JALAAS 2024
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
Submental blood collection in mice
Modified submental technique is a viable non-terminal blood collection technique and is equivalent to the submandibular site in regards to stress for juvenile and neonatal mice and may be the better option if small amounts of blood are needed
Vein for submandibular blood collection in mice
facial vein
Vein for submental blood collection in mice
inferior labial vein
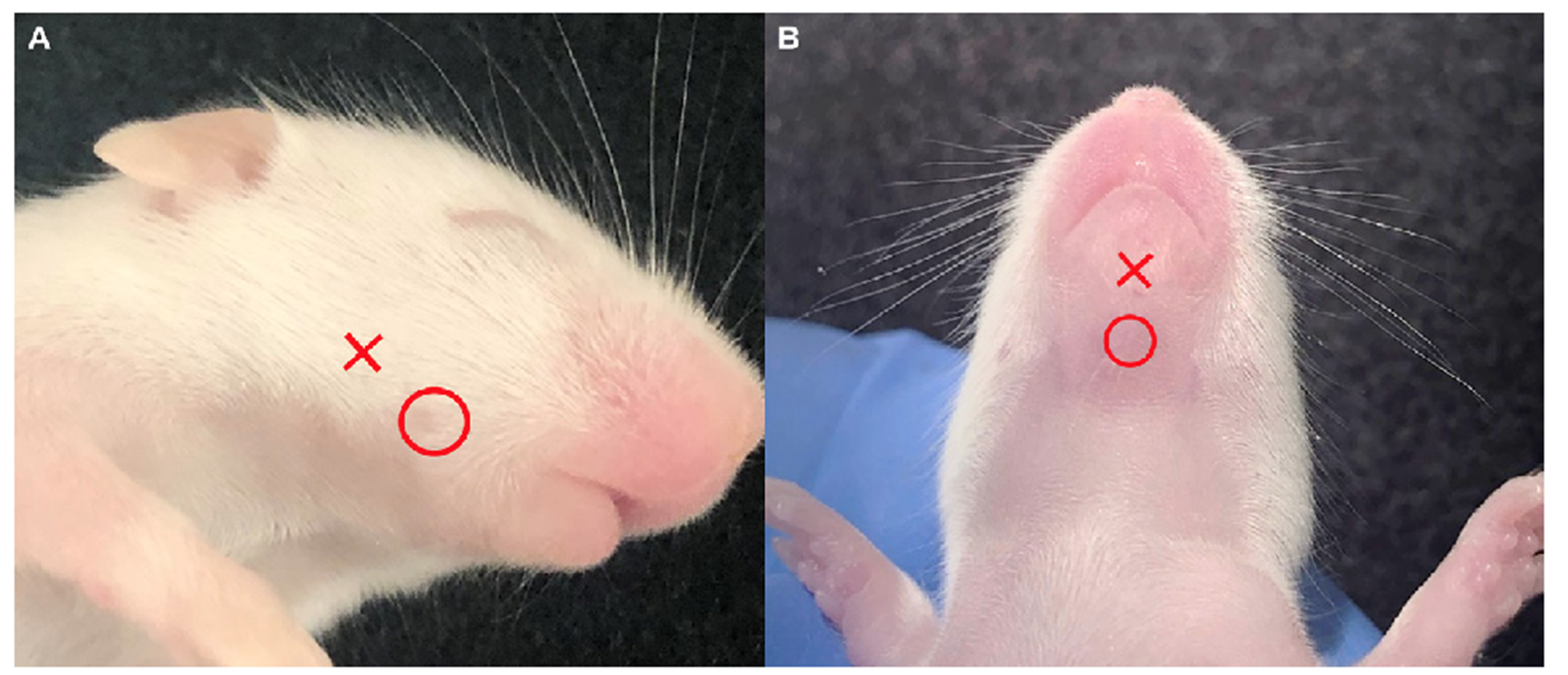
What is being represented by the X and O in A and B
A: X is blood draw site, O is the landmark for submandibular venipuncture
B: X is the blood draw site and O is the landmark for the submental blood draw site.
What is the picture representing?
Shows the gross pathology at 48 h after blood draw from the submental and submandibular locations in various age groups.
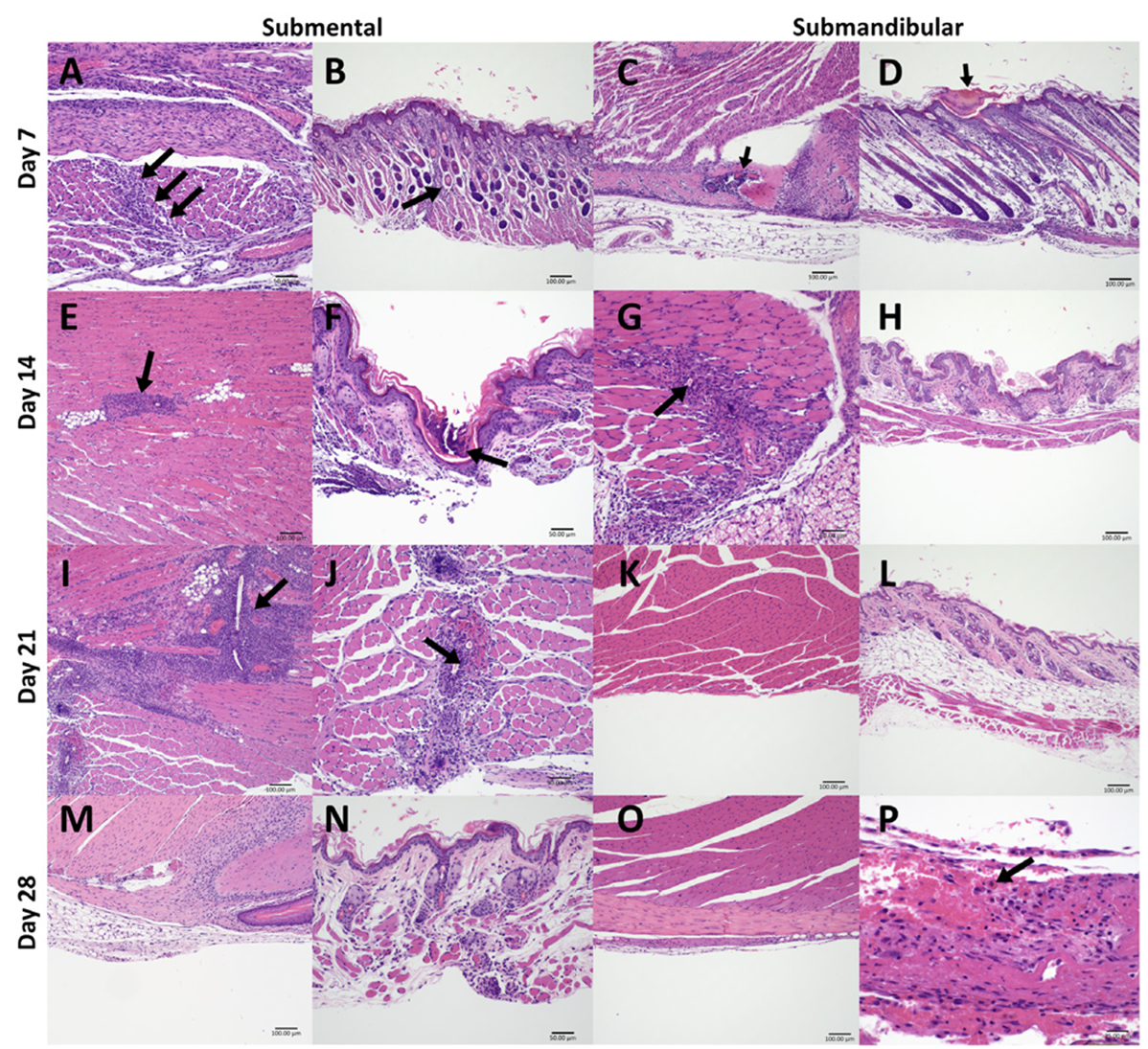
What is the picture representing?
