MNT 2 Final Exam -Acid-base balance & Renal
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/279
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:58 PM on 4/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
280 Terms
1
New cards
Movement of fluid across semi-permeable membrane from a lower concentration of solutes to a higher concentration of solutes
osmosis
\
\*water moves into teabag)
\
\*water moves into teabag)
2
New cards
Movement of fluids through a membrane
Filtration
3
New cards
Form of filtration that provides additional pressure to achieve more concentrated filtration
Ultrafiltration
\
*squeeze extra fluid through the membrane*
\
*squeeze extra fluid through the membrane*
4
New cards
Preferred permanent access site for dialysis
AV fistula
5
New cards
Fluid used by the dialysis procedure to assist in removal of metabolic by-product, wastes, and toxins
\
1. If a pt has hyperkalemia, then _____ will be added
2. If a pt has hypokalemia, then _____ will be added
\
1. If a pt has hyperkalemia, then _____ will be added
2. If a pt has hypokalemia, then _____ will be added
1. Dialysate
2. No K will be added (0 k bath)
3. K will be added (1 or 2 k bath)
6
New cards
high sodium food is considered:
>400 mg/Na/serving
\
\*General rule: ≤ 2.4 g/d
\
\*General rule: ≤ 2.4 g/d
7
New cards
What does “leaching” k from vegetables mean?
The process by which the K is leached from the potato is changes the texture of the potato (%%pull some of K out and into the water%%)
8
New cards
How much K is in a potato?
\~600 mg
9
New cards
A procedure done by a machine that functions as an artificial kidney that removes excessive and toxic by-products of metabolism from the blood; also called renal replacement therapy
Dialysis
10
New cards
What are they two types of RRT?
1. Hemodialysis
2. Peritoneal dialysis
11
New cards
When is dialysis needed?
Needed for end-stage renal disease
12
New cards
Most common type of dialysis and conducted in a dialysis center. How often is it administered?
1. HD
1. 3x/week 4h each time (individualized based on pt status)
13
New cards
utilizes the abdominal wall of the pt as the semi-selective membrane. Used at home
1. PD
14
New cards
T/F: Dialysis requires a semi-permeable membrane that allows passage of water and small to mid MW molecules and ions, excludes large MW molecules (PRO)
True
15
New cards
Used with acute renal failure or before HD/PD begins
1. Continuous renal replacement therapy
16
New cards
Passage of particles through a semipermeable membrane
Diffusion
17
New cards
Match the drugs:
1. Dec K+
2. Dec plasma PO4
3. Lower BP
4. Dec Bp
5. Dec chol, CVD
1. Dec K+
2. Dec plasma PO4
3. Lower BP
4. Dec Bp
5. Dec chol, CVD
1. Tums (kaexilate)
2. Phosphate binders
3. ACE inhibitor
4. Metformin, diabetes
5. Lipator, zocor
1. \
18
New cards
Define:
1. NIDDK
2. KDOGI
3. CKD
4. RRT
1. NIDDK
2. KDOGI
3. CKD
4. RRT
1. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
2. Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes
3. Chronic kidney disease
4. Relative retention time??
19
New cards
Kidney handles K well until GFR …..
20
New cards
21
New cards
Potassium for HD pt
2-3 g K+/d
22
New cards
Why would you need to restrict K when on an ACE inhibitor?
1. This drug dec aldosterone -→ Inc K
23
New cards
Why reduced activation of Vit D in CKD?
1. B/c pt cannot consume dairy
2. Vit D activation occurs in the kidney
24
New cards
25
New cards
Low potassium foods (200 mg or less)
1. Apple juice/applesauce
2. Cranberry juice
3. Carrots
4. kale
5. corn
26
New cards
What is osteodystrophy? What minerals is it apart of?
1. Osteitis fibrosa, osteomalancia
2. Ca and Phos
27
New cards
Foods higher in potassium (more than 200 mg)
1. Oranges/orange juice
2. Cantaloupe
3. Avocado
4. potatoes
5. Sweet potatoes/yams
28
New cards
29
New cards
Recommendations for fluid
1. ≥1 L fluid output: 2 L fluid intake
2. ≤1 L fluid output: 1-1.5 L fluid intake
3. Anuria: 1 L fluid intake + 2 g Na diet
4. HD: If edema occurs
1. Intake = output + 500 mL (covers insensible losses)
30
New cards
What GFR reflects the kidney fx of a healthy adult
130 mL/min/1.73m^2
31
New cards
BUN:Cr ratio normal range
10-15
\
\
32
New cards
Which hormone decreases BP?
