Biology Week 4: Photosynthesis
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is the formula for photosynthesis?
6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy → C6H1206 + 6O2 (AKA, the reverse of cellular respiration!)
If you were to build a photosynthesis machine, what parts would you need?
1. A way to capture CO2 (stroma)
2. Access to water (roots)
3. A way to capture light energy (chloroplastsl)
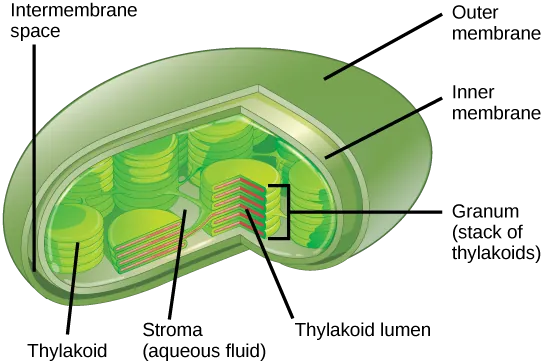
What is the site of photosynthesis?
Chloroplasts!
What are the two parts of photosynthesis?
Light Reactions & the Calvin Cycle
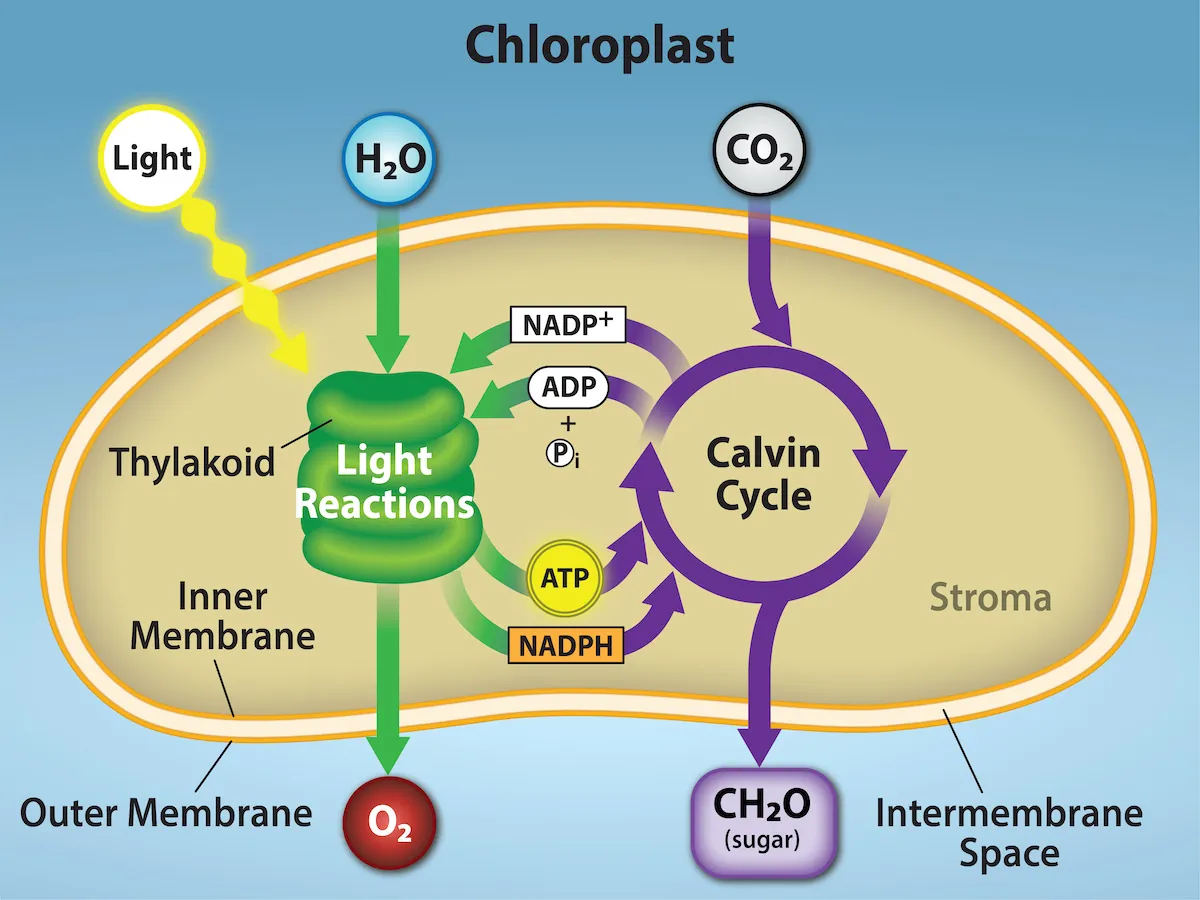
What takes place in the stroma?