Shows the histopathology at 48 h after blood draw from the submental and submandibular locations in various age groups.
Are there differences between strains and CO2 concentrations to induce loss of righting reflex?
Yes
Which rat strains have higher CO2 concentration requirements: Wistar, SD, Long-Evans
SD
Is there a possibility of pain occurring in rats before LORR occurs when CO2 euthanasia is occuring?
Yes
Is ethiqa XR appropriate for use in rabbits? What dose? And how long does it work for?
Ethiqa XR (dosed at 0.15 mg/kg SQ, once) provides therapeutic plasma concentrations of buprenorphine for 72 hr in rabbits, with minimal side effects and no sex differences. EXR achieved therapeutic plasma concentrations (>0.1ng/mL) by 4h and maintained for 72h. FP achieved therapeutic plasma levels (>0.5ng/mL) by 8h but dropped below threshold between 24-48h time points
Which of the following facial action units is assessed to indicate pain in the NC3Rs Rabbit Grimace Scale but not in the NC3Rs Mouse Grimace Scale?
Orbital tightening
Cheek flattening
Ear position
Whisker changes
Nose bulge
cheek flattening (also occurs in grimace scoring of rats)

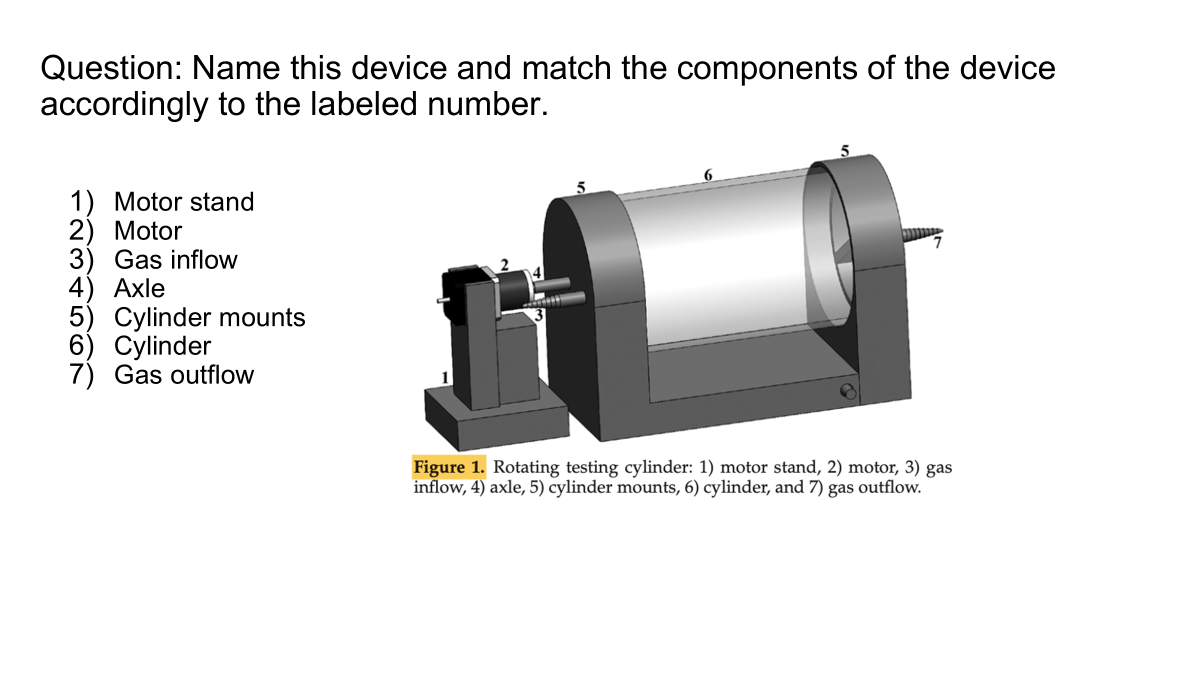
What is this device, and how is it used for environmental management, and how does it compare to classic sentinal programs for monitoring?
