Gastrointestinal Dysfunction
1/232
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
233 Terms
clinical manifestations of mild dehydration
changes in behavior, dry mucous membranes, anterior fontanel pulse, normal BP, slightly thirsty
behavior in mild dehydration
changes
mucous membranes in dehydration
dry
anterior fontanel in mild dehydration
pulsating
BP in mild dehydration
normal
how do you treat mild dehydration
oral rehydration of 50 mL/kg within 4 hours
clinical manifestations of moderate dehydration
capillary refill between 2-4 seconds, thirst and irritability, slightly increased pulse, normal to slightly low BP, dry mucous membranes, decreased tears, decreased skin turgor, normal to sunken fontanels in infants
capillary refill time in moderate dehydration
between 2-4 seconds
pulse changes in moderate dehydration
slightly increased
BP changes in moderate dehydration
normal to slightly low
tear production in moderate dehydration
decreased
skin turgor changes in moderate dehydraton
decreased
HR in moderate dehydration
slight tachypnea
fontanels in infants with moderate dehydration
normal to sunken
how do you treat moderate dehydration
oral rehydration of 100 mL/kg within 4 hours
clinical manifestations of severe dehydration
greater than or equal to 10% weight loss, capillary refill > 4 seconds, increased pulse, decreased BP, extreme thirst, dry mucous membranes, tented skin, no tears with sunken eyes, sunken anterior fontanel, oliguria/anuria
weight change in severe dehydration
greater than or equal to 10% weight loss
capillary refill time in severe dehydration
greater than 4 seconds
pulse change in severe dehydration
increased
BP change in severe dehydration
decreased
thirst in severe dehydration
extreme
integumentary changes in severe dehydration
tented skin
tear production in severe dehydration
no tears with sunken eyes
fontanel changes in severe dehydration
sunken anterior fontanel
urine changes in severe dehydration
oligura/anuria
how to treat severe dehydration
IV rehydration with isotonic solution at 20 mL/kg IV bolus over 30 minutes
questions you should ask parents to check for dehydration in their child
is there pee every 8 hours, are they still making tears, are their mouths wet?
what level of dehydration indicates hospitalization?
severe dehydration
if you need to give IVF for a child, what is the rate?
maintenance rate or 1.5x maintenance rate (100 mL/kg/day)
therapeutic management goals for dehydration
correct F/E imbalance, treat underlying cause
nursing care for dehydration
closely observe because changes can occur quick
first two signs that a child is ill
loss of appetite and decreased activity
if a child is "allowing" you to complete procedures and not fighting you, what could that indicate?
they are very ill
edema in children
unique to them due to water and body tissue make-up; they can have edema but be dehydrated
what is vomiting
complex process controlled primarily by CNS where there is forceful ejection of stomach contents through mouth
what is vomiting often accompanied with
nausea and retching
causes of vomiting
acute infectious agent, increased intracranial pressure, toxic ingestions, food intolerance or allergies, GI tract mechanical obstruction, metabolic disorders, renal disease, psychogenic problems
what can help determine cause of vomiting?
color and consistency of emesis
green bilious emesis can indicate
bowel obstruction
undigested or partially digested food vomited hours after ingestion can indicate
poor gastric emptying or high obstruction
forceful vomiting can indicate
pyloric stenosis
fever with vomiting and diarrhea can indicate
infection
therapeutic management for vomiting
treat underlying cause, prevent complications such as dehydration and malnutrition
when would you use anti-emetics
if child is not bale to tolerate anything PO; last chance resort
pharmacological management for vomiting
zofran or reglan; antiemetics
nursing care management
keep NPO if surgery, keep hydrated, advance diet when emesis stops, elevate HOB after feeding, encourage brushing of teeth
diarrhea results from
disorders of digestion, absorption, and secretory functions
etiology of diarrhea
most diarrhea caused by a pathogen through the fecal oral route in food or water
common causes of diarrhea
rotavirus, salmonella, shigella, giardia, AB administraton
Rotavirus accounts for how many fatalities caused by diarrhea
28%
what is Rotavirus
viral pathogen that infects children under 5 y/o; usually through person to person contact
Salmonella, shigella, and giardia
bacterial pathogens most commonly isolated in US; transmitted through raw or undercooked food
why does AB administration cause diarrhea?
