Anaesthesia
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:26 PM on 1/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
1
New cards
Anaesthesia
The reversible production of a state of unconsciousness
2
New cards
General anaesthesia
The state of unconsciousness across the whole body, produced by anaesthetic agents, with the absence of pain throughout the whole body
3
New cards
Regional anaesthesia
Insensibility caused by the interruption to sensory nerve conduction on an area of the body
4
New cards
Local anaesthesia
Lack of sensation in a specific area of the body
5
New cards
Sedation
State of reduced excitement or irritability. No loss of consciousness
6
New cards
Anxiolysis
State of reduced anxiety
7
New cards
Analgesia
State of a reduced sensibility to pain
8
New cards
Narcosis
A sleep-like state
9
New cards
Hypnosis
An artificially induced state of passivity (this term is often used interchangeably with 'narcosis')
10
New cards
Premedication
A combination of drugs given prior to GA induction to:
- Calm patients
- Aid restraint
- Provide pre-emptive analgesia
- Reduce induction agent and maintenance drug quantities
- Contribute to a smooth induction and recovery
- Calm patients
- Aid restraint
- Provide pre-emptive analgesia
- Reduce induction agent and maintenance drug quantities
- Contribute to a smooth induction and recovery
11
New cards
Induction phase
Phase where the patient is taken from a conscious to anaesthetised state. This involves:
- IV placement
- Pre-oxygenation
- Premed admin (if not already given)
- Induction agent admin
- Airway security
- IV placement
- Pre-oxygenation
- Premed admin (if not already given)
- Induction agent admin
- Airway security
12
New cards
Maintenance phase
Phase where anaesthesia is taking place:
- Maintenance drugs
- Placement of local/regional blocks
- Prep + procedure
- Maintenance drugs
- Placement of local/regional blocks
- Prep + procedure
13
New cards
Recovery phase
Cessation of gaseous maintenance or CRI:
- Airway device removal
- Move to recovery area
(this phase is smoother and less sudden with a good premed)
- Airway device removal
- Move to recovery area
(this phase is smoother and less sudden with a good premed)
14
New cards
Anaesthetic triad
Narcosis, analgesia, and muscle relaxation.
The 3 main components of anaesthesia
The 3 main components of anaesthesia
15
New cards
Balanced anaesthesia
The idea that anaesthesia produced by smaller doses of 2+ agents is safer than a large dose of 1 agent.
16
New cards
MDR1 gene mutation
A mutation of a gene found in collies, sheepdogs, shepherds, etc. This mutation means toxins can't be taken away, causing neurological symptoms.
17
New cards
Alfaxalone
A type of injectable anaesthesia agent that isn’t propofol
18
New cards
Chamber induction
Gas induction where a box is used. This is great for smallies, is cheap, and easy to set up.
However it is stressful to animals (stingy eyes, weird smell, etc), difficult for observation, and risks staff exposure.
However it is stressful to animals (stingy eyes, weird smell, etc), difficult for observation, and risks staff exposure.
19
New cards
Facemask induction
Gas induction by covering the nose + mouth with a mask. This is cheap, easy to use, and allows a quick change to oxygen or volatile gas.
However, this doesn't protect the airway, risks staff exposure, and has a lot of dead space.
However, this doesn't protect the airway, risks staff exposure, and has a lot of dead space.
20
New cards
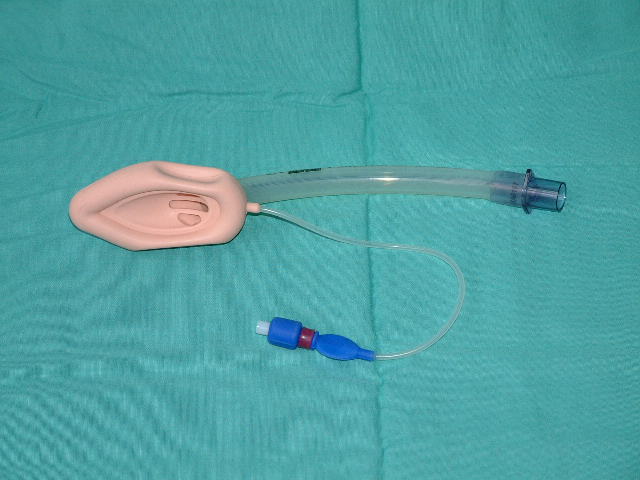
Laryngeal mask airway (LMA)
This airway management device sits over the larynx.
