Exam #3 with chapter 14
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 10:00 PM on 4/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
1
New cards
Endocrine gland
Cells, tissues and organs that make up the endocrine system
Are ductless
Secrete hormones into the bloodstream
Are ductless
Secrete hormones into the bloodstream
2
New cards
Exocrine gland
Secrete into ducts/tubes that lead to a body surface
Secrete externally
Deliver their products directly to a specific site
EXAMPLE: sweat glands
Secrete externally
Deliver their products directly to a specific site
EXAMPLE: sweat glands
3
New cards
Comparison between Nervous and Endocrine System
Both function in communication
Both communicate via chemicals that bind to receptor molecules
Both communicate via chemicals that bind to receptor molecules
4
New cards
Differences between Nervous and Endocrine System
Nervous System - releases Neurotransmitters into synapses
Endocrine System - secretes hormones into bloodstream
Endocrine System - secretes hormones into bloodstream
5
New cards
Steroid hormones
Steroids are lipids containing complex rings of carbon and hydrogen atoms
All steroid hormones are produced from cholesterol
EXAMPLE: sex hormones (testosterone, estrogen) and adrenal cortex hormones (cortisol, aldosterone)
All steroid hormones are produced from cholesterol
EXAMPLE: sex hormones (testosterone, estrogen) and adrenal cortex hormones (cortisol, aldosterone)
6
New cards
Steroid and thyroid hormones
Have poor water-solubility
Can diffuse through a lipid bilayer of cell membranes
Bind to receptors inside the cell - usually in the nucleus
Can diffuse through a lipid bilayer of cell membranes
Bind to receptors inside the cell - usually in the nucleus
7
New cards
Non-steroid hormones
Cannot penetrate the lipid bilayer of cell membranes
Bind to receptors on the target cell membrane
First messenger: hormone
Second messenger: the chemical that induces changes leading to the hormone’s effect (cyclic adenosine monophosphate; cAMP)
Bind to receptors on the target cell membrane
First messenger: hormone
Second messenger: the chemical that induces changes leading to the hormone’s effect (cyclic adenosine monophosphate; cAMP)
8
New cards
Pituitary gland
Lies at the base of the brain in sella turcica of sphenoid bone
Attached to hypothalamus by pituitary stalk
Attached to hypothalamus by pituitary stalk
9
New cards
Anterior pituitary hormone
Produced in the anterior lobe; hormones are released in response to a releasing hormone from the hypothalamus
10
New cards
Anterior pituitary hormone - hormones secreted
Prolactin (PRL)
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
11
New cards
Anterior pituitary hormone - hormones action
Prolactin: promotes milk production in females, uncertain function in males
Thyroid-stimulating hormone: stimulates secretion of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) from thyroid gland
Thyroid-stimulating hormone: stimulates secretion of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) from thyroid gland
12
New cards
Hypopituitary dwarfism
Deficiency of growth hormone during childhood
Short stature, but body proportions and mental development are normal
Treatment must start before bones completely ossify
Short stature, but body proportions and mental development are normal
Treatment must start before bones completely ossify
13
New cards
Gigantism
Caused by over secretion of growth hormone during childhood
Hight may exceed 8 ft and may have other metabolic problems
