Human Upper Limb Anatomy: Axilla, Brachial Plexus, Vasculature, Shoulder, Arm, Forearm, Wrist, and Hand
1/289
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
290 Terms
Axilla
Deep compartment of the armpit region, located inferior to the glenohumeral joint at the junction of the arm and thorax.
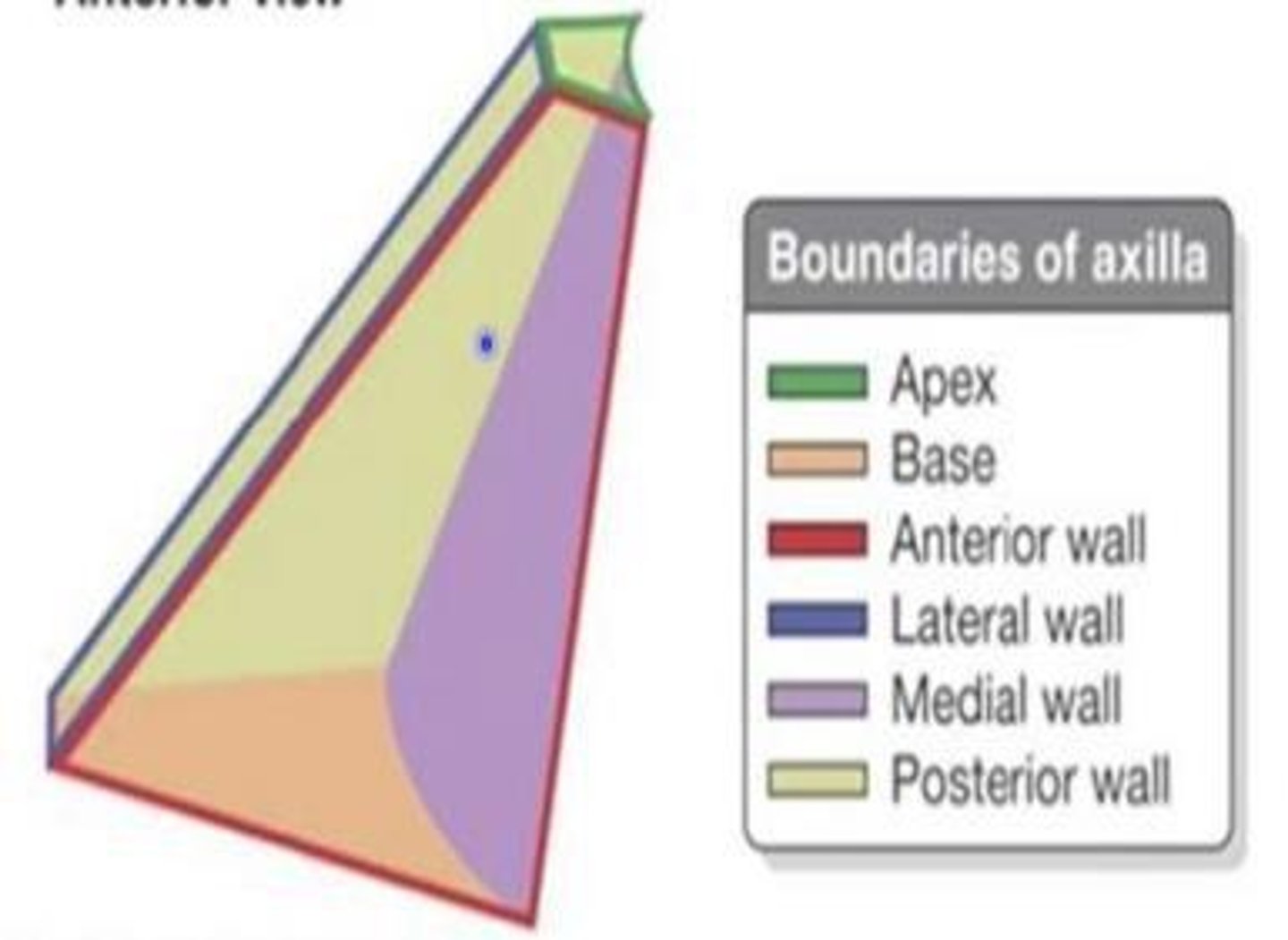
Apex of Axilla
Bordered by the clavicle anteriorly, scapular posteriorly, and the 1st rib; opening of the axilla for neurovascular structures.
Cervicoaxillary canal
The passageway for axillary vessels and brachial plexus components from neck to upper limb.
Base of Axilla
Bordered by skin, forming the 'armpit' we know.
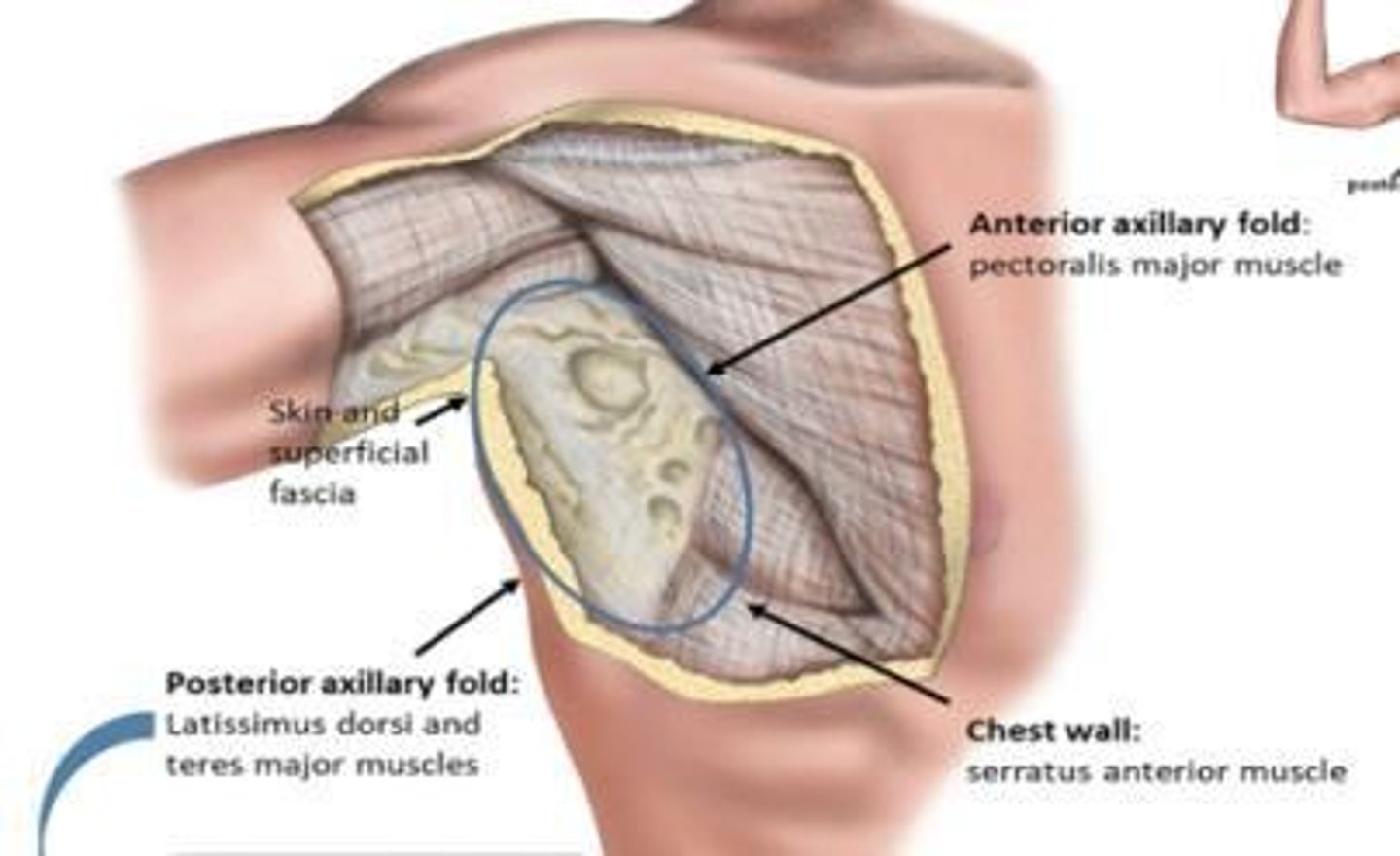
Anterior axillary fold
From the lateral border of pectoralis major.