It is more commonly used in humans, and less designed for animals.
It is more commonly used in humans, and less designed for animals.
21
New cards
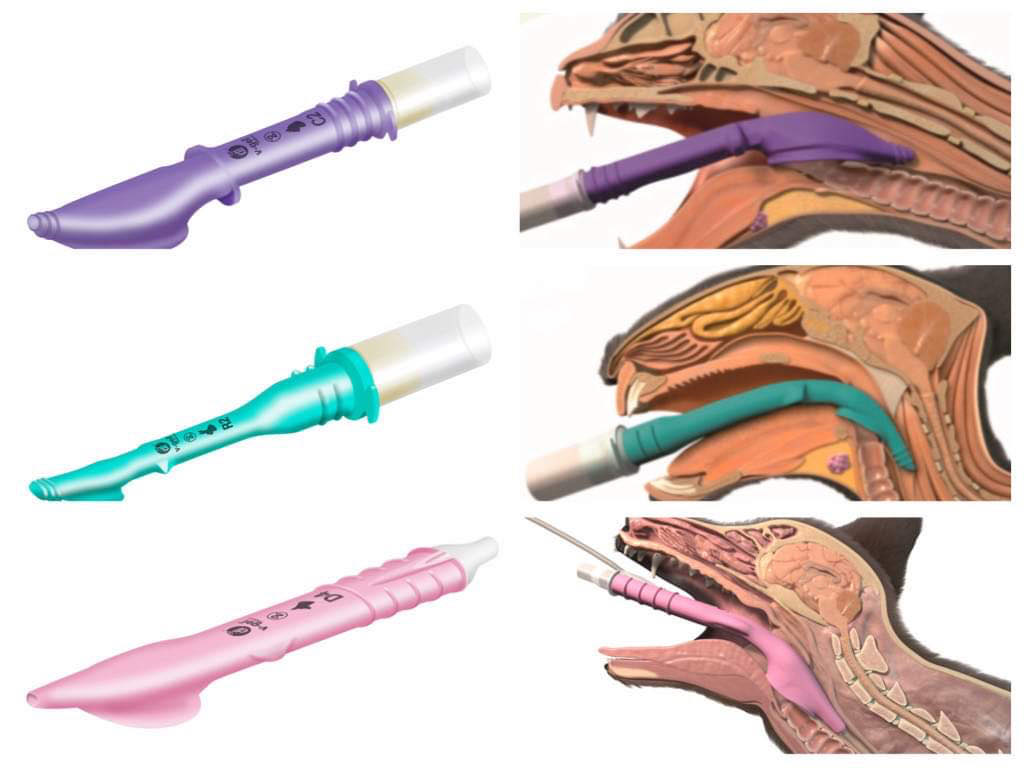
Supraglottic airway device (V-gel)
Airway management device that has a species and weight specific design. This requires training before use.
It blocks the oesophagus + is useful in rabbits!
It blocks the oesophagus + is useful in rabbits!
