Endocrine Glands & Hormones
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
anterior pituitary
the master gland; produces and secretes hormones that control that activity of other glands
posterior pituitary
this gland does not produce hormones, but stores and releases oxytocin and ADH.
thyroid gland
secretes thyroxine (T4), triiodothyronine (T3), calcitonin
parathyroid gland
produces parathyroid hormone (PTH)
adrenal cortex
secretes aldosterone and cortisol
adrenal medulla
secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine (NE)
pancreas
secretes insulin and glucagon
ovaries
secretes estrogen and progesterone
testes
secretes testosterone
pineal gland
secretes melatonin
thymus gland
secretes thymosin
hGH (human growth hormone)
stimulates secretion of hormones that stimulate body growth and metabolism
TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone)
stimulates growth of thyroid gland and secretions of its hormones
FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone)
stimulates sperm production; stimulates oocyte production and estrogen secretion
LH (luteinizing hormone)
stimulates secretion of testosterone; triggers ovulation and stimulates secretion of estrogen and progesterone
PRL (prolactin)
stimulates production and secretion of milk
ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone)
stimulates secretion of hormones by adrenal cortex
ADH (antidiuretic hormone)
decreases water loss in urine by returning water to the blood
OT (oxytocin)
stimulates uterine contractions and milk ejection during suckling
T4 (thyroxine)
increases metabolism and basal metabolic rate (BMR)
T3 (triiodothyronine)
increases metabolism and basal metabolic rate (BMR)
calcitonin
decreases blood calcium levels by inhibiting osteoclasts
PTH (parathyroid)
increases blood calcium levels by stimulating osteoclasts to break down bone matrix
aldosterone
decreases sodium and water loss in urine by returning sodium and water to the blood
cortisol
increases resistance to stress, increases blood glucose levels and decreases inflammation
epinephrine/ norepinephrine (NE)
promotes fight or flight response
insulin
decreases blood glucose levels by transporting glucose into body cells
glucagon
increases blood glucose by stimulating liver breakdown glycogen into glucose
estrogen/progesterone
stimulates development of female sex characteristics; helps regulate menstrual cycle
testosterone
stimulates development of male sex characteristics; stimulates male sex drive and regulates sperm production
melatonin
helps to set biological clock or circadian rhythm; regulates day and night cycle
thymosin
promotes the maturation of "T" cells for the immune response
hormones of the anterior pituitary
produces hGH, TSH, FSH, LH, PRL & ACTH
leptin
targets hypothalamus to signal satiety
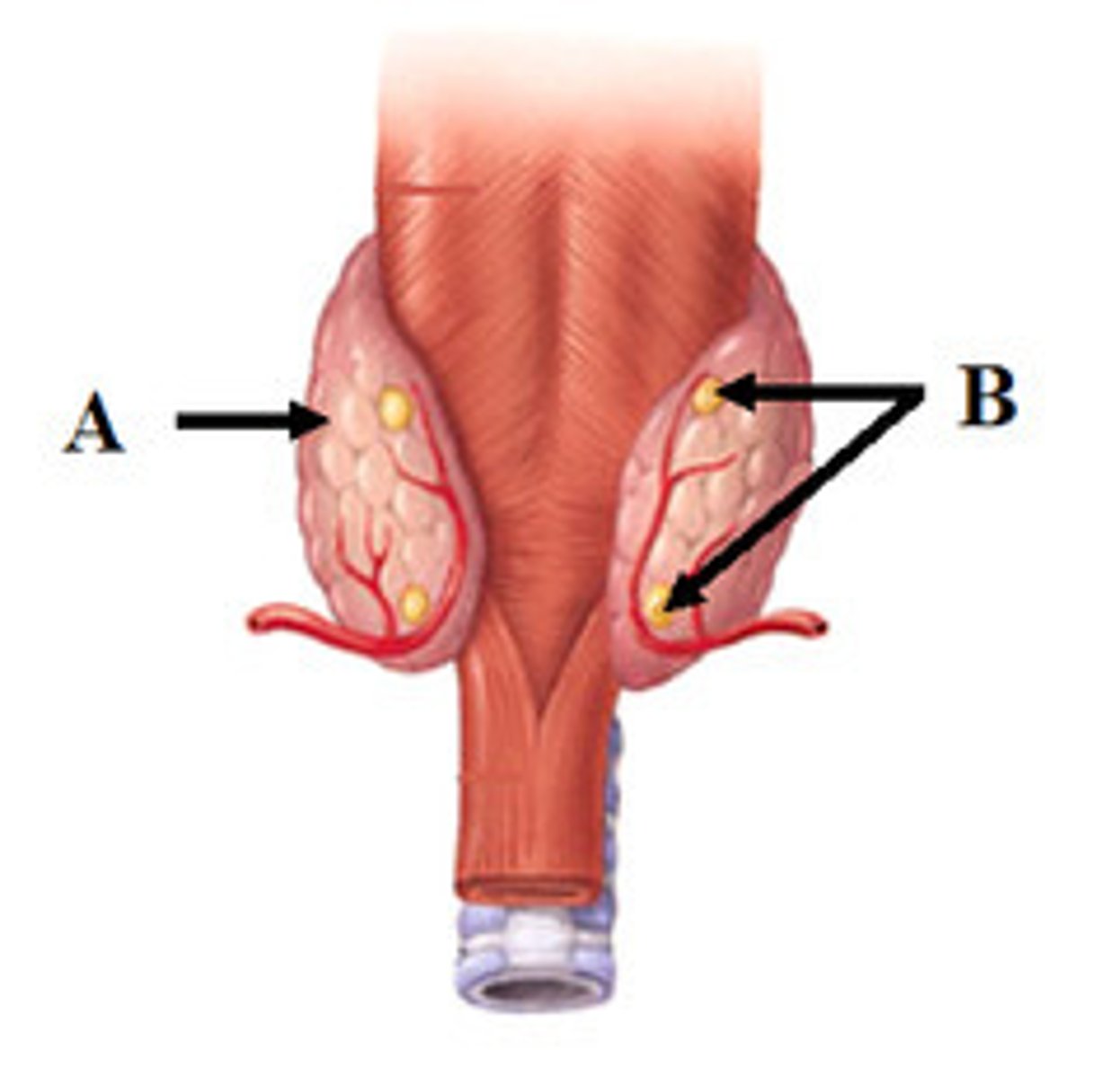
ovaries
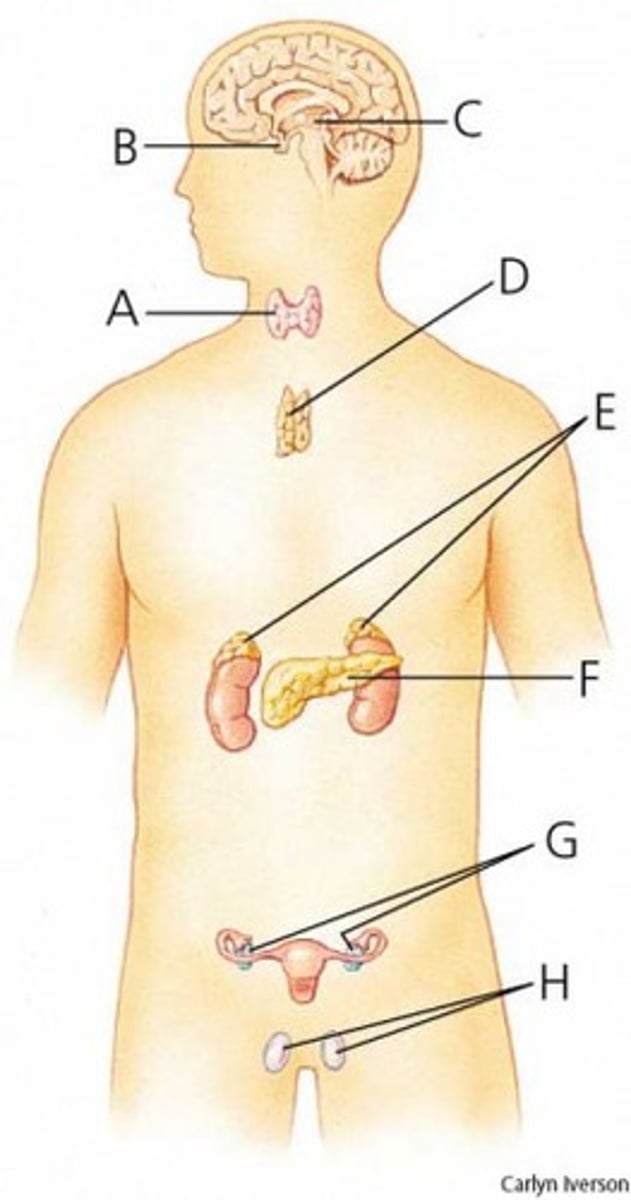
What is G?
