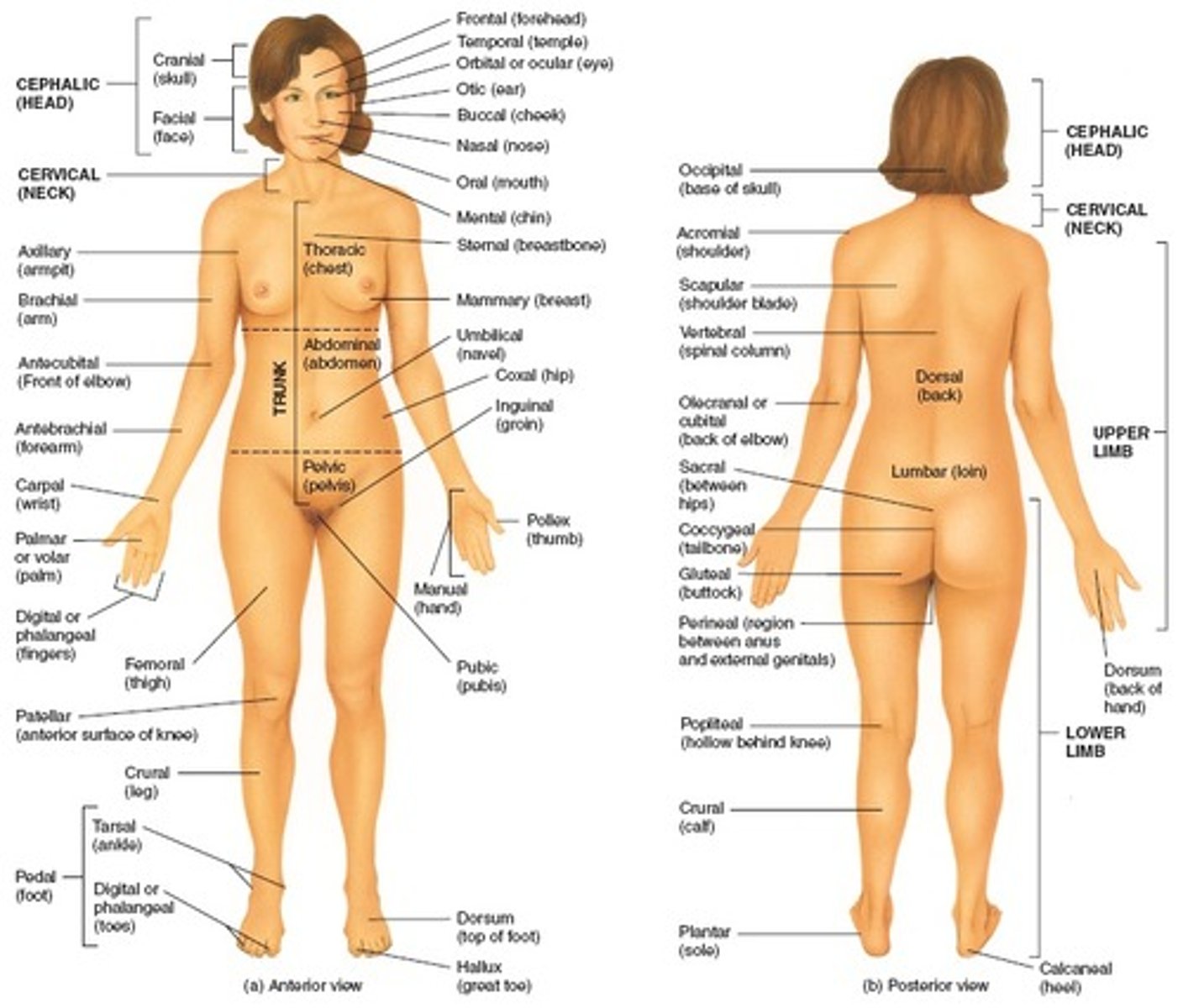
Axial
Relating to head, neck, and trunk, the axis of the body
Appendicular
Relating to limbs and their attachments to the axis
Abdominal
Anterior body trunk region inferior to the ribs
Acromial
Point of the shoulder
Antebrachial
Forearm
Antecubital
Anterior surface of elbow
Axillary
Armpit
Brachial
Arm
Buccal
Cheek
Carpal
Wrist
Cephalic
Head
Cervical
Neck region
Coxal
Hip
Crural
Leg
Digital
Fingers or toes
Femoral
Thigh
Fibular (peroneal)
Side of the leg
Frontal
Forehead
Hallux
Great toe
Inguinal