The Calvin Cycle
What takes place in the thylakoids?
Light Reactions
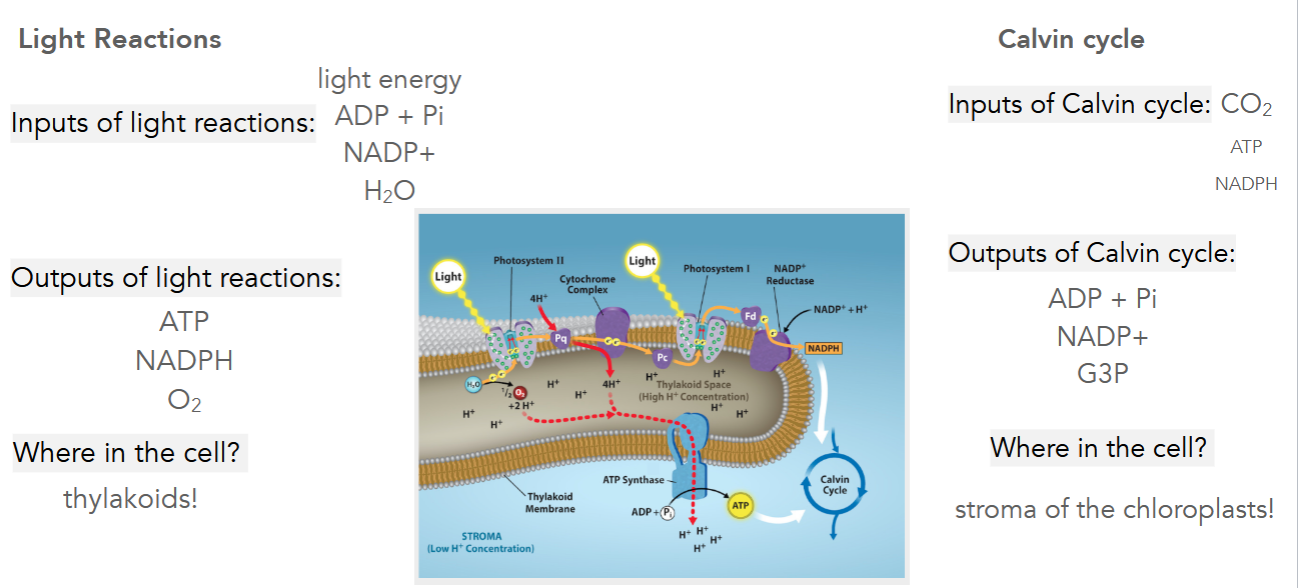
What happens during the light absorption phase of light reactions?
pigment molecules in the antenna complex absorb energy that excites electrons
energy from excitement of electrons is transferred to reaction center
electrons from pair of chlorophyll are passed to a primary electron acceptor
electrons from water replace electron “hole” in reaction center molecules
oxygen released
H+ remain in thylakoid lumen
