Invertebrates
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Animals are in what Domain and Kingdom?
Domain Eukarya, Kingdom Animalia.
What’s an invertebrate?
An animal without a backbone.
About how many animal species are there on Earth?
Roughly 1.5 to 2 million known species, with invertebrates making up over 95% of them.
What are Metazoa, Parazoa, and Eumetazoa?
Metazoa = All multicellular animals.
Parazoa = Animals without true tissues (like sponges).
Eumetazoa = Animals with true tissues (all others).
Why are sponges called “oddball animals”?
They lack true tissues and organs, are sessile filter-feeders, and reproduce sexually and asexually.
What’s unique about sponges relative to other animals?
They have no symmetry, no nervous system, and are the earliest branching animals.
How do we know sponges are older than comb jellies?
Molecular fossils like 24-isopropylcholestane (24-IPC) found in ancient rocks point to sponges as the first animals.
What’s the difference between a choanocyte and a choanoflagellate?
Choanocyte: A specialized sponge cell that filters food.
Choanoflagellate: A single-celled protist believed to be the closest living relative to animals.
What is a coral and why is it considered “two things”?
A coral is both an animal (polyp) and a symbiotic organism with algae (zooxanthellae).
Why are corals and jellies important?
They form reef ecosystems and are key indicators of ocean health.
What are stinging cells called?
Cnidocytes, which contain nematocysts used for defense and capturing prey.
Why are comb jellies NOT jellyfish?
They lack cnidocytes, have cilia for movement, and possess a complete gut.
How do Ctenophora (Comb Jellies) move?
With rows of cilia called ctenes, which diffract light and create a rainbow shimmer.
What are 2–3 important traits of flatworms?
Bilateral symmetry and cephalization.
No body cavity (acoelomate).
Many are parasitic (like tapeworms).

Why are flat worms important?
They help scientists study regeneration and evolution of organ systems.
What are 2–3 cool things about tardigrades?
They can survive extreme conditions (space, freezing, radiation).
They enter a state called cryptobiosis.
They have eight legs with claws.
Why is horseshoe crab “blood” harvested by humans?
Their hemolymph contains hemocyanin, used in biomedical research. Their blue blood contains Limulus Amebocyte Lysate (LAL), used to test vaccines and medical equipment for bacterial contamination.
What’s happening with Horseshoe natural populations?
Some are threatened by pollution and habitat loss.

What are the 3 main body parts of molluscs?
Foot, mantle, and visceral mass.
Why are molluscs important?
They’re vital to ecosystems and human food chains, and have evolved complex behaviors (e.g., octopus intelligence).
How did freshwater mussels evolve their lure display?
Through natural selection — their lures mimic prey to attract fish that help spread larvae.

Why are segmented worms important?
They aerate soil, recycle nutrients, and serve as food for many species.
Examples of segmented worms
Earthworms and leeches.

How many known species of arthropods exist?
Over 1 million (the largest animal phylum).
What are some examples of arthropods?
Insects, spiders, crabs, shrimp, centipedes.
Why are insects important?
Pollination, decomposition, and as a food source.
What’s special about insect flight?
It allows escape from predators, dispersal, and access to new food sources.
What’s up with mimicry in butterflies, bees, and hoverflies?
It’s a survival adaptation where harmless species mimic harmful ones (Batesian mimicry).
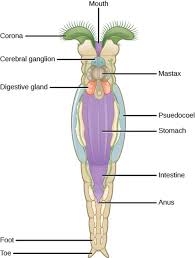
What are 2–3 facts about rotifers?
Have a crown of cilia (corona) that looks like spinning wheels.
Found in freshwater habitats.
Important as food for fish larvae.
Are rotifers on campus?
Yes, found in ponds and soil moisture.

2–3 facts about nematodes?
Round, unsegmented worms with a complete digestive tract.
Many are parasites of humans, animals, and plants.
Abundant in all soils.
Why are nematodes important?
They recycle nutrients and regulate populations of other organisms.
What’s the difference between protostomes and deuterostomes?
Protostomes: Mouth forms first (e.g., arthropods, molluscs).
Deuterostomes: Anus forms first (e.g., echinoderms, chordates).

2–3 traits of echinoderms?
Radial symmetry as adults, bilateral as larvae.
Water vascular system.
Calcareous endoskeleton.
Why are echinoderms important?
They maintain ocean floor ecosystems and are evolutionary relatives to humans (both deuterostomes).
How are echinoderms similar to humans?
Both share embryonic development patterns as deuterostomes.
Why isn’t the world covered in poop?
Because dung beetles like to collect it
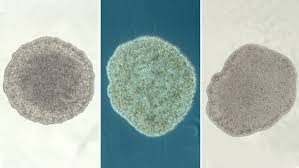
What are Placozoa?
Very simple, flat, multicellular animals lacking true tissues or organs.
Why don’t Placozoa fit neatly into animal phylogeny?
Their simplicity makes it unclear whether they evolved before or after more complex animals.
Why don’t biologists have all the answers?
Evolution is ongoing, and new molecular evidence can change phylogenetic relationships.