Cardiac conduction and Sudden Cardiac Death
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
what is the formula for stroke volume
HR x stroke vol
automaticity
ability to initiate an impulse spontaneously and continuously
excitability
ability to be electrically stimulated
conductivity
ability to be able to transmit an impulse along a membrane
contractility
ability to respond mechanically to an impulse
what is the normal rate for SA node
60-100
what is the normal for the AV node
40-60
what is the rate of the bundle of his and purkenje fibers
20-40
what is artifact caused by
leads not firmly placed or electrical interference from an outside source
muscle tremors
shivering
convulsions
strong respiratory movements
strong muscle movements
if the tele monitor is displaying a concerning heart ryththym what should be done first
check the patient
check the leads
what are the cardiac causes of dysrythmias
accessory pathways
cardiomyopathy
conduction defects
heart failure
MI
valve disease
non cardiac causes of dysrythmias
acid-base imbalances
alcohol, caffeine, tobacco
connective tissue disorder
drug effects
electric shock
electrolyte imbalances
emotional crises
herbal supplements
hypoxia
shock
metabolic conditions
near drowning
poisoning
diagnostic studies for dysrythmias
electrophysiology test
cardiac stress test
holter monitor
electrophysiology test
done in the cath lab
maps dysrythmias
like an in depth ECG
looks at the electrical mapping
cardiac stress test
done on a treadmill or a bike to see how the heart responds under stress
what 2 things stop the stress test
chest pain
EKG changes
what should be held before a stress test
beta blockers because you want to see what the pt’s heart does in response to stress
if a patient is unable to do the stress test what is given to get their heart racing
adenosine
holter monitor
worn for 30 days with a journal to accompany it
some can be under the skin
normal sinus rythym
60-100 bpm
regular rate and rythm
sinus bradycardia
less than 60bpm
regular rate and rythm
symptomatic vs asymptomatic bradycardia
some people have heart rates that are less than 60 bpm and that is normal for them and it does not need to be treated. If the person is experiencing sx such as
SOB
dizziness/lightheadedness
decreased LOC
that needs to be treated
what is the tx for symptomatic bradycardia
atropine
temporary pacemaker
permanent pacemaker
when can you move your arm on the side of the body that has the pacemaker
sinus tachycardia
HR over 100bpm-180bpm
regular rate and rythm
what are the causes of tachycardia
pain
excersise
fever
anemia
dehydration
anxiety
sepsis
HF
MI
PE
stimulant use
treatment for sinus tachy
treat the underlying cause
antipyretics
analgesics
fluids
blood products
avoiding caffeine or nicotine
relaxation techniques
PSVT
100-300bpm
usually cannot see the p wave
usually regular
what is the tx for PSVT
1 vagal maneuvers
2 adenosine
3 cardioversion
what are vagal maneuvers
coughing
squatting
breath-holding
ice on face
what are some considerations with vagal maneuvers
should not be done for more than 10 seconds
make sure oxygen, suction, a defib, and emergency meds are available
continuous ECG
do not use external ocular pressure
carotid massage is not reccomended
considerations for administering adenosine
want to have both the adenosine and a flush ready because as soon as the adenosine is administered the flush needs to be immediately pushed
adenosine is a bronchodilator so it may cause coughing, dyspnea, and bronchospasms
who should avoid adenosine and why
people with severe asthma because it is a mild bronchodilator
what is cardioversion
lower energy levels than the defib
medical procedure that needs consent
synchronized with the R wave
what does a pt need to prepare for a cardioversion
informed consent
recent ECG
18g IV with fluids
oxygen
sedation
NPO 6-8 hrs before the procedure
atrial fibrillation
irregular rate and rythym
many little bumps between QRS waves