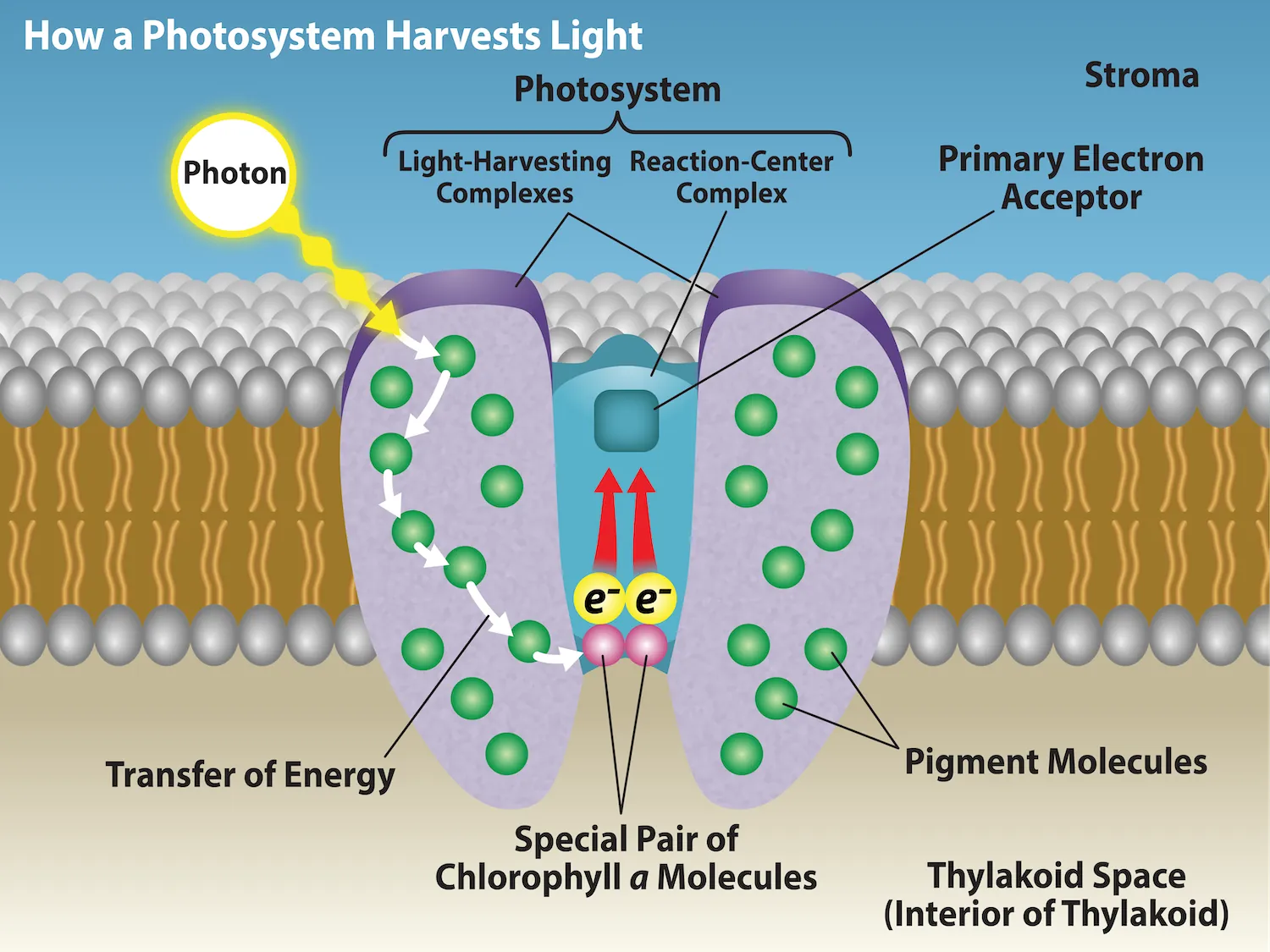
What is photosystem II linked to?
the splitting of water
What happens during the production of NADPH & ATP phase of light reactions?
electrons from excited chlorophyll passed to primary electron acceptor (pheophytin)
electrons passed along electron transport chain
H+ are pumped from stroma to thylakoid space
electrons ultimately end up reducing molecules of NADP+ to form molecules of NADPH that are then used in the Calvin Cycle
What is photophosphorylation?
