RTS - Infections
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What characterises impetigo, treatable via Pharmacy 1st Guidelines?
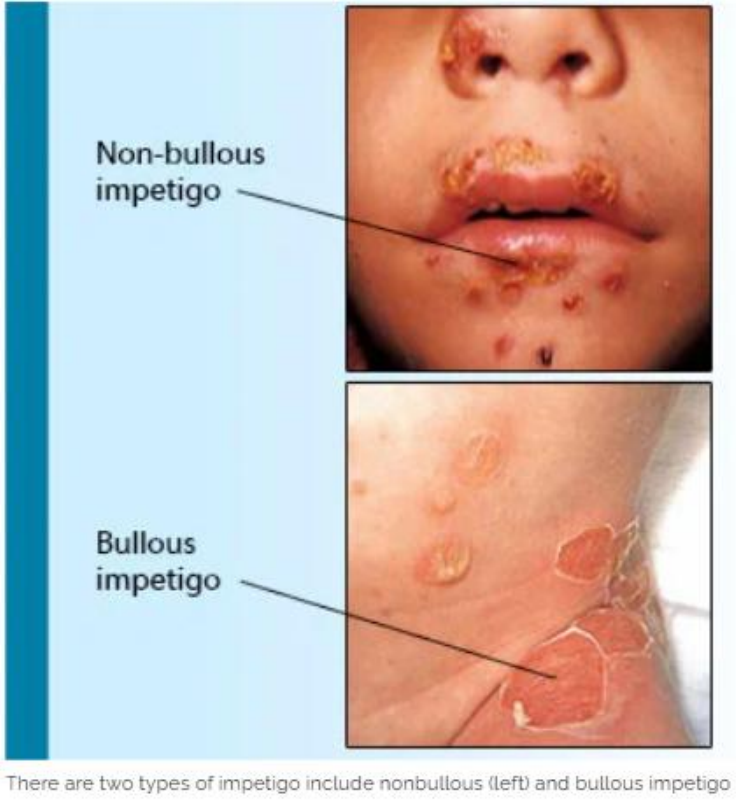
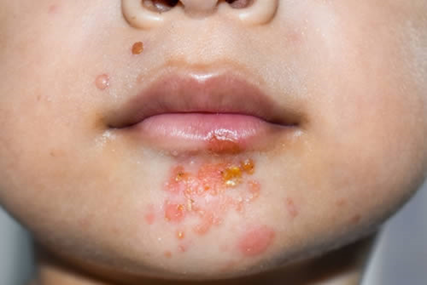
Non-bullous
Thin-walled, reddish vesicles that rupture easily
Forming golden/brown crusts
Typically around the mouth, nose, or limbs
—
For adults or anyone over 1 year
What is the Pharmacy First clinical pathway for impetigo?
Treats non-bullous impetigo
In adults or children over 1 year
With 3 or FEWER lesions
What are the exclusion criteria for treating impetigo under Pharmacy First?
Bullous impetigo
Recurrent episodes (>2)
Pregnant patients under 16 years.
More than 3 lesions!
What is the first-line treatment for localized non-bullous impetigo (3 or fewer lesions)?
Topical hydrogen peroxide 1% cream
Applied BD/TDS for 5 days
What is the second-line treatment for localized non-bullous impetigo?
Topical fusidic acid 2%
Applied TDS for 5 days.
What is the first-line treatment for widespread non-bullous impetigo?
Flucloxacillin QDS for 5 days
[500mg QDS] → As per PGD for dose, strength, and formulation.
What are alternative treatments for widespread non-bullous impetigo in case of penicillin allergy or pregnancy?
Contraindications:
Penicillin allergy: Clarithromycin BD for 5 days
or
Pregnant: Erythromycin QDS for 5 days
When should bullous or severe impetigo be treated, and how?
Refer for oral antibiotics (e.g., flucloxacillin, clarithromycin, erythromycin) per BNF guidelines
As it is not under Pharmacy First.
What are the types of conjunctivitis?
Infective (bacterial or viral)
Allergic (seasonal, perennial, contact, giant papillary)
Irritant (e.g., smoke, chlorine)
What questions should be asked to assess conjunctivitis?
Ask about:
Contact lens use
Visual disturbance
Pain
Immunocompromised status
Fever/nausea (glaucoma)
Other eye problems, or associated trauma
What are the characteristics of bacterial conjunctivitis?
Mucopurulent discharge which is yellow sticky
Affecting eyelashes, sticky and causing discomfort
—
Caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae / Staphylococcus aureus / Haemophilus influenzae
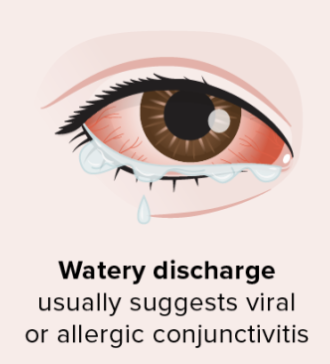
What are the characteristics of viral conjunctivitis?
Watery discharge
Red / Sore / Burning / Gritty / Swollen eyes
Often contagious → Starting in one eye and spreading to both
Why is conjunctivitis called "pink eye" in America?
Due to the red or pink appearance of the eyes caused by inflammation.
How long is conjunctivitis typically self-limiting, and why do patients seek treatment?
Self-limiting in 5-7 days
But patients seek treatment due to irritation.
How is conjunctivitis transmitted?
Through direct or indirect contact
Such as sharing towels or makeup products.
When should conjunctivitis be referred to a GP or A&E?
REFERRAL FOR:
Pain / Photophobia / Disturbed vision / Acute glaucoma / Recent eye surgery / Children under 2 / Pregnant or breastfeeding / Corneal abrasion / Foreign body / Recurrent cases / Keratitis / STIs / OTC treatment failure / Complications like meningitis or neonatal conjunctivitis
Why should conjunctivitis eye drops be discarded after 28 days?