New method for rodent environmental health monitoring programs
Best to use 1-month contact Reemay filter in a 10-minute tumbler for the highest % of viral and overall pathogens
1-month contact Reemay filter in a 60-minute tumbler for the highest % of bacterial and parasitic pathogens
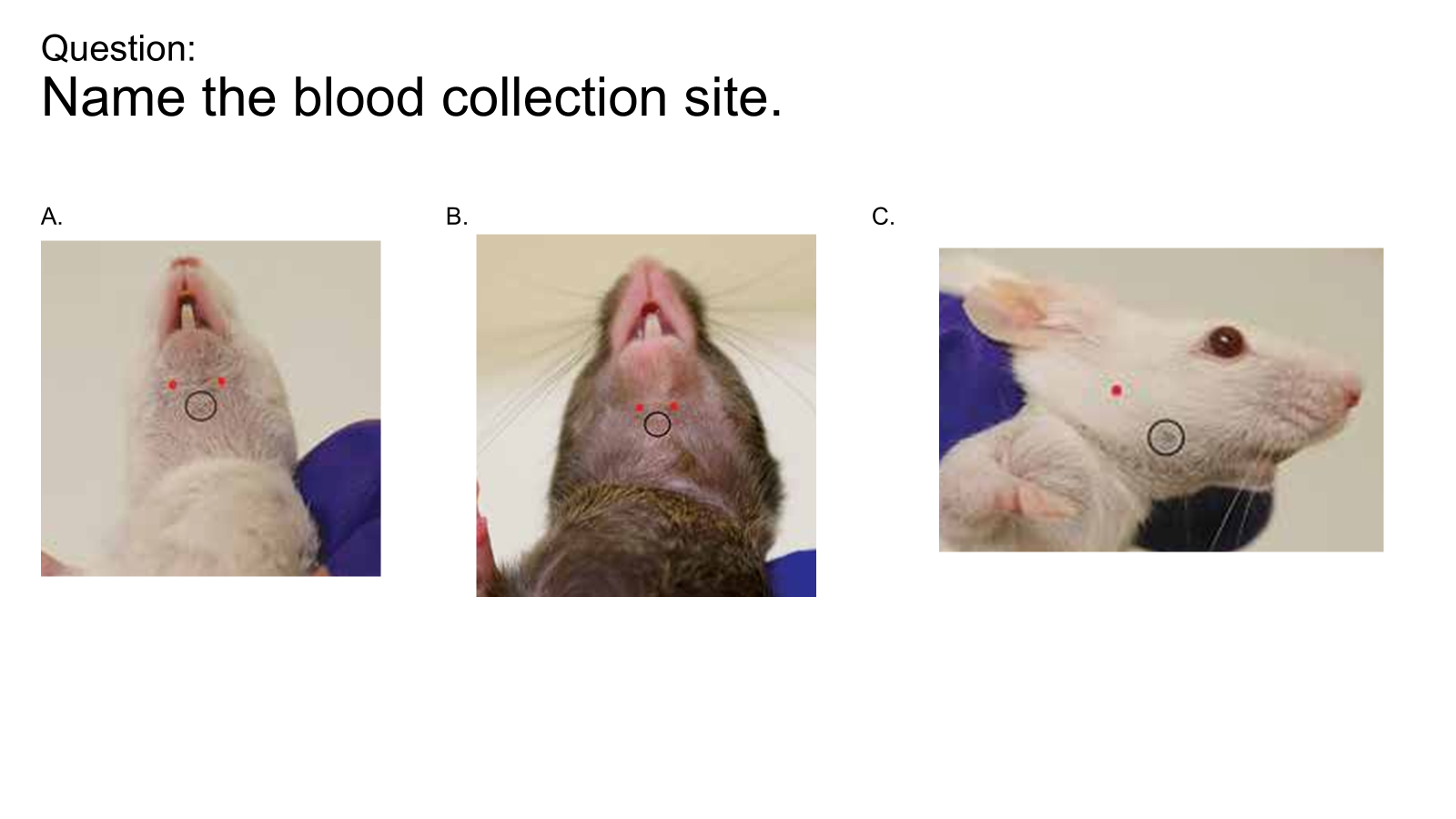
A / B submental location, veins are inferior labial and facial veins
C. linguofacial, submandibular, facial veins
Red is blood collection, circle is the anatomical location
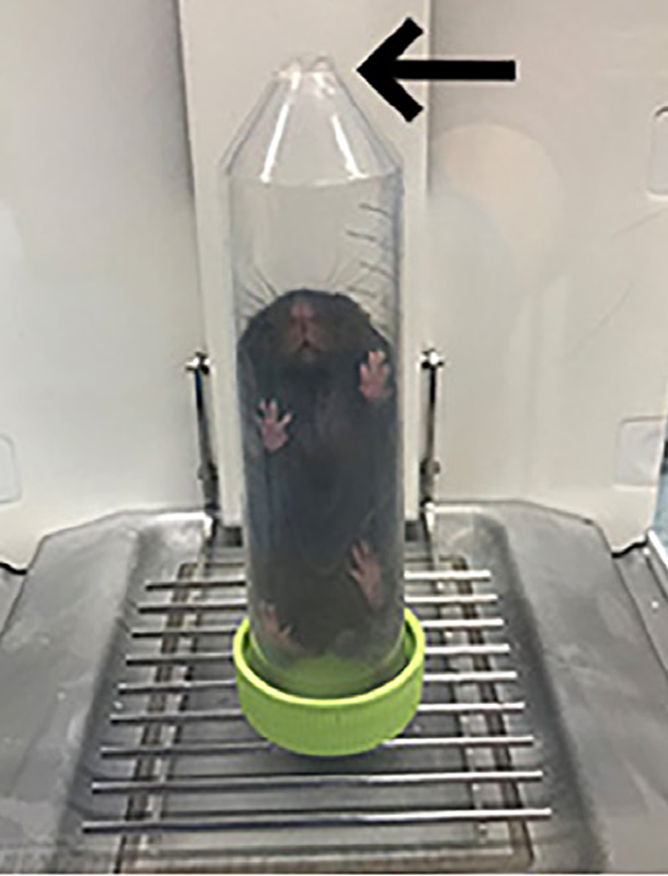

What could this restraint technique be used for?
Weighing mice as well as using for access to saphenous vein for blood collection and injections.
What vein appears be least stressful and reduce impact on post collection blood volume in mice?
Facial vein < saphenous < tail (best)
Does Chlamydia muridarum cause clinical disease in mice?
No, it typically causes asymptomatic infections except in immunodeficient mice
What is Chlamydia muridarum in mice a model for?