The production of ATP from ADP via the transformation of light energy to chemical energy
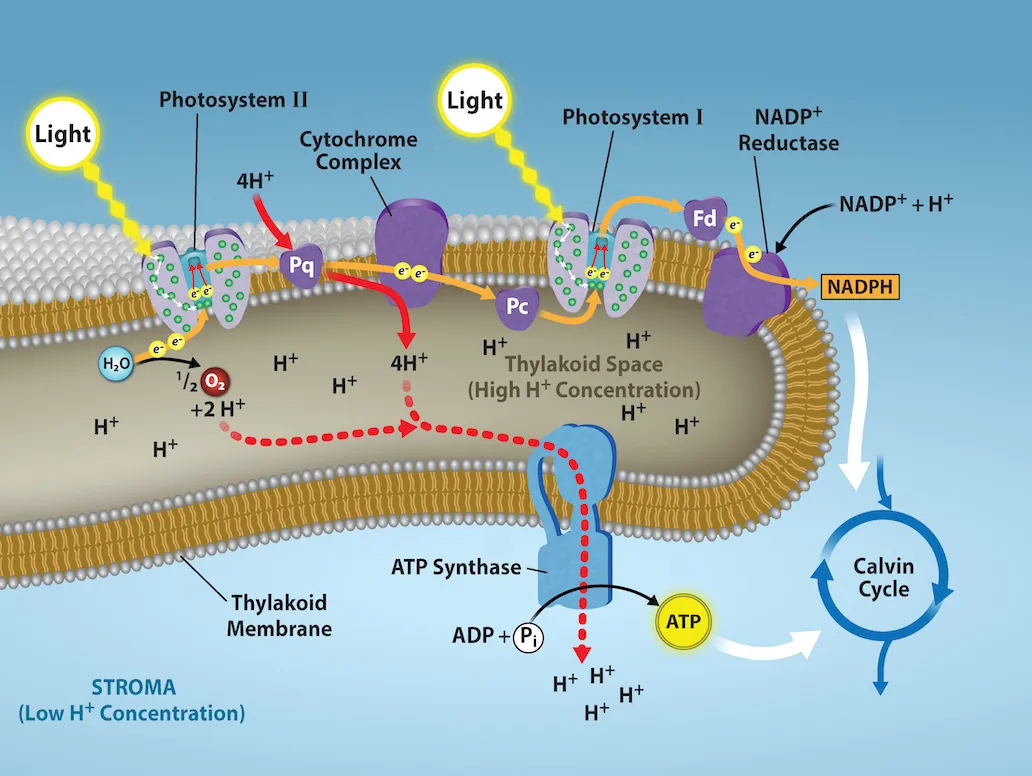
Inputs and Outputs of Light Reactions

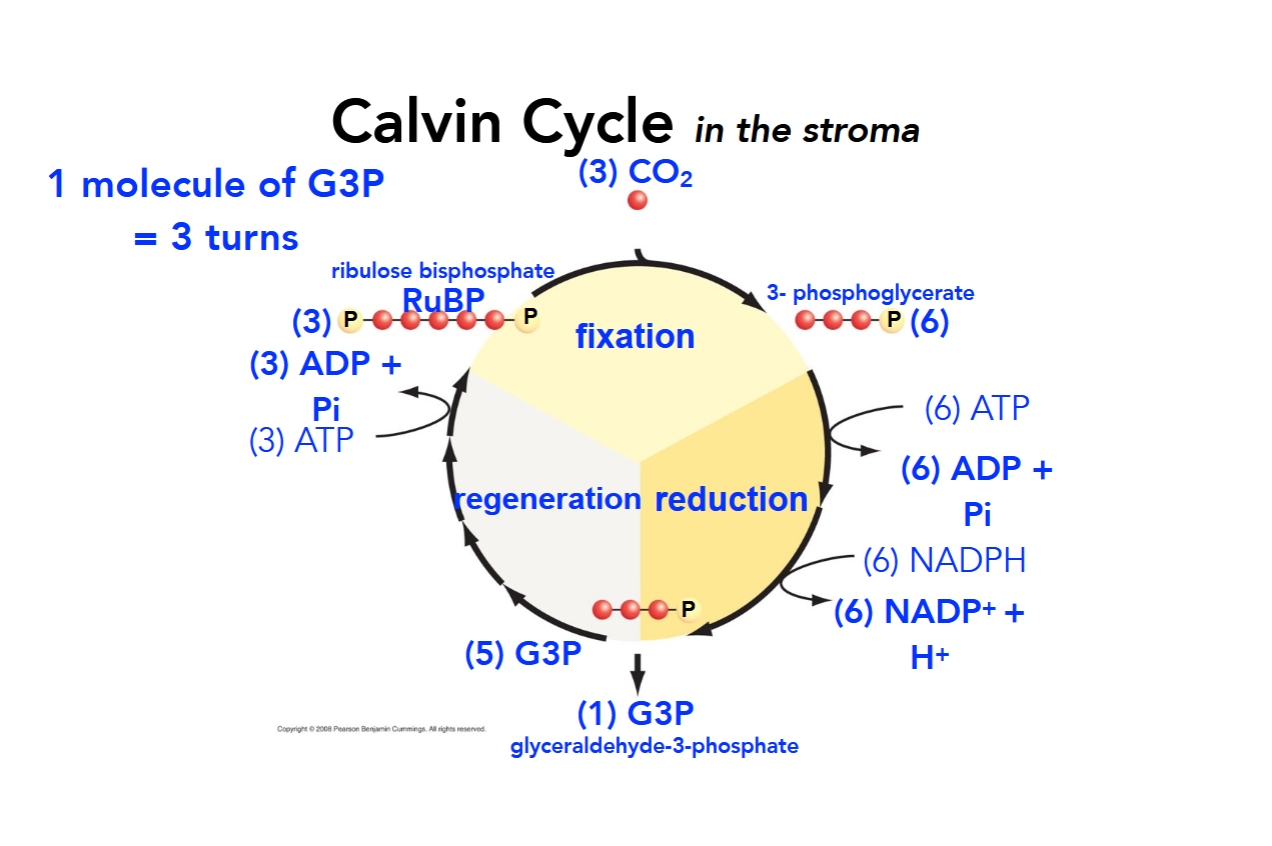
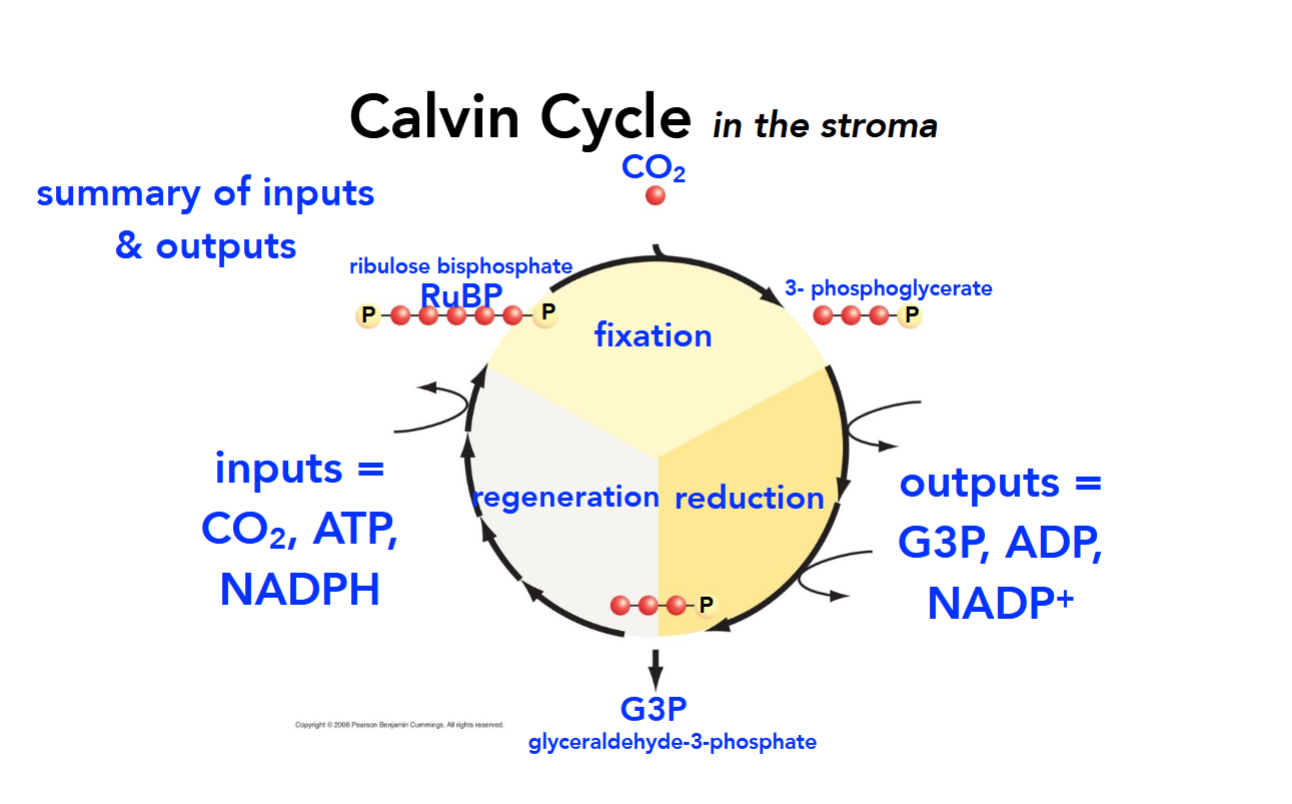
What is happening during the fixation phase of the Calvin Cycle?
CO2 is “fixed” from inorganic to organic by being incorporated into the enzyme rubulose biphosphate (RuBP) which the splits in half, becoming 3-phosphoglycerate.