22
New cards
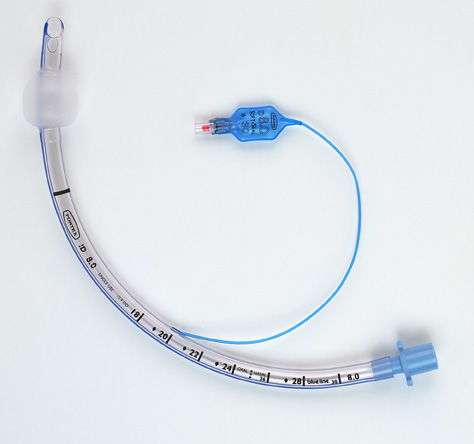
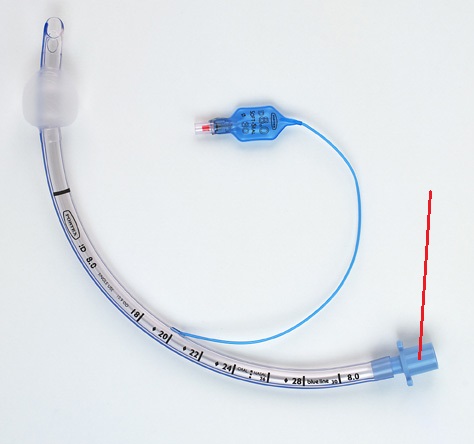
Endotracheal tube (ETT)
Gold standard airway management device for airway protection!
This prevents atmospheric exposure.
Measure from the incisors to the tip of the shoulders
This prevents atmospheric exposure.
Measure from the incisors to the tip of the shoulders
23
New cards
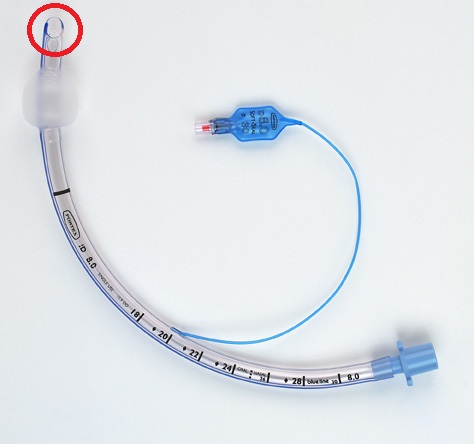
Bevelled edge
The diagonal cut of the end of the ET tube. This gives a wider surface area, helping with placement
24
New cards
Murphy's eye
The little hole in some ET tubes, allowing for breathing if the main tube gets blocked.
Like the little hole in lollypop sticks!
Like the little hole in lollypop sticks!
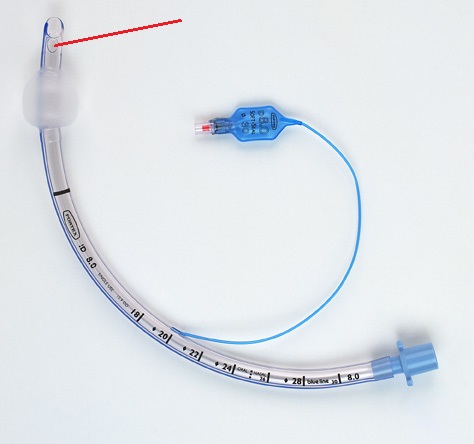
25
New cards
Adaptor
The end of the ET tube that connects to the breathing circuit
26
New cards
Pilot balloon
Part of the ET tube that connects to a tube, connecting to the cuff.
