RENAL DISEASE: CKD
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE
Progressive, irreversible deterioration of renal function
LONG standing disease, usually resulting from an untreated AKI
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE
Defined as
kidney damage or GFR of 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 for three months
POSSIBLE CAUSES / RISK FACTORS OF CKD
diabetes
hypertension
age >60
smoking
obesity
family history
heart disease
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF CKD
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
Confusion
Seizures
Coma
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF CKD
RENAL
Polyuria
Nocturia
Sodium + Water Retention
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF CKD
HORMONAL
Infertility
Loss of libido
Amenorrhoea
Impotence
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF CKD
BONE
Osteomalacia
pain
Osteosclerosis
Hyperparathroidism
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF CKD
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
Hypertension
Heart Failure
Pericarditis
Vascular disease
Peripheral oedema
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF CKD
GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT
Nausea
Vomiting
Weight Loss
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF CKD
PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY
Stage 1
Kidney damage- normal GFR
≥90 mL/min/1.73m²
stage 2
Kidney damage-mild ⭣GFR
60-89 mL/min/1.73m²
stage 3
Moderate ⭣GFR
30-59 mL/min/1.73m²
stage 4
Severe ⭣GFR
15-29 mL/min/1.73m²
stage 5
End-stage renal disease
<15 mL/min/1.73m² (or dialysis)
STAGES IN PROGRESSION OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE AND THERAPEUTIC STRATEGIES
stage 1
normal
Screening for CKD risk factors
STAGES IN PROGRESSION OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE AND THERAPEUTIC STRATEGIES
stage 2
increased risk
CKD risk reduction
Screening for CKD
STAGES IN PROGRESSION OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE AND THERAPEUTIC STRATEGIES
stage 3
Damage
Diagnosis & treatment
Treat comorbid conditions
Slow progression
STAGES IN PROGRESSION OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE AND THERAPEUTIC STRATEGIES
stage 4
⭣GFR
Estimate progression
Treat complications
Prepare for replacement
STAGES IN PROGRESSION OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE AND THERAPEUTIC STRATEGIES
stage 5
Kidney failure
Replacement by
Dialysis
Transplantation
STAGES IN PROGRESSION OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE AND THERAPEUTIC STRATEGIES
stage 6
CKD death
MEASUREMENT OF RENAL FUNCTION
gfr
creatinine clearance
urea
GFR
volume of filtrate produced by the glomeruli of both kidneys each minute
reliable indicator of renal function
Creatinine Clearance
eGFR equations for Adult & Pediatric patients
Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD)
Cockcroft-Gault
CKD-Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI)
Schwartz
Counahan-Baratt
MDRD EQUATION
Step 1: Determine if the patient has CKD.
Step 2: Check serum creatinine and calculate creatinine clearance (consider age and weight).
Step 3: Adjust medication based on clearance and literature guidelines.
Based on literature, 20-30 mL of serum creatinine clearance, adjust the medication to q8h; if 31-40 mL, give q12h.

COCKCROFT-GAULT EQUATION
men
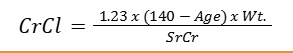
COCKCROFT-GAULT EQUATION
women
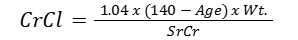
COCKCROFT-GAULT EQUATION

CKD-EPI EQUATION
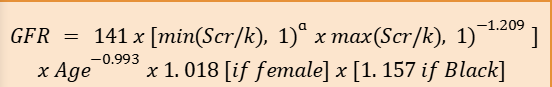
SCHWARTZ FORMULA
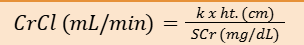
k = 0.45
Infants < 1 year of age
k = 0.55
Children and adolescent females
k = 0.7
Adolescent males
COUNAHAN-BARRATT EQUATION
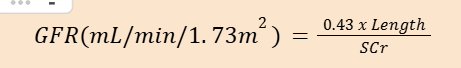
CLINICAL EVALUATION
physical findings: metabolic abnormalities
Hypo/hypernatremia
Metabolic acidosis
Hyperparathyroidism
