Schools of Thought
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
School of Thought
set of ideas and views common to a group of people
share similar beliefs and ideologies, similar reaserch methods
Father of Psychology
Windhelm Wundt at the University of Leipzig
Structuralism Contributors and Date
1879
Germany and US
Wilhelm Wundt and Edward Titchner
Structuralism
sought to breakdown consciousness in its most basic form - measure atoms of the mind
consciousness is static
Introspection
students would offer detailed self-reports of reactions to various stimuli,
mind could be measured
Criticism of Structuralism
poor reliability
subjective methods
reductionist, attempted to explain a complex phenomenon in simple terms
Functionalism Founder and Date
1890
USA
William James
Functionalism Theories
contents of the mind are constantly changing and consciousness is flowing
foucsed is on how and why an organism does something
influenced by Darwin’s Theory of Evolution, believed consciousness helped us adapt to our environment
Methods used by Functionalists
supplemented introspection with data from objective descriptions of behaviour
researched animal behaviour
Criticism of Functionalism
Consciousness is not directly observable
Psychoanalysis Founders and Date
1902
Vienna
Sigmund Freud
Theories of Psychoanalysis
man is born with strong animal like urges such as sex and aggression
these are rejected by society and are repressed in the first 5 years of our lives
FORMS THE UNCONSCIOUS
Unconscious is a collection of urges, thoughts, memories and feelings which completely determine the way one acts
no such thing as a random thought feeling motive or behavior
early childhood experiences determine character, making events in early life responsible for what happens to a person in adult life.
Conscious vs Unconscious Mind
Conscious Mind | Unconscious Mind |
contains thoughts and feelings we are aware of | thoughts urges or feelings that are unpleasant/socially unacceptable |
not hidden or suppressed | buried - bring about pain or conflict |
influenced by unconscious thoughts feelings or memories | be brought into awareness using certain techniques |
Methods used in Psychoanalysis
Free Association or Talk Therapy
Dream Analysis and Inkblot tests to reveal unconscious beliefs (what you see in the test is a symbol of whats in ur unconscious)
Criticism of Psychoanalysis
doesnt focus on obersvable behaviour
cannot be scientifically proven nor disproven
based his conclusions about all human nature on his own recollection of childhood/patients and applying it to human race in general
Behaviourism Founders and Date
1913
Usa
John. B Watson, Ivan Pavlov and B.F Skinner
Behaviorism Theories
Classical and Operant Conditioning (discussed later)
studied overt behavior
what cannot be seen cannot be studied
we are all born as a ‘tabula' rasa’ everything we know is molded by environmental factors
rejects free will, we are a product of what we learn from experience
Methods of Behaviorism
experiments to understand the relationship between stimulus and response
Operant and Classical Conditioning, Little Albert Experiment
Criticism of Behaviorism
generalizing animal findings to human behavior
underestimates complexity of human emotions
unable to fully explain human behavior as it neglected mental processes
Humanism Founder and Dates
1960s
USA
contributors- Carl Rogers and Abraham Maslow
Theories of Humanism
Hierarchy of Needs, Unconditional Positive Regard
see humans as growing, generous healthy beings in control of their destiny
Rogers; belief in basic goodness of humans, believed in the power of free will and determination
Maslow; how people can fulfil themselves and become self actualized, humans are more than animals, theory hierarchy of needs
list hierarchy of needs to achieve self actualization
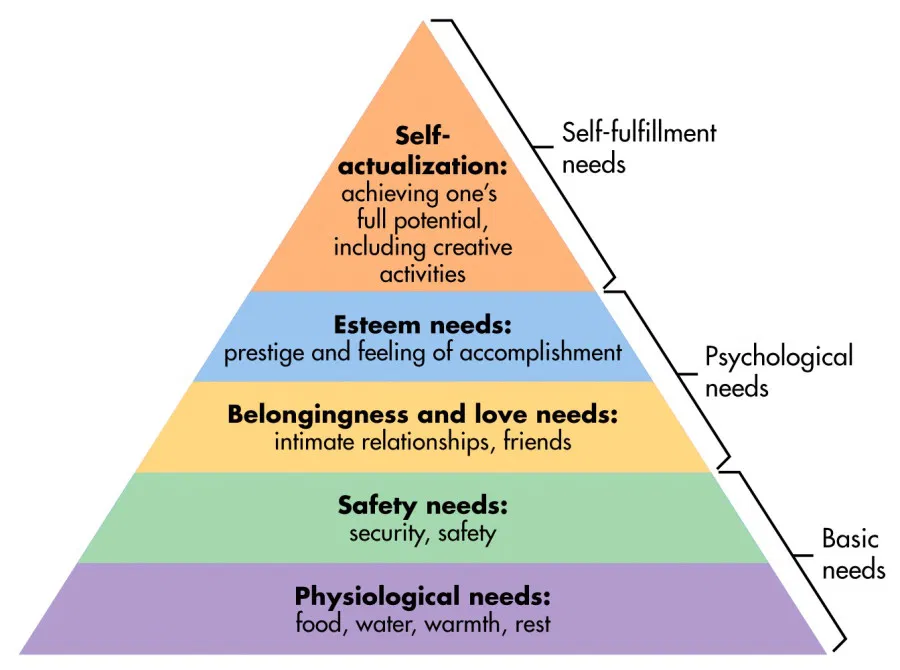
Where has humanism had its greatest impact
field of therapy
Criticism of Humanism
overly idealistic
ignores the complexities of human nature, such as the impact of social, cultural, or economic factors.
humanism doesn't pay enough attention to the darker sides of human behavior (like selfishness, violence, or greed), assuming that everyone will naturally strive to be their best.
Another criticism is that humanism can be too focused on individualism, which might neglect the importance of community or collective well-being.