testes
What is H?
adrenal glands
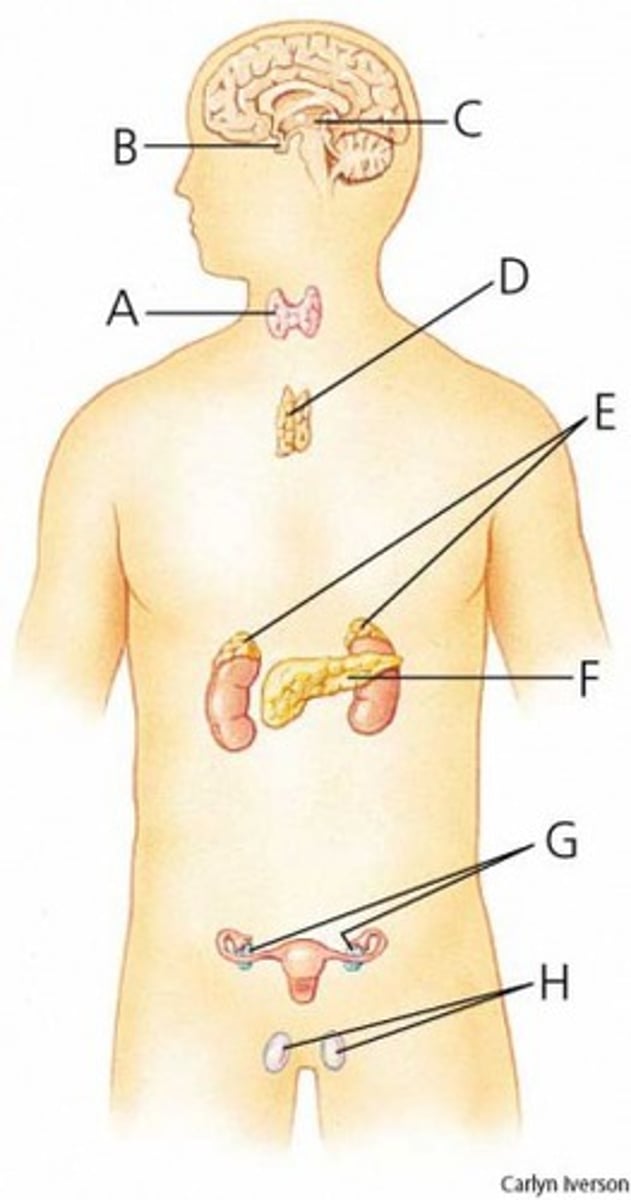
What is E?
pituitary gland
What is B?