Often caused by pituitary tumor
Hight may exceed 8 ft and may have other metabolic problems
Often caused by pituitary tumor
14
New cards
Acromegaly
Caused by over secretion of growth hormone during adulthood after epiphyseal ossification
No increase in height, but bones thicken
Enlargement of tongue, nose, hands, feet, jaw, heart, and thyroid gland
No increase in height, but bones thicken
Enlargement of tongue, nose, hands, feet, jaw, heart, and thyroid gland
15
New cards
Posterior pituitary hormone
Consists of nerve fibers from hypothalamus and neuroglia
2 hormones are produced by neurons in the hypothalamus; stored and released by PPH
Hormones are transported to the PPH via the pituitary stalk
2 hormones are produced by neurons in the hypothalamus; stored and released by PPH
Hormones are transported to the PPH via the pituitary stalk
16
New cards
Posterior pituitary hormone - hormones secreted
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Oxytocin (OT)
Oxytocin (OT)
17
New cards
Posterior pituitary hormone - hormones action
Antidiuretic hormone: causes kidneys to reduce water excretion; in high concentration → raises blood pressure
Oxytocin: contracts smooth muscle in the uterine wall; forces liquid from the milk glands into the milk ducts → ejects milk
Oxytocin: contracts smooth muscle in the uterine wall; forces liquid from the milk glands into the milk ducts → ejects milk
18
New cards
Thyroid gland
Lies below the larynx; anterior and lateral to the trachea
Has special ability to remove iodine from blood
Has special ability to remove iodine from blood
19
New cards
Thyroid gland - hormones secreted
T4 (thyroxine)
T3 (triiodothyronine)
Calcitonin
T3 (triiodothyronine)
Calcitonin
20
New cards
Thyroid gland - hormones actions
T4 (Thyroxine): increases rate of energy release from carbs; increases rate of protein synthesis; accelerates growth; stimulates activity in nervous system
T3 (Triiodothyronine): same as T4, but 5x more powerful
Calcitonin: involved in helping to regulate levels of calcium and phosphate in the blood; acts to reduce calcium levels in the blood
T3 (Triiodothyronine): same as T4, but 5x more powerful
Calcitonin: involved in helping to regulate levels of calcium and phosphate in the blood; acts to reduce calcium levels in the blood
21
New cards
Parathyroid glands
Located on the posterior surface of the thyroid gland
22
New cards
Parathyroid gland - hormone secreted
Parathyroid hormone/parathormone (PTH)
23
New cards
Parathyroid gland - hormone action
Parathyroid hormone/parathormone (PTH): regulates Ca^+2 and PO4^-2 concentrations in blood
24
New cards
Adrenal gland/suprarenal gland
Closely associated with the kidneys
Sit like a cap on each kidney
Sit like a cap on each kidney
25
New cards
Adrenal gland - hormones secreted
Adrenal cortex
Adrenal medulla
Adrenal medulla
26
New cards
Adrenal medulla
Central portion of glands, secretes amine hormones
Flight/fight response
Flight/fight response
27
New cards
Adrenal cortex
Outer portion of gland, secretes steroid hormones
Deals with stress
Deals with stress
28
New cards
Pancreas
Elongated, flattened organ
Posterior to stomach
Has both an endocrine and an exocrine gland
Endocrine function: secretes hormones into body fluids
Exocrine function: secretes digestive juices through a duct
Posterior to stomach
Has both an endocrine and an exocrine gland
Endocrine function: secretes hormones into body fluids
Exocrine function: secretes digestive juices through a duct
