Intro to cells
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
Feedback loops
These are control pathways that go with or against homeostasis
Homeostasis
Keeping the internal body the same with different external influences (heat, ph changes, etc)
Which of the organs is the control centre for homeostasis?
Hypothalamus
Which of these are not controlled by the hypothalamus to maintain homeostasis?
A) B and D
Circadian Rhythms
Controls when and where you are sleepy, based on the amount of light you get and the temperature of your body
Temperature increases as you reach bedtime
Set points
The way your body maintains homeostasis is not a set number but rather keeping it in a certain area (Ie 36.5 to 37.5)
Why does oscillation occur around the set points
Negative feedback
Positive feedback
This reinforces stimulus
oxytocin does this
Parts of the cells
Plasma membrane
Cytoplasm; Cytosol (gooey interior) and the organelles
Nucleus; Chromosomes and genes
Why do cells differentiate from each other?
Functions are different
Nucleus
Cell replication and repair
Usually only one
Which are the two exceptions that a cell only has one nucleus?
C) A and D
Why do red blood cells not have a nucleus
They must fit through the capillaries, a nucleus is too large
Why do long muscles have multiple nucleuses
they are long and under lots of stress, so repair must be quick
Ribosomes
Free or attached, they make proteins
muscles will have a lot of these
Attached proteins
Found on the rough ER, they make proteins for export
What are the 3 functions for the smooth ER?
Calcium storage; skeletal muscles
Detoxification; liver
Steroid production; reproductive organ
What are the functions of the rough ER?
Protein export
Creation of organelles
The pancreas will have a lot of these because elf insulin production
Golgi Complex
Re-packages the rough ER’s protein into vesicles to be transported out
pancreases will have a lot of these
Free ribosomes
Will make proteins for the cells
Peroxisomes
These are oxidative enzymes that remove free radicals
Metabolism for lipid synthesis
Detoxify waste into safer chemicals
Found in the liver!
Lysosomes
Sac of digestive enzymes
Repair and removal of forgiven matter
Found in white blood cells
What happens when homeostasis is not reached?
The body will then fall into diseases and illnesses
Negative Feedback
Stimulus is sent, causes a reaction that decreases the cause, the stimulus is turned off.
maintains homeostasis
What type of errors can occur in negative feedback loops?
overcompensation
disease
competing regulators
Proteosomes
Large protein complexes that removes old organelles (tagged organelles)
Cytoskeleton
Large, complex protein network to protect and maintain the cell
Microtubules
transports secretory vesicles
forms the spindle fibres in mitosis
Tubulin!
Microfilaments
Contract system
Muscles
Stiffeners
Myosin and Actin
Intermediate filaments
resist stress
Hair and skin
Keratins!
Centrosomes/Centrioles
Type of organelle found mainly in the skin for cell replication.
Creates spindle fibres
Cilia
One-way movement
found in the trachea and uterine tubes
power stroke and recovery stroke
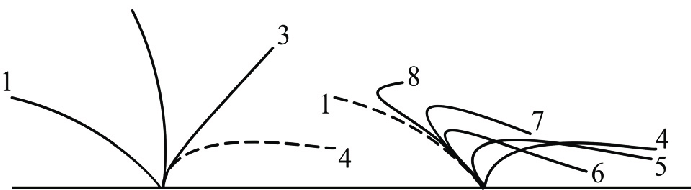
Flagella
On moving the cell
only located on the sperm
Mitochondria
Recycles energy for ATP production
TCA and ETC
How many types of cells are there in the body?
200
What are the two factors that play into the cell’s function?
Shape of the cell
Type of organelles present
What happens to our cells as we age?
Deterote
Loss of extracellular components
Free radicals
Free radical theory
Damaged byproduct from cellular metabolism
Damage to essential molecules (o2 to o3)
caused by aging
Mitochondrial theory
Decrease production of energy that weakens the cell with age
Genetic Theory
Aging is caused by our genes
With the replication of DNA, telomeres disappear, causing the chromosome to degrade
Signals the start of aging
What does the Plasma Membrane mainly contain?
Physical barrier
Gateway for exchange
Communication
Cell structure
What does the cell membrane contain?
Mainly phospholipids and cholesterol for fluidity
Phospholipids
Protect the cell externally
Choline head (polar)
Fatty acid tails (non-polar)
Glycocalyx
These are glycoproteins(on a protein) and glycolipids(within the cell membrane)
cell identity and cell orientation (pushes away other cells so there is room to growth)
What are the two types of membrane proteins?
Integral/transmembrane proteins
Peripheral proteins
What are the 7 functions of membrane protein?