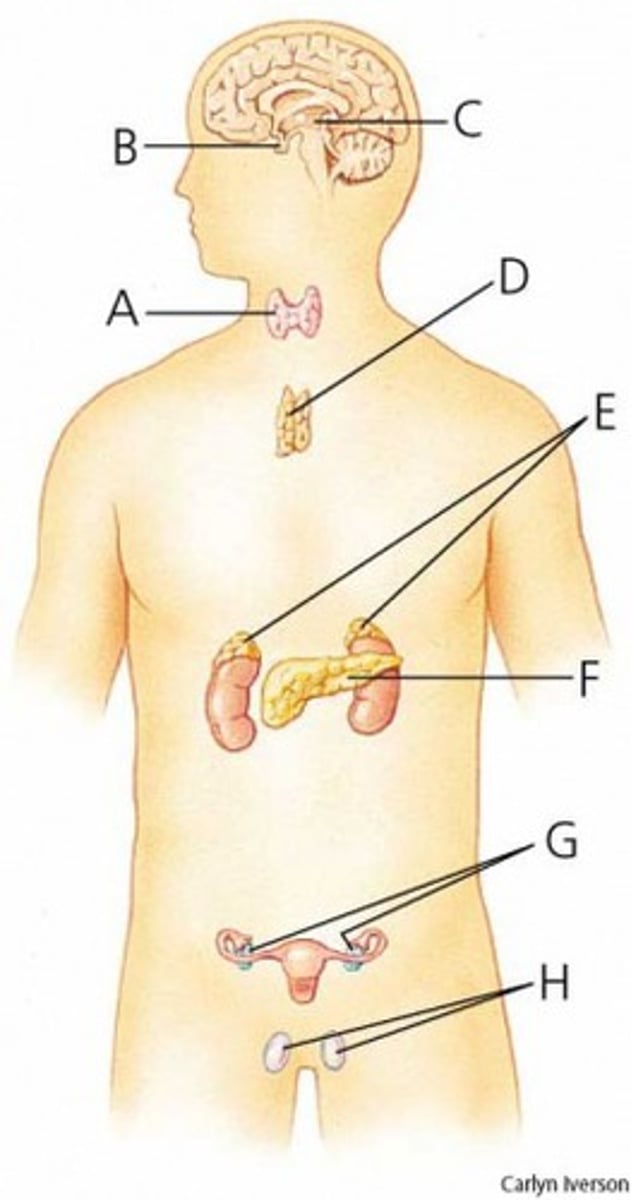
thymus
What is D?
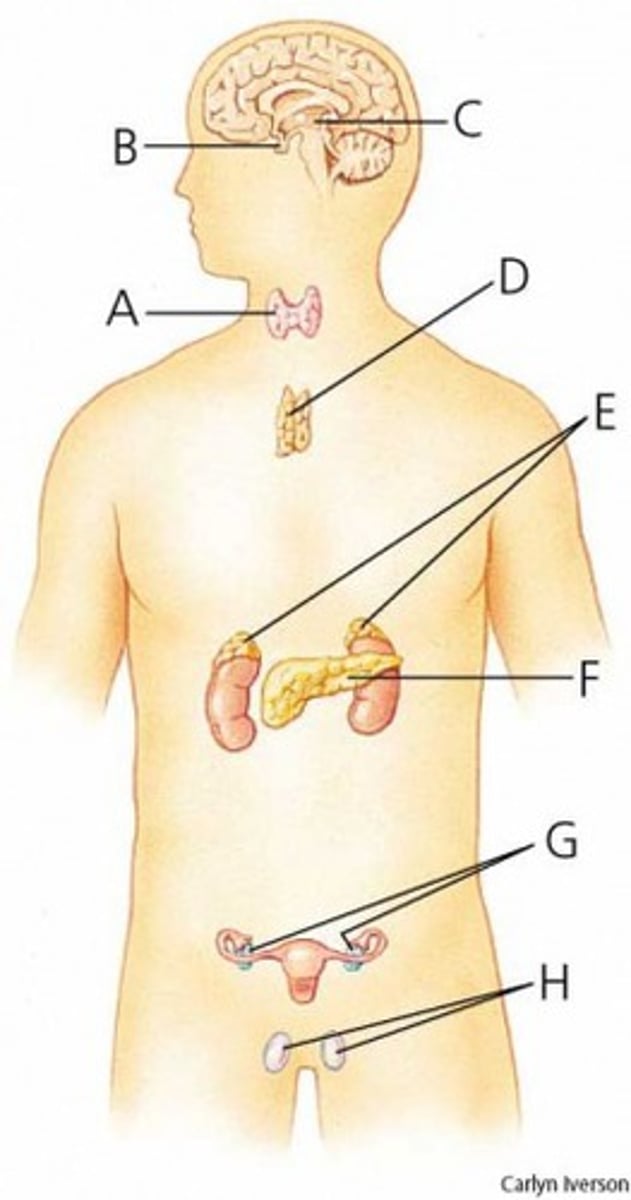
pancreas
What is F?
