Lab 1 - Directional Terminology, Topographic Anatomy, Vertebral Column
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Plane
A surface, real or imaginary, along which any two points can be connected by a straight line
Median plane
Divides the head, body, or limb longitudinally into equal right and left halves
Sagittal Plane
Passes through the head, body, or limb parallel to the median plane
Transverse Plane
Cuts across the head, body, or limb at a right angle to its long axis or across the long axis of an organ or a part.
Dorsal Plane
Runs at right angles, to the median and transverse planes and thus divides the body or head into dorsal and ventral portions
Dorsal
Toward or relatively near the upper surface (as opposed to the supporting surface) of the head, body, and tail. This surface is opposite to the supporting surface in the standing animal.
On the limbs, it applies to the upper or front surface of the carpus, tarsus, metapodium, and digits (opposite to the side with the pads).
Ventral
Toward or relatively near the supporting surface and the corresponding surface of the head, neck, thorax, and tail. This term is never used for the limbs.
Medial
Toward or relatively near the median plane
Lateral
Away from or relatively farther from the median plane
Cranial
Toward or relatively near the head; on the limbs it applies proximal to the carpus and tarsus. In reference to the head, it is replaced by the term rostral
Rostral
Toward or relatively near the nose; applies to the head only
Caudal
Toward or relatively near the tail; on the limbs it applies proximal to the carpus and tarsus. Also used in reference to the head
Internal/Inner
Close to, or in the direction of, the center of an organ, body, cavity, or structure
External/Outer
Away from the center of an organ or structure
Superficial
Relatively near the surface of the body or the surface of a solid organ
Deep
Relatively near the center of the body or in the center of a solid organ
Proximal
Relatively near the main mass or origin, in the limbs and tail, the attached end of that structure
Distal
Away from the main mass or origin; in the limbs and tail, the free end of that structure
Radial
On that side of the forearm (antebrachium) in which the radius is located
Ulnar
On that side of the forearm in which the ulna is located
Tibial/Fibular
On the corresponding sides of the leg (crus), the tibial side being medial and the fibular side being lateral
Palmar
The aspect of the forepaw on which the pads are located - the surface that contacts the ground in the standing animal and the corresponding surface of the metacarpus and carpus
Plantar
The aspect of the hindpaw on which the pads are located - the surface that contacts the ground in the standing animal - and the corresponding surface of the metatarsus and tarsus. The opposite surface of both forepaw and hindpaw is also known as the dorsal surface
Axis
The central line of the body or any of its parts
Axial/Abaxial
Of, pertaining to, or relative to the axis. In reference to the digits, the functional axis of the limb passes between the third and fourth digits.
The axial surface of the digit faces the axis
The abaxial surface faces away from the axis
Flexion
The movement of one bone in relation to another in such a manner that the angle formed at their joint is reduced. The limb is retracted or folded; the digit is bent; the back is arched dorsally
Extension
The movement of one bone upon another such that the angle formed at their joint increases. The limb reaches out or is extended; the digit is straightened; the back is straightened. Extension beyond 180 degrees is overextension
Abduction
The movement of a part away from the median plane
Adduction
The movement of a part toward the median plane
Circumduction
The movement of a part when outlining the surface of a cone (e.g., the thoracic limb extended drawing a circle)
Rotation
The movement of a part around its long axis (e.g., the action of the radius when using a screwdriver). The direction of rotation of a limb or segment of a limb on its long axis is designated by the direction of movement of its cranial or dorsal surface (e.g., in medial rotation of the arm, the crest of the greater tubercle is turned medially).
Supination
Lateral rotation of the appendage so that the palmer or plantar surface of the paw faces medially
Pronation
Medial rotation of the appendage from the supine position so that the palmer or plantar surface will face the substrate
Which bones are found in the thoracic girdle?
Scapula and clavicle
Which bones form the skeletal structure of the manus (i.e., the paw)?
Carpal bones, metacarpal bones, and phalanges
What is the anatomic term for “arm”?
Brachium
What is the anatomic term for “forearm”?
Antebrachium
Canine Vertebral Formula
C#7 T#13 L#7 S#3 Cd#20
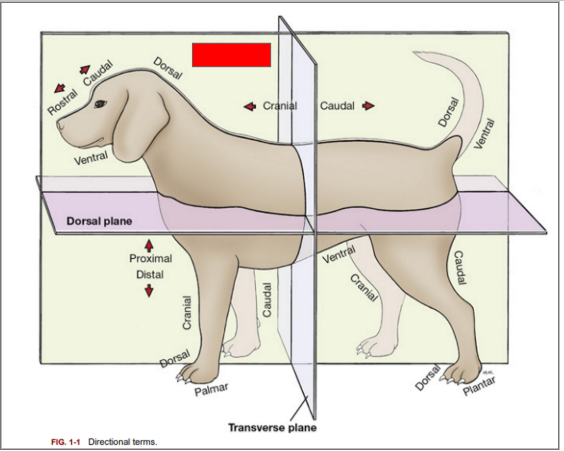
What is the name of the plane blocked out in red?:
Median Plane

What is the name of the plane blocked out in red?