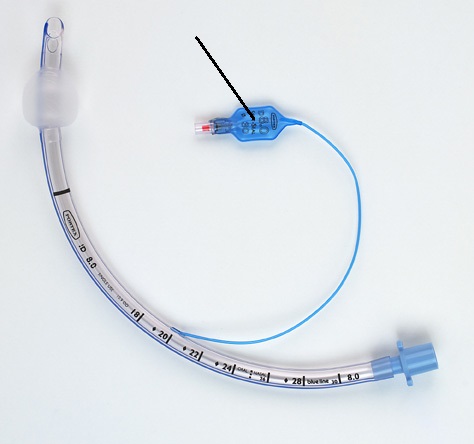
27
New cards
Silicone ETT
Soft and flexible ET tubes
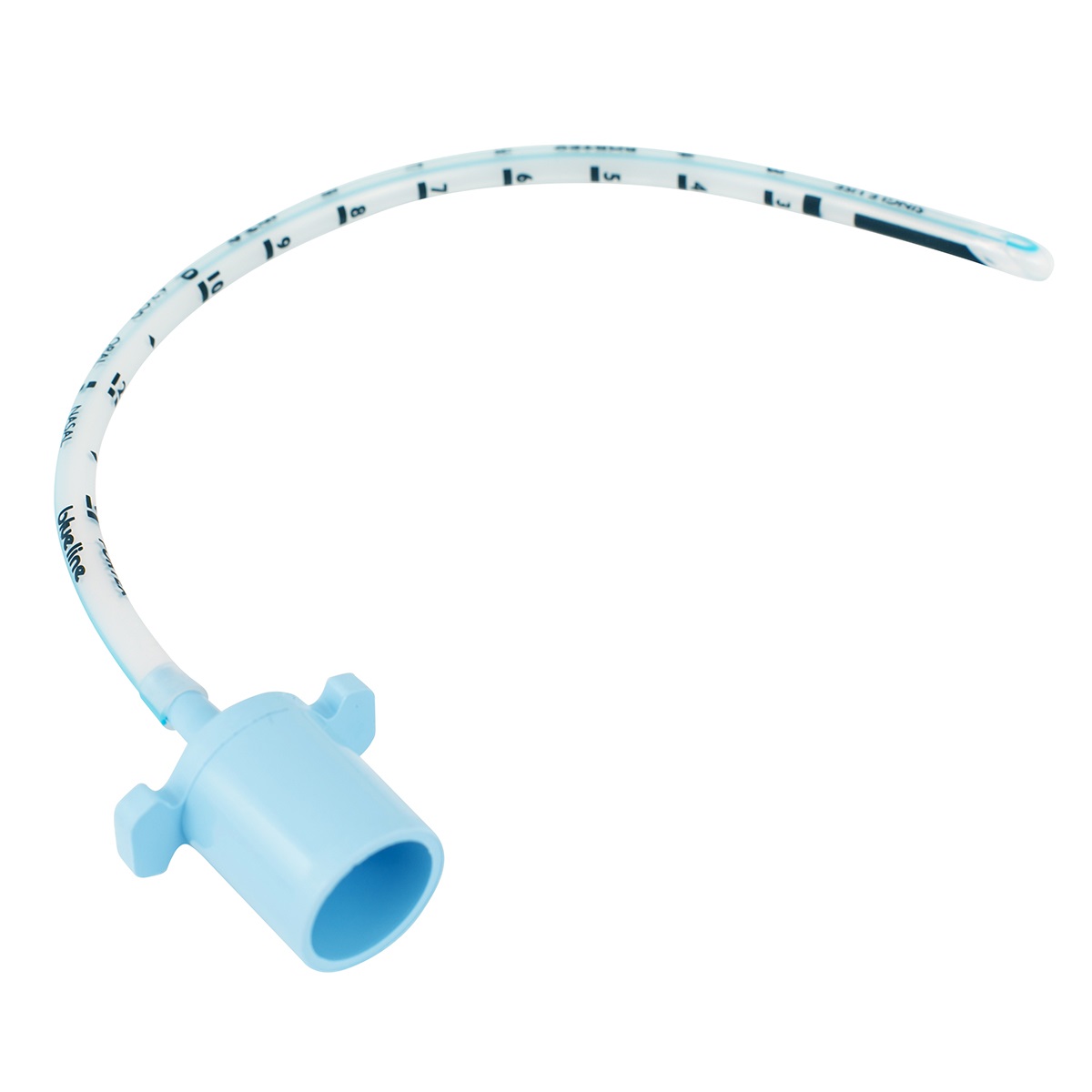
28
New cards
PVC ETT
"single use" ET tubes with high volume, low pressure cuffs.
These are clear so you can see blockages and condensation.
Cleaning can make them brittle
These are clear so you can see blockages and condensation.