•Translational model for human C trachomatis
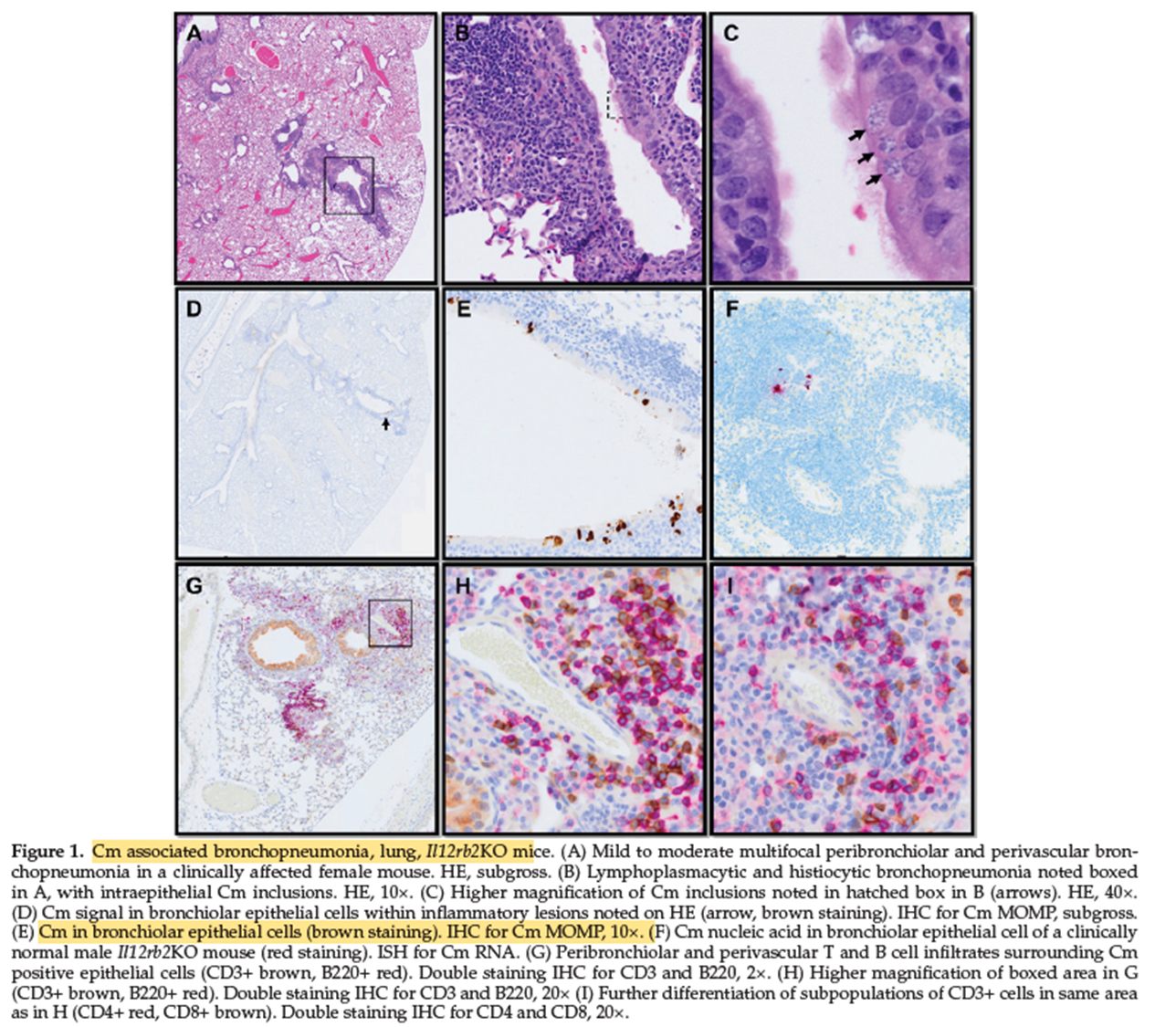
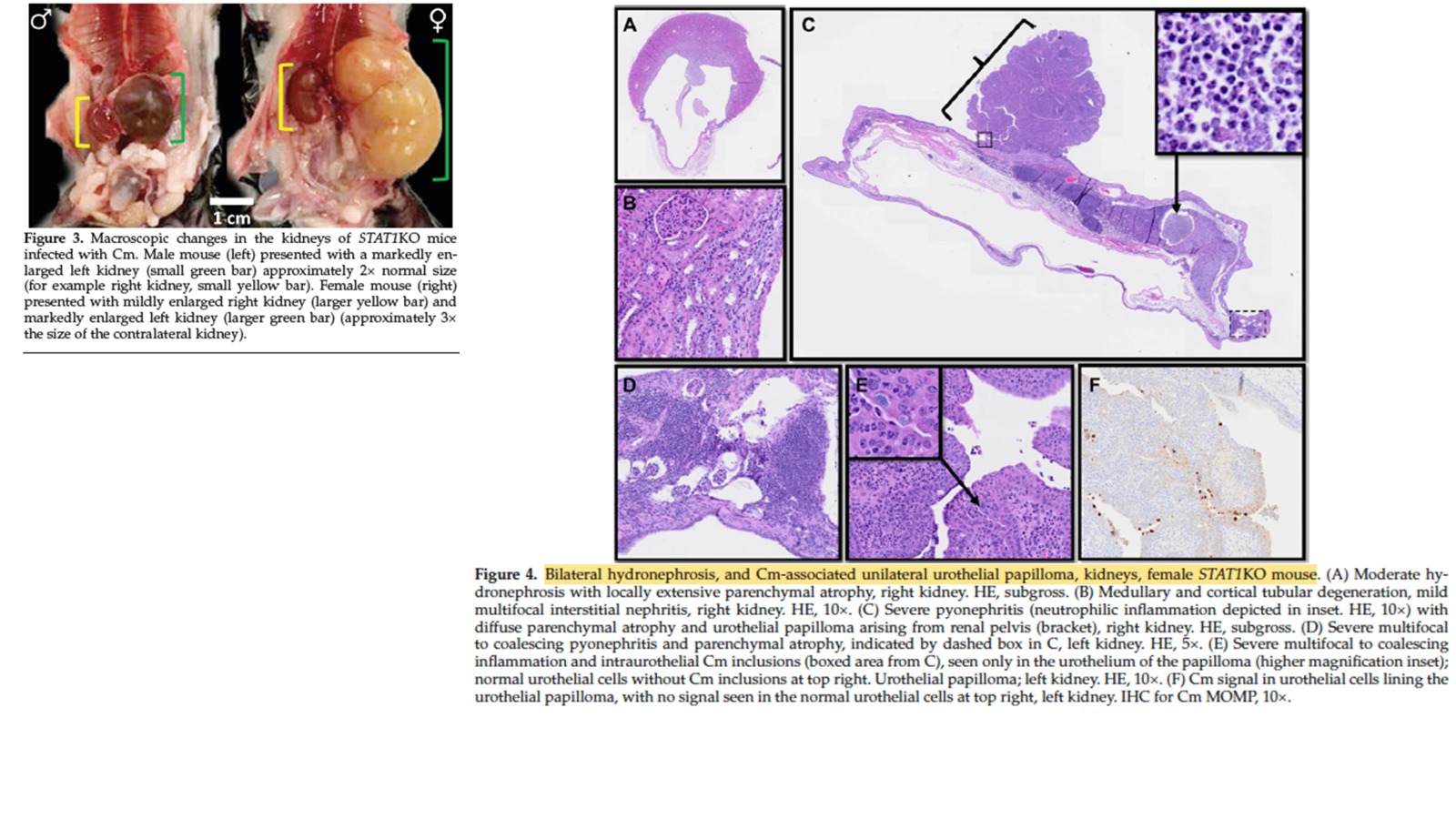
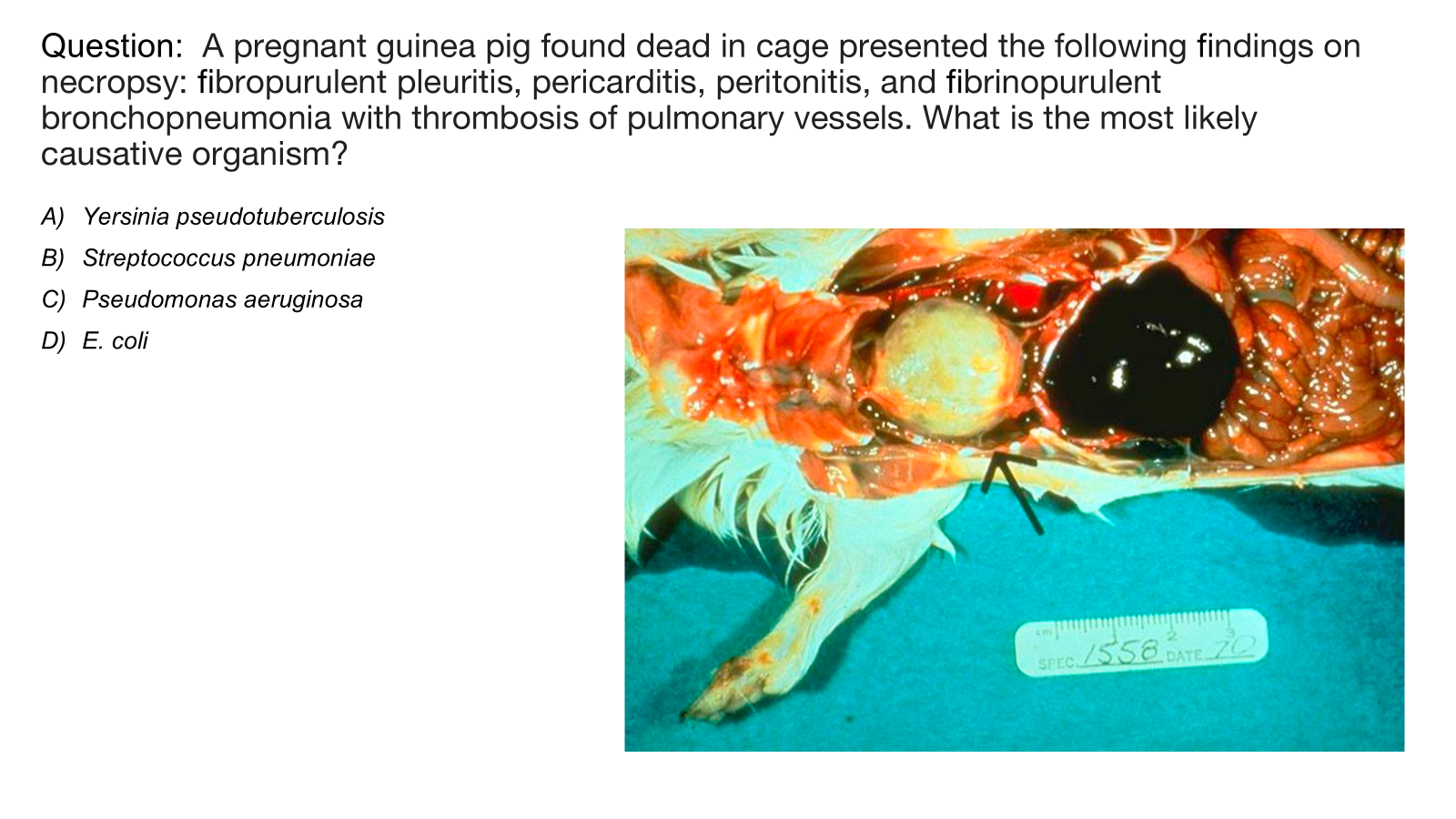
What is the caustative agent that causes renal papilomas and bronchopneumonia in STAT1KO mice?
Chlamydia muridarum

Question: Atropine may be ineffective in what species due to the enzyme atropinesterase?
Oryctolagus cuniculus
Macaca fascicularis
Cavia porcellus
Meriones unguiculatus
Oryctolagus cuniculus
Macaca fascicularis
Cavia porcellus
Meriones unguiculatus
Does SABER-B (sucrose acetate isobutyrate ER bupivacaine; Posimir) or Bupivacaine Meloxicam Polymer (BMP) have better analgesia regarding onset and longevity of effect in pigs?
SABER, onset was quick and provided pigs with 24 - 48 hours of analgesia
Is saliva cortisol comparable to blood cortisol in pigs?
Yes
The pig has a large population of what were initially considered ‘null’ cells, which lack expression of CD2, CD4, or CD8, but are known to express CD3, classifying them as which type of cells?
A) T cells
B) B cells
C) NK cells
D) IgG
A) T cells
B) B cells
C) NK cells
D) IgG
Answer: A - The pig has a large population of what were initially considered ‘null’ cells, which lack expression of CD2, CD4, or CD8, but are known to express CD3, classifying them as T cells. The lymphoid population is largely comprised of γδ Τ cells and is found in large numbers in various tissues, especially mucosal sites (such as the uterus). These are also highly prominent in the newborn. γδ T cells from swine are similar to the ones described from ruminants. Expression of CD4 (T-helper) and CD8 (T-cytotoxic) is mutually exclusive in most species, but swine (similar to human and monkey) have a unique lymphocyte subset that expresses both CD4 and CD8.
What is a possible causative agent for endocarditis in immunosupressed pigs after xenotransplantation?