Transverse Plane
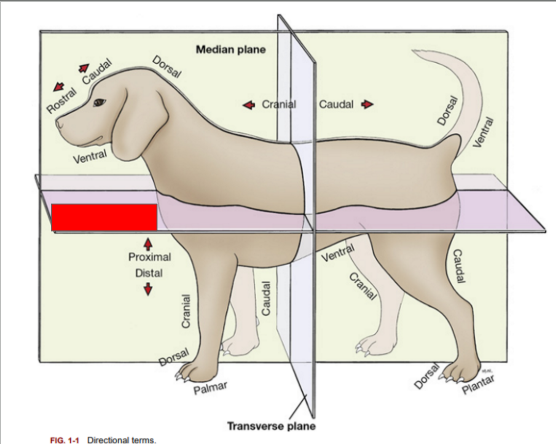
What is the name of the plane blocked out in red?
Dorsal Plane
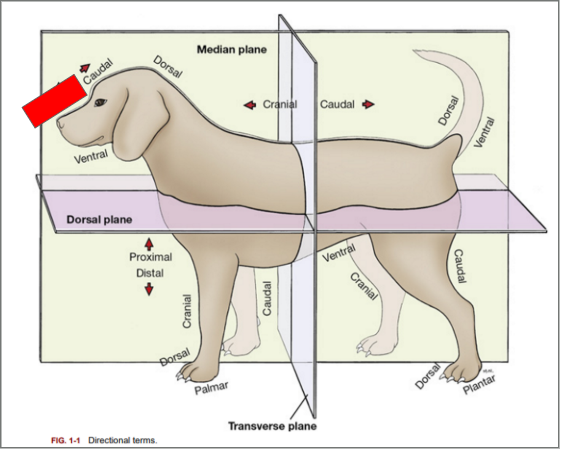
What is the directional term blocked out in red?
Rostral
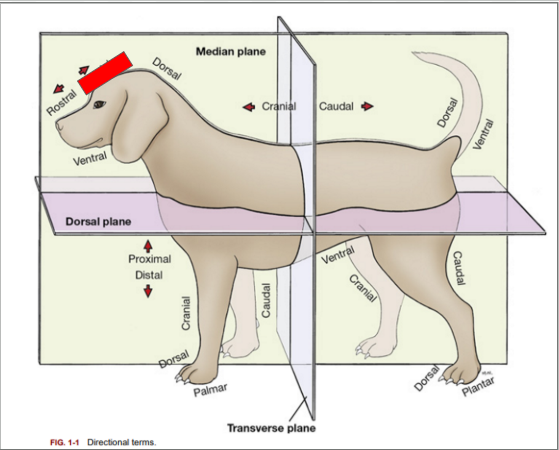
What is the directional term blocked out in red?
Caudal
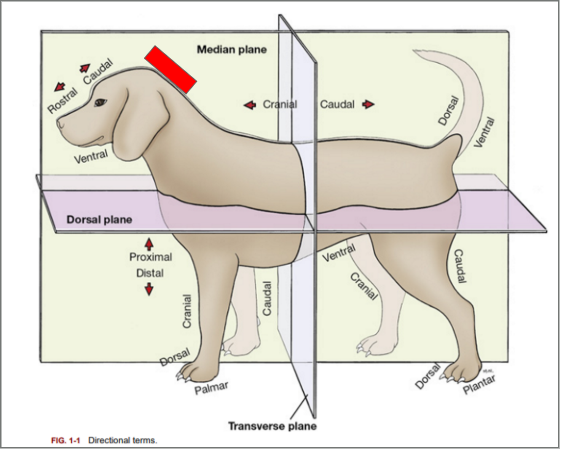
What is the directional term blocked out in red?
