01-02 - General Principles of Diagnostic Imaging
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Purpose of studying musculoskeletal imaging
Physical Therapists should expand their capabilities to know what could be the best tx or best dx that therapists could give to their patients
More comprehensive evaluation is obtained
Musculoskeletal imaging
A subspecialty of radiology concerned with the diagnostic evaluation of the musculoskeletal system
Musculoskeletal radiology / orthopedic radiology
Previous term for MSK imaging
2 uses of radiation
Diagnosis and treatment
Radiograph
Has been defined for over a century as an x-ray film containing an image of part of a patient’s anatomy
Image receptor
Other term for X-Ray
X-ray beam source
Patient
X-ray film / other image receptor
Production of a radiograph requires these 3 things:
X-rays are named after the letter “X” in the alphabet because they were discovered by accident, and at the time of their discovery, the nature of these rays was unknown.
The term “X” was used to signify the unknown or mysterious nature of these rays
Why is x-ray called x-ray?
Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen (Nov 8, 1895)
The German Physicist who discovered X-ray
Marie Curie and Pierre Curie
Discovered the radioactive elements polonium and radium; the beam of light/x-ray creates radiation
Bone portraits
First image caught by Roentgen (Hand of his wife)
Radiation
energy that is transmitted through space or matter
Ionization
process by which a neutral atom gains or loses an electron, thus acquiring a net charge
Falls ate ko 😘 (Lesser Ionization, gains electrons; higher ionization, lose electrons)
T or F: Lesser Ionization, lose electrons; higher ionization, gains electrons
Radio waves
Microwaves
Infrared radiation (IRR)
Visible light
UV radiation
Examples of Non-Ionizing Radiation
X-rays
Gamma rays
Certain particles (alpha and beta)
Examples of Ionizing Radiation
Plain X-ray
Most frequently performed radiological test worldwide
Chrew yan ate
T or F: The more an object absorbs the radiation, the more it appears white = if the object/tissue is solid (ionization).
Chest and Lung Dse
Heart Dse
Bone and Jt Dse
Trauma (Fracture)
Tumors
Requirements
Foreign body
Uses of Plain X-ray
Posteroanterior View
Anteroposterior View
Lateral View
Oblique View
Different views of Plain X-ray
Central Ray
The PA View and AP View have positioning that they use which is called _____.
PA View
Most commonly used chest x-ray to reduce the overlap of the anatomic structures
AP View
Mostly used for abdominal x-rays
T7 level
Central ray level
Jugular notch
Recommended landmark for the location of the CR for AP chest radiographs.
FALLS PO YAN ATE perpendicular yarne
T or F: The central ray (CR) is set parallel to the long axis of the sternum and the center of the cassette
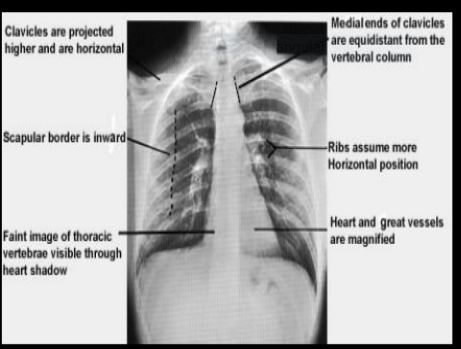
Standard appearance of a test in x-ray
Lateral view
View used to examine spine, ribs, and extremities
Oblique view
View used better used to visualize fractures that are maybe obscured by a standard view.
Scottie dog
Fracture
Spondylolysis
Spondylosis
Possible arthritis
Possible calcification
Uses of oblique view
Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DEXA)
Measures bone mineral density = amount of calcium + other minerals (mg/cm^2 of calcium)
Hips, Lumbar spine, Calcaneus, Forearm
Sites usually tested for DEXA
Postmenopausal women = > 65 y/o
Women < 65 with high risk for fractures
Men 70 y/o or older
Men 50-69 y/o with risk factors
Indications of DEXA
Smoker
3 or more alcohol intake/day
Chronic kidney dse
Family hX of osteoporosis
Early menopause < 45 y/o
Hx of fragility fractures
RA/ Systemic Arthritis
Chronic corticosteroids
Organ transplant
BMI < 21
Sedentary / lack of exercise
Low testosterone (prostate CA)
Loss of height (4 cm)
Identify atleast 3-5 High Risk Factors for Fx
Identify decreases in bone density before one gets a fracture
Determine risk of fragility fractures
Confirm a diagnosis of osteoporosis
Monitor osteoporosis treatment
Benefits of DEXA
Between 1 and -1 = normal
Between -1 and -2.4 = osteopenia
Between -2.5 and below = osteoporosis
T-Score
Between 1 and -1 = ______
Between -1 and -2.4 = ______
Between -2.5 and below = ______
Computed Axial Tomography Scan / CAT / CT Scan
More sensitive in detecting presence of blood; also uses ionizing radiation; size, shape, & position of internal organ / structure
Radiation
More costly
Pregnancy precaution
Disadvantages of CT Scan
MEDICAL ULTRASOUND / SONOGRAPHY
Evaluates ligaments, tendons, muscles, nerves, joints; view anatomical part as it moves in real time; no radiation, safe, non-invasive, portable, pregnant
15-30 mins
Duration of Medical Ultrasound
Hyperechoic (white); Hypoechoic (black/dark)
What do you call the white and black/dark portion of this ultrasound?