Cleaning can make them brittle
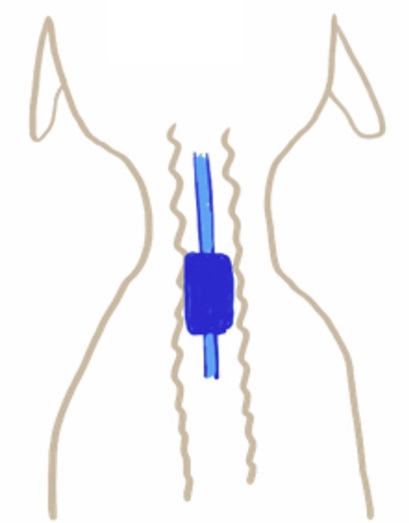
29
New cards
Red rubber ETT
ET tubes with low volume, high pressure cuffs. The cuffs are more rounded creating a small area of high pressure on the tracheal tissue
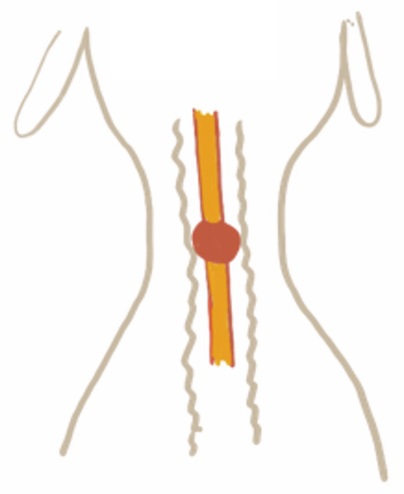
30
New cards
Armoured ETT
ET tube that is metal reinforcement on the inside. These allow movement of the neck.
*DON'T USE IN AN MRI MACHINE*
*DON'T USE IN AN MRI MACHINE*
31
New cards
ASA I
Anaesthetic risk - Normal + healthy
32
New cards
ASA II
Anaesthetic risk - Mild systemic disease (not a risk, but worth noting)
33
New cards
ASA III
Anaesthetic risk - Systemic disease that's well compensated or controlled by treatment
34
New cards
ASA IV
Anaesthetic risk - Severe disease that's uncompensated
35
New cards
ASA V
Anaesthetic risk - Unlikely to survive 24h without surgery
36
New cards
E
ASA notation added to any patient for
37
New cards
Checklists
Used in procedures to ensure everything is done and complete before/after.
Introduced by WHO in 2008 + mandated by NHS in 2009.
Reduced surgical complications/deaths by 1/3.
Introduced by WHO in 2008 + mandated by NHS in 2009.
Reduced surgical complications/deaths by 1/3.
38
New cards
Oxygen cylinder
Made of molybdenum steel, these store oxygen at over 10,000kPa for use in anaesthetics.
They should be stored undercover, dry, clean, and well ventilated, with no extreme temperatures.
Store full and empty separately.
They should be stored undercover, dry, clean, and well ventilated, with no extreme temperatures.
Store full and empty separately.
39
New cards
Pipeline gas
Oxygen is transmitted from a large storage outside to the anaesthetic circuit through pipes.
This is better to deal with larger caseloads.
It has 2 cylinders - one is a reserve
This is better to deal with larger caseloads.
It has 2 cylinders - one is a reserve
40
New cards
Cylinder yoke
Attachment point for cylinders of oxygen, nitrous, etc.
These are specific, preventing the wrong cylinder being attached.
These are specific, preventing the wrong cylinder being attached.

41
New cards
Bodok seal
Non-combustible copper ring that ensures a gas-tight seal between the cylinder and yoke

42
New cards
Pin index safety system
Each cylinder has 2 pins, which align with 2 holes on the yoke, like a lock/key mechanism. This prevents the wrong cylinder being attached.
There are 6 potential pin locations
There are 6 potential pin locations
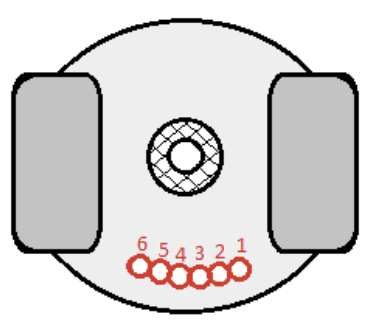
43
New cards
Schrader sockets
Sockets for probes to attach to, allowing for pipeline oxygen access.