Posterior axillary fold
From latissimus dorsi and teres major plus fat.
Chest wall
Medial border from serratus anterior muscle.
Anterior wall of Axilla
Formed by clavicle, subclavius muscle, pectoralis major, and minor.
Posterior wall of Axilla
Formed by scapula, subscapularis muscle, teres major, and latissimus dorsi.
Lateral wall of Axilla
Includes intertubercular sulcus/bicipital groove, tendon of long head of biceps, and coracobrachialis tendon.
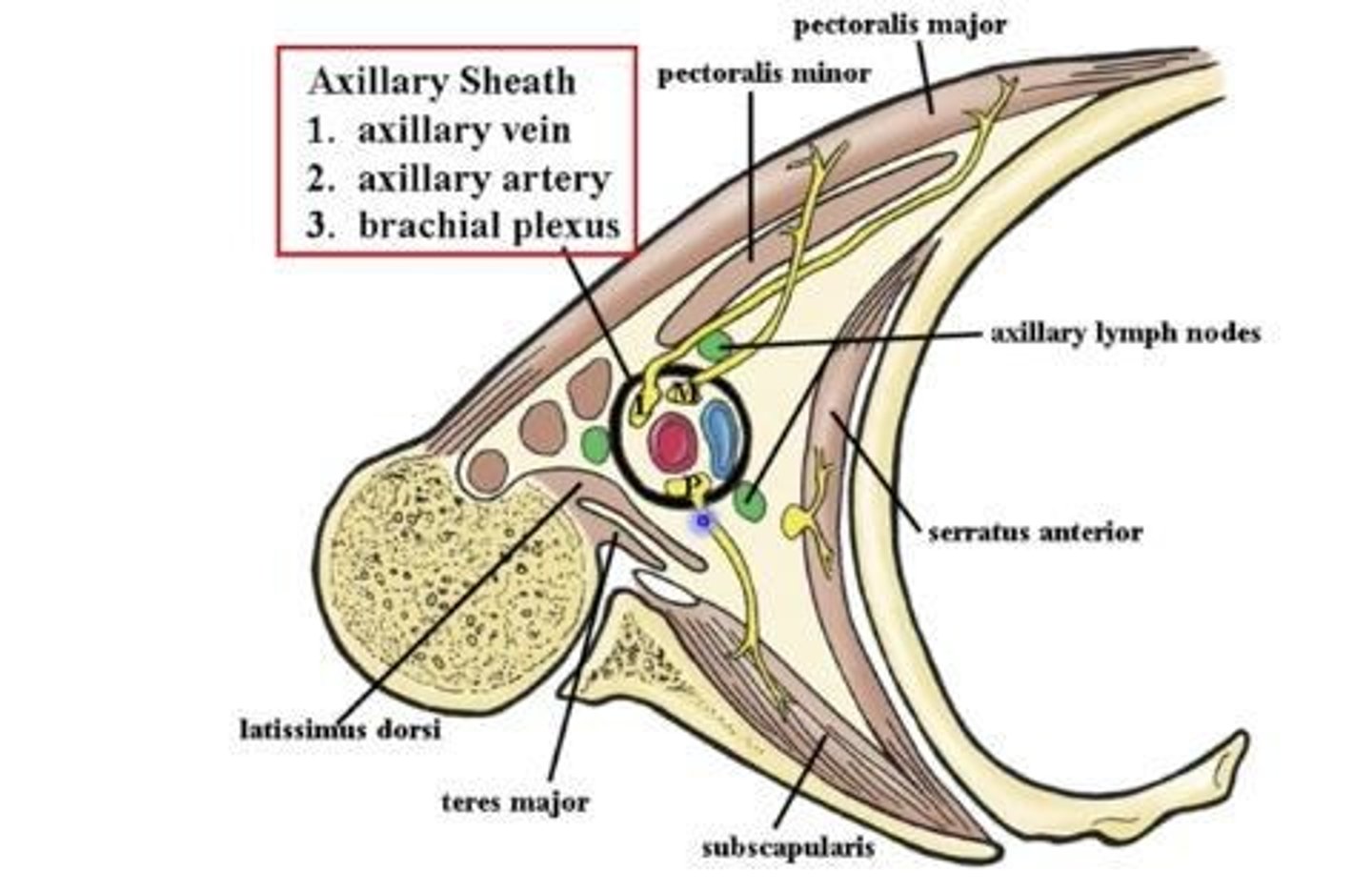
Axillary sheath
Contains axillary artery and vein, cords of the brachial plexus, and axillary lymph nodes.
Superficial fascia
Subcutaneous fatty tissue and skin, containing platysma muscle, supraclavicular nerves, and intercostal nerves.
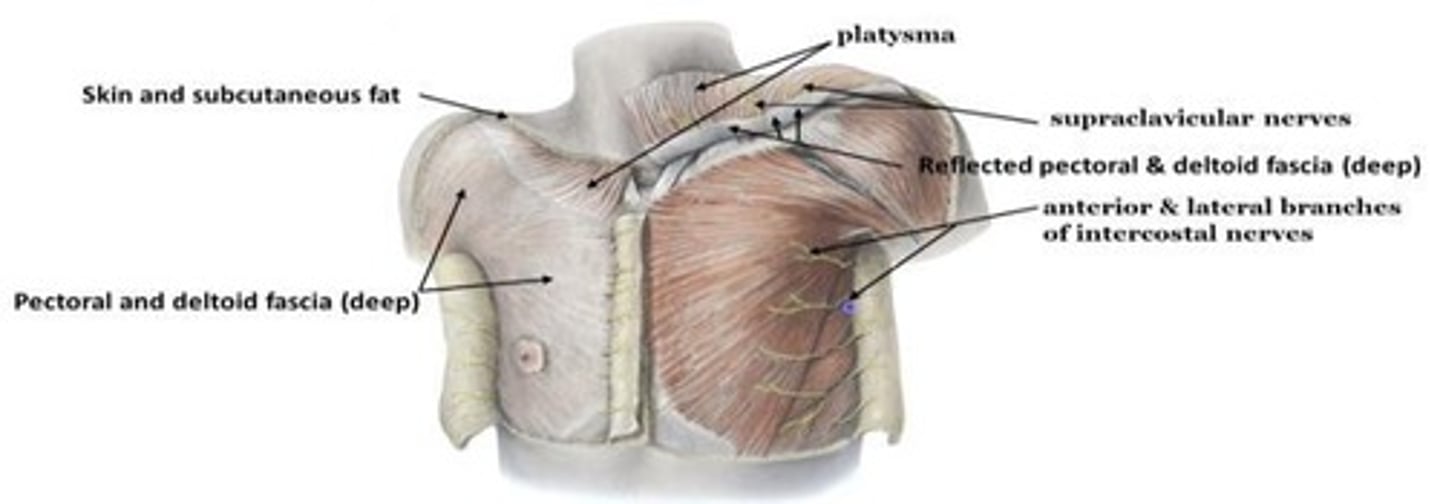
Deep fascia
Includes musculature fascia that compartmentalizes, surrounds muscles, and attaches to bone.