Groin
Mammary
Breast
Manus
Hand
Mental
Chin
Nasal
Nose
Oral
Mouth
Orbital
Bony eye socket (orbit)
Palmar
Palm of the hand
Patellar
Anterior knee (kneecap) region
Pedal
Foot
Pelvic
Pelvis region
Pollex
Thumb
Pubic
Genital region
Sternal
Region of the breastbone
Tarsal
Ankle
Thoracic
Chest
Umbilical
Navel (belly button)
Calcaneal
Heel of the foot
Dorsum
Back
Gluteal
Buttocks or rump
Lumbar
Area of the back between the ribs and hips; the loin
Occipital
Posterior aspect of the head or base of the skull
Olecranal
Posterior aspect of the elbow
Otic
Ear
Perineal
Region between the anus and the external genitalia
Plantar
Sole of the foot
Popliteal
Back of the knee
Sacral
Region between the hips (overlying the sacrum)
Scapular
Scapula or shoulder blade area
Vertebral
Area of the spinal column
Sural
Calf or posterior surface of leg
Superior
Above another structure
Inferior
Below another structure
Anterior
In front of another structure
Posterior
Behind another structure
Medial
Toward the midline
Lateral
Away from the midline
Cephalad
Toward the head
Caudal
Toward the tail
Dorsal