what medication are people on that have a-fib
coumadin or eliquis
to avoid blood clots
bc blood pools in the atria
what to do before a cardioversion
blood thinners and TEE
be careful with an a-fib patient because blood is pooling and they have a high risk for clots
a-fib with RVR
over 100bpm
irregular rate and rythym
what is the first thing you want to do with a-fib with RVR
control the rate with calcium channel blockers and beta blockers
signs and sx of afib and flutter
palpitations
weakness
dizziness
SOB
atrial flutter
sawtooth rythm
what are the tx for afib and aflutter
calcium channel blockers
cardioversion
cardiac ablation
what medications are used for afib and flutter
calcium channel blockers
beta blockers
antiarrythmics
antiplatelet aggregators
anticoagulants
cardiac ablation
destroy signals in the heart to get rid of multiple foci
patient teaching for pacemakers
know what kind of pacemaker you have
let all health care providers know about your pacemaker
wear a medical bracelet or necklace for emergencies
stay away from strong electrical devices
it is okay to be active but avoid contact sports
get the pacemaker checked regularly to make sure it is working properly
what does a pacemaker look like on a pacemaker strip
spikes then the p-wave (atrial)
spikes then the QRS (vetnricular)
failure to capture
pacemaker goes off but the ventricles did not contract and there is no QRS
failure to sense
when the pacemaker goes off at random times
vtach
very fast heart rythm
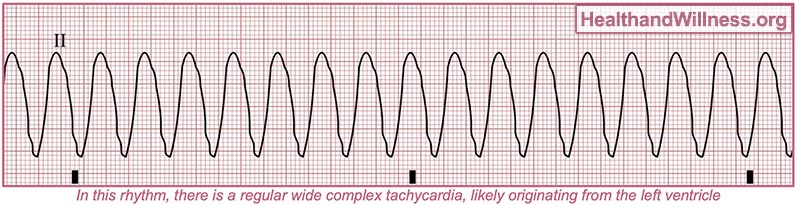
what is the special thing about vtach
can occur with or without a pulse
if there is no pulse with vtach what do you do
defib
what are the causes of vtach
coronary artery disease
cardiomyopathy
what can vtach lead to
vfib
vfib
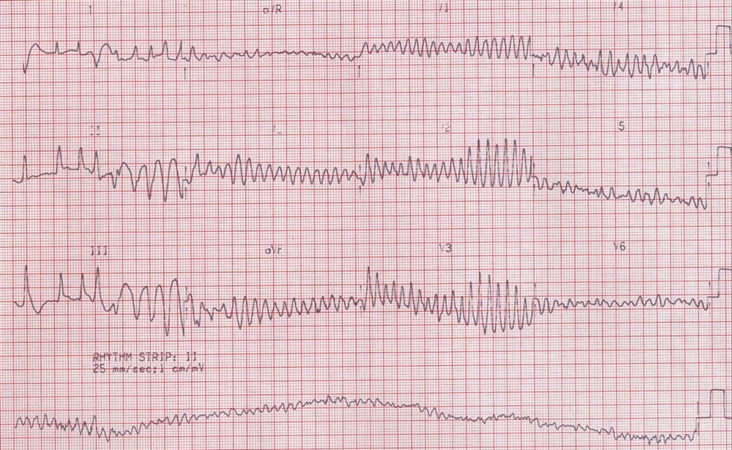
asystole
no movement on the strip
PEA
normal activity is on the strip but the pt has no pulse
what are the causes of PEA
6 H’s
hypovolemia
hypoxia
acidosis
hypo/hyperkalemia
hypoglycemia
hypothermia
5 T’s
toxins
tamponade
tension pneumothorax
thrombosis
trauma
what is sudden cardiac death caused by
vfib and vtach
what is TTM
targeted temperature management
preserves neuro function after cardiac death
do not rewarm the pt too fast becuase it can cause seizures
ICD
implantable cardioverter defib
monitors and corrects dangerous heart rythms (vfib and vtach)
how can you tell the difference between vtach and vfib
vtach is regular and vfib is irregular
p wave
atrial contraction
systole
atrial depolarization
PR interval
the time it takes for the electrical impulse to travel from the atrium to the ventricles
QRS
ventricles contracting
systole
ventricular depolarization
ST
time it takes to go from depol to repol
systole to diastole
T wave
total repolarization
diastole
autonomy
having the ability to make decisions for onesself
beneficence
going out of one’s way to do an act of kindness
nonmaleficence
avoiding causing harm to others
justice
fairness and equality
veracity
truthfullness or accuracy
delerium
can be hypoactive or hyperactive
treated with haloperidol and atypical antipsychotics
frequently reorient the patient first
DT
complication of alcohol withdrawal that is treated with lorazepam and diazepam
where does cardioversion. sync and where does it not want to sync
R wave
T wave causes scd
tx for PSVT
vagal
adenosine
cardioversion
RVR
calcium channel blocker
cardiovert
cardiac ablation
vtach causes
CAD
cardiomyopathy
SCD
gravestones
what is special about vtach
can have a pulse or no pulse
vtach with pulse
give drugs
CPR
vfib
never has a pulse
vtach without pulse
defib
CPR
drugs
what do you do i
vfib
defib
compressions
meds
asystole
CPR
drugs
not shockable
PEA
looks normal on the strip and then has no pulse
tx for PEA
find the cause
CPR
meds
not shockable
SCD
vfib and vtach
TTM
after SCD to prevserve neuro function
ICD
personal defibilator for someone that is at high risk for SCD
when adenosne is given what happened
a short period of asystole