44
New cards
Schrader probe
Unique end to each type of pipeline. These fit into their type of socket, preventing transmission of the wrong type of gas.

45
New cards
Hypoxic guards
A feature on some anaesthetic machines that link the Oxygen with Nitrous, maintaining the minimum ratio, and preventing delivery of hypoxic gases.
46
New cards
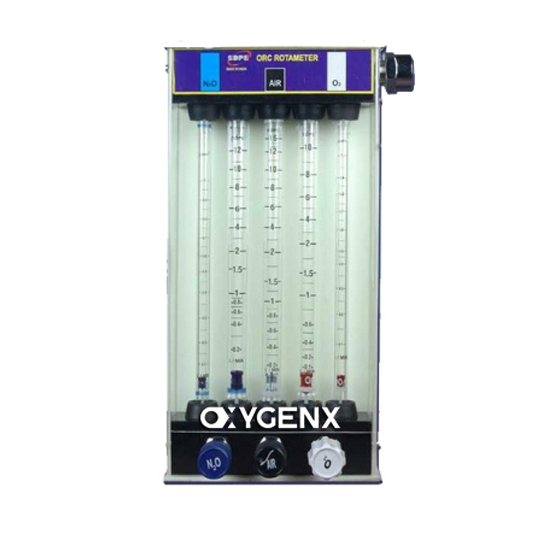
Flowmeters
Measure the flow of gas with an accuracy of +/-2.5%.
Consist of the flow control valve, tapered transparent tube, and lightweight rotating bobbin/ball
Consist of the flow control valve, tapered transparent tube, and lightweight rotating bobbin/ball

47
New cards
Flow control valve
The knob of the flowmeter that is used to control flow of gas

48
New cards
Tapered transparent tube
The tubes of the flowmeter

49
New cards
Lightweight rotating bobbin/ball
Component of the flowmeter that tells us the volume of each gas being delivered.
Read the bobbin from the top.
Read the ball from the middle
Read the bobbin from the top.
Read the ball from the middle

50
New cards
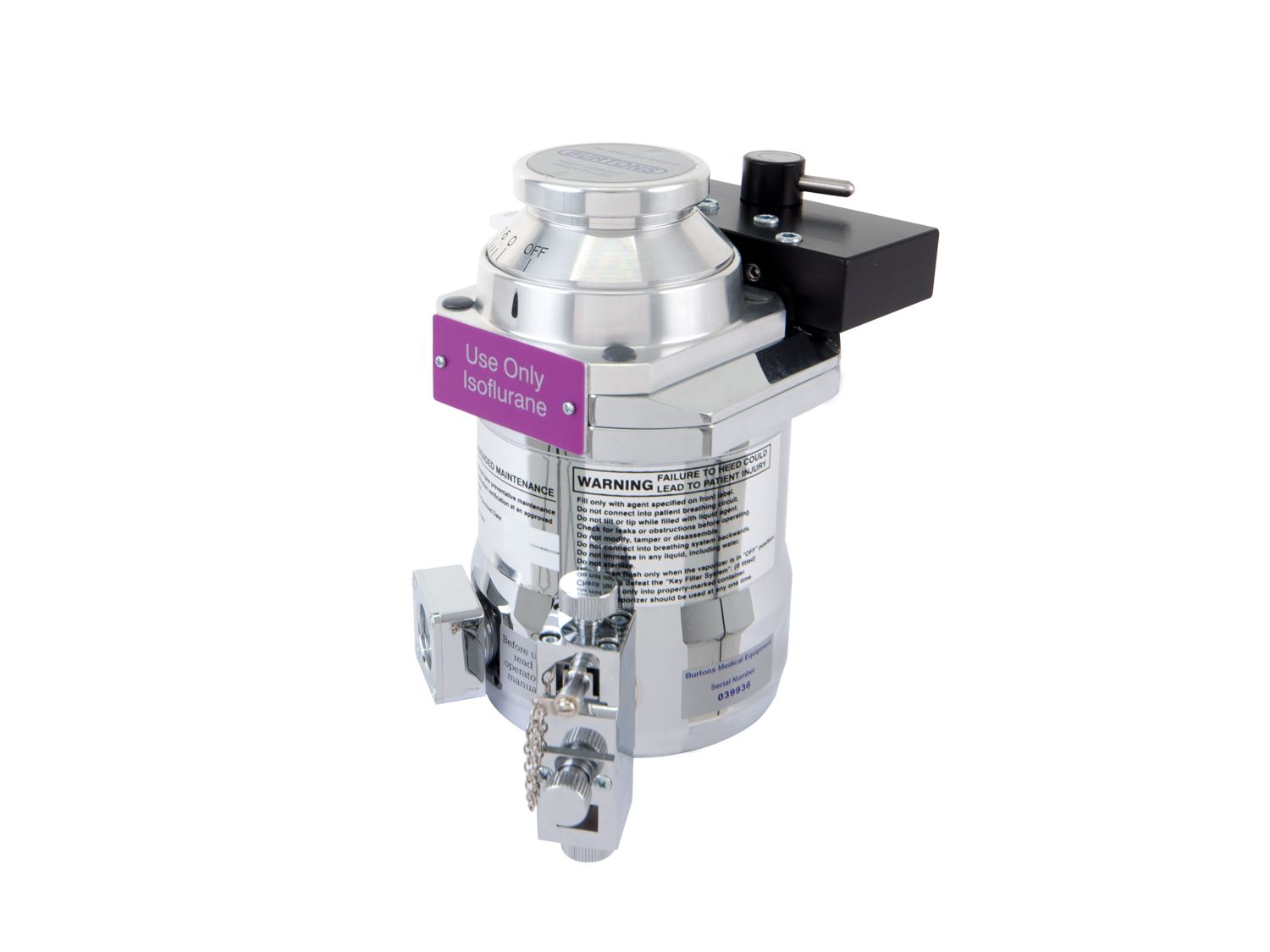
Vaporiser
Component of the anaesthetic machine containing liquid anaesthetic agent. Gases from the flowmeter flow through and pick up vapour, delivering it to the patient.

51
New cards
Back bar
Where the vaporiser attaches to the anaesthetic machine
52
New cards
Wicks
Part of the vaporiser that increases SA for anaesthetic liquid evaporation
53
New cards
Baffles
Part of the vaporiser that directs the FGF closer to the anaesthetic liquid surface.
54
New cards
Common gas outlet
Where we attach the inspiratory limb to receive FGF.
55
New cards
Oxygen flush button
Button near the common gas outlet that supplies oxygen really fast, bypassing the flowmeters and vaporiser.
400kPa - So can cause barotrauma.