CLINICAL EVALUATION
physical findings: neurological manifestations
Short attention span
Loss of memory
Confusion
Seizures
Peripheral neuropathy
Pain
Burning sensation
CLINICAL EVALUATION
physical findings: cardiovascular problems
Peripheral edema
Arterial HTN
CHF
CLINICAL EVALUATION
physical findings: respiratory problems
Dyspnea
pulmonary edema
CLINICAL EVALUATION
physical findings: gi manifestations
Hiccups
Nausea and Vomiting
Constipation
Anorexia
Stomatitis
CLINICAL EVALUATION
physical findings: integumentary findings
Pale
Dry scaly skin
Severe itching
Brittle nails or hair
CLINICAL EVALUATION
physical findings: musculoskeletal changes
Bone pain
CLINICAL EVALUATION
physical findings: hematologic disturbances
Anemia
Easy bruising
Pallor skin
CLINICAL EVALUATION
diagnostic test result
Ultrasonography
IV Urography (IVU)
Plain abdominal radiography
Mercaptoacetyltriglycine (MAG3)
Dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA)
Computed Tomography (CT)
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA)
Renal biopsy
TREATMENT OBJECTIVES
Avoid conditions that might worsen renal failure
Treat the secondary complications
Relieve symptoms
Implement regular dialysis treatment and/or transplantation at the most appropriate time
COMORBIDITIES
Hypertension
Edema
GI disturbances
Skin problems
Anemia
Metabolic disturbances
HYPERTENSION
treatment
ace/arbs
ccb
beta blockers
selective alpha 1 blocker
vasodilators
centrally acting drug
ACEI and ARBs
Treatment for all diabetic patients with micro or macroalbuminuria and CKD, regardless of the BP
Reduction in GFR by preventing angiotensin II-mediated vasoconstriction of the efferent glomerular arteriole
CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS
DOC for patients with proteinuria
Vasodilatation: reduced Ca influx into vascular muscle cells
Promote sodium excretion associated with fluid overload
BETA-BLOCKERS
Use the cardio-selective β-blockers (atenolol, metoprolol)
Atenolol
renal excretion
dosage adjustment required
Metoprolol:
liver excretion
no dosage adjustment required
SELECTIVE ALPHA 1 BLOCKER
Produce improvements in insulin sensitivity, adverse lipid profiles and prostate hypertrophy obstruction
Used rarely because of side effect: development of heart failure
VASODILATORS
Used as an alternative when other measures are inadequate
VASODILATORS
drugs
Hydralazine, Minoxidil
CENTRALLY ACTING DRUG
Rarely used because of adverse effect
CENTRALLY ACTING DRUG
drugs
Methyldopa, Clonidine
EDEMA
dietary modifications
diuretics
DIURETICS
Loop diuretics: Furosemide > 250 mg/day (advanced cases) - First-line for edema
Spironolactone with ACEI/ARBS in reducing proteinuria (raise hyperkalemia risk)
DIETARY MODIFICATION
Sodium and potassium restriction
GI DISTURBANCES
Antiemetic
help control nausea and vomiting
GI DISTURBANCES
docusate sodium, methylcellulose, enema
prevent constipation
SKIN PROBLEMS
Diphenhydramine:
antipruritic to alleviate itching
ANEMIA
iron folate supplement
Recombinant Human Erythropoietin (Epoetin alfa and beta, SQ)
Novel Erythropoiesis
Novel Erythropoiesis
Stimulating Protein (Darbepoetin alfa)
METABOLIC DISTURBANCES
acidosis
hyperphosphatemia
hypocalcemia
ACIDOSIS
Oral doses of sodium bicarbonate (1–6 g/day)
HYPERPHOSPHATEMIA
Dietary phosphate restriction
Administration of phosphate binder (aluminum hydroxide, calcium acetate, calcium carbonate, sevelamer)
HYPOCALCEMIA
Oral calcium salt, vitamin D
RENAL TRANSPLANT
Treatment of choice for patients with ESRD who are fit to receive
RENAL TRANSPLANT
considerations
lderly, comorbidities, tolerate immunosuppressive drugs
RENAL TRANSPLANT
notes
Donor kidneys supply — living or cadaver
Histocompatibility
Immunosuppressants
TRANSPLANT REJECTION TYPES
hyperacute
Immediate, graft loss within minutes–hours after transplantation
TRANSPLANT REJECTION TYPES
hyperacute: symptoms (intra-op)
Acute urine flow cessation and bluish or mottled kidney discoloration