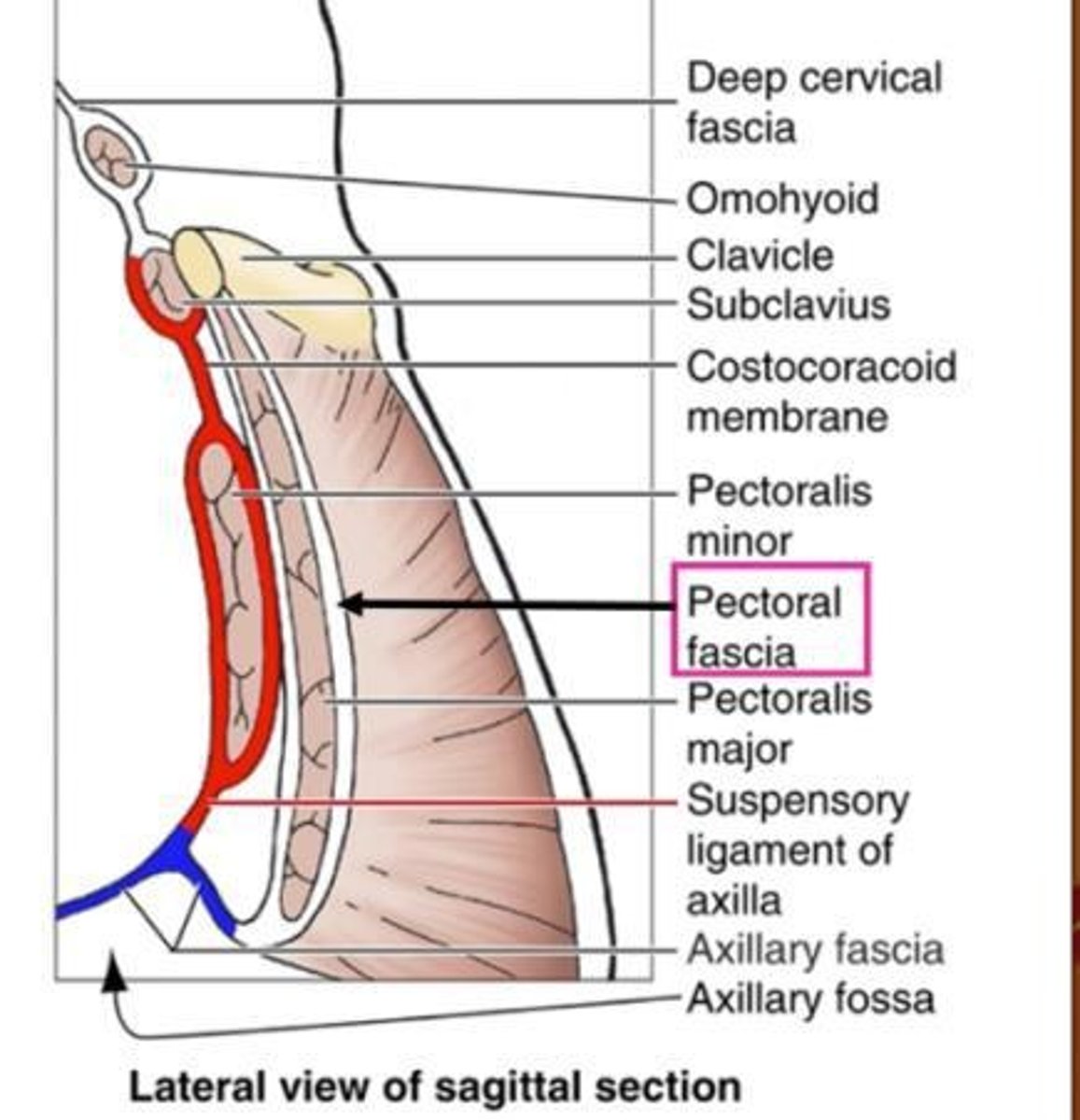
Pectoral fascia
Surrounds pectoralis major and is continuous with deltoid fascia.
Suspensory ligament of axilla
Formed by the combination of axillary fascia and clavipectoral fascia.
Clavipectoral fascia
Covers pectoralis minor and subclavius, united by costocoracoid membrane, and attaches to clavicle.
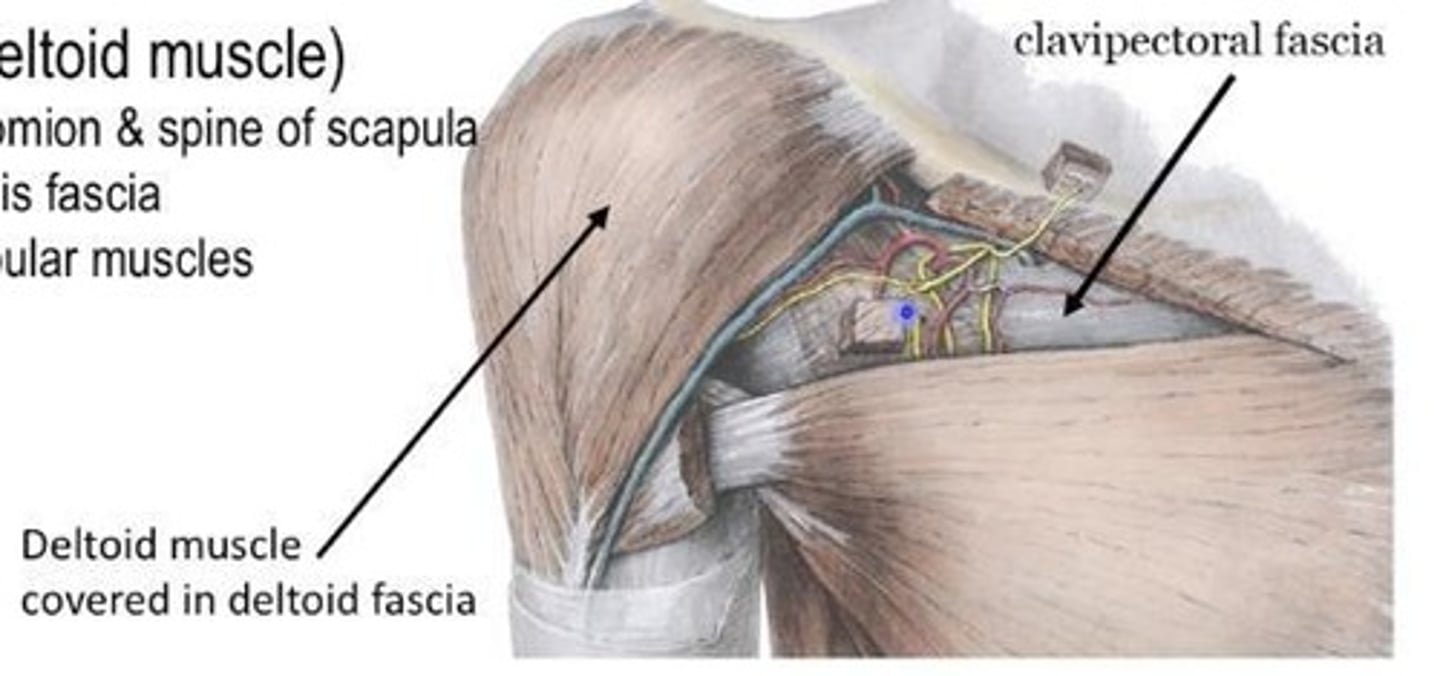
Deltoid fascia
Covers the surface of the deltoid and helps compartmentalize scapular muscles.
