Respiratory Tract Infections, Neoplasms, and Childhood Disorders
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Dr. Berry
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
where does gas exchange not occur?
respiratory pathways like nasal passages, pharanyx
ventiliation
air simply moving in and out
respiration
breathing on a cellular level with mitochondria
which pathogen is the most common cause of respiratory infections?
viruses
what are the 3 classifications of respiratory tract infections?
upper respiratory- nose, oropharnyx, larnyx
lower respiratory- lower airways and lungs
upper and lower- trachea, bronchi
this respiratory tract infection is viral and occurs more frequently than any other respiratory infection and typically enters via nasal mucosa and eye membranes
the common cold (rhinoviruses)
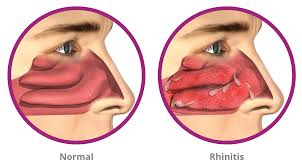
rhinitis
runny nose
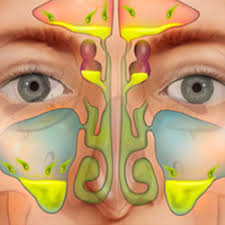
rhinosinusitis
inflammation of the sinuses
most common causes are conditions that obstruct the ostia (parts of your sinuses that are hollow and open) that drain the sinuses
ex: upper respiratory infection, allergic rhinitis, nasal polyps(allergy related), barotrauma(pressure), swimming/diving, abuse of nasal decongestants
acute vs chronic rhinosinusitis
viral, bacterial, or both….lasts 5 days to 4 weeks based on pathogen
>12 weeks
s/s and diagnosis and treatment of rhinosinusitis
s/s: similar to common cold or allergic reaction, facial pain, headache, purulent nasal drainage
Diagnosis: Recent history an upper respiratory infection or allergic rhinnitis, Face pain on bending, unilateral maxillary pain, teeth pain, headache, purulent drainage, Inspection of the nose and throat
Treatment: depends on cause
this respiratory infection is highly contagious via respiratory droplets, is viral with 3 types, and prevented via yearly vaccination
influenza (flu)
Types: A, B, C
prevention of influenza?
yearly immunization bc formulation changes yearly in response to evolving virus
everyone 6 months of age and older
what is each years flu vaccine based on?
each year the flu vaccine is estimated based on the southern hemispheres bc their summers are different than the US
s/s and diagnosis and treatment
s/s: malaise(tiredness), fever, chills, muscle aches, headache, non-productive cough, sore throat.
D/treatment: early/accurate diagnosis is essential to limit spread of flu…treat symptoms

avian flu
began in birds, now found in pigs, cows, and humans
contamination from birds/droppings
No vaccine available; high mortality in humans

swine flu
H1N1
most virulent in young adlts <25 years of age
older adults typically have immunity due to previous exposure
vaccine availble
inflammation of lower respiratory tract due to infectious and non-infectious agents due to inhalation.
pneumonia
what are the 3 classifications of pneomonia
typical vs atypical
lobar vs bronchopneumonia
community vs hospital acquired (nosocomial)
typical vs atypical
Typical caused by bacteria, atypical caused by viruses and mycoplasma
ex: mold, yeast, etc
lobar vs bronchopneumonia
Lobar involves part or all of a lobe of the lung, bronchopneumonia involves more than one lobe of the lung
community vs hospital acquired (nosocomial)
Community acquired due to pathogens acquired outside of the hospital/nursing home and is diagnosed within 48 hours of admission to a hospital
Hospital acquired lower respiratory tract infection not present on admission to the hospital and diagnosed > 48 hours after admission (hard to treat)
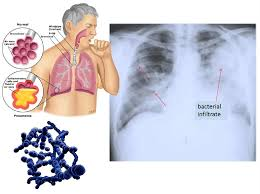
serves as an important cause of mortality in older adults due to aspiration…smokers have a higher risk of developing this type of pneumonia
acute bacterial pneumonia
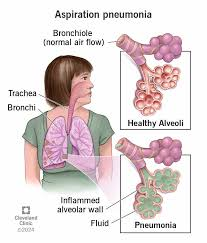
aspiration
swallowing gastric contents which can lead to acute bacterial pneumonia
A rod-shaped aerobic bacteria that is difficult to eradicate and can lay dormant for many years…acid fast bacilli and is an airborne infection
Tuberculosis (TB)
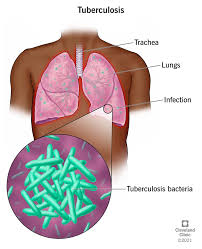
most frequent site of infection for TB? What type of damage? pg. 789 in textbook
Permeant lung damage
even with all the technology we still cant technically test for ____ ______
Ghon complex (looks like a golf ball with cottage cheese)
primary vs latent TB
Primary develops in previously unexposed persons while latent is someone previously exposed
TB has to be _____ to transmit to others
active; symptoms worse than a cold
diagnosis of TB
TB skin test, CXR, sputum culture (definitive takes up to 8 weeks)
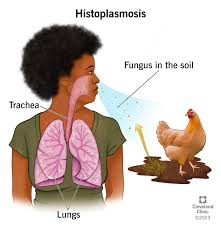
histoplasmosis
a fungal lung infection, or pneumonia, caused by breathing in spores of the fungus Histoplasma from the environment.