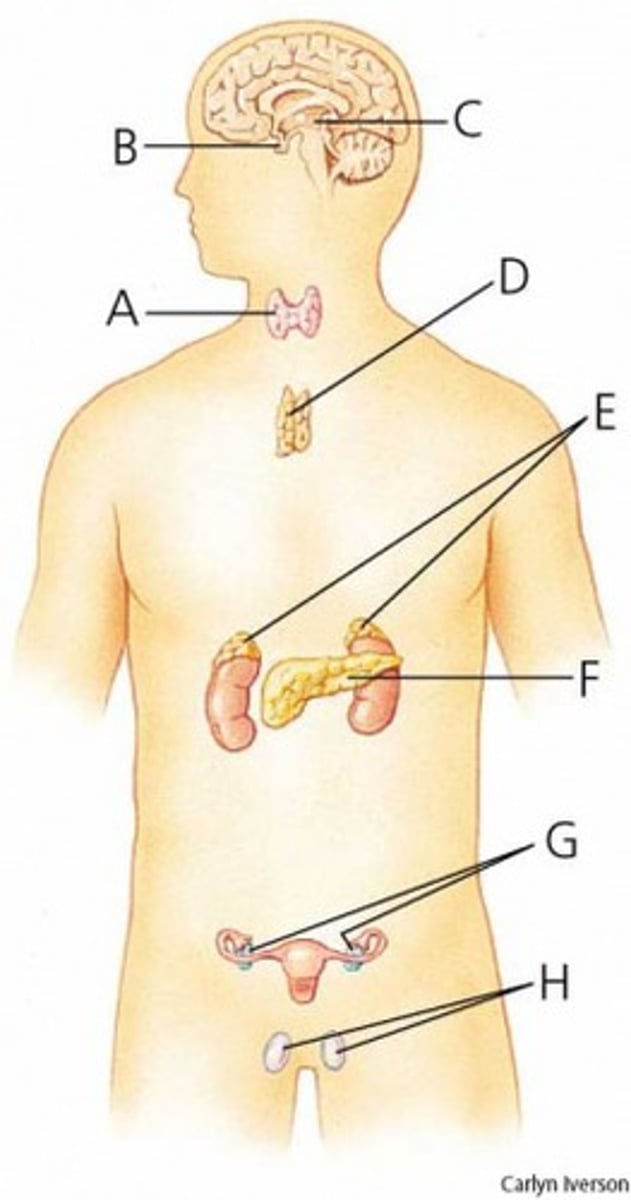
pineal gland
What is C?