Mycoplasma hyorhinis-induced endocarditis in an immunosuppressed juvenile pig following allogeneic pulmonary valve (PV) transplantation. Commensal species in Upper respiratory tract of pigs
What are some possible antimicrobial drugs that can be used for treatment of Mycoplasma hyorhinis in immunosuppressed pigs?
Either enrofloxacin or combination azithromycin and doxycycline treatment for suspected cases of MHR in immunosuppressed swine
What pathogen can cause this gross and histologic presentation in immunosuppressed swine recently xenotransplanted with mitral valve?
Mycoplasma hyorhinis, will see vegetative lesions on the heart valves.
There are several potential mechanisms for cross-species infections. Which answer is not correct about transmission of an animal pathogen?
A) An organism could be infectious to both the animal donor and the human recipient (example: T. gondii).
B) Animal viruses that are similar to human viruses, even if not currently known to be zoonotic, could infect humans with this novel access to human cells (examples: animal herpesviruses; cytomegalovirus (CMV) and Epstein–Barr virus (EBV)).
C) A nonpathogenic animal microbe could cause disease after xenotransplantation due to hyper-immunity.
D) A viral recombination between animal and human viruses leading to a virulent recombinant strain.
Answer: C) A nonpathogenic animal microbe could cause disease after xenotransplantation due to immunosuppression.
Reference/Notes: Laboratory Animal Medicine, 3rd edition. ACLAM, eds, Fox, et al, 2015, pg 1373 Chapter 29
Question: According to the AWA, what is false with regards to the correct use of this piece of equipment by a research institution?
A) The tag number shall be correctly listed in the records of purchase, acquisition, disposal, or sale of the dog or cat it identifies and to which it is affixed.
B) Unweaned puppies or kittens do not need tags while they are maintained as a litter with their dam in the same primary enclosure, provided the dam has been individually identified.
C) When an animal dies or is euthanized, this tag shall be retained by a research facility until called for by an APHIS official or for a period of 3 years.
D) No tag number shall be used to identify more than one animal or shall be reused within a 5-year period.
E) This tag is not less than 1-1⁄4 inches in diameter.
Answer: c. When an animal dies or is euthanized, this tag shall be retained by a research facility until called for by an APHIS official or for a period of 3 years.
Answer is ONE year.
How often should the IACUC review CSF protocols for NHPs?
annual
What is a type of catheter used for serial collection of CSF for NHPs?
Serial collection of CSF may be accomplished through a chronically implanted cisternal catheter that is connected to a subcutaneous access port.
What is the CSF volume for adult macaque?
CSF volume in adult male rhesus macaques (8.0 to 10.6 kg) was 10 ± 0.06 mL
How often does Public Health Service Policy on Humane Care and Use of Laboratory Animals require an IACUC to conduct a complete review of ongoing activities?
A) At least once every 3 years
B) At least once every year
C) At least once every 5 years
D) At least once every 6 months
A at least once every 3 years
Question: The pictured animal displays which of the following captive breeding behaviors?
Eusocial, one breeding queen with several non-reproductive workers participating in cooperative brood care
Harem breeding, one male for every 4-6 females
Monogamous, one male, one female pairings
Promiscuous, females and males mate multiple times with multiple mates with no cooperative brood care
Answer: a. Eusocial, one breeding queen with several non-reproductive workers participating in cooperative brood care
Question: All of the following are characteristics of the animal shown that make it a useful animal model EXCEPT:
a. Sociable, cooperative behavior
b. Long life span
c. Resistance to cancer
d. Lack of pain-related responses to mechanical stimuli
Answer: d. Lack of pain-related responses to mechanical stimuli
References: 1) Laboratory Animal Medicine, 3rd edition, pp. 328-330; 2) The Laboratory Rabbit, Guinea Pig, Hamster, and Other Rodents, ACLAM, pp. 1069-1071; 3) JAALAS, Vol 53, No. 1, pp. 89-91.
Domain 3-Tertiary Species
What is being assesed here?
Vehicular vibration similar to what humans experience everyday on the spine.
What are they testing here and which picture us optimal for assessing it?
A/B are optimal for assessing vibrations associated with a vehicle
Question: Match the following species to the field of research for which it is used frequently.
Macaca nemestrina
Macaca arctoides
Macaca radiata
Macaca fascicularis
Balding
HIV research
Pharmaceutical research
Kyasanur Forest disease
Pig-tailed macaque
Stumptail macaque
Bonnet macaque
Crab-eating or cynomolgus
Balding - Macaca arctoides
HIV research: Macaca nemestrina
Pharmaceutical research: Macaca fascicularis
Kyasanur Forest disease: Macaca radiata
What is guanfacine, what is it used for in NHPs?
Adrenoreceptor agonist
Guanfacine showed efficacy in 2 pigtail macaques (Macaca nemstrina) in reducing agonistic and anxiety-related behaviors at a dose of 10 mg/patient.
Guanfacine administration has proven effective at reducing wounds in these colonies, resultant from aggression.
Do Timothy hay based diets reduce dietary calcium reducing risks of urolithiasis in guinea pigs?
No, Transitioning from an Alfalfa hay pellet (AHP) diet to a Timothy hay based (THP) diet with practices to reduce overall reduction in dietary calcium were not sufficient to mitigate risk factors for urolithiasis in guinea pigs.
What guinea pig strain most commonly have uroliths?
Strain 13/N form calcium carbonate uroliths
Do juvenile vs. adult guinea pigs have varying crystal loads in urine?
juveniles have more
What is being shown from this guinea pigs?
uroliths
Is LED lighting an acceptable alternative for lighting for breeding and nonbreeding zebra finches?
Yes
Is LED better than CWF (Cool-white flouresence) regarding hatchling survival?
yes, up to 100%
What is a noninvasive way to assess cortisol in finches?
Feces
Corynebacterium bovis is most severe in juvenile or adult athymic nude mice?
juvenile
Is age important for C. bovis clinical progression in athymic nude mice?
yes
Can mice become infected by dirty bedding from clinically affected mice with Corynebacterium bovis?
Yes
What microbe is this pictograph scoring?
C. bovis
Clinical scoring of C. bovis in mice?
