Introduction to Pathology
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Pathos
Greek — “feeling or suffering”
Pathologization
The process of defining a condition or behavior as pathological
-path
Used to indicate a disease
Pathologies
aka diseases
Etiology - cause
Pathogenesis - mechanism of development
Morphologic changes - structural alterations of cells
Clinical manifestations - consequences of changes
4 components of pathology
System being studied
Focus of examination
Divisions of pathology
General pathology
A broad and complex scientific field which seeks to understand the mechanisms of injury to cells and tissues, as well as the body's means of responding to and repairing injury
Forms the foundation of pathology, the application of this knowledge to diagnose diseases in humans and animals
Describe the practice of both anatomical and clinical pathology
19th century
Pathological anatomy/morbid anatomy as a subject
Late 19th-20th century
Pathology as a field of medicine
Late 1920s-Early 1930s
Pathology deemed as medical specialty
Juristic
Classification of disease by speed of advent of death
Epidemiological
Classification of disease by incidence, distribution, and control of disorders in a population
Statistical
Classification of disease by the incidence and prevalence of disease
Diagnose and characterize disease in living patients by examining biopsies or bodily fluids
Cancer diagnosis
Analyzes blood samples
Set guidelines and standards for medical laboratory testing
May conduct autopsies to investigate causes of death
Works done by pathologists
Naked eye examination
Method of Pathology
Gross examination (ex. colon cancer)
Light microscopy
Method of Pathology
Determination of morphology (ex. adenocarcinoma)
Immunocytochemistry
Method of Pathology
Demonstration of specific proteins (ex. renaut bodies in nerve fascicles)
Electron microscopy
Method of Pathology
Examination of organelles (ex. junctional complexes)
Molecular biology
Method of Pathology
Chromosomal analysis and chip technology
Sequencing
Fixing
Laboratory Procedure
Formaldehyde, cryostat
Preserves tissue cells from degradation
Processing
Laboratory Procedure
Dehydration
Clearing and infiltration embedding
Sectioning
Staining
Haematoxylin
General staining when paired with eosin
Eosin
General staining when paired with haematoxylin
Connective tissue
Masson’s trichrome stain is used for?
Connective tissue
Mallory’s trichome stain is used for?
Reticular fibers, nerve fibers, fungi
Silver stain is used for?
Elastic fibers
Orcein stain is used for?
Blood cells
Wright’s stain is used for?
Basement membrane, localizing carbohydrates
Periodic acid-Schiff stain (PAS) is used for?
Elastic fibers
Weigert’s elastic stain is used for?
Distinguishing cells from extracellular components
Heidenhain’s AZAN trichome stain is used for?
Functional derangement
The disruption or malfunction of an organ's normal function, often as a direct consequence of morphological (structural) changes, and is the basis for a disease's clinical signs, symptoms, course, and prognosis
Clinical manifestation