400kPa - So can cause barotrauma.
56
New cards
Active scavenging
Scavenging using a fan and vent system to suck waste gases out of the building.
57
New cards
Air break
Component of active scavenging that prevents negative pressure sucking the patients lungs and FGF.
58
New cards
Passive scavenging
Scavenging where the patients expiratory effort pushes waste gases into tubing to either:
* Outside
* Into activated charcoal container (doesn’t absorb nitrous)
* Outside
* Into activated charcoal container (doesn’t absorb nitrous)
59
New cards
Oxygen concentrators
Machines that purify normal room air to supply oxygen to patients
60
New cards
Dead space
Volume of gas that does not eliminate CO2
61
New cards
Tidal volume
Volume of gas entering the lungs per inspiration
62
New cards
Metabolic oxygen requirement
Amount of oxygen required to carry out metabolic processes
63
New cards
Rebreathing
When inspired gases reaching the alveoli contain more CO2 than accounted for by mere re-inhalation from dead space gases
64
New cards
Coaxial
Tube within a tube
65
New cards
T-piece
Non-rebreathing system for
66
New cards
Bain
Non-rebreathing system for >8-10kg
Circuit factor 2-3
Circuit factor 2-3
67
New cards
Parallel lack
Non-rebreathing system for >10kg
Circuit factor 0.8-1
Circuit factor 0.8-1
68
New cards
Magill
Non-rebreathing system for >5kg
Circuit factor 1
Circuit factor 1
69
New cards
Minimum alveolar concentration (MAC)
Effective dose of volatile agent to prevent a noxious stimuli response in 50% of the population
70
New cards
Volatile agent
Liquid that changes to vapour at room temperature
71
New cards
Second gas effect
The concept that if volatile agent is given with N20, N20 quickly diffuses into capillaries, resulting in a high alveolar concentration of volatile gas.