Dorsal
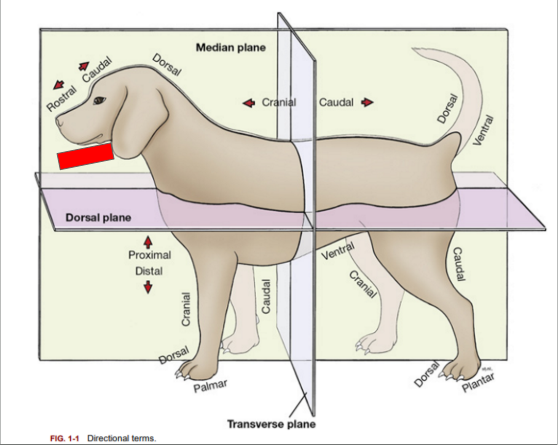
What is the directional term blocked out in red?
Ventral
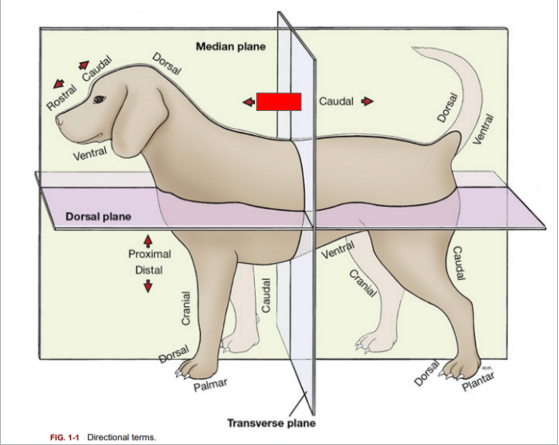
What is the directional term blocked out in red?
Cranial
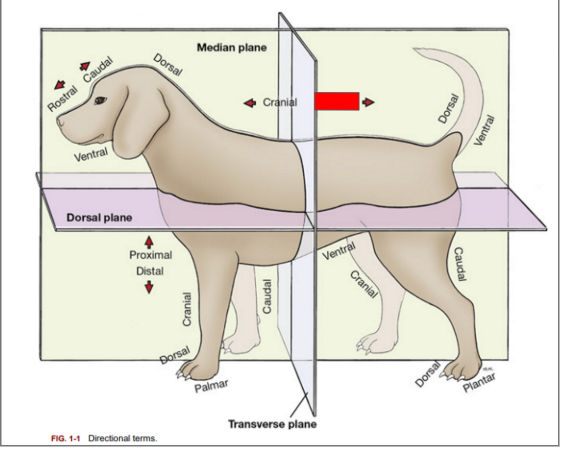
What is the directional term blocked out in red?
Caudal
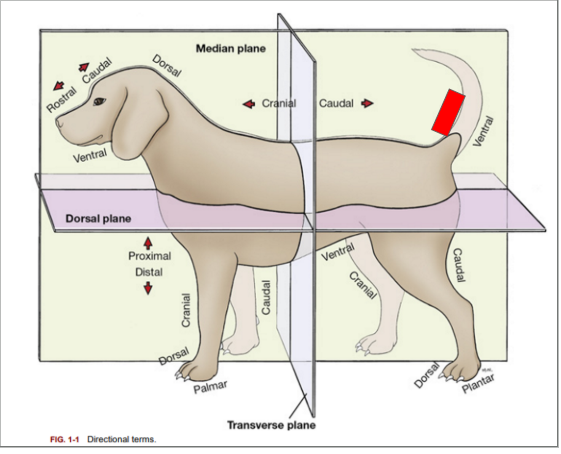
What is the directional term blocked out in red?
Dorsal
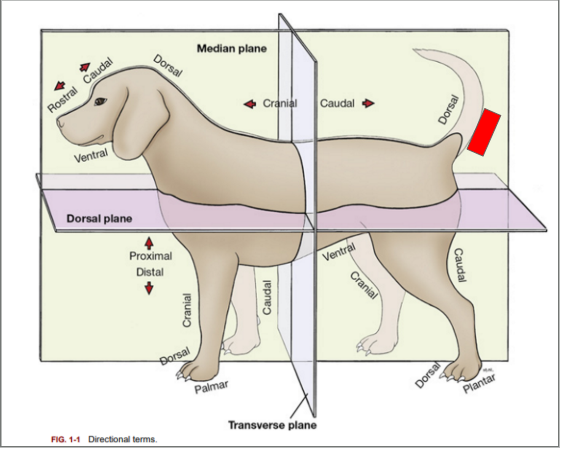
What is the directional term blocked out in red?