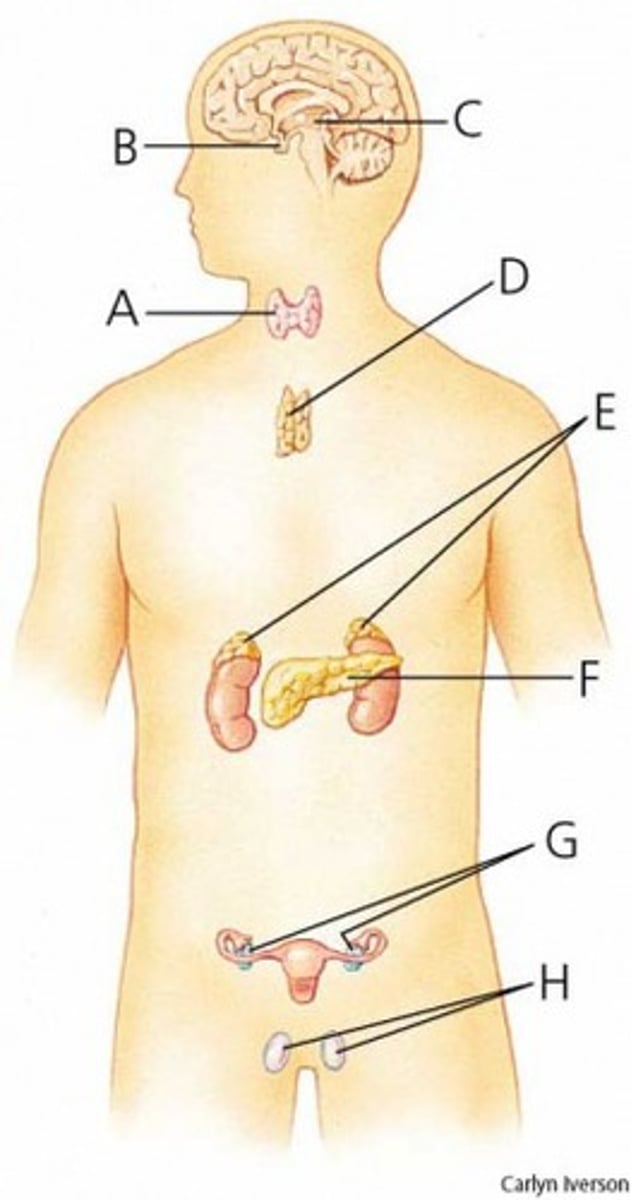
thyroid
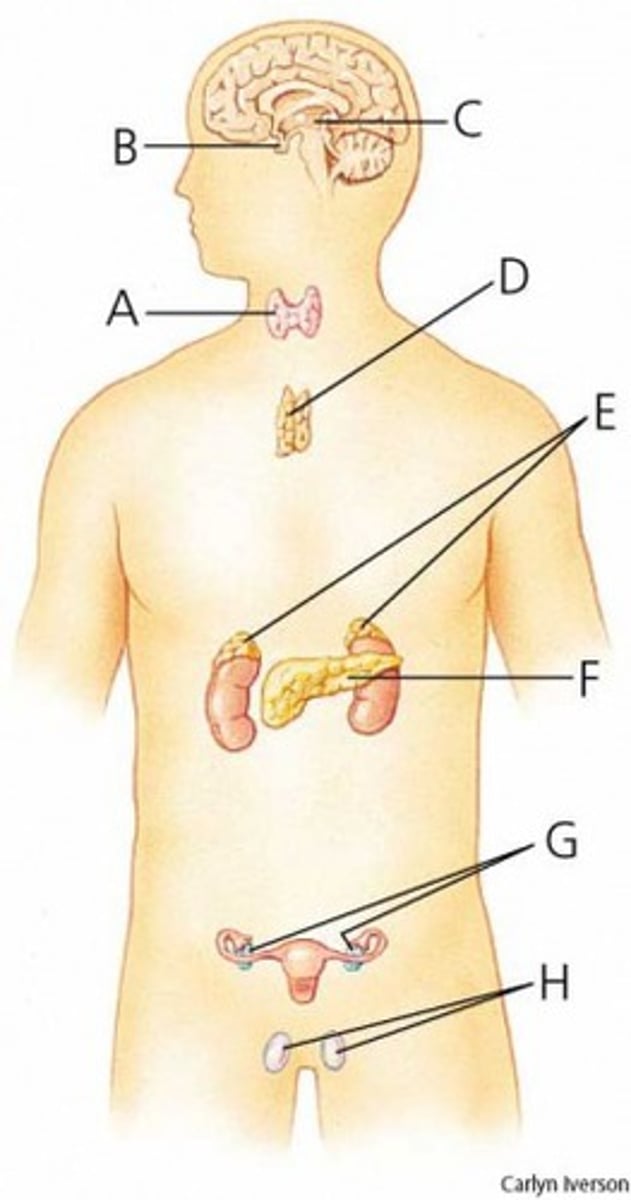
What is A?
thyroid
What is A?