Clavipectoral Triangle
Allows passage of neurovascular structures between axilla and pectoral region.
Axillary artery
Continuation of subclavian artery, providing blood to the shoulder, thorax, and axillary region.

Brachial artery
Continuation of the axillary artery into the arm.
Axillary vein
Formed by basilic vein and brachial veins.
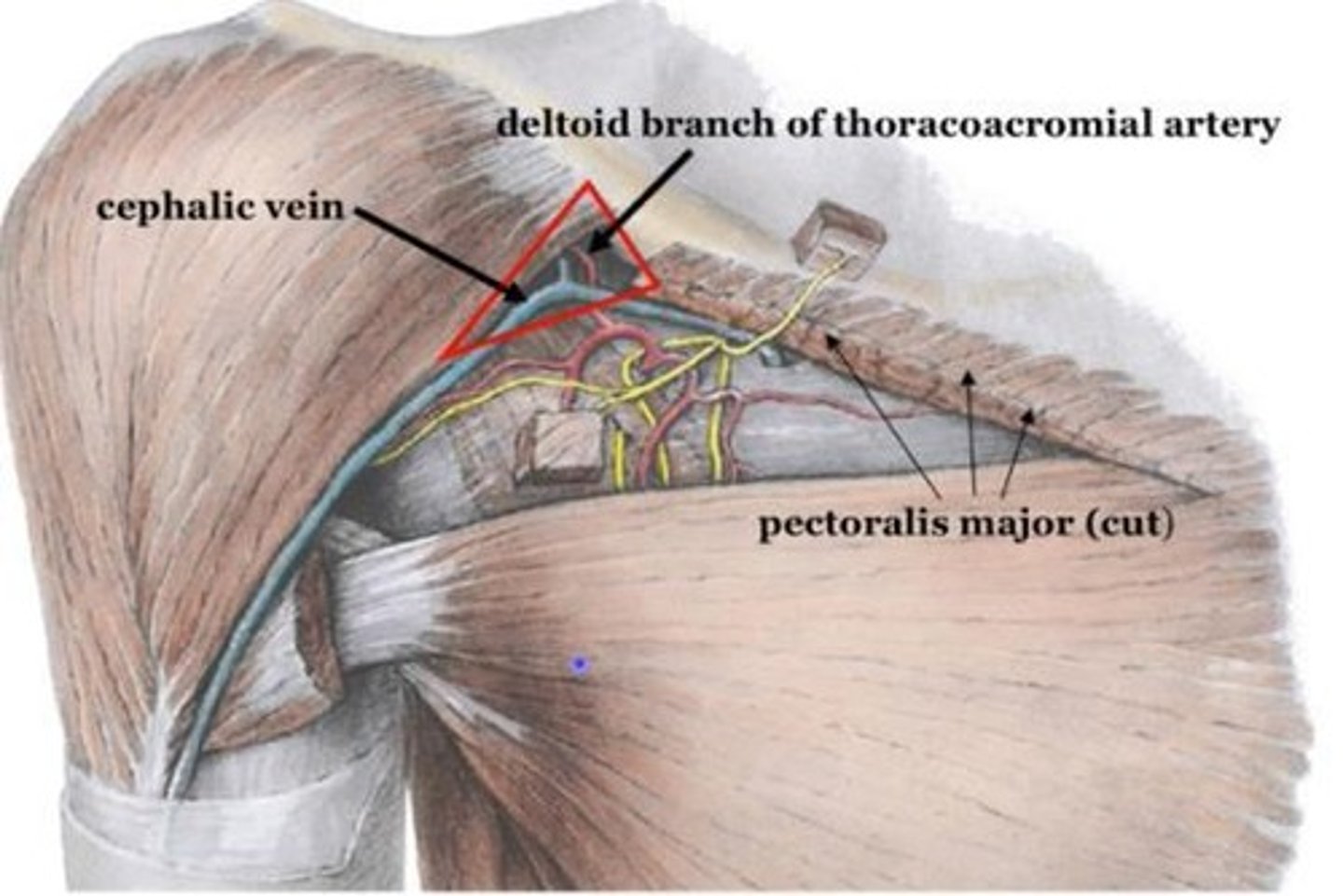
Cephalic vein
Superficial continuation that joins into axillary then subclavian vein.
Basilic vein
Medial vein that joins with brachial veins to form axillary vein.
Axillary lymphatics
Consist of 5 groups, each associated with a wall of the axillary region and a vein.
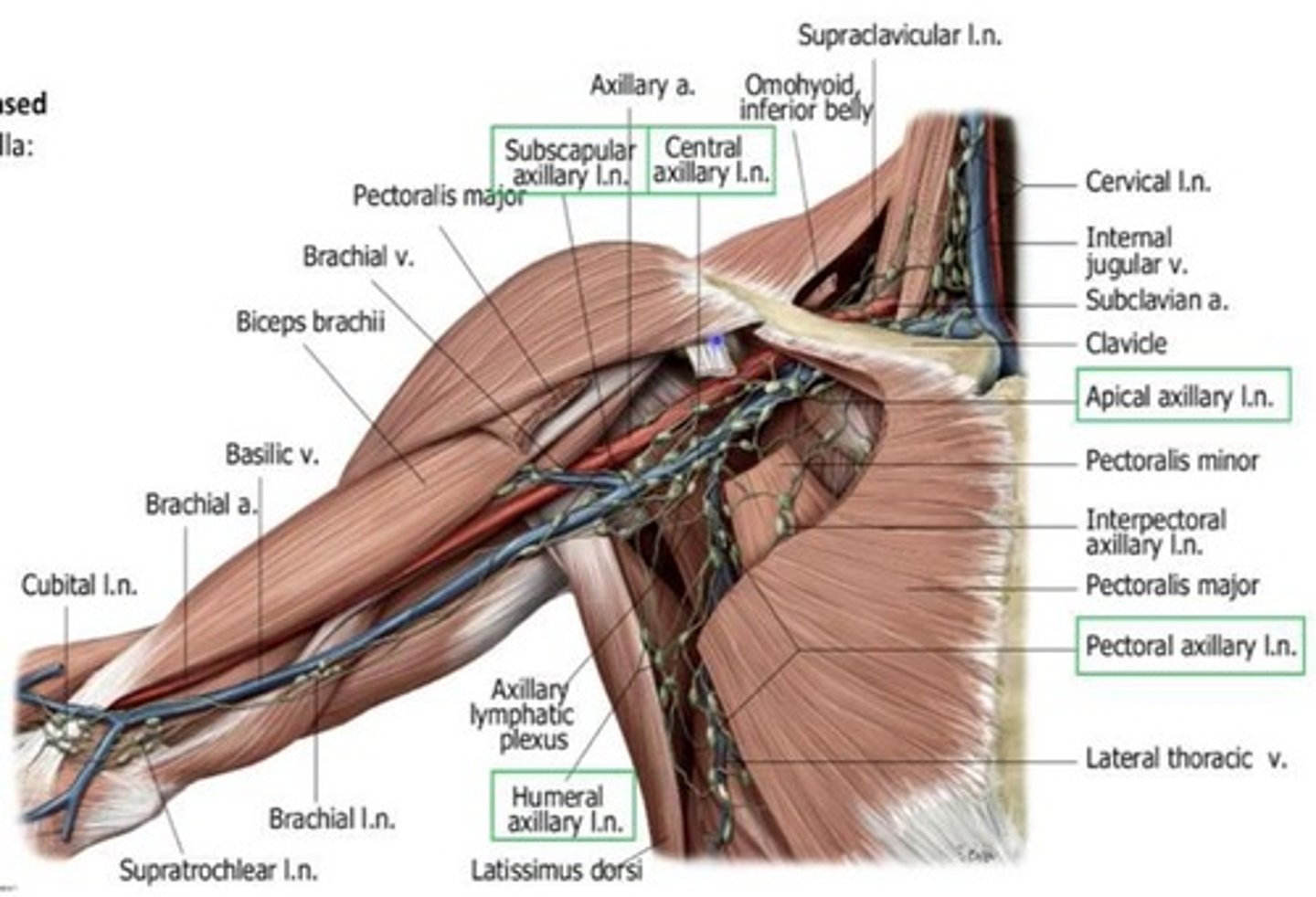
Subscapular lymph nodes
Located at the posterior axillary fold, clustered near subscapular vessels.