A symptom or sign of a disease that can be observed or detected by a healthcare provider or patient, representing the physical or functional outcome of a disease process at the macroscopic level
Atrophy
Hypertrophy
Hyperplasia
Metaplasia
Cellular adaptations
Hypertrophy
Increase in the size of organ because of the increase in the size of component cells
Hyperplasia
Increase in the size of the organ because of the increase in the number of component cells in the organ
Hypergenesis — confused with benign hyperplasia
Metaplasia
The conversion, during postnatal life, of one differentiated cell type to that of another
Pathological condition that commonly occurs in the context of chronic inflammation and carries an increased risk of cancer
Cell death
Ultimate result of cell injury
Major consequence of ischemia, toxins and immune reactions
Critical during normal
Embryogenesis
Lymphoid tissue development
Hormonally induced involution
Aim of cancer radiotheraphy and chemotherapy
Ischemia
Lack of blood flow to tissues
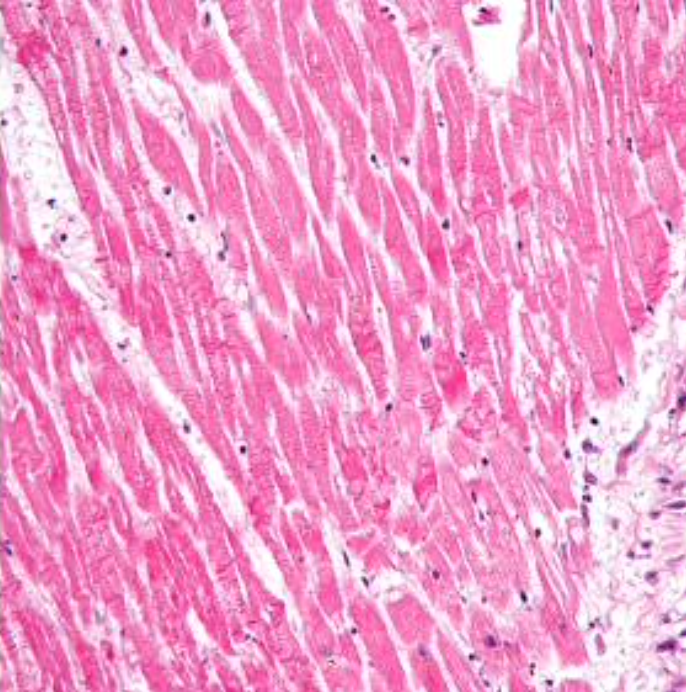
Coagulation necrosis
More common type of necrosis
By exogenous stimuli
Manifested by
Severe cell swelling or cell rupture
Denaturation
Coagulation of cytoplasmic proteins
Breakdown of cell organelles
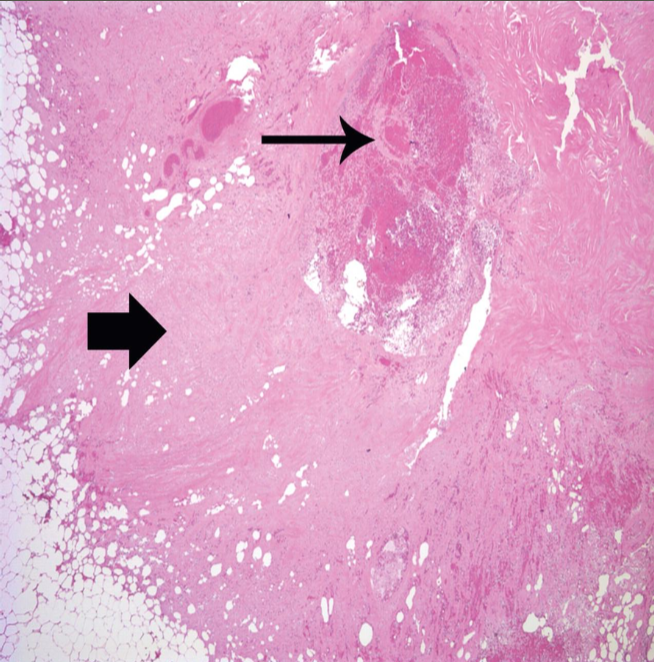
Myocardial infarct
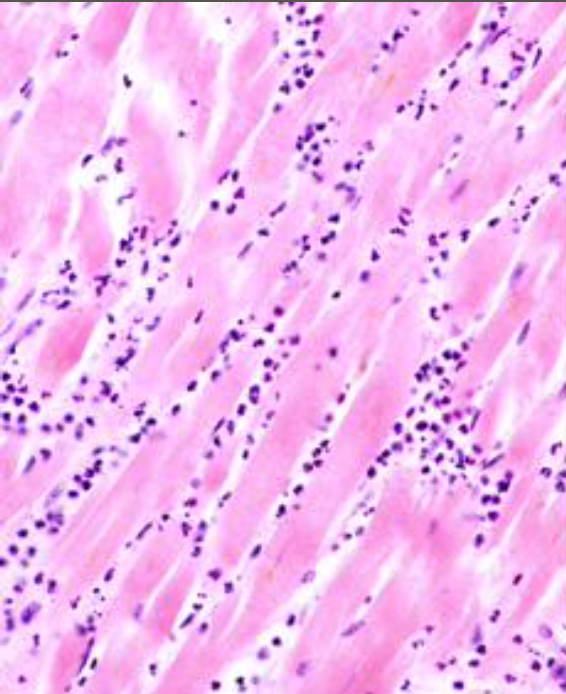
Residual oagulative necrosis
Apoptosis
More regulated event
Designed for normal elimination of unwanted cell populations (embryonic and physiologic process)
No inflammation
Chief morphologic features
Chromatin condensation
Fragmentation
Reversible injury
Cell death
Subcellular alterations and cell inclusions
Intracellular accumulations
Pathologic calcifications
Acute cell injury
Subcellular alterations
Acute cell injury as a response to more chronic or persistent injurious stimuli
Intracellular accumulations
Lipids, carbohydrates, proteins
Occur as a result of derangements in cell metabolism or excessive storage
Pathologic calcifications
A common consequence of cell and tissue injury
Hypoxia
Physical agents
Chemical agents and drugs
Infectious agents
Immunologic reactions
Genetic derangements
Nutritional imbalances
Causes of cell injury
Hypoxia
Ischemia
Arteriosclerosis
Thrombi
Inadequate oxygenation of blood due to cardiorespiratory failure
Loss of oxygen-carrying capacity of blood due to anemia and carbon monoxide poisoning
Physical agents
Mechanical trauma
Extremes of temperature
Radiation
Electric shock
Chemical agents and drugs
Glucose or salt
Oxygen
Poisons
Environmental and air pollutants
Poisons (arsenic, cyanide, mercuric salts
Insecticides and herbicides
Industrial and occupational hazards
Social stimuli
Therapeutic drugs
Infectious agents
Submicroscopic viruses
Rickettsiae
Bacteria
Fungi
Tapeworms
Ascaris
Immunologic reactions
Anaphylactic reaction to a foreign protein or drugs
Endogenous self-antigens (autoimmune diseases)
Genetic derangements
Congenital malformations associated with Down’s Syndrome
Subtle alteration of the coding of hemoglobin S in Sickle Cell Anemia
Enzyme lack
DNA alterations
Nutritional imbalances
Protein-calorie deficiencies
Vitamin deficiencies
Nutritional excesses
Atherosclerosis
Obesity