Backside
Ventral
Bellyside
Proximal
Nearer the trunk or attached end
Distal
Farther from the trunk or attached end
Superficial
Toward or at the body surface
Deep
Away from the body surface
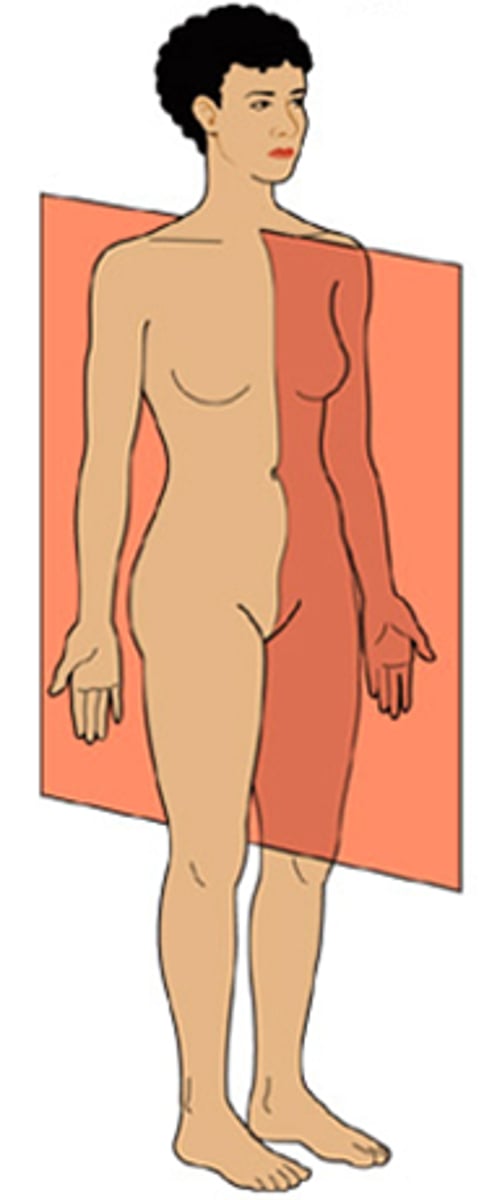
Sagittal plane
Divides body into left and right parts
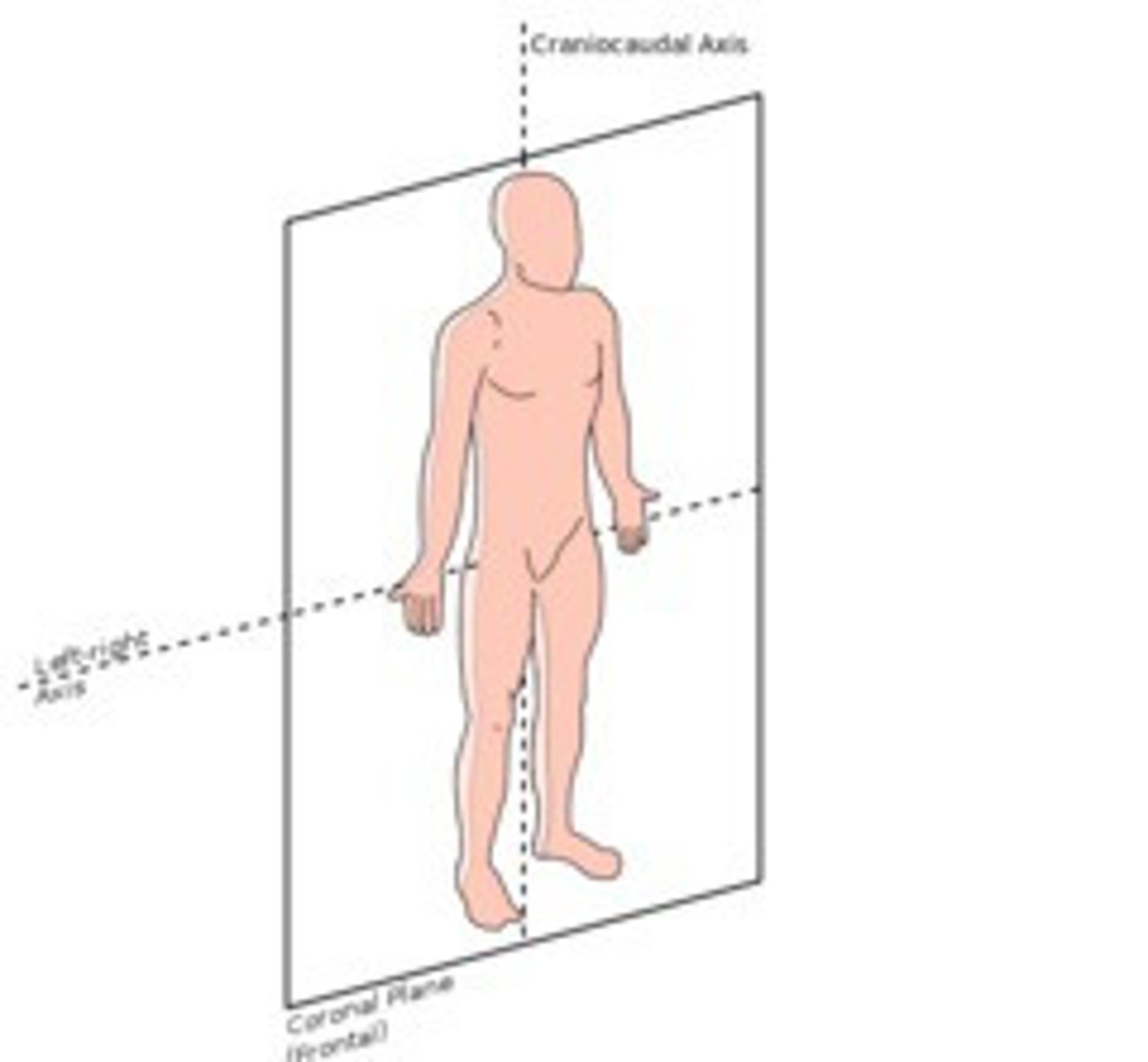
Frontal plane
Divides body into anterior and posterior parts
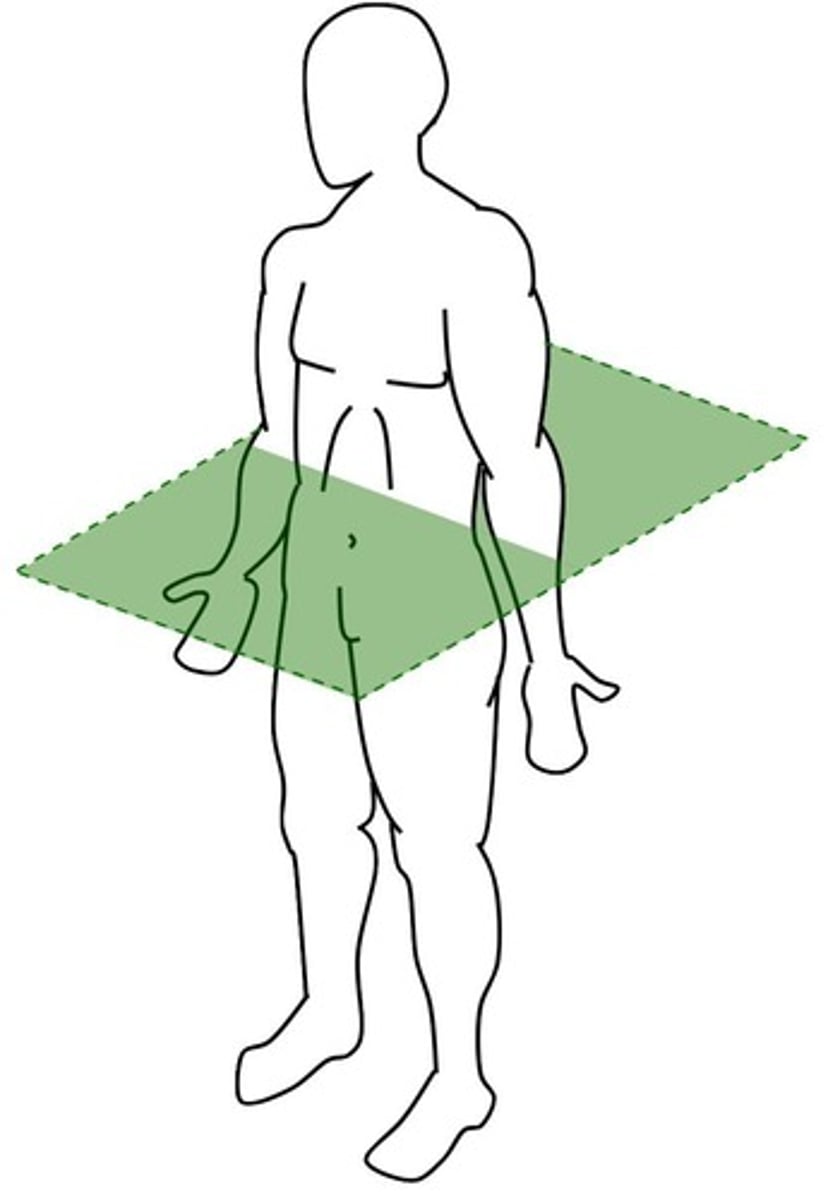
Transverse plane
Divides body into superior and inferior parts
Dorsal body cavity
Contains the cranial cavity and the spinal cavity