Central lymph nodes
Located at the base, near the axillary vein.
Apical lymph nodes
Located at the apex, near the axillary vein.
Pectoral lymph nodes
Located at the anterior and medial wall, clustered near the lateral thoracic vein.
Humeral lymph nodes
Located at the lateral wall, near the axillary vein.
Breast
Bilateral glandular structures, more developed in females for nourishment of young.
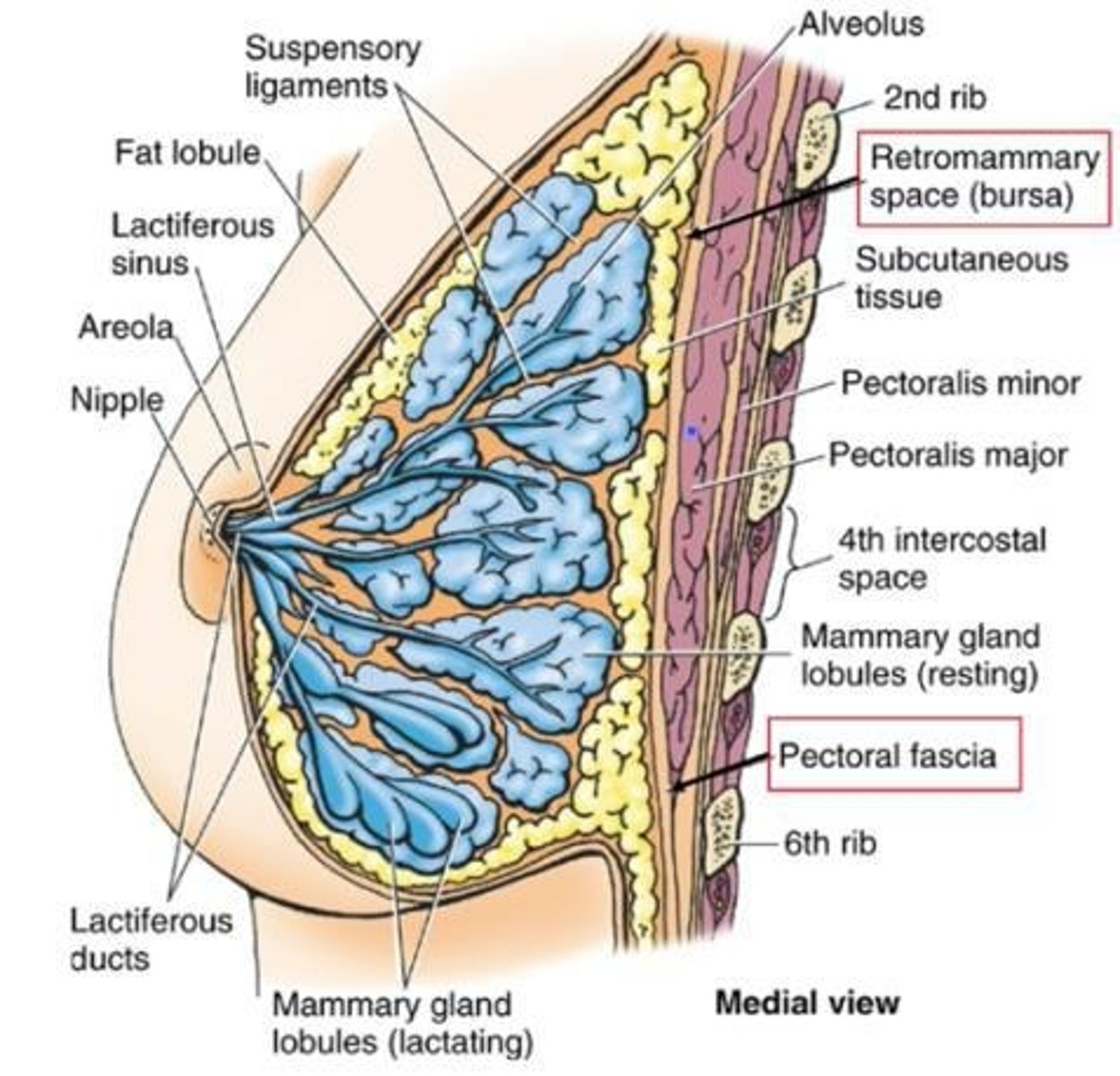
Retromammary space
Space between the pectoral fascia and breast tissue.