disrupts normal intestinal flora that allows overgrowth of other bacteria; most common is C. DIFF
what to recommend to parents if their child is on antibiotics
probiotic supplement or yogurt every day they're on ABs
how to diagnose diarrhea
Hx, physical exam, recent travel, stool testing, appearance of stool
watery, explosive stools indicate
too much glucose
foul smelling, greasy, bulky stools indicate
malabsorption
when should you do stool testing
if they had diarrhea over 1 to two weeks, worried about bacterial infection, constant blood in stool
why do we not recommend pedialyte to rehydrate for diarrhea in children?
may cause too much glucose
what can we give to children to help treat diarrhea
usually water, something lower in sodium due to risk of hypertonic dehydration in infants
for diarrhea do we limit fluid intake?
no
if diarrhea continues but the child is not dehydrated, what should we do
alternate ORS with another low sodium fluid (water, breast milk, formula)
what diet should we start with for patients with diarrhea
BRAT or blan diet and gradually advance
replacing stool loss ratio
1:1 with hydration fluids
if you have a diaper weighing 50 grams, how much liquids should you give them
50 mL over 4 hours to replace that loss
education for diarrhea management
causes and preventions, ORS and advancing diet
diaper rash interventions for diarrhea
apply protective ointments when diarrhea starts (very acidic)
what is constipation
decreased stool frequency and increased hardness of stool with difficulty passing
constipation stool qualities
painful or blood streaked (anal fissure) and can cause abdominal pain, lack of appetite, may lead to incontinence of stool
what is encopresis
Fecal soiling of clothing; fecal deposition in inappropriate places
causes of constipation
structural disorders, systemic disorders, medicatons, spinal cord lesions, idiopathic
structural disorders that cause constipation
strictures, ectopic anus, Hirschsprung disease
systemic disorders that cause constipation
hypothyroidism, hypercalcemia, vitamin D excess, lead poisoning
medications that cause constipation
narcotics, diuretics, antacids, antihistamines, iron supplements
why do spinal cord lesions cause constipation
loss of rectal tone and sensation
most common cause of constipation
idiopathic (no underlying cause); often as a result of illness, withholding, psychosocial factors, dietary habits
#1 cause of constipation in children
iron supplements
how to diagnose constipation
history and physical
therapeutic management of constipation
#1 modify diet (water and fiber)