29
New cards
Pancreas - hormones secreted
Glucagon
Insulin
Somatostatin
Insulin
Somatostatin
30
New cards
Pancreas - hormones action
Glucagon: stimulates the liver to break down glycogen and convert non-carbs into glucose; stimulates breakdown of fats (increases blood glucose when too low)
Insulin: allow glucose to enter cells to be used as energy and to maintain the amount of glucose found in the bloodstream within normal levels (lowers blood glucose when too high)
Somatostatin: helps regulate glucose metabolism
Insulin: allow glucose to enter cells to be used as energy and to maintain the amount of glucose found in the bloodstream within normal levels (lowers blood glucose when too high)
Somatostatin: helps regulate glucose metabolism
31
New cards
Pineal gland
Located on posterior part of brain
32
New cards
Pineal gland - hormone secreted
Melatonin
33
New cards
Pineal gland - hormone action
Regulates circadian rhythms
34
New cards
Thymus gland
Located on medial part of chest
35
New cards
Thymus gland - hormone secreted
Thymosin
36
New cards
Thymus gland - hormone action
Produces T-lymphocytes (T-cells)
Important in the role of immunity
Important in the role of immunity
37
New cards
Reproductive organs
Ovaries produce estrogens and progesterone
Testes produce testosterone
Placenta produces estrogens, progesterone and gonadotropin
Testes produce testosterone
Placenta produces estrogens, progesterone and gonadotropin
38
New cards
Endocrine system
Regulates all biological processes in the body from conception to adulthood to old age
39
New cards
Cardiovascular
Refers to both heart and blood vessels
Pumping action of heart transports blood through blood vessels
Pumping action of heart transports blood through blood vessels
40
New cards
2 Circuits of blood flow
Pulmonary circuit
Systemic circuit
Systemic circuit
41
New cards
Pulmonary circuit
Transports oxygen-poor blood from heart to lungs and back to heart
In lungs, blood picks up O2 and drops off CO2
In lungs, blood picks up O2 and drops off CO2
42
New cards
Systemic circuit
Transports oxygen-rich blood from heart to all body cells and back to heart
Blood delivers nutrients to cells and removes wastes
Blood delivers nutrients to cells and removes wastes
43
New cards
Disorders of the cardiovascular system
Heart murmur
Heart attack
Heart attack
44
New cards
Heart murmur
A blowing, whooshing or rasping sound heard during a heartbeat
Caused by turbulent (rough) blood flow through the heart valves/near the heart
Caused by turbulent (rough) blood flow through the heart valves/near the heart
45
New cards
Heart attack
Flow of blood to the heart is severely reduced or blocked
The blockage is due to a buildup of fat, cholesterol and other substances in the heart arteries
The blockage is due to a buildup of fat, cholesterol and other substances in the heart arteries
46
New cards
Artery (blood vessel) - structure
Thick, strong wall, thicker than walls of veins
Has 3 layers: tunica interna, tunica media, tunica externa
Has 3 layers: tunica interna, tunica media, tunica externa
47
New cards
Arteriole (blood vessel) - structure
Thinner muscular walls and elastic layers than arteries
Only contain a few muscle fibers in their walls
Only contain a few muscle fibers in their walls
48
New cards
Capillary (blood vessel) - structure
Smallest diameter blood vessel
Connect the smallest arterioles and the smallest venules
Connect the smallest arterioles and the smallest venules
49
New cards