72
New cards
Stage 1
Time of induction to unconsciousness.
* Breath holding
* High HR and RR
* Dilating pupils
* Breath holding
* High HR and RR
* Dilating pupils
73
New cards
Stage 2
Rhythmic breathing returns under unconsciousness
* Hyperactive cranial nerve reflexes
* Hyperactive cranial nerve reflexes
74
New cards
Stage 3: Plane 1
* Regular deep inspiration
* Absent limb movement
* May have brisk pinch reflex
* Ventromedial eyeball
* Absent limb movement
* May have brisk pinch reflex
* Ventromedial eyeball
75
New cards
Stage 3: Plane 2
* Absent palpebral reflex
* Relaxed muscles
* Ventromedial eye position
* Reduced tidal vol, RR, HR and BP
* Regular and deep inspiration
* Relaxed muscles
* Ventromedial eye position
* Reduced tidal vol, RR, HR and BP
* Regular and deep inspiration
76
New cards
Stage 3: Plane 3
* Central eyeball
* Increased pupil diameter
* Loss of pedal reflex
* Relaxation of abdo muscles
* Low BP + HR
* Increased pupil diameter
* Loss of pedal reflex
* Relaxation of abdo muscles
* Low BP + HR
77
New cards
Stage 4
* Progressive respiratory failure
* Rapid or v slow impalpable pulse
* Central eye
* No palpebral reflex
* Extended capillary refill time
* Accessory muscle twitching (e.g. twitching of throat)
* Rapid or v slow impalpable pulse
* Central eye
* No palpebral reflex
* Extended capillary refill time
* Accessory muscle twitching (e.g. twitching of throat)
78
New cards
Doppler unit
Microphone of a doppler set
79
New cards
Sphygmomanometer
Doppler puffer
80
New cards
Sidestream capnography
Capnography sample tube connects to the side of the breathing tube adapter
81
New cards
Mainstream capnography
Connecter between the Et tube and breathing tube, using an infrared light source and sensor to give real time CO2 activity, without sampling FGF.
82
New cards
Plethysmograph
The waveform trace given on some pulse oximeters
83
New cards
Low flow anaesthesia
A method of environmental anaesthesia, using a FGF of 0.5-1L/min. This often needs a circle system and high levels of training
84
New cards
Waste heirarchy
Classification of how we can dispose of different types of waste
85
New cards
Acepromazine
A mild sedation used for hoses.
30 minute onset
4-6 hour action.
Used in initial horse premed
30 minute onset
4-6 hour action.
Used in initial horse premed
86
New cards
Alpha2-adrenoreceptor agonists
Drug that relaxes horse muscles and provides analgesia to some degree
Used pre-GA in horses
Used pre-GA in horses
87
New cards
Diazepam
Induction agent (alternative to ketamine) used in horses.
Give as a bolus
Give as a bolus
88
New cards
Equine post-anaesthetic myopathy
Condition occurring in the post-GA recovery period where muscles harden and cause lameness
89
New cards
Convection
Heat transfer from the body → air
\
e.g. from cold air or draughts
\
e.g. from cold air or draughts
90
New cards
Conduction
Heat transfer from the body → surfaces
91
New cards
Radiation
Heat transfer from the body → structures not touching the patient
92
New cards
Moisture evaporation
Heat loss from the body from water loss from the body surfaces.
\
e.g. surgical scrub/alcohol evaporation, respiration, or an open body cavity.
\
e.g. surgical scrub/alcohol evaporation, respiration, or an open body cavity.