Ventral
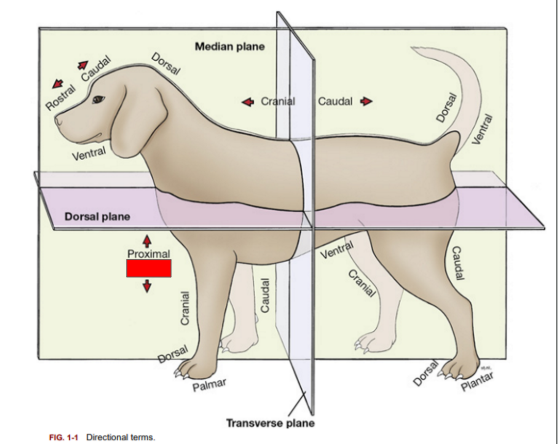
What is the directional term blocked out in red?
Proximal
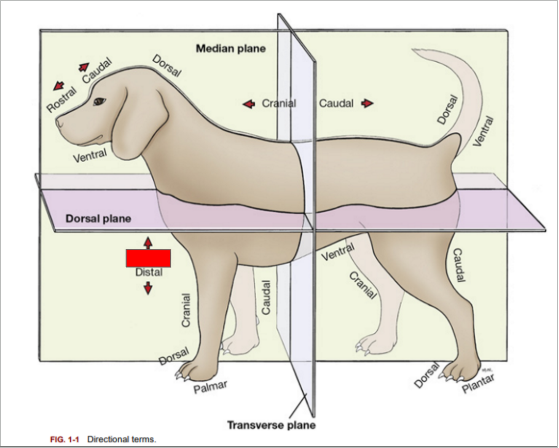
What is the directional term blocked out in red?
Distal
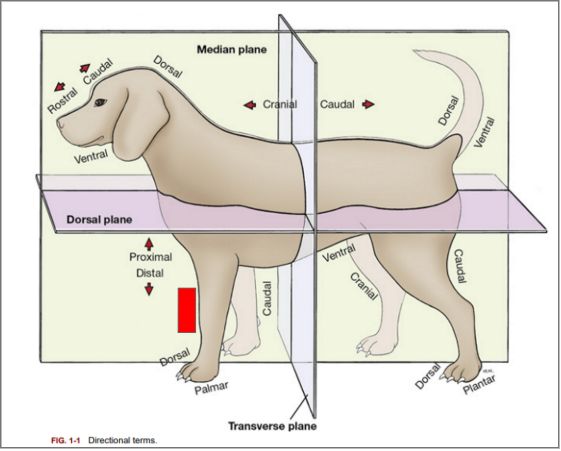
What is the directional term blocked out in red?
Cranial
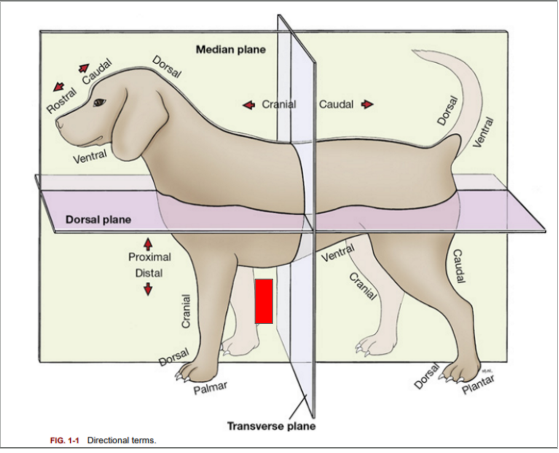
What is the directional term blocked out in red?
Caudal
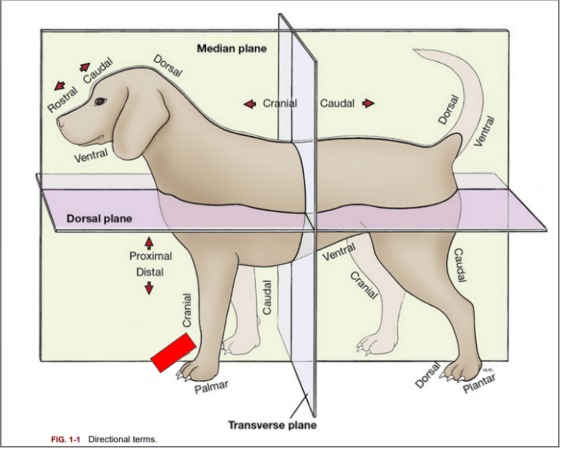
What is the directional term blocked out in red?