Allows
for free movement of the breast tissue
Structure
Attaches to dermis of overlying skin via suspensory ligaments
Mammary gland lobules
converge on the nipple
Lactiferous ducts
drain into lactiferous sinuses which open at the nipple
Lactiferous sinuses
"balloons" that can pool milk expressed through 5-12 openings in the nipple
Nipple
is surrounded by pigmented areola
Breast innervation
intercostal nerves 4-6, supraclavicular nerve
Somatosensory innervation
to skin and autonomic to blood vessels and smooth muscle
Blood Supply to breast
Arterial supply: from tributaries of subclavian and axillary arteries
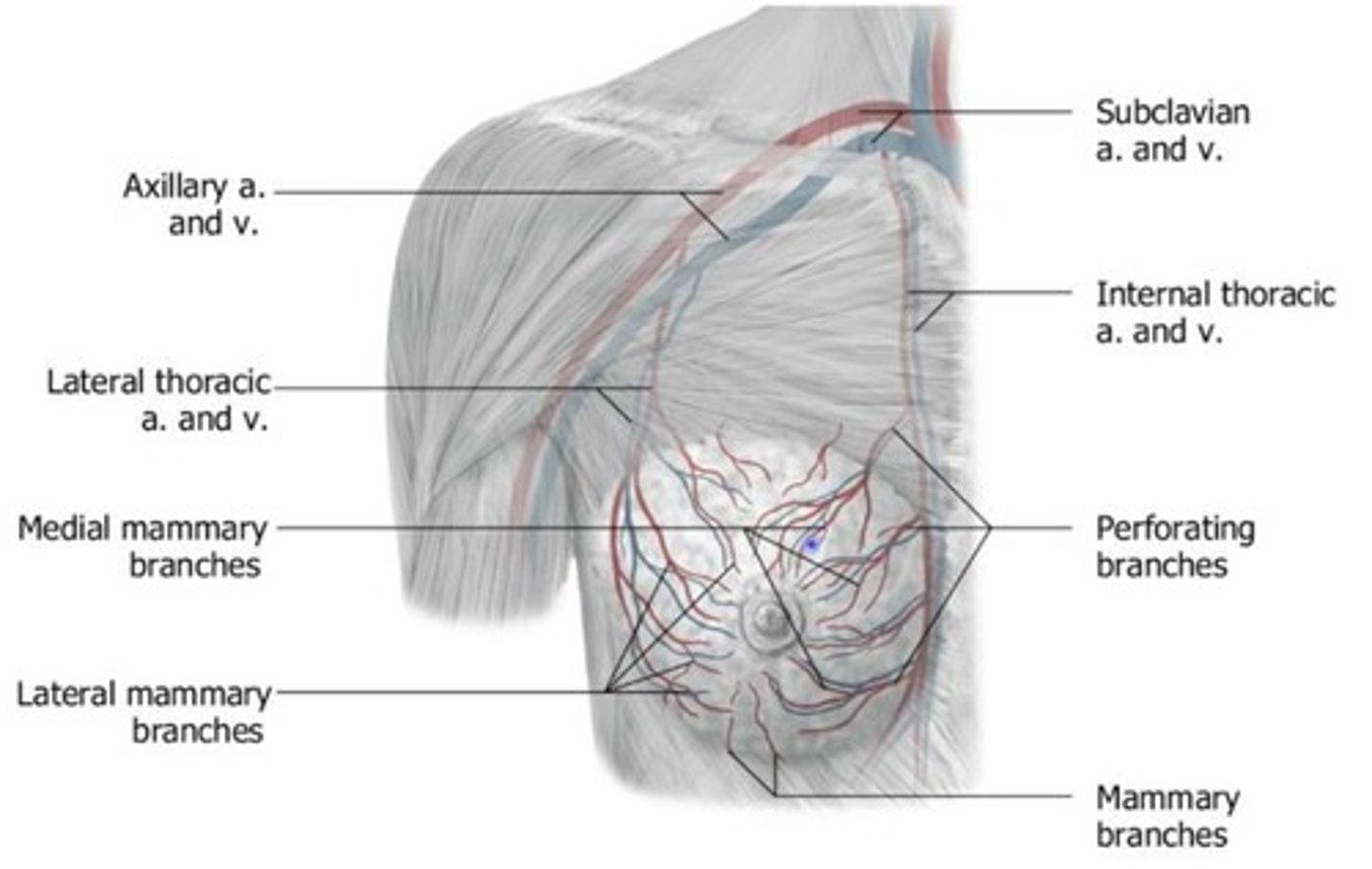
Medial mammary branches
via internal thoracic branch from subclavian artery
Lateral mammary branches
via lateral thoracic branch from axillary
Venous drainage
lateral mammary branches draining into the lateral thoracic vein and then into the axillary vein
Lymphatic drainage to breast
Axillary lymph nodes: 75+ % will drain here (pectoral, central, and apical groups)
Remaining nodes
Subareolar lymph nodes: near nipple and areola; Parasternal lymph nodes: drain into internal mammary nodes
Polymastia
accessory breast tissue
Polythelia
accessory nipple
Carcinoma in the breast
Causes various retraction signs: skin dimpling, nipple retraction and deviation, edema (peau d'orange skin), and abnormal bumps/contours
Invasion of retromammary space
will cause breast to elevate, a common clinical sign of breast cancer
Cancer spread
via axillary and parasternal nodes with communication to venous system forming metastasize to other areas in the body
Most common metastases
lung, liver, bone, and brain
Brachial plexus