Venule (blood vessel) - structure
Microscopic vessel
Thinner walls and less smooth muscle than arterioles
Thinner walls and less smooth muscle than arterioles
50
New cards
Vein (blood vessel) - structure
Thinner walls than arteries
Has 3 layers/tunics
Have flap-like valves
Has 3 layers/tunics
Have flap-like valves
51
New cards
Artery (blood vessel) - function
Transport blood under high blood pressure away from the heart
Give rise to smaller arterioles
Give rise to smaller arterioles
52
New cards
Arterioles (blood vessel) - function
Reduces the pressure and velocity of blood flow to enable gas and nutrient exchange to occur within the capillaries (control the diameter)
53
New cards
Capillary (blood vessel) - function
Site of gas exchange
Are semi-permeable
Are semi-permeable
54
New cards
Venule (blood vessel) - function
Transport blood from the capillaries to veins
55
New cards
Vein (blood vessel) - function
Carry blood under relatively low pressure back to the heart
Function as blood reservoirs
Function as blood reservoirs
56
New cards
Right atrium (heart chamber)
Receives blood returning from systemic circuit (from superior/inferior vena cava and coronary sinus)
Pumps blood to right ventricle
Pumps blood to right ventricle
57
New cards
Right ventricle (heart chamber)
Receives blood from the right atrium
Pumps blood to lungs
Pumps blood to lungs
58
New cards
Left atrium (heart chamber)
Receives blood from the pulmonary veins
Pumps blood to left ventricle
Pumps blood to left ventricle
59
New cards
Left ventricle (heart chamber)
Receives blood from the left atrium
Pumps blood to systemic circuit
Pumps blood to systemic circuit
60
New cards
Cardiac cycle
Events of a heartbeat
Pressure in the heart chambers rise and fall
Pressure changes open and close the valves
Pressure in the heart chambers rise and fall
Pressure changes open and close the valves
61
New cards
Systole
Heart muscle contracts and pumps blood out of the chambers
62
New cards
Diastole
Heart muscle relaxes after contraction and allows the chambers to be filled with blood
63
New cards
Atrial systole & ventricular diastole
Ventricles are relaxed
The AV valves open and the semilunar valves close
About 70% of blood flows passively from atria into ventricles
Atrial systole pushes remaining 30% of blood into the ventricles - causes ventricular pressure to increase
The AV valves open and the semilunar valves close
About 70% of blood flows passively from atria into ventricles
Atrial systole pushes remaining 30% of blood into the ventricles - causes ventricular pressure to increase
64
New cards
Ventricular systole & atrial diastole
The AV valves close
The chordae tendinea prevent the cusps of the valves from bulging too far backward into atria
Atria relaxes
Blood flows into atria from the vena cava and pulmonary veins
Blood flows into the pulmonary trunk and aorta
The chordae tendinea prevent the cusps of the valves from bulging too far backward into atria
Atria relaxes
Blood flows into atria from the vena cava and pulmonary veins
Blood flows into the pulmonary trunk and aorta
65
New cards
Cardiac conduction system
Group of clumps and strands of specialized cardiac muscle tissue
Initiates and distributes impulses throughout the myocardium
Coordinates the events of the cardiac cycle
Initiates and distributes impulses throughout the myocardium
Coordinates the events of the cardiac cycle
66
New cards
Major components - cardiac conduction system
SA (sinoatrial) node
Internodal atrial muscle