Aldosterone
33
New cards
The majority of bicarbonate is reabsorbed in the
Proximal convoluted tubule
34
New cards
Consequences of high solute load
1. Fever
2. Weight loss
3. Oliguria
4. Hypernatremia
35
New cards
Fx of parathyroid hormone
Increase calcium concentrations in blood
36
New cards
Potassium control…
Diet, drugs, dialysis
37
New cards
Phosphorus controls…
Diet and drugs
38
New cards
Protein controls
Diet, dialysis
39
New cards
Fluid is managed with…
Diet, drugs, dialysis
40
New cards
Kayexlate
1. Cation exchange resin used for trt of hyperkalemia
\
41
New cards
May increase losses of Mgand Ca; inc serum Na
Kayexlate
42
New cards
T/F: You should use kayexlate with a high K diet
False, low K diet
43
New cards
How is kayexlate administered?
Orally
44
New cards
High in water soluble vitamins lost in dialysis, lower in _____ soluble vitamins retained in dialysis
Nephrovite, fat
45
New cards
Stimulates erythropoiesis (RBC) production
EPO (epogen, procrit)
46
New cards
What should you do with Fe and Ca with EPO drug?
1. Give w/ Fe supplement if Fe stores inadequate
2. Don’t give at the same time as Ca supplement
47
New cards
Want ferritin >______ ng/mL for EPO
>100
48
New cards
controls hyperphosphatemia by binding phosphorus from food in GI tract
Phosphate binders
\
reduce the amount of phosphate being absorbed in the blood stream
\
reduce the amount of phosphate being absorbed in the blood stream
49
New cards
Why are phosphate binders given 1/2 before 1/2 after eating?
1. Taking a dose on an empty stomach can cause nausea and vomiting
2. Helps prevent phosphorus from being absorbed into the bloodstream by “binding” to the food and carrying it through the rest of the gut
50
New cards
Consequences of long-term use with phosphate binders
1. Al (aluminum containing) deposits in bone and brain -→ Alzheimer’s
2. If \[Phos\] >6.0 use AI containing Phos binders %%short term%%
3. Ca-containing binders (tums) don’t use when serum \[phos\] >6.0 or if serum Ca product >60
1. Can cause calciphylaxis in soft tissue
51
New cards
T/F: Only give Aluminum phosphate binders short term d/t toxicity tissues
True
52
New cards
Active vitamin D supplements
Rocaltrol (po) / Calcijex (IV)
53
New cards
Why are vitamin D supplements used?
Given to maintain serum Ca WNL and suppress PTH levels in order to prevent 2\* hyper PTH and metabolic bone disease
54
New cards

Identify foods high in K, Phos, or both
1. Banana: high K, low Phos
2. Soybeans: High K, high Phos
3. Milk: High K, High Phos
4. Coffee creamer: low K, low phos
5. Steak: low K, high Phos
6. Sprite: low K, low Phos
7. Potato: high K, low Phos
8. PB: High K, high Phos
9. Eggs: low K, low Phos
55
New cards
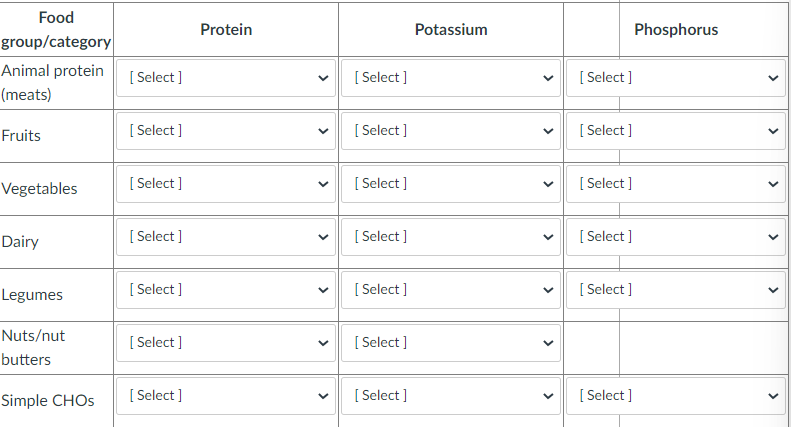
Identify how each food category does for PRO, K, Phos
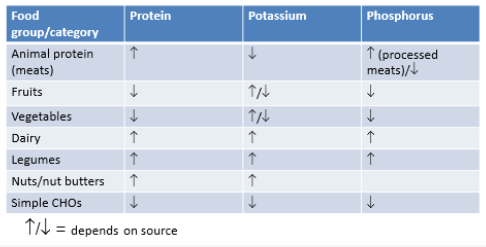
56
New cards
When should you not use active vit D supplements?
1. Ser phos > 6.0 mg/dL
2. Ser Ca >11.5 mg/dL
3. Ca\*PO product >60
4. Intact PTH
57
New cards
Describe the function of ACE inhibitors
Rennin -→ angiotension I -→ angiotension II (vasoconstriction) -→ aldosterone resorbs Na+ -→ Inc BP
58
New cards
What are common ACE inhibitors?