Dorsal
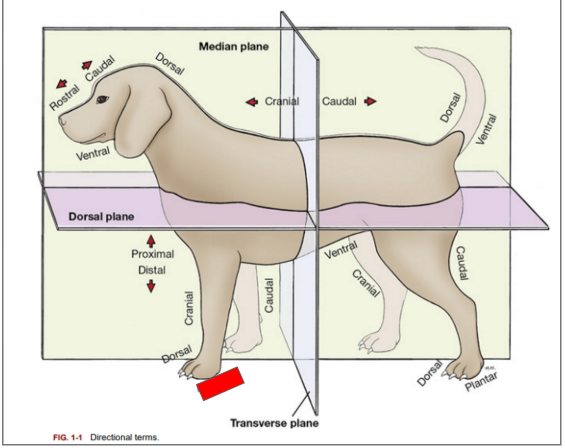
What is the directional term blocked out in red?
Palmar
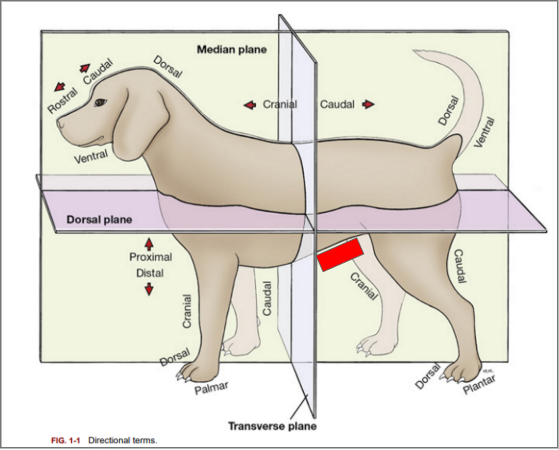
What is the directional term blocked out in red?
Ventral
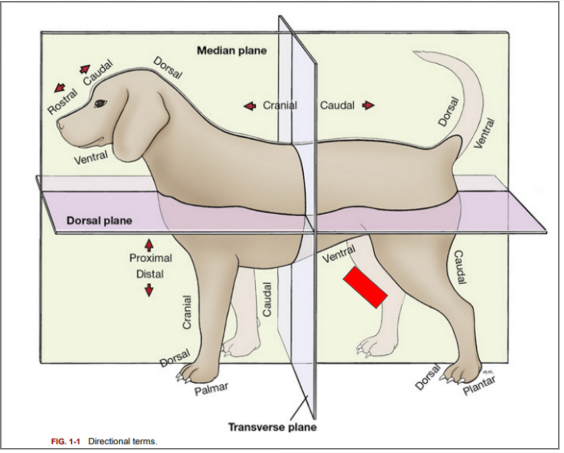
What is the directional term blocked out in red?
Cranial
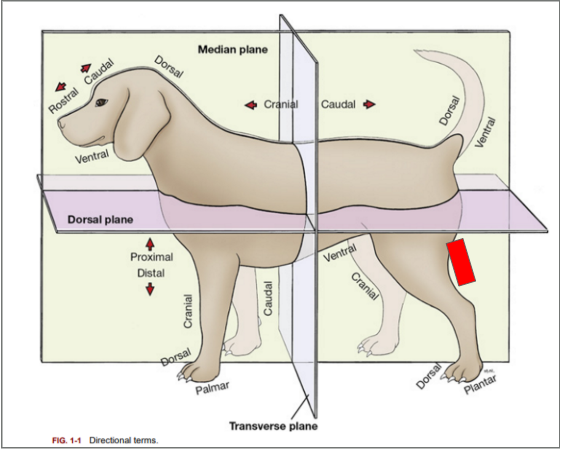
What is the directional term blocked out in red?
Caudal
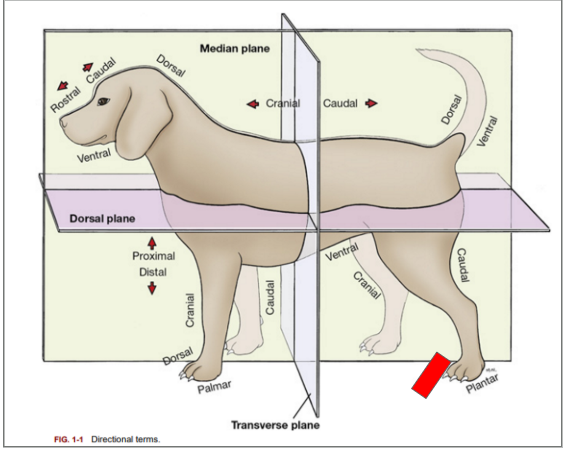
What is the directional term blocked out in red?
Dorsal

What is the directional term blocked out in red?
Plantar
Which bones are located in the antebrachium?
Radius and ulna
Which term is the opposite of proximal?
Distal
What term indicates “toward the head?”
Cranial
Which term describes the action when one bone moves toward another with a reduction of the angle between them?
Flexion
What is the correct number of thoracic vertebrae in the canine spine?
13