Ion channels (small, charged chemicals)
Carrier (larger uncharged molecules)
Receptor sites (identify)
Enzymes (triggers)
Pores (movement of H2O)
Structural (maintain shape)
Cell adhesion (Groups proteins)
The membrane is selectively permeable
True
How do molecules move into the membrane
Small uncharged and non-polar molecules move through the membrane
Transmembrane proteins more polar particles
Macromolecules use vesicles
What is the difference between passive and active transport
Passive goes with the gradient and active goes against, using AT in the process
What are the 3 types of gradients
Concentration
Electrical
Electrochemical
Simple diffusion
Movement of molecules from a high to low concentration because of collisions
No usage of proteins
Ie, steroids and small, non polar molecules
Net movement
The total amount of molecules moving in or out of the cell membrane
What controls simple diffusion
Temperature
Concentration
Distance
Mass
Diffusion across the membrane is controlled by what 4 factors
Permeability
Surface area
Gradient
Temp
Osmosis
The movement of water down its own concentration radiant
Tonicity
The total number of non-diffusible particles
Hypertonic
Tonicity is high, pulling water out (crenation)
Isotonic
Tonicity is the same
Hypotonic
Tonicity is low, water is pulled in (hemolysis)
What is facilitated diffusion
Usage of proteins to move molecules without ATP
What are the two types o facilitated diffusion
Open and closure of these proteins allows to move along the concentration gradient
Channel: molecules can move down or up (Na and K)
Carrier: will attach and move (Glucose)
What is an example of primary active transport
Na/K ATP pump
Co-Transport Mechanism
Secondary active transport
One against one with in the same direction
Symporter
Counter-Transport Mechanism
One with and one against moving in opposite directions
Anti-porter
Receptor/ligand-mediated endocytosis
Binds and takes in molecules via a vesicles
Ie, Lipids, vitamins, iron, antibodies
Phagocytosis
Removal of molecules from the cell
Ie, white blood cells
Pinocytosis
Movement of water into the cell (can come with molecules)
Epithelial Transport
Combination of diffusion and active transport for movement
Ie, Gut and Kidney
Ligands
Special molcules that bind with receptors
Channel-linked receptors
Allows ions to move in and out of the cell through ligands binding, initiating electoral changes and opening channels.
Ie, neurotransmitters
Enzymatic Receptors
Ligand binds to the receptors releasing protein kinase enzymes that turns on enzymatic activity
G-Protein coupled receptors
Indirectly activates the protein kinase enzymes
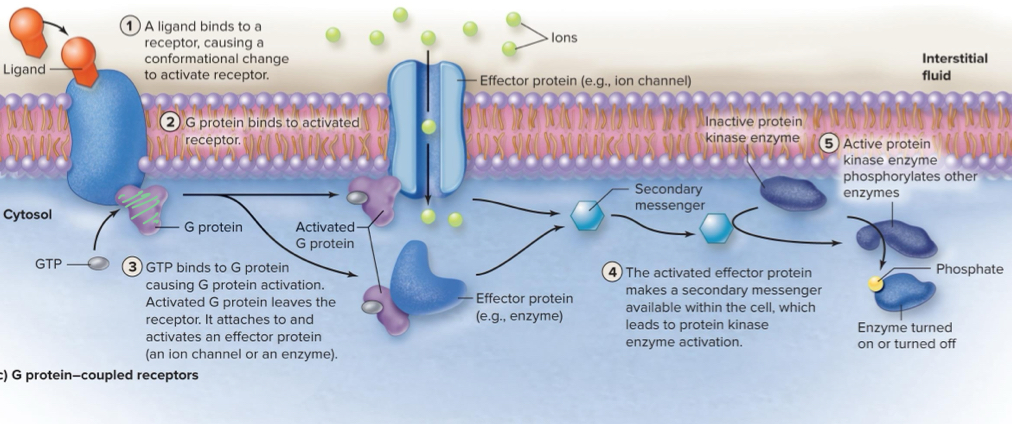
Secondary Messenger response
Creates a response by activating a 2nd part of the line
cAMP
Activates protein kinase which in turn, create a rapid response
Calcium
Activated IP3 releases Ca2+ from the ER
DAG and IP3 activate enzymes and kinase
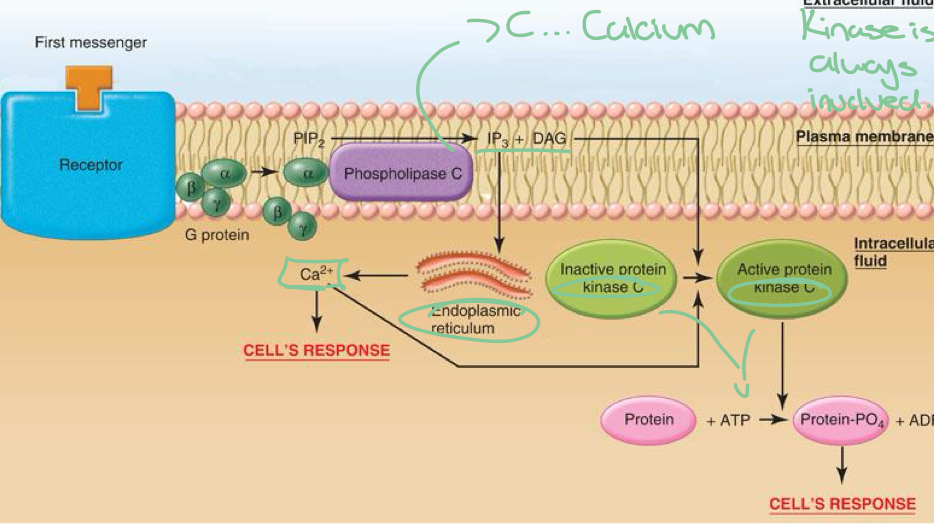
Calmodulin
Activates kinase protein (same as cAMP)