Cranial cavity
contains the brain
Vertebral cavity
contains the spinal cord
Ventral Body cavity
Contains the thoracic cavity and the abdomino-pelvic cavity
Thoracic cavity
Contains heart and lungs
Abdominal cavity
contains the stomach, intestines, liver and other organs
Pelvic Cavity
Contains the reproductive organs, bladder, and rectum
Nucleus
Control center of the cell. Contains DNA.
Chromatin
Genetic material loosely dispersed throughout the nucleus
Chromosomes
Rodlike bodies of tightly coiled chromatin, formed during cell division
Nucleoli
Small round bodies in nucleus composed primarily of proteins and RNA
Nuclear envelope
Double-layered porous nucleus memberane
Nuclear pores
Openings in the nuclear envelope that control the movement of substances between the nucleus and cytoplasm
Plasma membrane
Phospholipid bilayer, cell membrane
Cytoplasm
Consists of organelles, cytoskeleton, and cytosol
Organelles
"small organs" of the cell
Cytosol
fluid cytoplasmic material, intracellular fluid
Ribosomes
Sites of protein synthesis
Endoplasmic reticulum
Transport of proteins, A system of membranes that is found in a cell's cytoplasm and that assists in the production, processing, and transport of proteins and in the production of lipids
Golgi apparatus
Stack of flattened sacs that plays a role in packaging proteins or other substances for export from the cell
Lysosomes
Contains digestive enzymes to digest worn out cell organelles and foreign substances
Peroxisomes
Contains oxidase enzymes that detoxify alcohol, hydrogen, and peroxide
Mitochondria
Site of ATP production
Centrioles