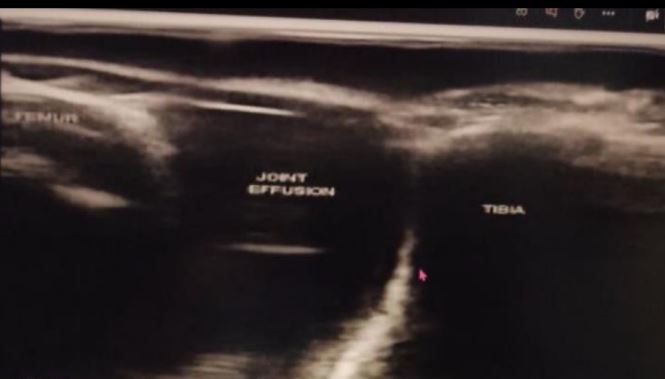
Tendinitis vs tear
Muscle tear, mass, fluid collection
Ligament sprain vs Tear
Joint effusion, Bursitis
Early changes of RA
Nerve entrapment
Soft tissue tumors
Ganglion cyst
Hernias
Foreign body (splinters)
Give atleast 3 indication of MSK Ultrasound
Non-invasive, Safe, Painless, No radiation
Widely available, Cheaper
Gives a clear picture of soft tissues not visible on
Real time images - Interventions (aspiration, injection, biopsy)
Pt. with metal implants
Alternative to claustrophobic patients
Shows mvts of soft tissue structures
15-30 mins
Benefits of MSK Ultrasound
Depth of penetration (NOTE: only capable of shallow penetration)
Cannot penetrate bones
Obese & large individuals
LIMITATIONS OF MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASOUND
Echocardiogram / Echo / 2D Echo
anatomical images of heart only
Doppler echocardiogram
can see how fast the pump blood
Identify cardiac causes of dyspnea
Cardiomegaly, ventricular or atrial hypertrophy
Cardiomyopathy — weakened heart muscles
Valvular heart disease
Congenital heart disease
Blood clot or tumors
Pumping strength of the heart
To monitor effectiveness of treatment
INDICATIONS FOR ECHOCARDIOGRAM
TRANSESOPHAGEAL ECHOCARDIOGRAM
Catheter containing the transducer is inserted into esophagus; more accurate picture of heart
TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAM
Pt. supine c transducer on chest ; sometimes pt. might feel a really deep pressure/ some discomfort; chambers of heart, mitral and tricuspid valves, etc
STRESS ECHOCARDIOGRAM
Done while pt. is exercising to the point of exhaustion (done on treadmill or stationary bike c electrodes attached)
Monitor for ischemic changes, CAD
No food, drinks for 4 hours
No caffeine, chocolates, tea for 24 hours
No cardiac medications (e.g. beta-blockers & nitroglycerin)
Stress Echocardiogram Conditions to Follow
DOBUTAMINE STRESS ECHOCARDIOGRAM
Done when pt. cannot exercise; clinician will give medicine that will cause an effect like the person is exercising
Cardiomyopathy
Congenital heart disease
Heart failures
Aneurysm
Valvular heart dse (stenosis or regurgitation)
Cardiac tumors
Tumors outside heart, inside chamber, in myocardium
Pericarditis
Pericardial effusion/tamponade
Fluid in the pericardial sac
Septal defects
Shunts
INTRAVASCULAR ULTRASOUND USES
DOPPLER ECHOCARDIOGRAM
Determines speed & direction of blood flow (echocardiogram)
Cardiac function
Valves
Septal defect
Regurgitation
Cardiac output
VELOCITY MEASUREMENT (DOPPLER ECHOCARDIOGRAM)
safe
portable
can get a lot of info
ADVANTAGES OF DOPPLER ECHOCARDIOGRAM
Thickness of heart
Functions of valves
Appearance of blood vessels
Flow of blood
Size & shape of heart
How is it in its function in pumping blood to the circulation
THINGS THAT CAN BE EVALUATED USING DOPPLER ECHOCARDIOGRAM
20-40 mins
Duration of Doppler Echocardiogram