Junctional fibers
AV (atrioventricular) node
AV (atrioventricular) bundle
Left and right bundle branches\]
Purkinje fibers
Internodal atrial muscle
Junctional fibers
AV (atrioventricular) node
AV (atrioventricular) bundle
Left and right bundle branches\]
Purkinje fibers
67
New cards
SA (sinoatrial) node
Pacemaker
Initiates rhythmic contractions of the heart
Initiates rhythmic contractions of the heart
68
New cards
Internodal atrial muscle
Conducts impulses from SA node to atria
69
New cards
Junctional fibers
Conduct impulses from SA node to AV node
70
New cards
AV (atrioventricular) node
Conducts impulses to AV bundle
Delays impulse so atria can finish contracting before ventricles contract
Delays impulse so atria can finish contracting before ventricles contract
71
New cards
AV (atrioventricular) bundle
Conducts impulses rapidly between AV node and bundle branches
72
New cards
Left and right bundle branches
Split off from AV bundle
Conduct impulses to purkinje fibers on both sides of heart
Conduct impulses to purkinje fibers on both sides of heart
73
New cards
Purkinje fibers
Large fibers that conduct impulses to ventricular myocardium
74
New cards
Electrocardiogram (ECG, EKG)
Recording of electrical changes that occur in the myocardium during the cardiac cycle
Used to assess the heart’s ability to conduct impulses
Used to assess the heart’s ability to conduct impulses
75
New cards
P wave
Atrial depolarization
Occurs just prior to atrial contraction
Occurs just prior to atrial contraction
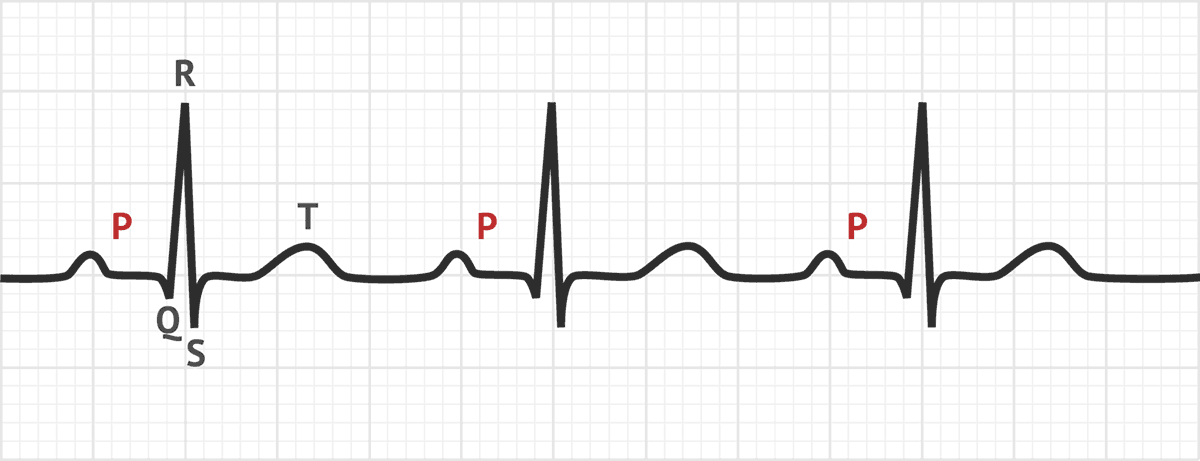
76
New cards
QRS complex (3 waves)
Ventricular depolarization
Occurs just prior to ventricular contraction
Occurs just prior to ventricular contraction
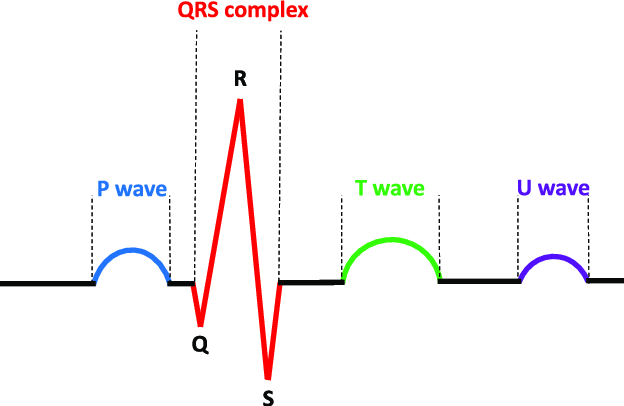
77
New cards
T wave
Ventricular repolarization
Occurs just prior to ventricular relaxation
Occurs just prior to ventricular relaxation
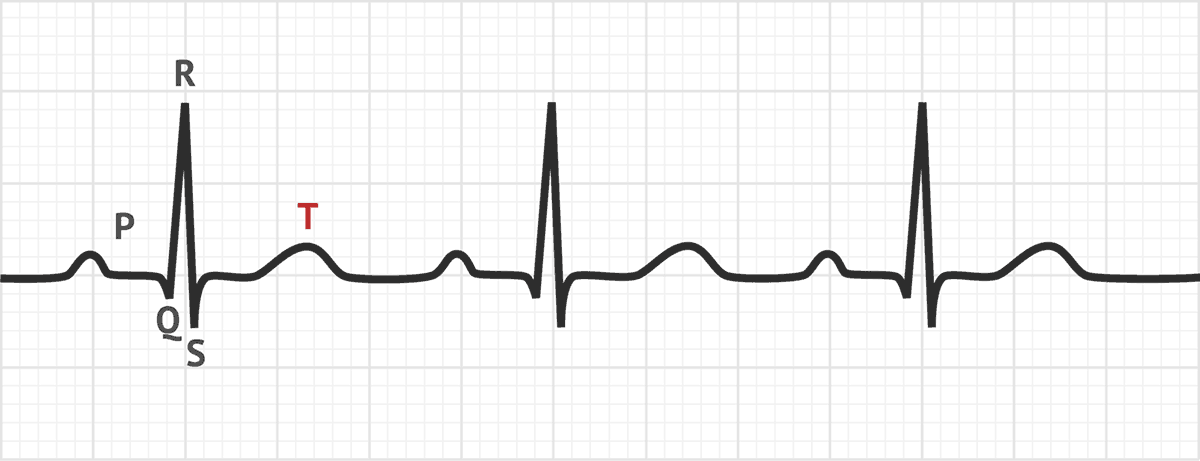
78
New cards
Steps in signal transduction pathway
Receptor: process by which a cell detects a signal in the environment
Transduction: process of activating a series of proteins inside the cell from the cell membrane
Response: change in behavior that occurs in the cell as a result of the signal
Transduction: process of activating a series of proteins inside the cell from the cell membrane
Response: change in behavior that occurs in the cell as a result of the signal
79
New cards
Lymphatic system
Defends body against infection by pathogens
Contains a network of vessels that assist in circulating fluids
Closely associated with the cardiovascular system
Contains a network of vessels that assist in circulating fluids
Closely associated with the cardiovascular system
80
New cards
Functions - lymphatic system
Transports excess fluid away from the interstitial spaces (space between cells) and returns it to bloodstream
Absorbs lipids from digestive system and transports them to bloodstream
Defends the body against diseases
Absorbs lipids from digestive system and transports them to bloodstream
Defends the body against diseases
81
New cards
Lymph
S: colorless fluid containing white blood cells
F: managing the fluid levels in the body
F: managing the fluid levels in the body
82
New cards
Lymphatic vessel
S: thin tube
F: carries lymph and white blood cells through lymphatic system
F: carries lymph and white blood cells through lymphatic system
83
New cards
Lymph node
S: small bean-shaped structure
F: filter substances which travel through the lymphatic fluid