1. Capoten
2. Vasotec
3. %%pril -→ MOST COMMON%%
4. Lotensin
5. Altace
59
New cards
May cause elevated K due to renal K resortion
ACE Inhibitor
60
New cards
If serum K > 5.6 mEq/L, dietary *should be restricted &* ________ containing salt substitutes avoided on what drug?
K, K, ACE inhibitor
\
\*\*\*If pt is near the end of life, don’t restrict, remember Campbell’s story in class
\
\*\*\*If pt is near the end of life, don’t restrict, remember Campbell’s story in class
61
New cards
Why would you need a K restriction when on an ACE inhibitor?
This drug dec. ADH -→ Inc \[K\]
62
New cards
Is N balance appropriate method to assess protein status for a renal patient?
Not useful in renal pt d/t decrease N clearance
\
(aka N is being reabsorbed and not excreted)
\
(aka N is being reabsorbed and not excreted)
63
New cards
The amount of N waste and minerals that must be excreted daily by the kidneys.
What is RSL
64
New cards
A diet high in RSL requires what?
Increases fluid
65
New cards
Indicator of renal fx. What indicates “good” function
GFR, >125 mL/min/1.73m^2
66
New cards
Part of RASS system, reabsorb Na for BP control
Aldosterone
67
New cards
Permeability of distal tubule and collecting duct to increase H20 resorption
ADH
68
New cards
4 classic renal indicators
BUN, Serum Cr, Serum K, Serum PO4 or PHOS
69
New cards
Other labs that influence renal disease
1. Sodium
2. Albumin
3. PAB
4. Calcium
5. TG/Cholesterol
6. H/H
70
New cards
In anthropometrics, weight is complicated by _____
1. Fluid retention
1. Weight is complicated by fluid status
71
New cards
4 descriptive criteria for edema-free BW
aka dry weight
1. Weight at normal hydration, not edematous
2. Normal BP
3. No evidence of edema
4. Serum Na+ WNL
1. Weight at normal hydration, not edematous
2. Normal BP
3. No evidence of edema
4. Serum Na+ WNL
72
New cards
What is dialysis pt dry weight?
\
1. Weight at end of dialysis WHEN normal BP is reached
1. Weight at end of dialysis WHEN normal BP is reached
73
New cards
What is standard body weight (SBW)
1. %SBW = Actual body weight / SBW x 100
74
New cards
An indicator of nutritional status (similar to IBW)
SBW
75
New cards
SBW >115% is considered ____ __&
1. obese
2. malnutrition
76
New cards
How do you calculate ABW?
ABW = BWef = BWef + (\[SBW - BWef\] \* 0.25)
1. Use wt
1. Use wt
77
New cards
List…
1. NIDDK
2. KDOQI
3. CKD
4. RRT
1. NIDDK
2. KDOQI
3. CKD
4. RRT
1. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Disease
2. Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative
3. Chronic Kidney Disease
4. Renal replacement therapy
78
New cards
Define CKD
1. Presence of irreversible nephron damage
2. Inability of kidney fx to return to normal after ARF OR progressive renal decline from disease
79
New cards
Dx criteria for CKD
1. GFR
80
New cards
What are the risk factors of chronic kidney disease?