Decreased stability of medication
Preservatives may degrade
Increasing infection risk if reused
What is a stye, and how is it characterized?
A small, painful pimple or boil with pus on or in the eyelid
Usually self-limiting
How should a stye be treated?
Apply a warm compress
Use paracetamol or ibuprofen for pain relief
When should a stye be referred for further treatment?
If it persists over a few weeks
or
Feels very hard
—
Can refer for possible surgical removal
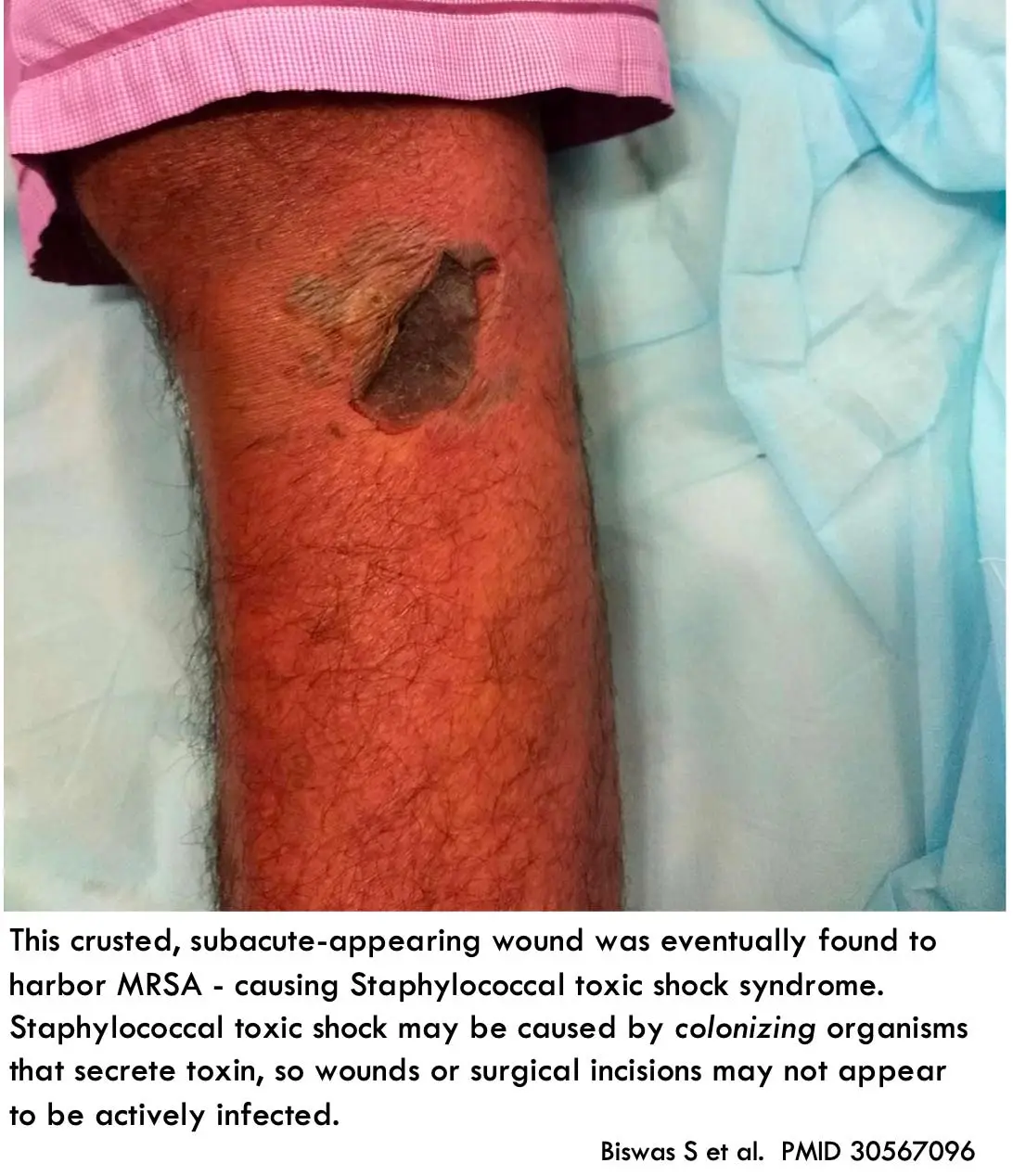
What is toxic shock syndrome, and what causes it?
A rare, life-threatening condition caused by Staphylococcus aureus, caused by an infection. It can happen when using a tampon or menstrual cup, or from an infected wound.
Symptoms include:
a high temperature
muscle aches
a raised skin rash that feels like sandpaper
flu-like symptoms
What are the risk factors for toxic shock syndrome?
Tampon use (especially high-absorbency or infrequent changes)
Female barrier contraceptives
Post-surgical wound infections
What are the symptoms of toxic shock syndrome?
Symptoms of Streptococcal Infection:
Skin peeling (especially on palms and soles)
Red eyes, lips, or tongue / Sunburn-like rash
Sudden high fever (>38.9°C) / Flu-like symptoms / Nausea and/or vomiting
Hypotension / Fainting / Dizziness / Confusion
Diarrhoea
How can the risk of toxic shock syndrome be reduced through education?
Sanitation to REDUCE RISK of infection regarding TAMPONS:
Wash hands before and after tampon insertion
Use the lowest absorbency tampon needed
Alternate tampons with sanitary towels when possible
Change tampons frequently (every 4–8 hours)
Use only one tampon at a time
Insert a fresh tampon before bed and remove it as soon as you wake up
Remove the tampon at the end of your period