#2 behavior modification (scheduled 30 min potty time after meal)
#3 stool softeners (miralax)
nursing management of constipation
education; how to help and stop recurrence
Hirschsprung Disease (Congenital Aganglionic Megacolon)
congenital anomaly resulting in mechanical obstruction due to lack of motility of a portion of the intestine
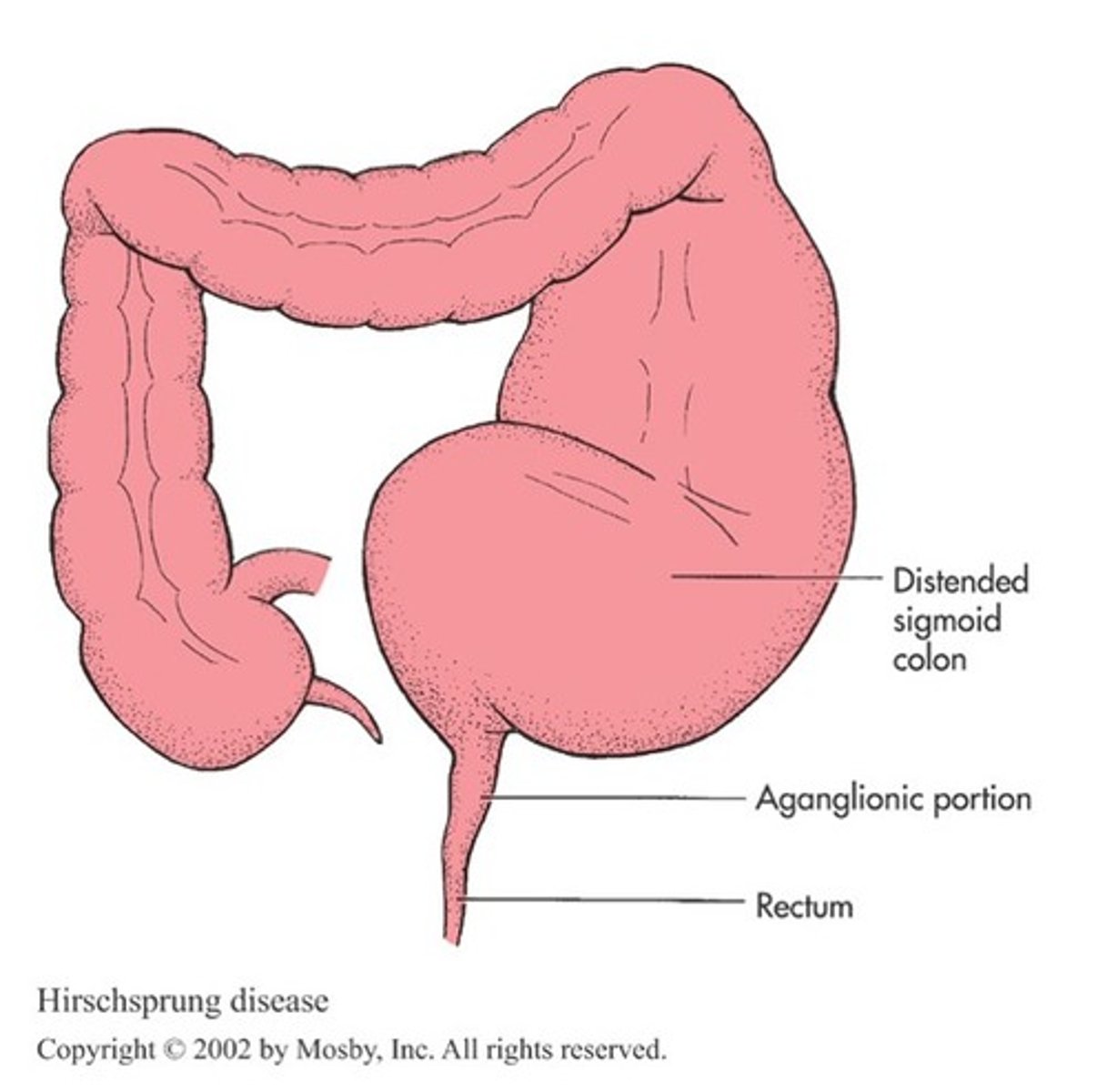
The absence of ganglion cells due to Hirschsprung Disease can cause
loss of rectosphinceteric reflexes and an abnormal microenvironment of the cells of the intestine
what body parts are affected by Hirschsprung Disease
internal sphincter, rectum and a few cm of the sigmoid colon;
what happens to areas affected by Hirschsprung Disease
cannot relax and stool cannot pass
newborn clinical manifestations of Hirschsprung Disease
failure to pass meconium in the first 24-48 hours (#1 sign), refusal to feed, bilious vomiting, abdominal distension
infant clinical manifestations of Hirschsprung Disease
failure to thrive, constipation, abdominal distension, episodes of vomiting and diarrhea
how to diagnose a child with Hirschsprung disease
99% of infants will pass first meconium in the first 24-48 hrs of life; rectal biopsy will show absence of ganglion cells
therapeutic management of Hirschsprung Disease
surgical removal of dysfunctional bowel (need), temporary colostomy
nursing care for Hirschsprung Disease
encourage parent-child bonding, educate on pre/post op care, manage pain, monitor abdominal circumference, educate about complications
Gastroesophageal reflux (GER)
transfer of gastric contents into the esophagus (NOT GERD)
GERD
symptoms or tissue damage that results from having GER
When does GER occur
throughout the day but more common after meals and at night when laying down
How to treat GER
sit up for 30-60 minutes after eating
Peak incidence of GER
children that are at 4 months of age but most instances resolve by 12 months of age
complications from GER
FTT, respiratory problems, dysphagia
Incidence and prevalence of GER
impaired neuro status, hiatal hernia, morbid obesity, premature, tracheoesophageal/esophageal atresia, scoliosis, CF, cerebral palsy
clinical manifestations of GER in infants
recurrent spitting up, excessive crying, poor weight gain, respiratory problems, refusal to feed
clinical manifestations of GER in children
heartburn, abdominal pain, chronic cough/hoarse voice, dysphagia, asthma, recurrent vomiting
how to diagnose GER
H & P, Upper GI series (look for abd. abnormalities), intraesophageal pH monitoring (gold standard)
if a child with GER is thriving, what interventions are done
no interventions are neccessary