Nervous pathway of upper limbs: carry somatosensory and somatomotor fibers as well as parasympathetics
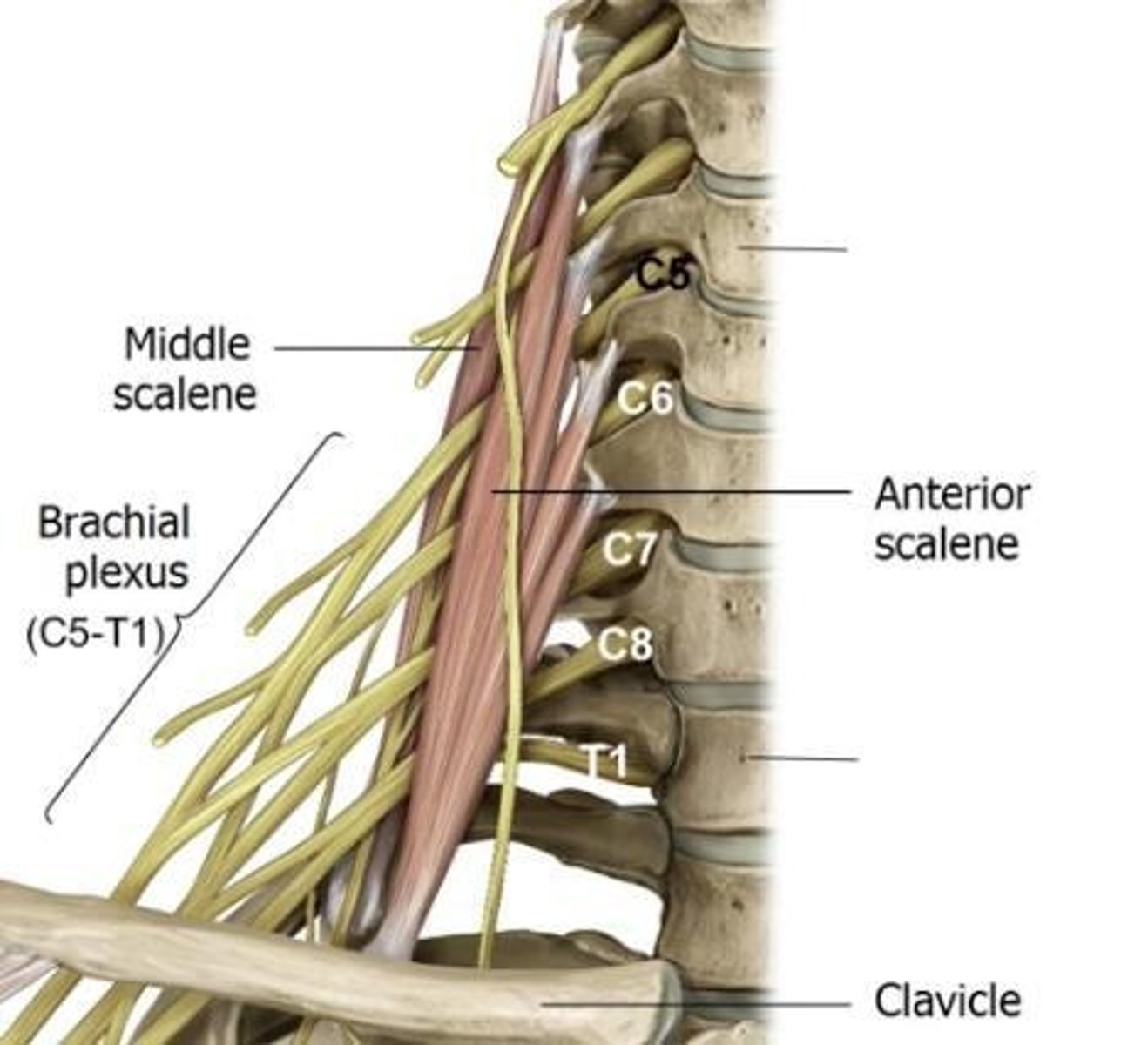
Autonomic innervation
also picked up from middle and inferior cervical ganglia of sympathetic trunk in neck
Dorsal horn
sensory
Ventral horn
motor
Brachial plexus origin
ventral (anterior) rami of spinal nerves C5—T1
Supraclavicular region
Contains: brachial plexus, interscalene muscles, subclavian a and v, sternocleidomastoid muscle, omohyoid muscle
Infraclavicular region
Contains: axillary a and v (continuation of subclavian)
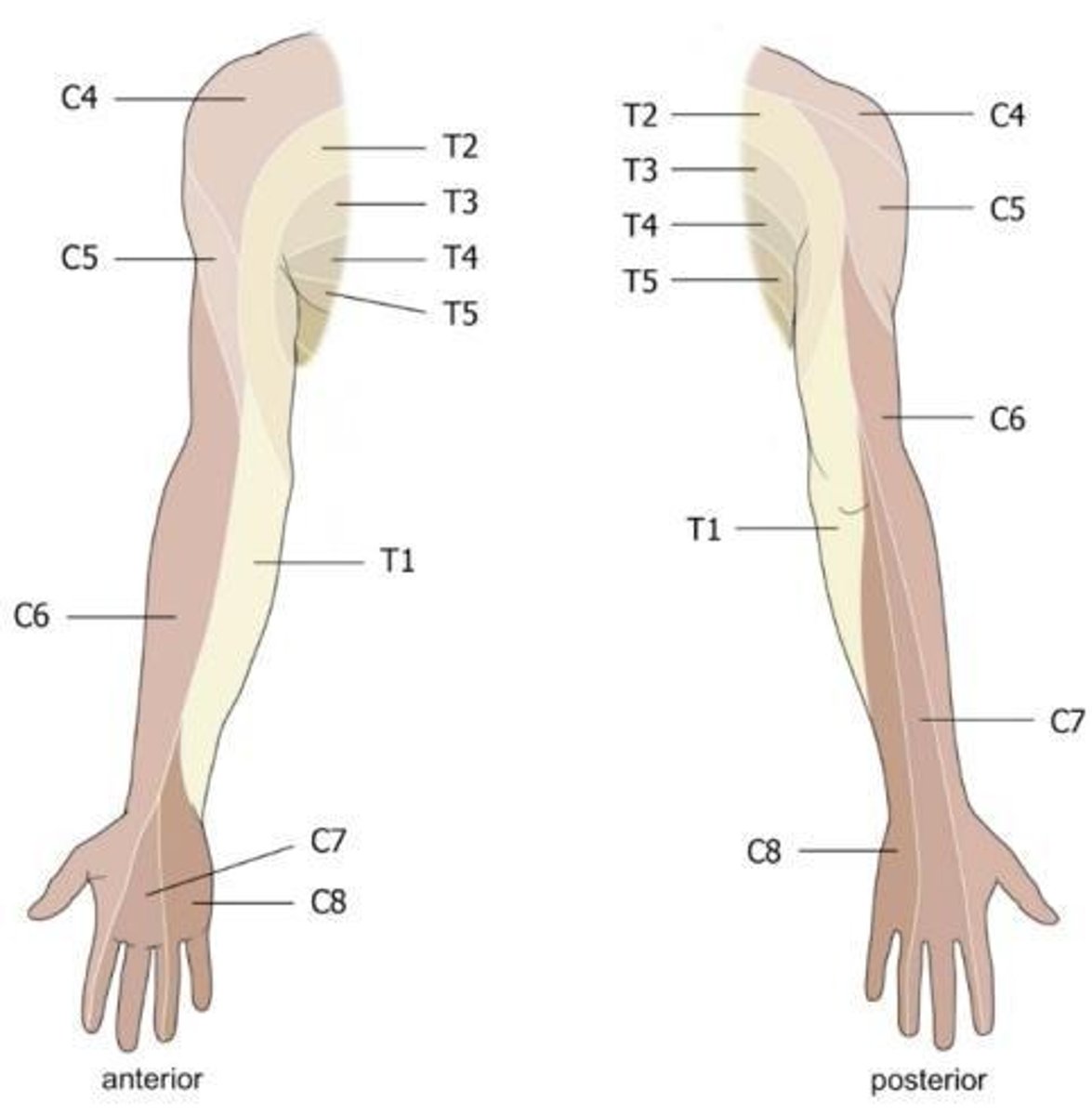
Cutaneous innervation
sensory to the skin that can be mapped onto dermatomes and regions supplied by named nerves

C4
Supplies the supraclavicular and upper shoulder region.
C5
Supplies the upper lateral arm and shoulder.
C6
Supplies the posterolateral arm and lateral forearm.
C7
Supplies the middle of forearm and hand.
C8
Supplies the posteromedial forearm and medial hand.
T1
Supplies the medial arm.
T2-T5
Supplies the axillary and pectoralis region.
Dermatomes
Sensory regions of the skin supplied by specific spinal nerves.
Myotomes
Groups of muscles that receive innervation from a single spinal nerve.
C4 Myotome
Responsible for shoulder elevation.
C5 Myotome
Responsible for shoulder abduction and elbow flexion.
C6 Myotome
Responsible for elbow flexion and wrist extension.
C7 Myotome
Responsible for elbow extension and wrist flexion.
C8 Myotome
Responsible for thumb and finger extensions.
T1 Myotome
Supplies intrinsic hand muscles.
T2-T5 Myotome
Supplies intercostal muscles.
Anterior compartment of the arm
Contains biceps and brachialis muscles.
