bio e
1/23
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Plasma Membrane
the boundary that separates a living cell from its surroundings
fluid mosaic model
what is used to describe the structural functions of the cell membrane
unsaturated fats
health fats
liquid at room temperature
saturated fats
unhealthy fats
solid at room temperature
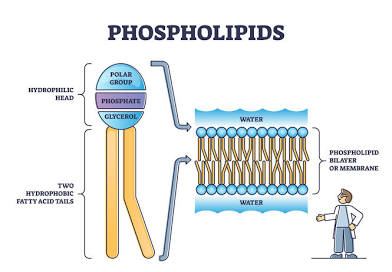
Phospholipids
are amphipathic
head (round part) is hydrophilic
tail (fatty bottom) is hydrophobic
high permeability
gases have high permeability; they are very small uncharged molecules
CO2 (carbon dioxide)
N2 (nitrogen)
O2 (oxygen)
ethanol
moderate permeability
allows for this to pass through the artificial bilayer at a neither fast or slow rate
water (H2O) and urea (H2NCONH) have moderate permeability
low permeability
does not allow for fluids or minerals to pass through the artificial bilayer easily
polar organic molecules (sugars) have low permeability
very low permeability
does not let fluids or minerals to pass through (artificial bilayer) easily
ions (Na+, K+, Mg2+, Ca2+, Cl+
charged polar molecules
macromolecules (amino acids, ATP, proteins, polysaccharides, nucleic acids; DNA and RNA)
Phospholipids
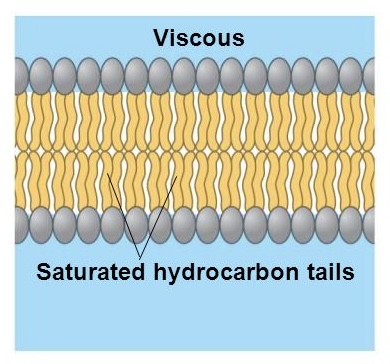
saturated hydrocarbon tails
increases the viscosity (thickness)
their shape is tightly packed, leaving minimal space between the molecules
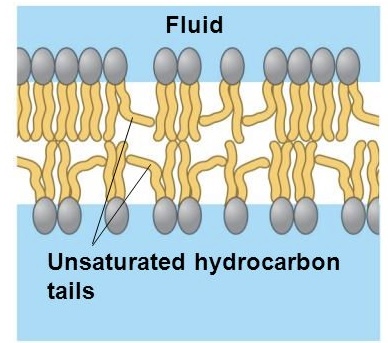
unsaturated hydrocarbon tails
have double bonds
promotes more fluidity
plasma cell membrane
regulates and allows certain things to come in and out
is a fluid mosaic model (functionally)
it’s is selectively permeable (structurally)
amphipathic
having both hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts; having both polar and nonpolar parts;
Passive Transport
diffusion of a substance across a membrane with out energy investment
EX: CHANNEL PROTEINS
diffusion and osmosis
both are passive transport since no energy is required by cells to make it happen
what does passive transport do
diffuses substances DOWN their concentration gradient
solute will move from the side that has more to the side with less
isotonic solution
a solution that has the same solute concentration as the inside cell
no water movement
hypertonic solution
a solute concentration that is higher than that inside cell
cell loses water
hypotonic concentration
a solute concentration is less than that inside cell
cell gains water
Transport Proteins
allows for hydrophilic substances to pass through the membrane
some allow passive transport; some do active transport
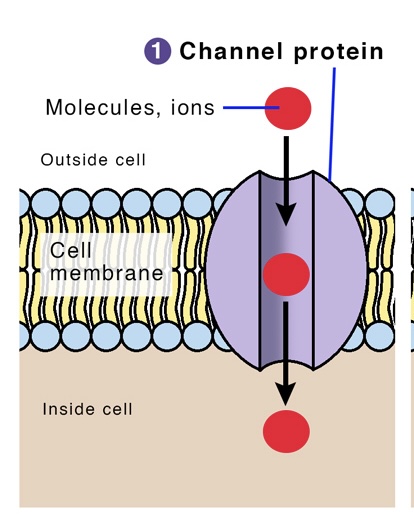
Channel Proteins
transports molecules and ions faster than carrier proteins
have a hydrophilic channel that certain molecules and ions can pass through and use as a tunnel
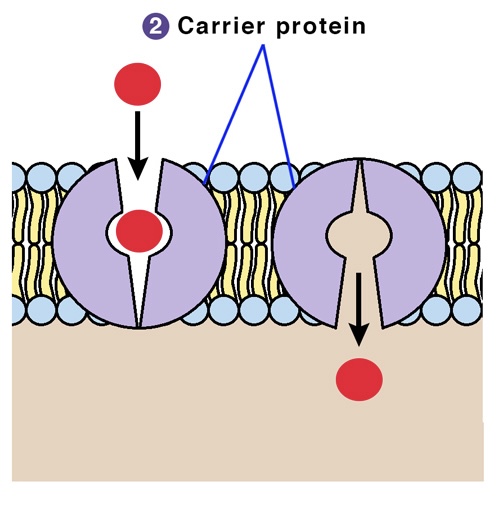
Carrier Proteins
requires energy to transport molecules
binds to molecules or ions on one side of the membrane and releases it on the other side of the membrane (does not provide a tunnel for transport)
Active Transport
moves substances AGAINST their concentration gradients and requires energy (ATP)
EX: CARRIER PROTEINS