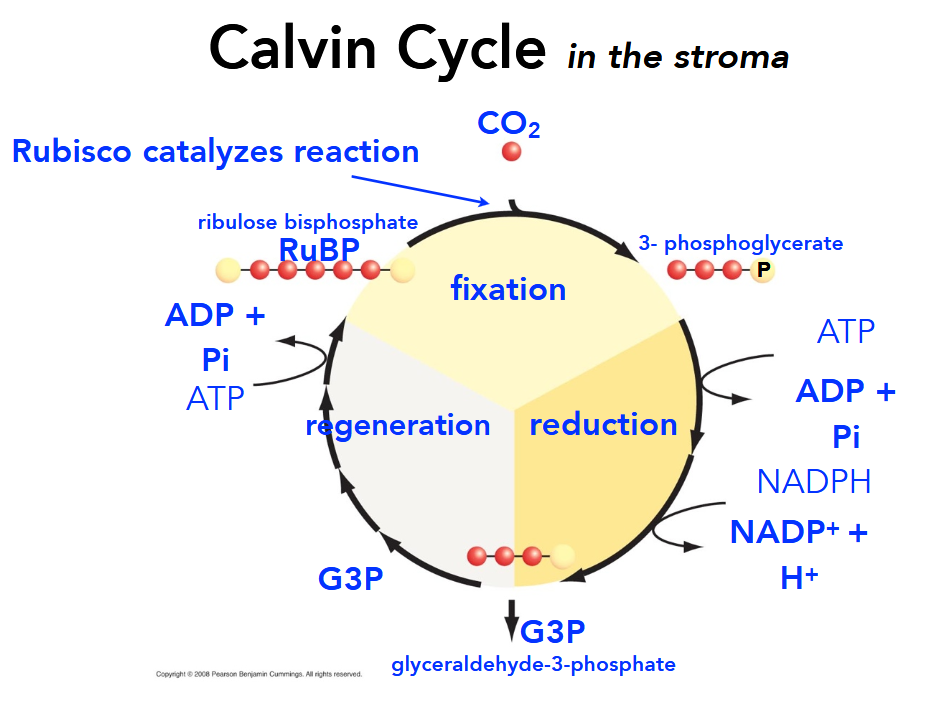
What is happening during the reduction phase of the Calvin Cycle?
3-phosphoglycerate is reduced using electrons supplied by NADPH and ATP (which are oxidized) and becomes G3P. After three turns of the cycle, one G3P leaves the Calvin Cycle to be made into carbohydrates (sugars) while the other five stay for regeneration.
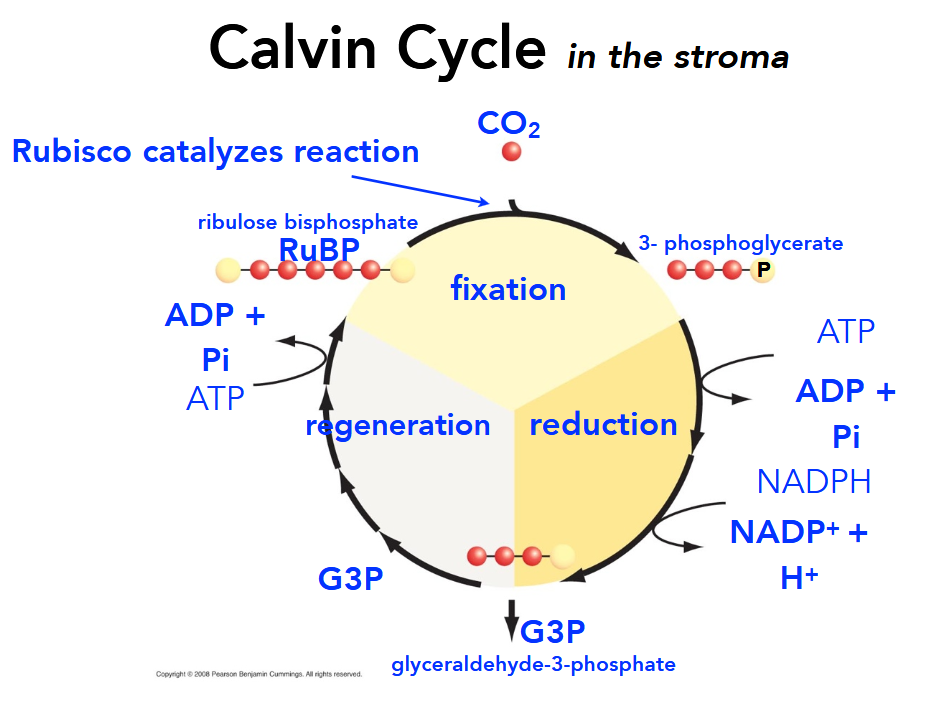
What is happening during the regeneration phase of the Calvin Cycle?