Cylinder structures that are composed of microtubules, direct formation of the mitotic spindle during cell division
Cytoskeletal elements
Support the cell
Interphase
Cell carries out normal metabolic activities and grows

Early Prophase
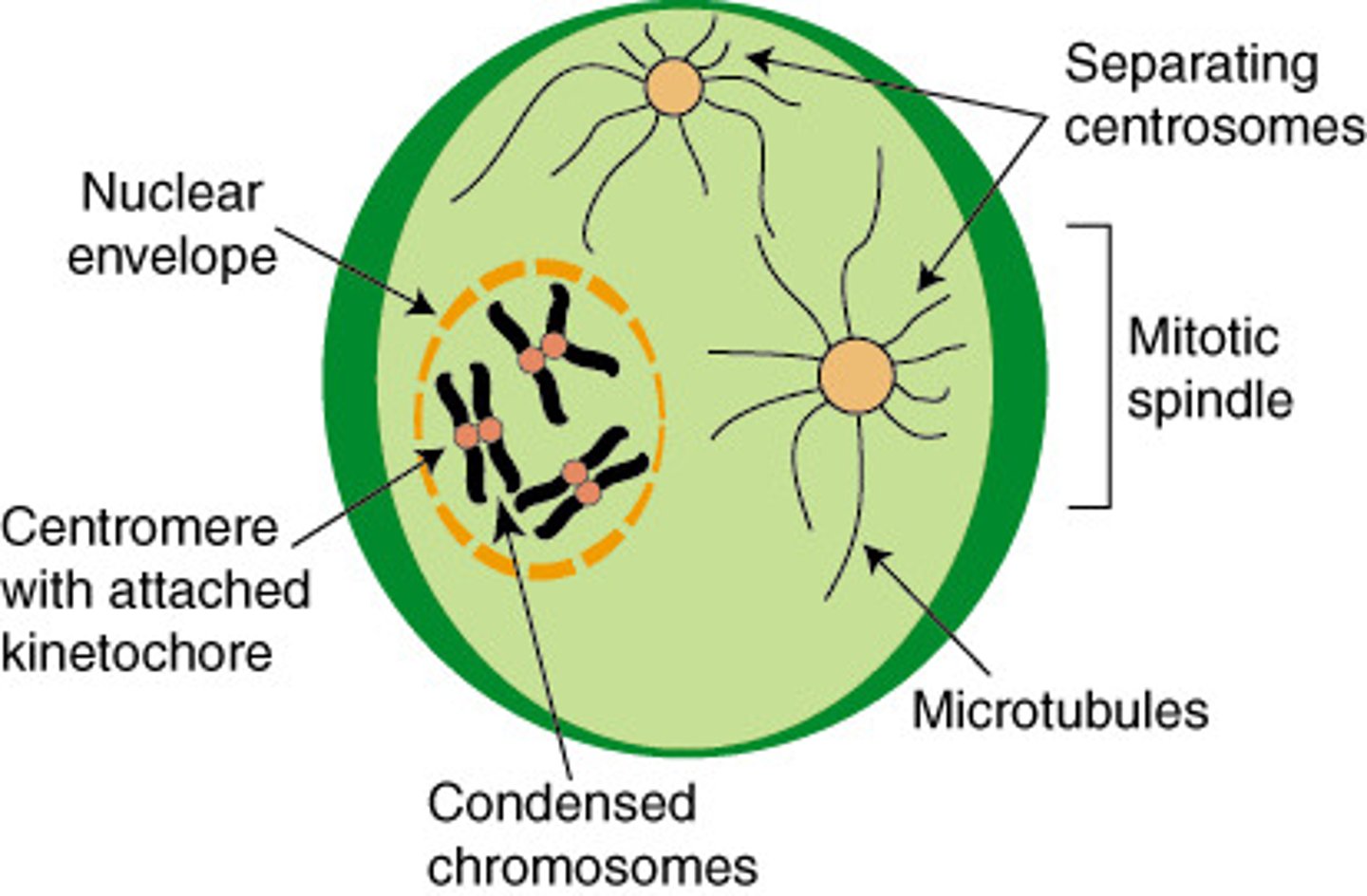
Late Prophase
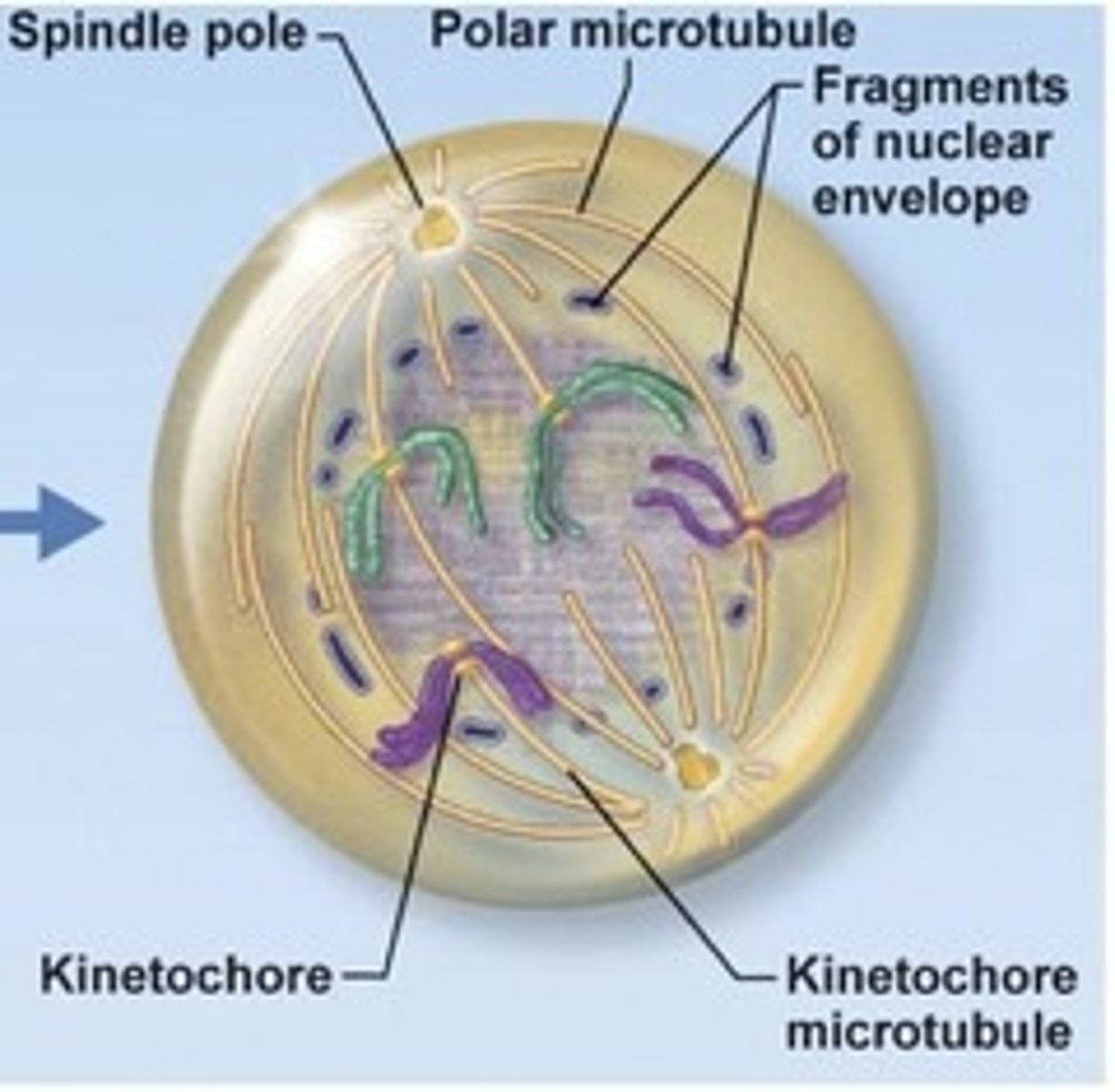
Metaphase
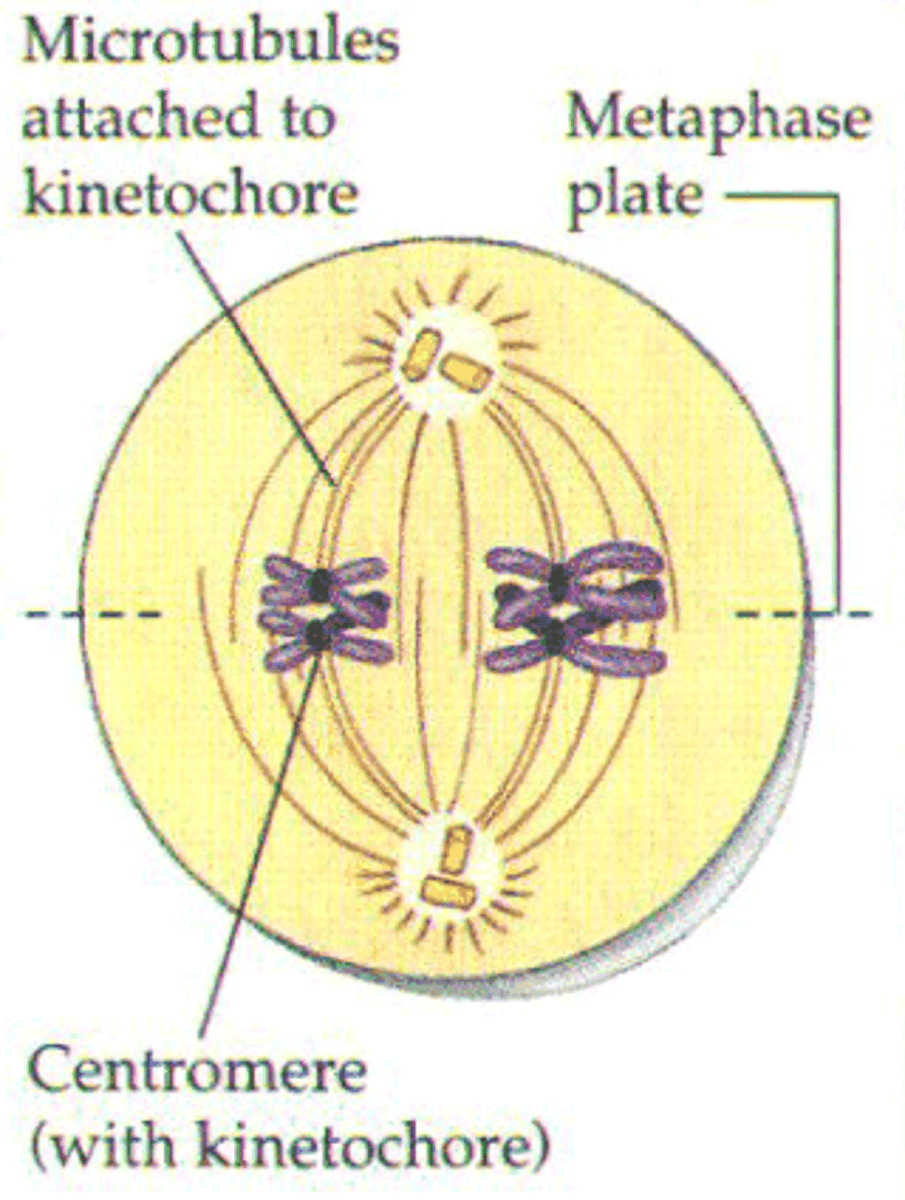
Anaphase
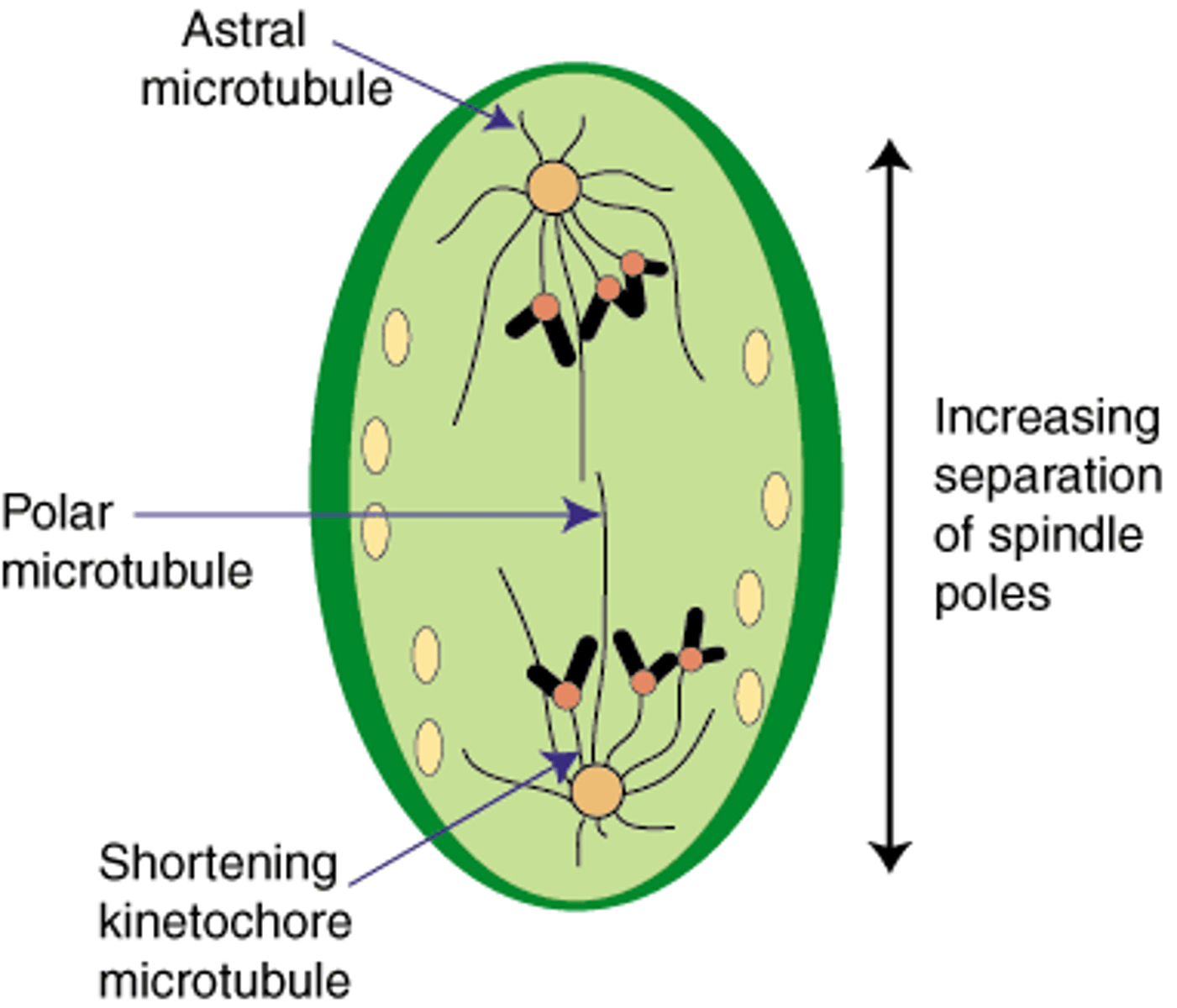
Telophase
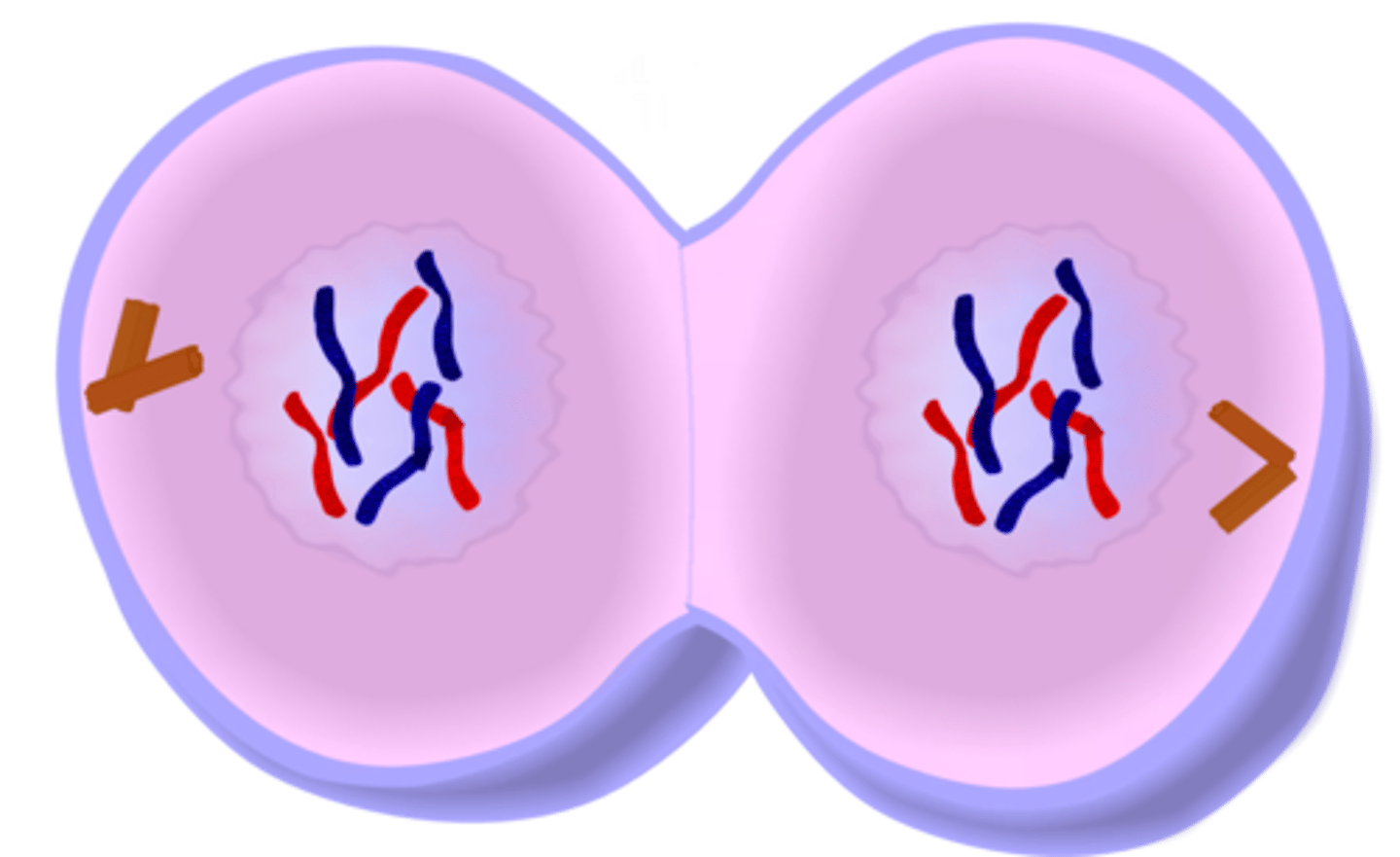
Cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm during cell division