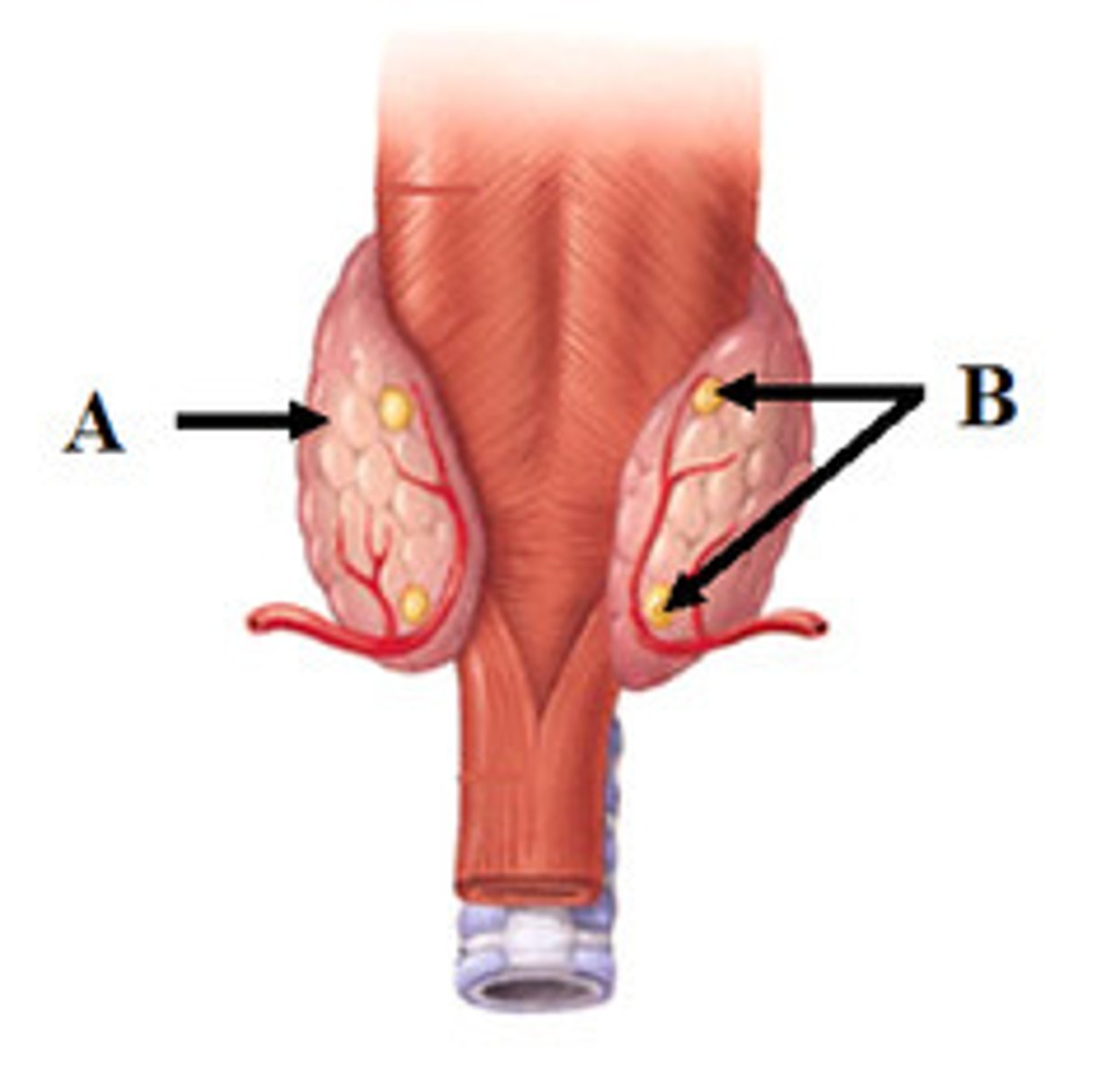
parathyroid
What is B?