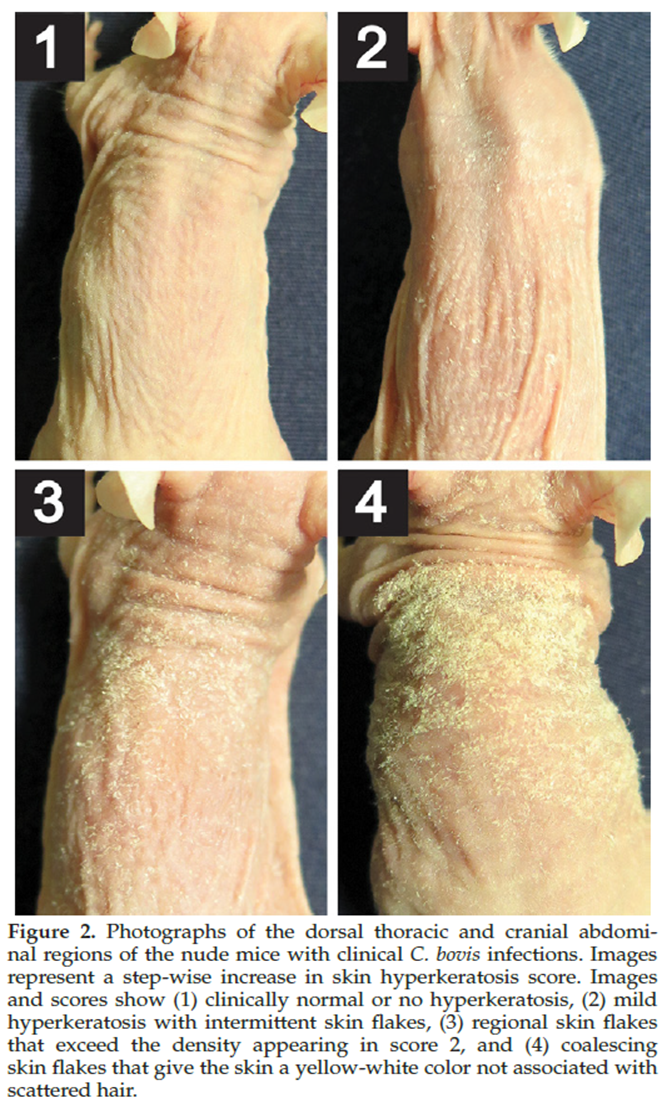
What does C. bovis look like clinically in mice?
Why do female mice have increased temperatures compared to males?
There is evidence that female mice are more active and thus have increased metabolisms.
What is this photo demonstrating?
A study demonstrating induction warming in mice prior to procedures.
Question: What is the definition of a coisogenic strain?
A) A variant inbred strain of mice that differs from an established inbred strain by a mutation at only a single gene
What are some gentle handling techniques to assess / carry fragile mouse models that are prone to handling / stress related preweaning mortality?
Hand warmer inside the glove of the hand that the animal would rest in, dirtying gloves with soiled bedding, and applying gentle pressure to stimulate a warm nesting environment while the snip was obtained from the distal end of the tail. Also softened diets, diet gel too.
What is a better way for testing, sentinel mice vs. plenum and cage level filter exhaust testing?
Soiled-bedded Sentinel (SBS) cage-level exhaust filter and exhaust dust test plenums are superior to SBS
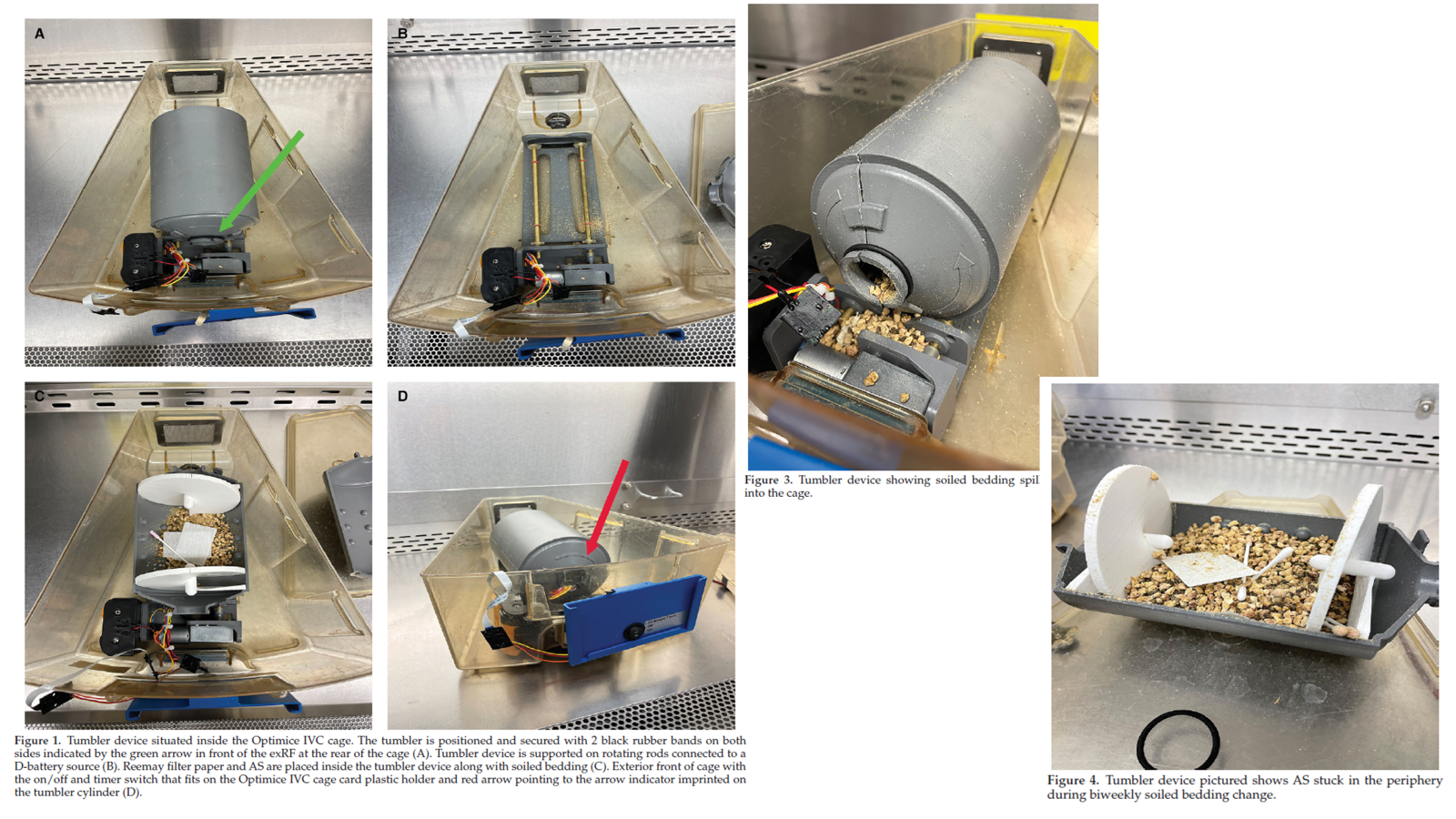
What are these used for?
sentinal testing for colony management

What are these used for?
sentinal testing for colony management
Question: Which agent causes the following pathology?

