chemistry - organic chemistry
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is a homologous series?
A group of compounds that can all be represented by the same general formula
What is a hydrocarbon?
A compound that contains hydrogen and carbon atoms only
What is fuel?
A substance that releases energy when burned
What is combustion?
Burning in air (specifically oxygen)
What is a functional group?
An atom or group of atoms that determine the chemical properties of a compound.
What are structural isomers?
Molecules with the same molecular formula but different structural formulae.
What are polymers?
Large molecules that are made of repeated monomers joined by covalent bonds.
What is cracking?
The process in which long chain alkanes are converted into lake es and smaller chain alkanes.
What is cracking an example of?
Thermal decomposition
What are shorter chain alkanes used for?
To make Petronio, to meet demand
That are alkenes used for?
To make polymers (plastics)
What conditions are needed for cracking?
600-700°C and a Cary list of silicon dioxide and aluminium oxide
Why is carbon monoxide dangerous?
Colourless, odourless gas, poisonous
Binds to the haemoglobin, reducing the ability of the blood to carry oxygen around the body.
How is carbon monoxide formed?
Incomplete combustion.
What is carbon monoxide?
CO + H2O
As the carbon chain increases, hydrocarbons become
____ viscous
____ flammable
____ volatile
____ boiling points
____ in colour
More viscous
Less flammable
Less volatile
Higher boiling points
Darker in colour
Explain how crude oil is fractionalised:
Crude oil is heated up and vaporised. The vapours run un the column.
The column has a temperature gradient. Hot at the bottom, cool at the top.
As the vapours rise, they condense when they reach the temperature just below their boiling point.
Longer hydrocarbons have higher boiling points so they condense near the bottom of the column.
Describe the temperature gradient of the fractional column!
Hot at the bottom, cool at the top.
What is a saturated hydrocarbon?
Hydrocarbons that only contain single bonds.
What is an unsaturated hydrocarbon?
Hydrocarbons that contain one or more double bonds.
When does incomplete combustion happen?
When there is not enough oxygen around for complete combustion.
Describe the disposal of addition polymers:
Addition polymers are non bio-degradable (cannot be broken down by bacteria in the environment).
This is because they have seeing bonds and are unreactive.
It is best to recycle them.
What are the two ways to dispose of addition polymers?
Landfill and incineration
What are the pros and cons of landfill?
Pros: no greenhouse gases produces, cheap
Cons: ugly, smelly, uses lots of land, waste can be there for many years.
Discuss the pros and cons of incineration:
Pros: require little space, can produce heat and electricity.
Cons: expensive to build and maintain plant, produces greenhouse gases, ash produces still has to go to landfill.
What is polymerisation?
The joining of lots of small molecules (monomers) to make one big molecule (polymers)
How do you test for unsaturated hydrocarbons and describe the colour change?
Add bromine water. Is there are unsaturated molecules, the bromine water will turn from orange to colourless.
What is an isomer?
Molecules with the same molecular formula but a different structural formula.
Describe the reaction of ethane + bromine:
Substitution reaction
Only works in uv light
Orange bromine solution slowly looses colour
Describe the reaction of ethene + bromine
Addition reaction
Works without uv light
Orange bromine solution quickly looses its colour.
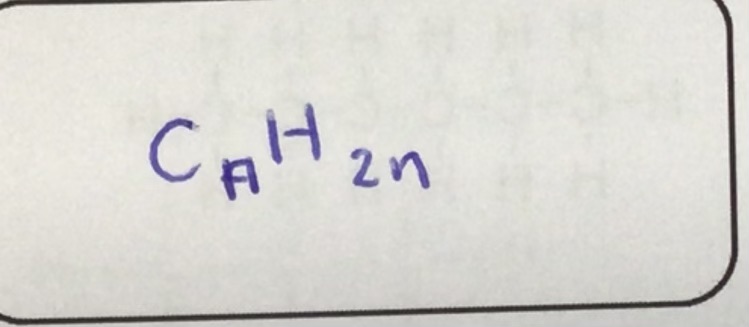
What is the alkane formula?
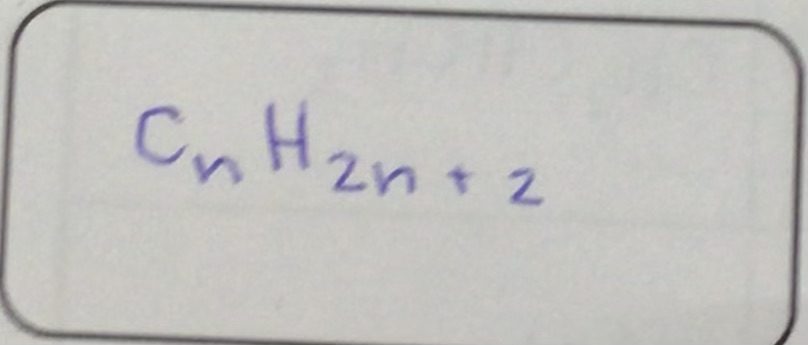
What is the alkene formula?