overview of fungal infections? Where? Symptoms?
yeast and molds that are inhaled…most cases along major river valleys
healthy people: mild, febrile, respiratory illness
very young/old/immunosuppressed: high fever, generalized lymph node enlargement, enlarged spleen and liver, muscle wasting, anemia, etc.
leading cause of death in the US and highly correlated to smoking…and is increasing in women and young children
lung cancer
what percentage of lung cancer cases are correlated with smoking? Pack year history?
>80%
“pack year history” = # of years smoked x packs smoked per day
classification system of lung cancer?
non-small cell: can produce paraneoplastic syndormes (tumor releasing something it shouldn't...comes malignant very quickly)
small cell carcinoma: highly malignant, brain metastasis common (tiny cells about the size of white blood cells..not really treatable)
3 classes that fall under non-small cell
squamous cell- common in male smokers, hypercalcemia
adenocarcinoma- common in females and non-smoker, poor prognosis
large cell carcinoma- metastasize early, poor prognosis
S/S of lung cancer are based on what 3 categories?
lung involvement (chronic cough, hemoptysis, wheezing)
metastasis
paraneoplastic manifestations (hypercalcemia- increases falls and bone fractures, ADH)
diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer
careful history and physical
CXR, bronchoscopy, cytologic studies, needle biopsy, CT scan, MRI, PET scan to identify metastasis
staging
surgery, chemo, radiation
what are the 2 respiratory disorders in neonates?
respiratory distress syndrome (RDS)
bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)
respiratory distress syndrome (RDS)…treatment?
baby can look normal when born but then central cyanosis, retractions (chest caving inwards), grunting, decreased tidal volume (VT), increased respiratory rate
very high; very shallow respiratory breaths
artificial surfactant; doesn’t work for adults
bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)
chronic lung disease in premature infants who were treated with long-term mechanical ventilation
lungs are stuff which makes it hard to contract; most BPD babies are on ventilator dependent for life
S/S of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)
chronic respiratory distress, persistent hypoxemia on room air (21%), reduced lung compliance, increased air way resistant, serve expiratory flow limitation, ventilation/perfusion mismatch
respiratory disorders in children
upper airway infections: epiglottis, croup
lower airway infection: bronchiolitis
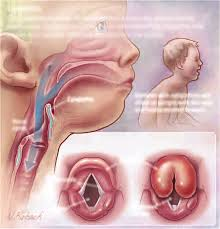
epiglotitis
bacterial, potentially fatal, anxious, respiratory distress
develops rapidly; if we don’t catch early on child will die
airway is too swollen...a tiny incision on neck/trachea to get air ventilation
croup
viral, inspiratory stridor, hoarseness, barking cough
most common in children…adults don’t typically get croup
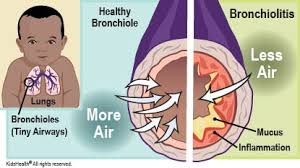
bronchiolitis (lower airway infection)
history of upper respiratory infection
respiratory syncytial virus
respiratory failure (pg. 830 for help)
Increased work of breathing, grunting, decreased chest movement
Cyanosis not relieved by oxygen administration
Increased heart rate -> 150 beats per minute
Very rapid breathing –rate is age dependent
Very slow breathing –rate is age dependent
Extreme anxiety or agitation
Fatigue