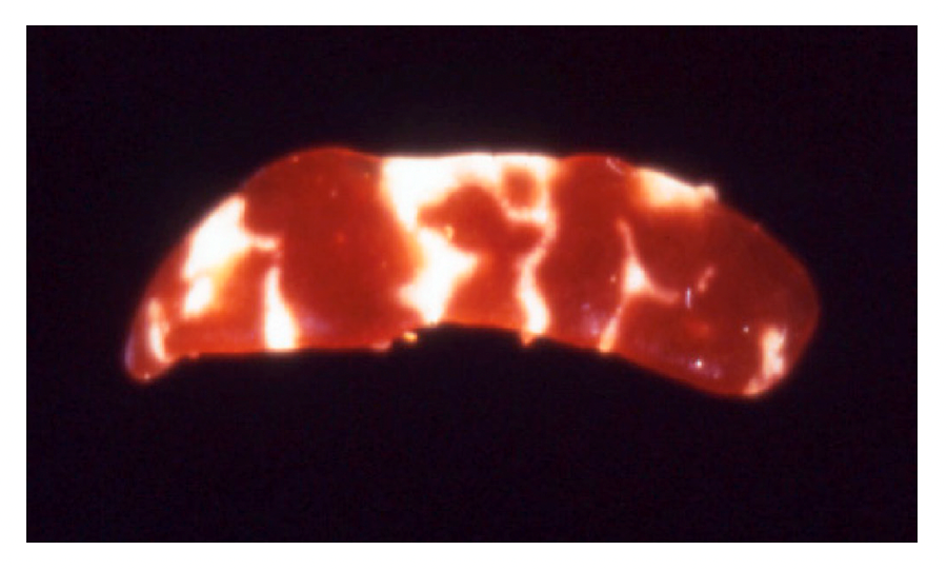
A) Polyoma Virus
B) Minute Virus of Mice
C) Ectromelia virus
D) Reovirus 3
Answer: C- Ectromelia virus
What can automated neural networks be used for in NHPs?
Automated neural networks can be used/trained for automated facial recognition and classification of pain in Japanese macaques
What technology is being demonstrated here?
automated neural network training to assess for pain in NHPs.
Question: The minimum cage size for a singly-housed male Macaca fuscata NHP (weighing 11 kg) in an AAALACi accredited facility is sq ft and inches high.
4.3; 30
6.0; 30
4.3; 32
6.0; 32
7.4; 30
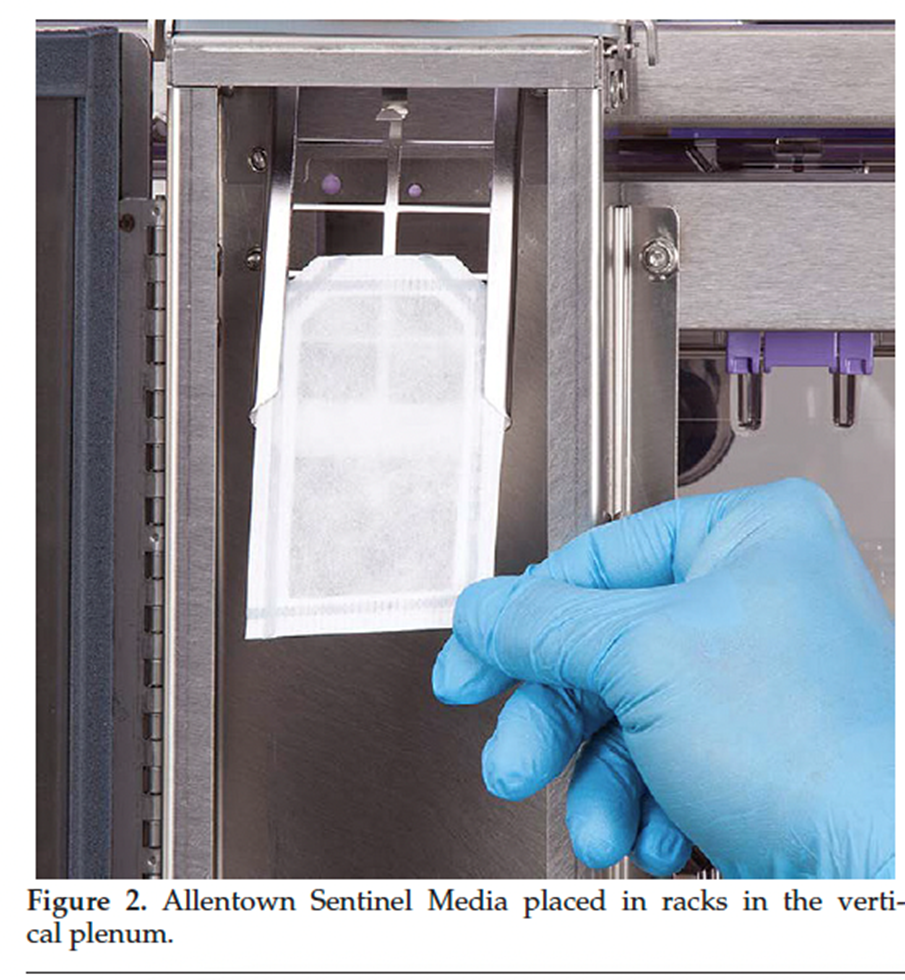
What is recommended for detecting helicobacter in colony monitoring?
Combining a direct colony sampling method, such as fecal pellet Helicobacter spp. PCR, with in-cage filter paper or another environmental health monitoring (EHM) method, has the potential to increase Helicobacter spp. detection rates. (PCR of fecal pellets has 100% sensitivity)
Is testing with filter paper in dirty bedding cages effective for detecting helicobacter?
no