TRANSPLANT REJECTION TYPES
hyperacute: symptoms (post-op)
Fever, anuria, local pain, sodium retention, and hypertension
TRANSPLANT REJECTION TYPES
hyperacute: treatment
Immediate nephrectomy
TRANSPLANT REJECTION TYPES
acute
4–60 days after transplantation
TRANSPLANT REJECTION TYPES
chronic
>60 days after transplantation
TRANSPLANT REJECTION TYPES
chronic: symptoms
Low-grade fever
increased proteinuria
Azotemia
Hypertension
Oliguria
Weight gain
Edema
TRANSPLANT REJECTION TYPES
chronic: treatment
Give immunosuppressing agents: Alkylating agents, cyclosporine, antilymphocyte globulin, and corticosteroids
In some cases: nephrectomy
IMMUNOSUPPRESSANTS
goals
Maximize kidney function
Minimize rejection risk
Mitigate risk of adverse effects
IMMUNOSUPPRESSANTS
2 phases
induction immunosuppression
maintenance immunosuppression
INDUCTION IMMUNOSUPPRESSION
Protect the transplant from the high immunological risk that is present in the first few weeks after surgery
Targets specific immune cells or pathways to rapidly suppress immune response
MAINTENANCE IMMUNOSUPPRESSION
Provide long-term immunosuppression to prevent both acute and chronic rejection, more broadly and continuously
TRANSPLANT MEDICATION
Anti Rejection Steroid
Tacrolimus (Prograf)- 0.5 mg; 1 mg; 5 mg
Mycophenolate mofetil (Mycolate)- 250mg
prednisolone- 5mg
Tacrolimus (Prograf)- 0.5 mg; 1 mg; 5 mg
Dose varies depending on levels, take at 10am and 10pm
Should be taken on an empty stomach i.e. 1 hour before or 2 hours after food
Do not take prior to blood level being taken on day of clinic visit
Mycophenolate mofetil (Mycolate)- 250mg
Take 2 caps at 10am and 10pm
Chemist may supply 500mg tab (purple tablet)
Dose may be increased by Renal Team
The only brands you should receive are Mycolate or Cellcept if the chemist cannot supply Mycolat
prednisolone- 5mg
Take 4 tabs at 10am
Dose will be reduced by Renal Physician after discharge
Also available in enteric coated tablets
TRANSPLANT MEDICATION
Antibacterial to prevent PCP Pneumonia:
Co-trimoxazole (Septrin)
450 mg
1 tab at night
TRANSPLANT MEDICATION
Antiviral to prevent CMV infections:
Valganciclovir (Valcyte)
450 mg
Not all patients will require this therapy
Dose is dependent upon renal function
Initial dose is usually 1 tablet three times a week. This may increase to 1-2 tablets once daily as renal function improves
TRANSPLANT MEDICATION
To protect the stomach:
ranitidine 150 mg
Certain patients will continue on PPI therapy e.g. Lanzaprole, Omeprazole, and not receive Ranitidine
TRANSPLANT MEDICATION COMBINATIONS
steroids
ciclosporin
tacrolimus
sirolimus
mycophenolate
azathioprine
muromonab (OKT3, Mouse monoclonal anti-CD3)
POLYCLONAL HORSE/RABBIT ANTITHYMOCITE or ANTILYMPHOCYTE GLOBULIN (ATG, ALG)
HUMANISED or CHIMAERIC ANTI-CD25 (Basiliximab, Daclizumab)
STEROIDS
Bind to steroid receptors and inhibit gene transcription and function of T-cells, macrophages, and neutrophils
CICLOSPORIN
Forms complex with intracellular protein cyclophilin → inhibits calcineurin
Ultimately inhibits interleukin-2 synthesis and T-cell activation
TACROLIMUS
Forms complex with an intracellular protein → inhibits calcineurin
SIROLIMUS
Inhibits interleukin-2 cell signaling → blocks T-cell cycling and inhibits B-cells
MYCOPHENOLATE
Inhibits inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase → reduces nucleic acid synthesis → inhibits T- and B-cell function
AZATHIOPRINE
Incorporated as a purine in DNA → inhibits lymphocyte and neutrophil proliferation
MUROMONAB (OKT3, Mouse monoclonal anti-CD3)
Binds to CD3 complex → blocks, inactivates or kills T-cell
Short t1/2
POLYCLONAL HORSE/RABBIT ANTITHYMOCITE or ANTILYMPHOCYTE GLOBULIN (ATG, ALG)
Antibodies against lymphocyte proteins → alter T- and B-cell activity
HUMANISED or CHIMAERIC ANTI-CD25 (Basiliximab, Daclizumab)
Monoclonal antibodies that bind CD25 in interleukin-2 complex → prevent T-cell proliferation