The remaining five G3p molecules are used to regenerate RuBP and the cycle begins anew.
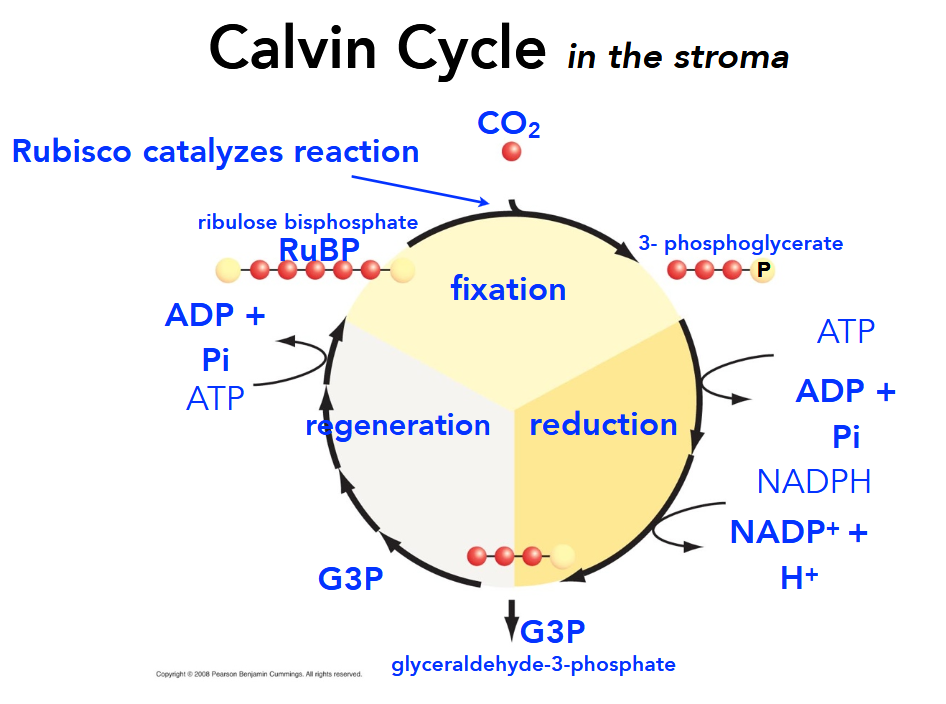
How many turns does it take in the Calvin Cycle to make one molecule of G3P?
3 turns
Inputs and Outputs of the Calvin Cycle
Summary of Photosynthesis:
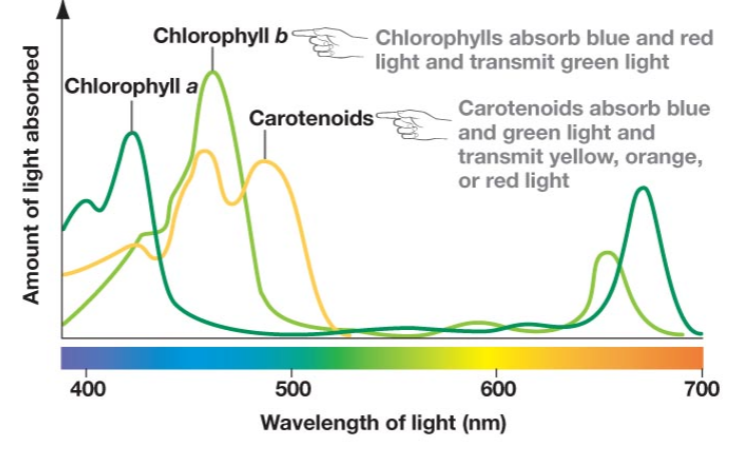
What macromolecule class are photosynthetic pigments a part of?
Lipids! (they have hydrocarbon tails)
What is b-carotene?
An accessory pigment
What do chlorophylls a and b do?
They drive photosynthesis!
Why are most plants green?
Because they absorb every other color of wavelength aside from green, which is reflected.