F: filter substances which travel through the lymphatic fluid
84
New cards
Thoracic duct
S: main vessel of lymphatic system
F: collects and transports lymph back into the circulatory system
F: collects and transports lymph back into the circulatory system
85
New cards
Right lymphatic duct
S: combination of neck muscles; formation varies
F: drains fluid that has leaked from the blood vessels into the tissues; empties it back into the bloodstream via lymph nodes
F: drains fluid that has leaked from the blood vessels into the tissues; empties it back into the bloodstream via lymph nodes
86
New cards
Thymus gland
S: asymmetrical flat shape with a lobular structure
F: makes white blood cells (T-cells) which protect the body against infections
F: makes white blood cells (T-cells) which protect the body against infections
87
New cards
Spleen
S: consists of two types of tissue: white pulp and red pulp
F: controls the level of blood cells; removes any old or damaged red blood cells
F: controls the level of blood cells; removes any old or damaged red blood cells
88
New cards
Pathogens
Disease-causing agents
Bacteria, viruses and complex microorganisms
Bacteria, viruses and complex microorganisms
89
New cards
Innate (non-specific) defenses
General defenses
Protect against many types of pathogens
Protect against many types of pathogens
90
New cards
Adaptive (specific) defenses
Immunity
More specific and precise - targets specific antigens
Carried out by lymphocytes that recognize certain foreign molecules
More specific and precise - targets specific antigens
Carried out by lymphocytes that recognize certain foreign molecules
91
New cards
Mechanical barriers
First line of defense
Skin and mucous membranes form mechanical barriers
EXAMPLES: hair traps, tears, saliva, urine
Skin and mucous membranes form mechanical barriers
EXAMPLES: hair traps, tears, saliva, urine
92
New cards
Chemical barriers
Second line of defense
* Enzymes
* Interferons
* Complement
* Enzymes
* Interferons
* Complement
93
New cards
Natural kill (NK) cells
Second line of defense
Defend against viruses and cancer cells by secreting cytolytic substances (perforins: disintegrate cell membranes)
Defend against viruses and cancer cells by secreting cytolytic substances (perforins: disintegrate cell membranes)
94
New cards
Inflammation
Second line of defense
Walls off infection site and stops spread of infection
Walls off infection site and stops spread of infection
95
New cards
Phagocytosis
Second line of defense
Removes foreign particles from the lymph
* Neutrophils
* Monocytes
Removes foreign particles from the lymph
* Neutrophils
* Monocytes
96
New cards
Fever
Second line of defense
Produces cells that secrete interleukin-1 (endogenous pyrogen) which is a fire maker from within
Produces cells that secrete interleukin-1 (endogenous pyrogen) which is a fire maker from within
97
New cards
Adaptive (specific)
Third line of defense
Immunity
* Cell-mediated immune response
* Humoral immune response
Immunity
* Cell-mediated immune response
* Humoral immune response
98
New cards
Antigens
Non-self molecules that elicit an immune response
99
New cards
3 types of blood cells
red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets (thrombocytes).
100
New cards
function of red blood cell
Red blood cells, also known as erythrocytes, are responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to the body's tissues and transporting carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs to be exhaled.