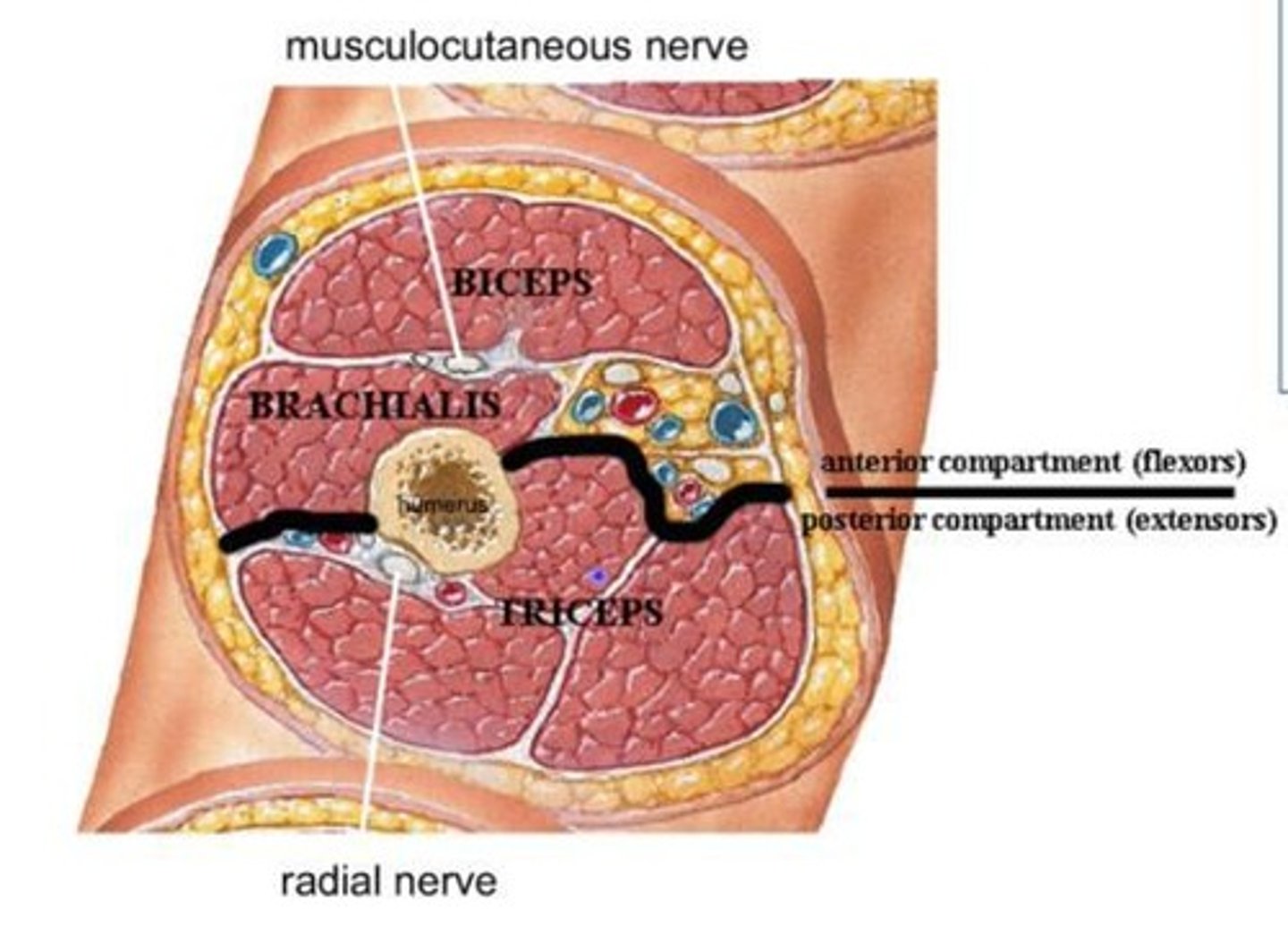
Posterior compartment of the arm
Contains triceps muscle.
Median nerve
Innervates flexors of wrists and digits in the anterior compartment of the forearm.
Radial nerve
Innervates extensors of wrist and digits in the posterior compartment of the forearm.
Superior trunk
Formed by C5-C6, gives off nerve to subclavius and suprascapular nerve.
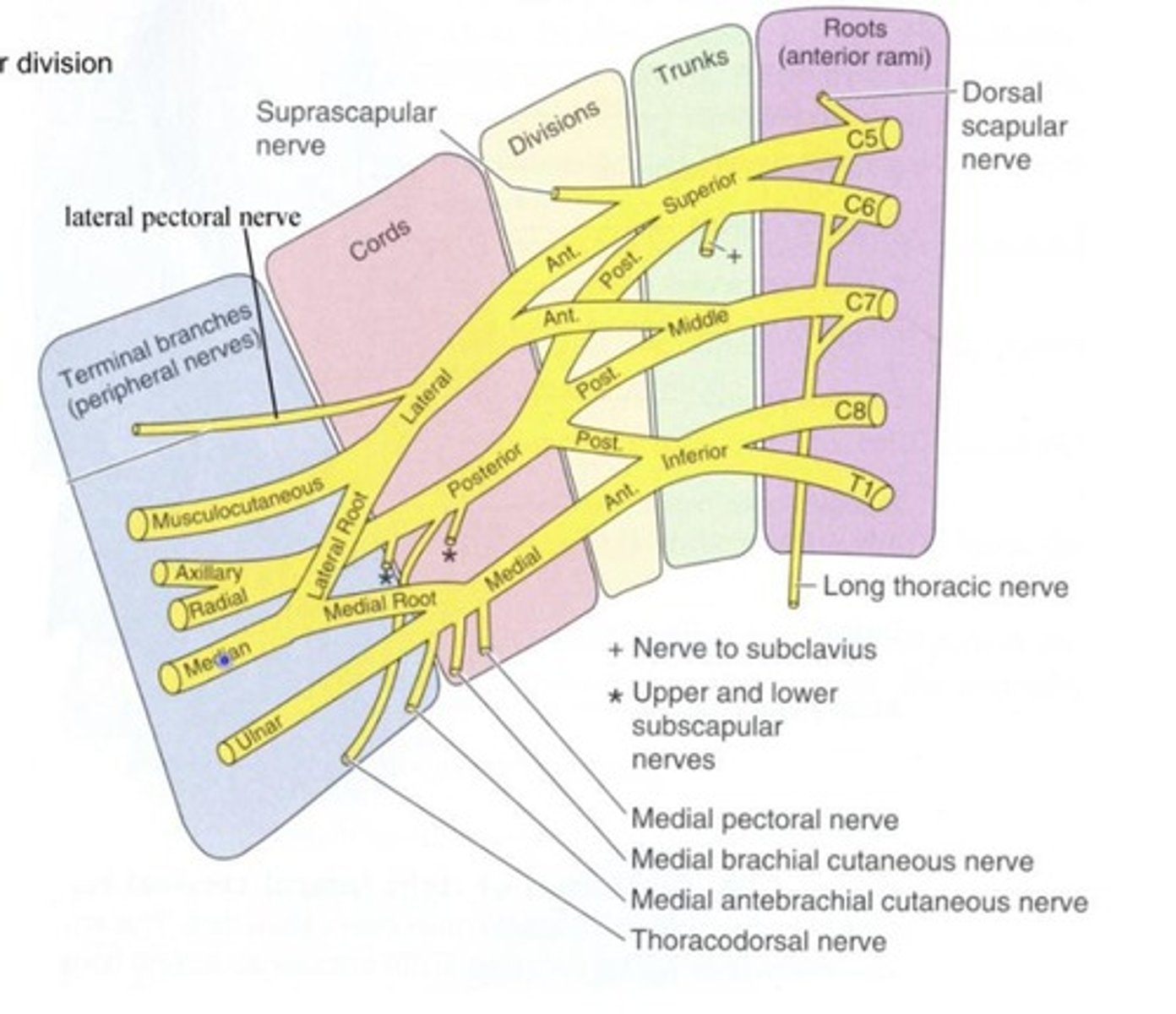
Middle trunk
Formed by C7.
Inferior trunk
Formed by C8-T1.
Anterior divisions
Supplies medial or lateral cord that serves the anterior compartment of the upper limb.
Posterior divisions
Supplies posterior cord that serves the posterior compartment of the upper limb.
Lateral cord
Made up of anterior divisions from middle and superior trunks.
Lateral pectoral nerve
Nerve given off by the lateral cord.
Posterior cord
Made up of posterior divisions from superior, middle and inferior trunks.
Upper subscapular nerve
Nerve given off by the posterior cord.
Thoracodorsal nerve
Nerve given off by the posterior cord.
Lower subscapular nerve
Nerve given off by the posterior cord.
Medial cord
Made up of anterior division of inferior trunk.
Medial pectoral nerve
Nerve given off by the medial cord.
Medial brachial cutaneous nerve
Nerve given off by the medial cord.
Medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve
Nerve given off by the medial cord.
Musculocutaneous nerve
Nerve from the lateral cord.
Axillary nerve
Nerve from the posterior cord.
Ulnar nerve
Nerve from the medial cord.
Supraclavicular compartment
Superior to clavicle; contains roots and trunks.
Infraclavicular compartment
Inferior to clavicle; contains divisions, cords, and branches.
C5, C6, C7
Spinal nerve contributions for the lateral cord.