Memory- The working memory model AO1
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AO1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
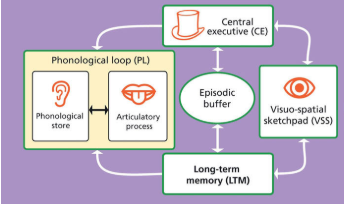
what is central executive?
The component of the WMM that co-ordinates the activities of the three subsystems in memory. It also allocates processing resources to those activities.
what is episodic buffer?
The component of the WMM that combines material from the other subsystems into a single memory rather than separate strands. It also provides a bridge between working memory and long-term memory.
what is phonological loop?
The component of the WMM that processes information in terms of sound. This includes both written and spoken material. It’s divided into the phonological store and the articulatory process.
what is visuo-spatial sketchpad ?
The component of the WMM that processes visual and spatial information, often called our ‘inner eye’.
what is the Working memory model ?
A representation of short-term memory (STM). It suggests that STM is a dynamic processor of different types of information using subcomponents co-ordinated by a central decision-making system.
What is the function of the Central Executive in the WMM?
Acts as a ‘supervisory’ system.
Monitors, focuses, and divides attention between tasks.
Allocates resources to the subsystems (PL, VSS, EB).
Has very limited capacity and does not store information.
What is the role of the Phonological Loop and its subcomponents?
Deals with acoustic (sound) information – both spoken and written.
Coding is acoustic.
Divided into:
Phonological Store: Holds words/sounds you hear.
Articulatory Process: Rehearses sounds/words (‘looping’) to keep them in STM.
Capacity: About two seconds’ worth of what can be said.
What is the function and structure of the Visuo-Spatial Sketchpad?
Stores and processes visual and spatial information (our ‘inner eye’).
Used for visualising layouts, objects, or spatial tasks (e.g., counting windows).
Has limited capacity – about three or four objects (Baddeley 2003).
Subdivided into:
Visual Cache: Stores visual data.
Inner Scribe: Records arrangement of objects in visual field.
What is the role of the Episodic Buffer in the WMM?
Added by Baddeley (2000) as a temporary store that integrates information from the PL, VSS, and LTM.
Combines information into episodes or sequences.
Provides a bridge between working memory and long-term memory (LTM).
Has a limited capacity but supports wider cognitive processes like perception and reasoning.
What does the Working Memory Model (WMM) explain?
The WMM (Baddeley and Hitch, 1974) is an explanation of how one aspect of memory (short-term memory) is organised and how it functions.
It is concerned with the ‘mental space’ that is active when we are temporarily storing and manipulating information (e.g., doing maths or understanding language).
The model suggests that STM is not just one store, but consists of several components that differ in coding and capacity.
These components work together while we are performing tasks that require immediate memory and processing.
WMM