1. Have DM
2. High BP
3. Family hx of kidney failure
4. Older
5. Belong to a population group with a high rate of diabetes
81
New cards
Characteristics of CKD
1. Severity defined by decreased Cr and urea clearance
2. increase serum Cr and urea
82
New cards
Symptoms of CKD
1. Severe headache
2. Dyspnea
3. Pitting edema of extremities
4. Failing vision
5. Decrease appetite
6. N/V
7. Abdominal and or joint pain
83
New cards
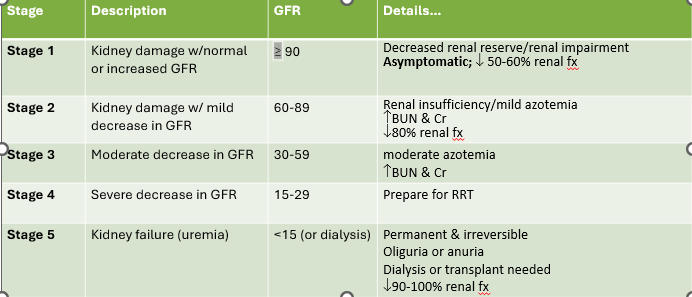
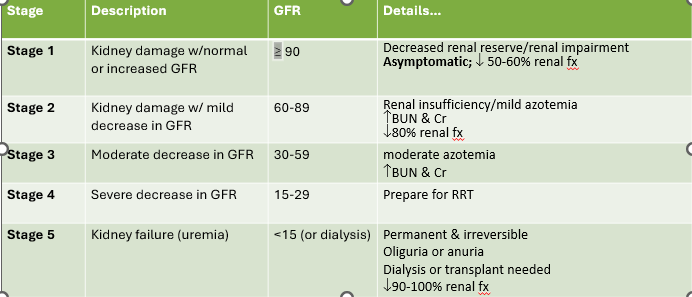
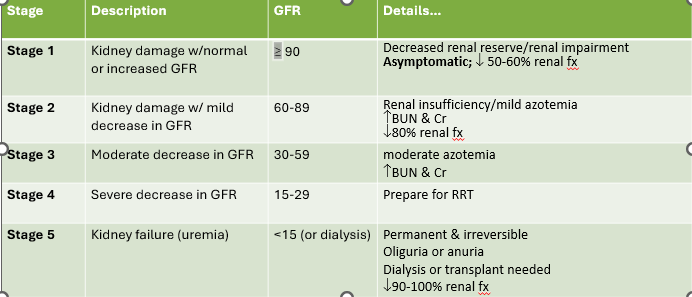
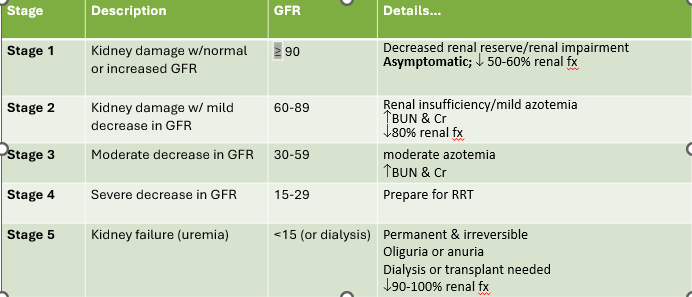
Stage 1 CKD
1. Kidney damage w/normal or increased GFR
1. GFR ≥90
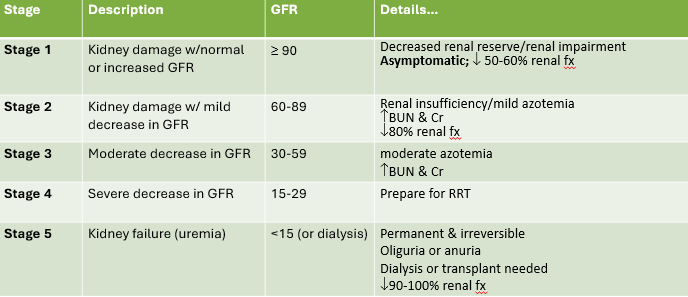
84
New cards
1. Decreased renal reserve/renal impairment
2. Asymptomatic; decreased 50-60% renal fx
Stage 1 CKD
85
New cards
Stage 2 CKD
1. Kidney damage w/mild decrease in GFR
86
New cards
1. Renal insufficiency/milkd azotemia
2. Increase BUN and CR
3. Dec. 80% renal fx
Stage 2 CKD
87
New cards
Stage 3 CKD
1. Moderate dec, in GFR
2. GFR = 30-59
88
New cards
Moderate azotemia, increase BUN and CR
Stage 3 CKD
89
New cards
GFR in stage 2 CKD
60-89
90
New cards
Stage 4 CKD
1. Severe decrease in GFR
2. GFR = 15-29
91
New cards
What stage do you prepare for RRT
Stage 4
92
New cards
Stage 5 CKD
1. Kidney failure (uremia)
2.
93
New cards
What are our main goals for CKD MNT?
1. Still provide adequate energy to maintain/achieve IBW and *prevent malnutrition*
2. Prevent/alleviate symptoms of *uremia*
3. *Treat micronutrient deficiencies*
4. *Normalize blood lipids*
94
New cards
CKD progression of tx
1. Conservative management with diet and drugs
2. Dialysis (RRT; along with diet and drugs) Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis
3. Transplant
95
New cards
General nutrition intervention for Stages 1-2

96
New cards
General nutrition intervention for Stages 3-4

97
New cards
General nutrition intervention for Stage 5
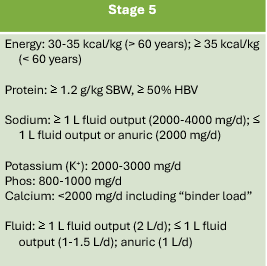
98
New cards
What does a complete protein mean?
has all 9 essential AA
99
New cards
Most plant sources are _____ PRO and are considered
Incomplete, low biological value
100
New cards
Predialysis is considered what stage? Dialysis?
1. Stages 3-4 2/3 HBV
2. Stag3 5: 50% HBV